ansible-乱
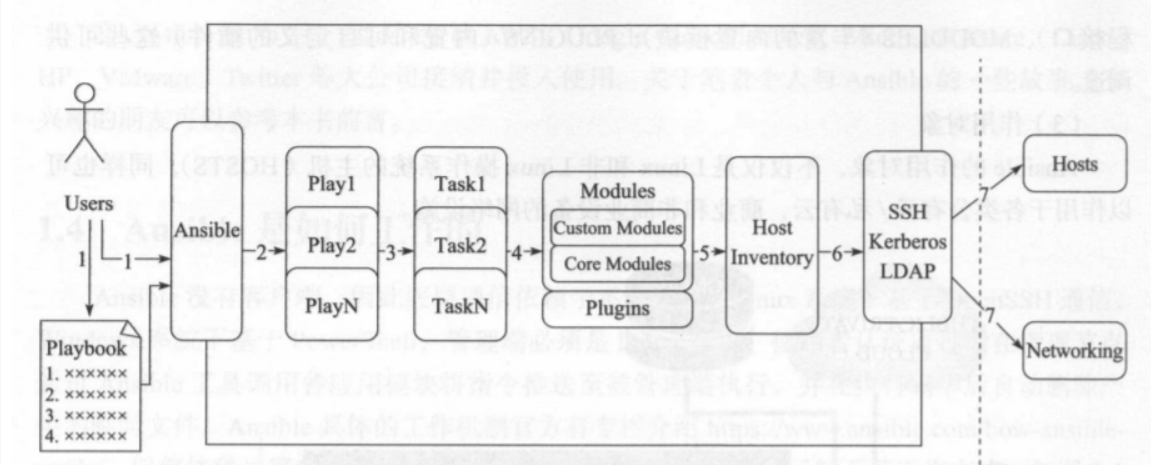
工作机制:ssh 无客户端
工作方式:
1,CMDB
2,公有云私有云API
3,使用ad-hoc
4,ansible-playbook
ansible 执行命令,底层调用传输连接模块,将命令或文件传输至远程服务器的/tmp目录,远程执行,操作完后删除,返回结果。
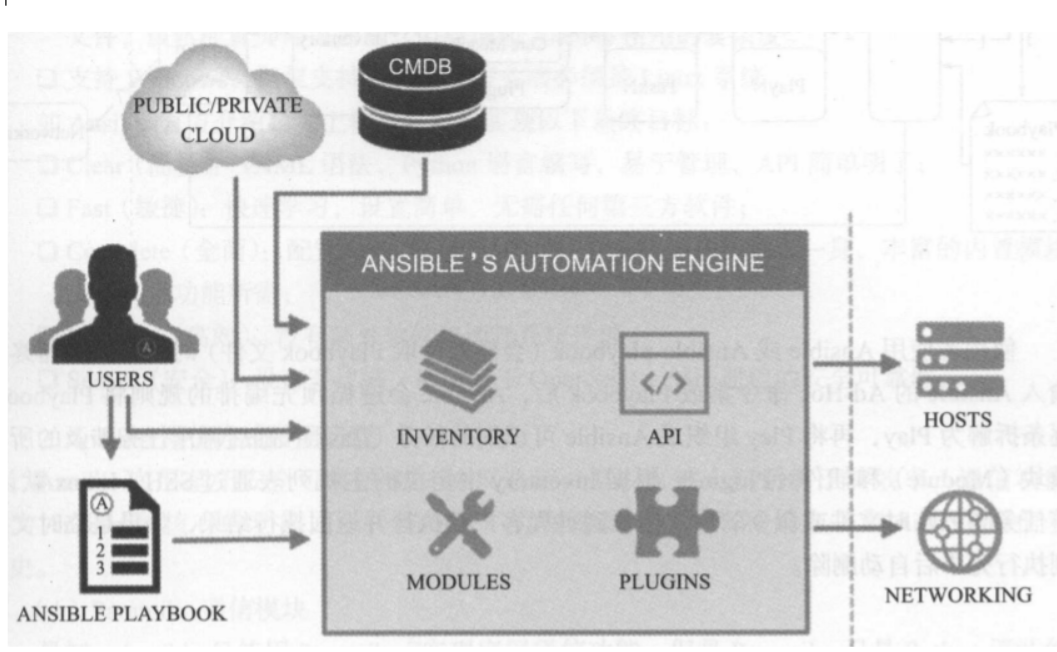
配置文件
/etc/ansible 功能;inventory 主机信息配置 工具功能
/usr/bin 系列命令默认存放位置
ansible 读取命令的顺序:
当前执行命令目录----用户家目录下 .ansible.cfg ------/etc/ansible.cfg ,先找到,先使用
ansible 配置项


2)[privilege_escalation] sudo 用户提权
3)
4)【ssh_connection】
5)【accelerate】
6)【selinux】
7)【colours】
公私钥
ssh-keygen -N " " -b 4096 -t rsa -C " " -f /root/.ssh/stanley.rsa
本机添加认证
ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/stanley.rsa root@localhost
ssh -i /root/.ssh/stanley.rsa root@local
命令格式
ansible [options]
执行后命令状态
红色: 过程异常,终止剩余任务
绿色: 执行结束后目标没有状态变化
橘黄色:执行正常,目标状态有变化
ansible-doc
-l l列出模块
ping 显示说明
ansibl-playbook .yml
ansibl-vault 加密配置文件
Inventory 是管理主机的配置文件,默认存放在 /etc/ansible/hosts
使用(默认只有一个inventory时不需要指定路径
ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webs -m ping
inventory 在其他路径时可以使用-i 指定位置
ansible all --list
Inventory 配置
定义主机及组
192.168.22.1
ntp.cnedu.com:2222
nfs.cnedu.com
分组
[webserv]
web1.cnedu.com
web[10:20].cnedu.com 10-20 之间所有数字
主机变量 定义主机时定义变量
[webserv]
web1.cnedu.com http_port=808 maxRequestsPerchild=801
组变量
[groupeservers]
web1.cnedu.com
web2.cnedu.com
[groupeservers:vars]
ntp_server=ntp.cnedu.com 组中所有主机的ntp_serve值
com
nfs_server=nfs.cnedu.com
com
定义组嵌套变量及组变量
[apache]
httpd1.cnedu.com
httpd2.cnedu.com
[nginx]
ngx1.cnedu.com
ngx2.cnedu.com
[webservers:children]
apache
nginx
