【Leetcode周赛】从contest-121开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 121 (题号981~984)(2019年1月27日)
链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-121
总结:2019年2月22日补充的报告。当时不想写。rank:1093/3924,AC:2/4。还是太慢了。
【984】String Without AAA or BBB(第一题 4分)(Greedy, M)
给了两个数字,A 代表 A 个 ‘A’, B 代表 B 个‘B’ 在字符串里面。返回一个可行的字符串,字符串中包含 A 个‘A’, B 个 ‘B’,但是没有连续的 'AAA' 或者 'BBB'。
题解:当时写的很长。现在说下greedy的方法,我们每次只想着只放一个a或者一个b,然后如果当前字符串的长度大于等于2,就需要判断前面是不是有两个连续的a或者连续的b。如果有的话,那么当前肯定不能放a或者放b。
class Solution {
public:
string strWithout3a3b(int A, int B) {
string res;
while (A > || B > ) {
if (res.size() >= ) {
int size = res.size();
if (res[size-] == 'a' && res[size-] == 'a') {
res += "b"; --B;
} else if (res[size-] == 'b' && res[size-] == 'b') {
res += "a"; --A;
} else if (A >= B) {
res += "a"; --A;
} else {
res += "b"; --B;
}
} else {
if (A >= B) {
res += "a"; --A;
} else {
res += "b"; --B;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
【981】Time Based Key-Value Store(第二题 5分)
【983】Minimum Cost For Tickets(第三题 5分)(DP)
某个旅游景点有日票,周票和月票三种类型的票价。给了一个array,代表一年中的第几天去景点,问遍历完这个数组最少需要多少花费。
Train tickets are sold in 3 different ways:
- a 1-day pass is sold for
costs[0]dollars; - a 7-day pass is sold for
costs[1]dollars; - a 30-day pass is sold for
costs[2]dollars.
Input: days = [1,4,6,7,8,20], costs = [2,7,15]
Output: 11
Explanation:
For example, here is one way to buy passes that lets you travel your travel plan:
On day 1, you bought a 1-day pass for costs[0] = $2, which covered day 1.
On day 3, you bought a 7-day pass for costs[1] = $7, which covered days 3, 4, ..., 9.
On day 20, you bought a 1-day pass for costs[0] = $2, which covered day 20.
In total you spent $11 and covered all the days of your travel.
题解:动态规划,dp[i] 代表前 i 天的最小花费。转移方程:
如果第 i 天不在访问的列表里面: dp[i] = dp[i-1]
else: dp[i] = min(dp[i-1] + cost[0], dp[i-7] + cost[1] + dp[i-30] + cost[2])
时间复杂度是: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
//dp[i] represents minimum money need cost in first i days
int mincostTickets(vector<int>& days, vector<int>& costs) {
const int totDays = ;
vector<int> dp(totDays, INT_MAX);
dp[] = ;
set<int> st(days.begin(), days.end());
for (int i = ; i < totDays; ++i) {
if (st.find(i) == st.end()) {
dp[i] = dp[i-];
continue;
}
dp[i] = dp[i-] + costs[];
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[max(i-, )] + costs[]);
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[max(i-, )] + costs[]);
}
return dp[];
}
};
【982】Triples with Bitwise AND Equal To Zero(第四题 7分)
Contest 122(题号985~988)(2019年2月3日,新春大礼包)
链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-122
总结:这周题目非常简单,四题都过了。
【985】Sum of Even Numbers After Queries(第一题 4分)
给了一个数组,以及一个修改的序列。序列中的一个 pair 代表 p[0] 代表在原来数字上加上的值 val , p[1] 代表数组中需要修改元素的下标。求每次修改之后整个数组的偶数的和。
数据规模:
1 <= A.length <= 10000-10000 <= A[i] <= 100001 <= queries.length <= 10000-10000 <= queries[i][0] <= 100000 <= queries[i][1] < A.length
题解: 用一个变量curSum存储当前数组偶数的和,然后每次执行一个query之后,看当前元素是奇数变成偶数,还是偶数变成奇数,还是偶数变成偶数。来做不同的处理。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sumEvenAfterQueries(vector<int>& A, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
const int n = A.size(), m = queries.size();
vector<int> ret;
int curSum = ;
for (auto num : A) {
if ((num & ) == ) {
curSum += num;
}
}
for (auto q : queries) {
int val = q[], idx = q[];
int oriVal = A[idx];
int newVal = oriVal + val;
if ((oriVal & ) == ) {
if (newVal & ) {
curSum -= oriVal;
} else {
curSum += val;
}
} else {
if ((newVal & ) == ) {
curSum += newVal;
}
}
ret.push_back(curSum);
A[idx] = newVal;
}
return ret;
}
};
【988】Smallest String Starting From Leaf(第二题 5分)
给了一棵二叉树,树上的每个结点代表一个字母(0-25),问从叶子结点开始到根节点的字典序最小的单词是哪个?