[webservers:vars]
ntp_server=ntp.cnedu.com
多重变量
变量可在INventory 定义,也可在之外定义,单独存储在YAML配置文件中,以.yml .yaml .json 后缀
或无后缀,从以下位置检索:
inventory 配置文件中 默认 /etc/ansible/hosts
Playbook 中vars 定义的域
Roles vars 目录下文件
Roles 同级目录 group_vars hosts_vars 目录下文件
优先级:

DINGY
正则表达式
针对inventory 中主机列表使用
ansible <pattern_goes_here > -m <moudle_name> -a
对webserver 匹配
ansible webservers -m service -a "name=httpd state=restart "
全量匹配
ansible all -m ping
ans- "" -M ping
ans- 192.168.1. -m ping
逻辑或 or 匹配
ans- "web1:web2" -m ping
逻辑非 !
webservers:!phoenix (所有在webservers 组但不在phonenix 中的主机)
逻辑与
webservers:&phoenix 2组同时存在
多条件组合
webservers:dbservers:&staging:!phoenix webservers,dbservers所有主机在staging存在后且在phoenix 中不存在
模糊匹配
0或 多个任意字符
.cnedu.com
one.cnedu.com
域切割
str = '123456'
print str[0:1]
例子:
[webservers]
web1
web2
web3
webservers[0] # web1
webservers[-1] web3
webservers[0:1] #webservers[0] webservers[1]
webservers[1:] webservers[1] webservers[2] web2 web3
正则匹配 ~ 表示正则匹配开始
~(web|db).*.example.comans- ~192.168.[0-9]{\2}.[0-9]{2,} -m ping
限定主机做变更
ansible app -m command -a "service ntpd status" --limit "192.168.36.3"
ansible 192.168.36.1 -m command -a "service ntpd status"
playbook 正式运行前使用 --check 或 -C 检测playbook改变哪些内容
ansible-playbook --check
ansible-playbook xxxx.yml --limit webserver 限定webserver组
inventory 内置参数
General for all connections:
ansible_host
The name of the host to connect to, if different from the alias you wish to give to it.
ansible_port
The ssh port number, if not 22
ansible_user
The default ssh user name to use.
Specific to the SSH connection:
ansible_host
The name of the host to connect to, if different from the alias you wish to give to it.
ansible_port
The ssh port number, if not 22
ansible_user
The default ssh user name to use.
Specific to the SSH connection:
ansible_ssh_pass
The ssh password to use (never store this variable in plain text; always use a vault. See Variables and Vaults)
ansible_ssh_private_key_file
Private key file used by ssh. Useful if using multiple keys and you don’t want to use SSH agent.
ansible_ssh_common_args
playbook 语法检测
ansible-play nginx.yml --syntax-check
--list-hosts

ansible test70 -m blockinfile -a 'path=/testdir/rc.local block="systemctl start mariadb\nsystemctl start httpd" ' 末尾插入2行
效果:
BEGIN ANSIBLE MANAGED BLOCK
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl start httpd
BEGIN ANSIBLE MANAGED BLOCK
自定义标记
ansible test70 -m blockinfile -a 'path=/testdir/rc.local block="systemctl start mariadb\nsystemctl start httpd" marker="#{mark} serivce to start" '
ansible test70 -m blockinfile -a 'path=/testdir/rc.local block="systemctl start mariadb" marker="#{mark} serivce to start" ' 更新上条语句块的内容
ansible test70 -m blockinfile -a 'path=/testdir/rc.local block="" marker="#{mark} serivce to start" ' 删除内容
ansible test70 -m blockinfile -a 'path=/testdir/rc.local marker="#{mark} serivce to start" state=absent' 删除内容
ansible test70 -m blockinfile -a 'path=/testdir/rc.local block="####blockinfile test####" marker="#{mark} test reg" insertafter="^#!/bin/bash" ' 指定位置插入
lineinfile ,确保某一行存在指定文本中。
确保指定的一行文本 存在于文件中,如果指定的文本存在,不做操作,否则在文件末尾添加
ansible test70 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test line="test text"'
根据正则表达式替换某一行,如果有许多行匹配,只有最后一个匹配的行才会被替换,被替换为指定的文本,如没有匹配得到任一行,line 内容添加到最后一行
ansible test70 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test regexp="^line" line="test text" '
根据正则表达式替换某一行,如果有许多行匹配,只有最后一个匹配的行才会被替换,被替换为指定的文本,如没有匹配得到任一行,不操作
ansible test70 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test regexp="^line" line="test text" backrefs=yes '
匹配到的行删除
ansible test70 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test line="lineinfile -" state=absent'
根据正则表达式匹配,并删除
ansible test70 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test regexp="^lineinfile" state=absent'
开启后向引用匹配
ansible test70 -m lineinfile -a 'path=/testdir/test regexp="(H.{4}).*(H.{4})" line="\2" backrefs=yes'
变量的定义
变量名由字母数字,下划线组成,变量名以字母开头,内置的关键字不能作变量名
变量优先级
文件定义的变量优先级大于playbook hosts内的变量
定义;
- hosts: test70
vars:
testvar1: testfile #定义
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: task1
file:
path: /testdir/{{ testvar1 }} #引用
state: touch
定义多个变量:
vars:
testvar1: testfile
testvar2: testfile2
yaml语法定义
vars:
- testvar1: testfile
- testvar2: testfile2
以属性值方式定义
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx:
conf80: /etc/nginx/conf.d/80.conf
conf8080: /etc/nginx/conf.d/8080.conf
tasks:
- name: task1
file:
path: "{{nginx.conf80}}" #或者 "{{nginx['conf8080']}}" 引用
state: touch
- name: task2
file:
path: "{{nginx.conf8080}}"
state: touch
引用变量时使用了双引号,变量在引用时处于开头位置。
path: /testdir/{{ testvar1 }} 不处于开头可以不用双引号
可使用等号赋值,不需要引号
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx:
conf80: /etc/nginx/conf.d/80.conf
conf8080: /etc/nginx/conf.d/8080.conf
tasks:
- name: task1
file:
path={{nginx.conf80}}
state=touch
- name: task2
file:
path={{nginx['conf8080']}}