题解:dfs 这颗树,把所有单词找出来。然后排序。注意这个题要求是从叶子结点开始,如果一个结点只有一个儿子,那么它本身不能算叶子结点,从它开始的单词要忽略掉。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
string smallestFromLeaf(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> words;
string str;
if (!root) {
return "";
}
dfs(root, words, str);
sort(words.begin(), words.end());
return words[];
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<string>& words, string& str) {
if (!root) { return; }
char c = root->val + 'a';
str += string(, c);
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
reverse(str.begin(), str.end());
words.push_back(str);
reverse(str.begin(), str.end());
str.pop_back();
return;
}
if (root->left) {
dfs(root->left, words, str);
}
if (root->right) {
dfs(root->right, words, str);
}
str.pop_back();
return;
}
};
【986】Interval List Intersections(第三题 5分)
给了两组左闭右闭的线段,返回这两组线段的交集。
Input: A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Reminder: The inputs and the desired output are lists of Interval objects, and not arrays or lists.
题解:2 pointers 扫描一遍。
/**
* Definition for an interval.
* struct Interval {
* int start;
* int end;
* Interval() : start(0), end(0) {}
* Interval(int s, int e) : start(s), end(e) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<Interval> intervalIntersection(vector<Interval>& A, vector<Interval>& B) {
const int size1 = A.size(), size2 = B.size();
int p1 = , p2 = ;
vector<Interval> ret;
while (p1 < size1 && p2 < size2) {
Interval seg1 = A[p1], seg2 = B[p2];
int s = max(seg1.start, seg2.start), e = min(seg1.end, seg2.end);
if (s > e) {
if (seg1.end > seg2.end) { p2++; }
else { p1++; }
continue;
}
Interval seg(s, e);
ret.push_back(seg);
if (seg1.end > seg2.end) {
p2++;
} else if (seg2.end > seg1.end) {
p1++;
} else {
p1++, p2++;
}
}
return ret;
}
};
【987】Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree(第四题 5分)
给了一棵二叉树,给了树的结点上坐标的定义。根结点是 (0, 0), For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1). 按照 X 轴升序, Y 轴降序, 然后 value 升序的条件,返回这颗树的值。
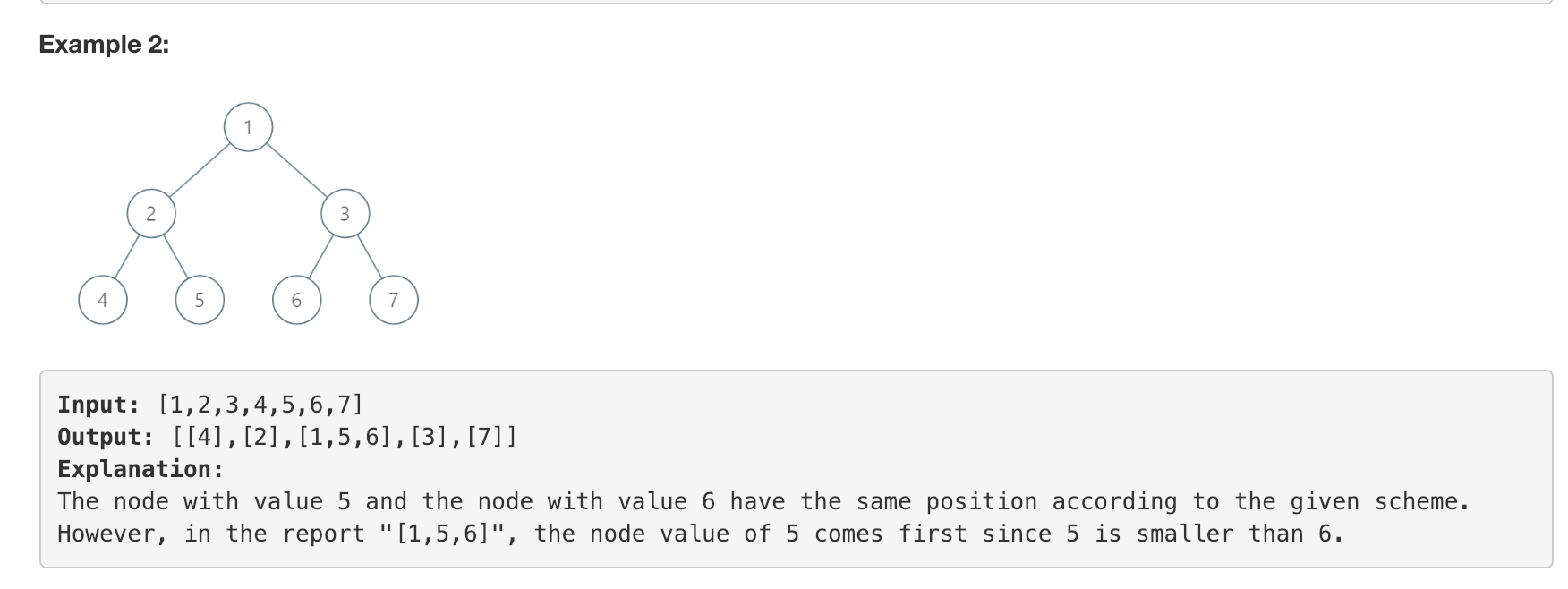
题解:dfs一遍树,用map存起来。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if (!root) {return ret;}
dfs(root, , );
for (auto& pp : memo) {
int x = pp.first; map<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> mp = pp.second;
vector<int> temp;
for (auto& ele : mp) {
sort(ele.second.begin(), ele.second.end());
for (auto& num : ele.second) {
temp.push_back(num);
}
}
ret.push_back(temp);
}
return ret;
}
map<int, map<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>> memo; // x-idx, list of values, and height
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int x, int y) {
if (!root) {return;}