state=touch
在单独文件中定义变量并应用,文件名为nginx_vars.yml 在文件中定义变量不需要vars关键字,直接定义。
语法一示例:
testvar1: testfile
testvar2: testfile2
语法二示例:
- testvar1: testfile
- testvar2: testfile2
语法三示例:
nginx:
conf80: /etc/nginx/conf.d/80.conf
conf8080: /etc/nginx/conf.d/8080.conf
引用
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars_files:
- /testdir/ansible/nginx_vars.yml
tasks:
- name: task1
file:
path={{nginx.conf80}}
state=touch
- name: task2
file:
path={{nginx['conf8080']}}
state=touch
可以引用多个文件,
vars 和vars_files可同时使用
vars:
- conf90: /etc/nginx/conf.d/90.conf
vars_files:
- /testdir/ansible/nginx_vars.yml
ansible test70 -m setup 显示收集的信息(很多信息
使用关键字查看想要的信息
ansible test70 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_memory_mb'
通配符过滤
ansible test70 -m setup -a "filter=mb"
在远程主机写入自定义的信息
在远程主机 /etc/ansible/facts.d/testinfo.fact 写入信息
[root@test70 facts.d]# cat testinfo.fact
[testmsg]
msg1=This is the first custom test message
msg2=This is the second custom test message
json格式
{
"testmsg":{
"msg1":"This is the first custom test message",
"msg2":"This is the second custom test message"
}
}
调用
ansible test70 -m setup -a "filter=ansible_local"
默认会查找远程主机 /etc/ansible/facts.d目录,如果将local tacts信息放入其他目录,需指定
ansible test70 -m setup -a 'fact_path=/testdir'
debug 模块
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: touch testfile
file:
path: /testdir/testfile
state: touch
- name: debug demo
debug:
msg: this is debug info,The test file has been touched
执行后控制台会输出信息
debug 模块输出自定义及变量信息
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars:
testvar: value of test variable
tasks:
- name: debug demo
debug:
var: testvar
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars:
testvar: testv
tasks:
- name: debug demo
debug:
msg: "value of testvar is : {{testvar}}" #msg引用了变量 变量引用前有: 需要使用“”
获取主机内存信息
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: debug demo
debug:
msg: "Remote host memory information: {{ansible_memory_mb}}"
语法一示例:
debug:
msg: "Remote host memory information : {{ansible_memory_mb.real}}"
语法二示例:
debug:
msg: "Remote host memory information : {{ansible_memory_mb['real']}}"
上述两种语法前文中已经进行过示例,此处不再赘述。
注册变量:
模块运行时会返回值,默认不显示(使用-vvvv显示),可以将其写入变量后通过引用进行提取
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test shell
shell: "echo test > /var/testshellfile"
register: testvar #注册变量
- name: shell module return values
debug:
var: testvar # 引用
返回的值
changed: [192.168.36.73] => {
"changed": true,
"cmd": "echo test1 > /data/testfile",
"delta": "0:00:00.002276",
"end": "2019-04-23 18:30:31.285899",
可以通过指定的key获取其value,方式;
语法一
- name: shell module return values
debug:
msg: "{{testvar.cmd}}"
语法二
- name: shell module return values
debug:
msg: "{{testvar['cmd']}}"
返回值含义文档: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/2.4/shell_module.html
提示用户输入信息:
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars_prompt:
- name: "your_name"
prompt: "What is your name"
#默认输入不显示;希望显示
private: no
- name: "your_age"
prompt: "How old are you"
tasks:
- name: output vars
debug:
msg: Your name is {{your_name}},You are {{your_age}} years old.
为提示信息设置默认值
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars_prompt:
- name: "solution"
prompt: "Choose the solution you want \n
A: solutionA\n
B: solutionB\n
C: solutionC\n"
private: no
default: A
tasks:
- name: output vars
debug:
msg: The final solution is {{solution}}.
脚本:用户输入密码后创建账户(需要对密码加密,使用passlib库,python.用户可以确认密码
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars_prompt:
- name: "user_name"
prompt: "Enter user name"
private: no
- name: "user_password"
prompt: "Enter user password"
encrypt: "sha512_crypt"
confirm: yes
tasks:
- name: create user
user:
name: "{{user_name}}"
password: "{{user_password}}"
通过命令行传入变量
playbook中未定义变量,想直接引用可通过命令行传入
ansible-playbook cmdvar.yml --extra-vars "pass_var=cmdline pass var" #传入长变量
ansible-playbook cmdvar.yml -e 'pass_var="test" pass_var1="test1"' 短变量
如果未定义变量,也没有传入变量,会报错,可playbook在playbo添加默认变量
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars:
pass_var: test_default
tasks:
- name: "Passing Variables On The Command Line"
debug:
msg: "{{pass_var}}"
在清单中为主机添加变量,主机变量的使用范围仅限于对应的主机
test70 ansible_host=10.1.1.70 testhostvar=test70_host_var 应用。使用{{testhostvar}}
yaml语法配置
all:
hosts:
test70:
ansible_host: 10.1.1.70
ansible_port: 22
testhostvar: test70_host_var
testhostvar1: test70_host_var1
主机组变量
[testB]
test70 ansible_host=10.1.1.70
test71 anisble_host=10.1.1.71
[testB:vars]
test_group_var1='group var test'
test_group_var2='group var test2'
YAML
all:
children:
testB:
hosts:
test70:
ansible_host: 10.1.1.70
ansible_port: 22
test71:
ansible_host: 10.1.1.71
ansible_port: 22
vars:
test_group_var1: 'group var test1'
test_group_var2: 'group var test2'
通过set_fact 定义变量
可以通过set_fact将一个变量的值赋予另一个变量,示例如下
- hosts: test70
remote_user: root
vars:
testvar1: test1_string
tasks:
- shell: "echo test2_string"
register: shellreturn
- set_fact:
testsf1: "{{testvar1}}"
testsf2: "{{shellreturn.stdout}}"
- debug:
msg: "{{testsf1}} {{testsf2}}"
http://www----zsythink.net/archives/2698 最后有不懂得
内置变量
ansible all -m debug -a "msg={{ansible_version}}"
hostvars
inventory_hostname 当前被操作的主机名称,是对应清单中的主机名,
inventory_hostname_short ,主机名更短
play_hosts 当前play 所操作的所有主机的列表
groups 分组的信息 每个分组的主机,以及没有被分组的单独的主机
group_names
inventory_dir
uncomment this to disable SSH key host checking
71 #host_key_checking = False 第一次检查key 取消注释,默认回答yes
以sudo执行,需要输入sudo口令,使用-K
chrony 同步 playbook
server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
allow 192.168.0.0/16
local stratum 10
计划任务
不输入确认口令 visudo NOPASSWORD:ALL
ansible all -m ping -u yon -b -K
-u 使用-u 默认使当前用户(即在控制端使用的用户)
启用日志 log_path
ansible 'appservers:!webservers' -m ping
ansible 命令行选项
修改ansible 默认模块 -m shell 默认使用shell执行
user 创建家目录,但是不生成家目录的文件
文件分类放置,yaml和配置文件
变量优先级 变量文件 > playbook > -e > hosts主机变量 > hosts公共变量
跨角色 引用文件,从roles/httpd/files/xxxx.index.html
角色默认的路经
ansible-乱的更多相关文章
- ansible+packer+terraform在aws上布署web服务器
各工具所扮演的角色 ansible: 配合packer生成安装有apache的基础镜像 packer: 生成amazon AMI terraform: 以packer生成的镜像为基础,布署web服务器 ...
- Ansible配置文件ansible.cfg详解
Ansible是一个系列文章,我会尽量以通俗易懂.诙谐幽默的总结方式给大家呈现这些枯燥的知识点,让学习变的有趣一些. Ansible系列博文直达链接:Ansible入门系列 前言 此时外面小雨淅淅沥沥 ...
- 五十五.ansible概述、ansible基础 、ad-hoc、批量配置管理
1.环境准备 (自动化工具,批量操作) 6台 2cpu,1.5G以上内存,20G硬盘,1网卡 1.1 基础环境准备 1)启动6台虚拟机,ansible.sh 2)真机配置yum仓库 ]# tar ...
- Ansible--03 ansible 变量
目录 Ansible 变量 变量概述 定义变量的方式 如何定义变量 Ansible变量优先级测试 变量注册 ansibl e层级定义变量 facts缓存 Ansible 变量 变量概述 变量提供了便捷 ...
- Ansible Ad-Hoc与常用模块
ansible 执行结果信息–各颜色说明:ansible Ad-Hoc 说明:ansible 如何查看帮助文档与常用模块详解 主机规划 添加用户账号 说明: 1. 运维人员使用的登录账号: 2. 所有 ...
- Ansible Playbook 初识
Ansible Playbook 基本概述与使用案例 主机规划 添加用户账号 说明: 1. 运维人员使用的登录账号: 2. 所有的业务都放在 /app/ 下「yun用户的家目录」,避免业务数据乱放: ...
- Ansible Playbook 变量与 register 详解
ansible 定义变量方式与[多层]变量引用,以及 register 详解 主机规划 添加用户账号 说明: 1. 运维人员使用的登录账号: 2. 所有的业务都放在 /app/ 下「yun用户的家目录 ...
- Ansible Facts 变量详解
Ansible Facts 变量详解与使用案例 主机规划 添加用户账号 说明: 1. 运维人员使用的登录账号: 2. 所有的业务都放在 /app/ 下「yun用户的家目录」,避免业务数据乱放: 3. ...
- Ansible playbook 编程
Ansible playbook 编程详解与各种小案例 主机规划 添加用户账号 说明: 1. 运维人员使用的登录账号: 2. 所有的业务都放在 /app/ 下「yun用户的家目录」,避免业务数据乱放: ...
- Ansible playbook Vault 加密
Ansible playbook Vault 加密详解与使用案例 主机规划 添加用户账号 说明: 1. 运维人员使用的登录账号: 2. 所有的业务都放在 /app/ 下「yun用户的家目录」,避免业务 ...
随机推荐
- 2019.8中关村、OGeek(oppo)比赛
中关村writeup https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU3MzczNDg1OQ==&mid=2247484106&idx=1&sn=62a ...
- magento下载地址
https://download.magentochina.org/magento/2/ https://www.magentochina.org/blog/download-install-mage ...
- vue-cli 3 ----- 项目频繁发送‘sockjs-node/info’请求
在vue-cli3跑项目时发现了这个问题,浏览器一直在频繁发送这个请求,导致联调时很不方便,而且本地开发时项目也不能实时更新. 看了网上很多的 (1) 解决方案, 大多都是直接去node_modul ...
- Nginx配置与使用
一.简单介绍 由俄罗斯程序员IgorSysoev研发,2004年开源公布,特点是:内存cpu占用低,并发能力强,稳定,配置示例,反向代理:互联网企业 70%以上公司都在使用 nginx: 二.安装 1 ...
- Java初始和环境搭建
前世今生 Java语言是什么? 一种计算机编程语言.名字取自咖啡. Java语言发展简史 Java语言之父:James Gosling SUN(Stanford University Network ...
- spring配置添加多个事务(转)
大多数项目只需要一个事务管理器.然而,有些项目为了提高效率.或者有多个完全不同又不相干的数据源,最好用多个事务管理器.机智的Spring的Transactional管理已经考虑到了这一点,首先分别定义 ...
- spring aop之父子容器
需求;项目对外提供接口,要求每个对外接口都要进行token认证. 解决办法:写一个token认证的工具类,在每个需要认证的接口方法开始的地方,调用工具类中的token认证方法. 问题:因为要满足指定条 ...
- C语言 --- 高级指针
1. 指针赋值: C语言允许使用赋值运算进行指针的赋值,前提是两个指针具有相同的类型. int i,*p,*q; p = &i; ...
- Bug快到碗里来
Bug快到碗里来 python错误--'list' object is not callable 原因及解决方法1 你定义了一个变量的变量名和系统自带的关键字冲突,调用变量时关键字被传到调用的位置,就 ...
- Python 入门之 内置模块 -- re模块
Python 入门之 内置模块 -- re模块 1.re 模块 (1)什么是正则? 正则就是用一些具有特殊含义的符号组合到一起(称为正则表达式)来描述字符或者字符串的方法.或者说:正则就是用来描述一类 ...