memo[x][y].push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->left, x-, y-);
dfs(root->right, x+, y-);
} };
Contest 123(题号985~988)(2019年2月10日)
Contest 124(题号993~996)(2019年2月17日)
Contest 125(题号997~1001)(2019年2月24日)
链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-125
总结:这周四道题都不难,最后一题看错题了,导致浪费了很多时间。结果:3/4,rank:1008/4288
【997】Find the Town Judge(第一题 4分)
在一个小镇里,按从 1 到 N 标记了 N 个人。传言称,这些人中有一个是小镇上的秘密法官。
如果小镇的法官真的存在,那么:
- 小镇的法官不相信任何人。
- 每个人(除了小镇法官外)都信任小镇的法官。
- 只有一个人同时满足属性 1 和属性 2 。
给定数组 trust,该数组由信任对 trust[i] = [a, b] 组成,表示标记为 a 的人信任标记为 b 的人。
如果小镇存在秘密法官并且可以确定他的身份,请返回该法官的标记。否则,返回 -1。
输入:N = 4, trust = [[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[4,3]]
输出:3
题解:遍历trust数组,用count数组, count[i] 表示标记第 i 个人有几个人信任, 用 exist 数组, exist[i] 表示 第 i 个人是否信任别人。然后按照规则... 最后有一个corner case,就是当 N = 1, trust 为空的时候,应该返回1.
class Solution {
public:
int findJudge(int N, vector<vector<int>>& trust) {
const int size = trust.size();
if (N == && size == ) {return ;}
vector<int> count(N+, );
vector<int> exist(N+, );
for (auto& t : trust) {
int u = t[], v = t[];
count[v]++;
exist[u] = ;
}
int res = -;
for (int i = ; i <= N; ++i) {
if (count[i] == N- && exist[i] == ) {
if (res != -) {
res = -;
break;
} else {
res = i;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
【999】Available Captures for Rook(第二题 4分)
在一个 8 x 8 的棋盘上,有一个白色车(rook)。也可能有空方块,白色的象(bishop)和黑色的卒(pawn)。它们分别以字符 “R”,“.”,“B” 和 “p” 给出。大写字符表示白棋,小写字符表示黑棋。
车按国际象棋中的规则移动:它选择四个基本方向中的一个(北,东,西和南),然后朝那个方向移动,直到它选择停止、到达棋盘的边缘或移动到同一方格来捕获该方格上颜色相反的卒。另外,车不能与其他友方(白色)象进入同一个方格。
返回车能够在一次移动中捕获到的卒的数量。
题解:先找到rook的位置,然后上下左右四个方向, 往前走,如果当前方向能够捕获到 pawn 的话,就 res++。res 最多四个,题目描述不好,不要想太多。
class Solution {
public:
int numRookCaptures(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
vector<int> begin();
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i) {
for (int j = ; j < ; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == 'R') {
begin = {i, j};
break;
}
}
}
const int dirx[] = {-, , , };
const int diry[] = {, -, , };
int res = ;
for (int k = ; k < ; ++k) {
int x = begin[], y = begin[];
while (x >= && x < && y >= && y < ) {
if (board[x][y] == 'B') {break;}
if (board[x][y] == 'p') {
++res; break;
}
x += dirx[k], y += diry[k];
}
}
return res;
}
};
【998】Maximum Binary Tree II(第三题 6分)
最大树定义:一个树,其中每个节点的值都大于其子树中的任何其他值。
给出最大树的根节点 root。
就像之前的问题那样,给定的树是从表 A(root = Construct(A))递归地使用下述 Construct(A) 例程构造的:
- 如果
A为空,返回null - 否则,令
A[i]作为 A 的最大元素。创建一个值为A[i]的根节点root root的左子树将被构建为Construct([A[0], A[1], ..., A[i-1]])root的右子树将被构建为Construct([A[i+1], A[i+2], ..., A[A.length - 1]])- 返回
root
请注意,我们没有直接给定 A,只有一个根节点 root = Construct(A).
假设 B 是 A 的副本,并附加值 val。保证 B 中的值是不同的。
返回 Construct(B)。
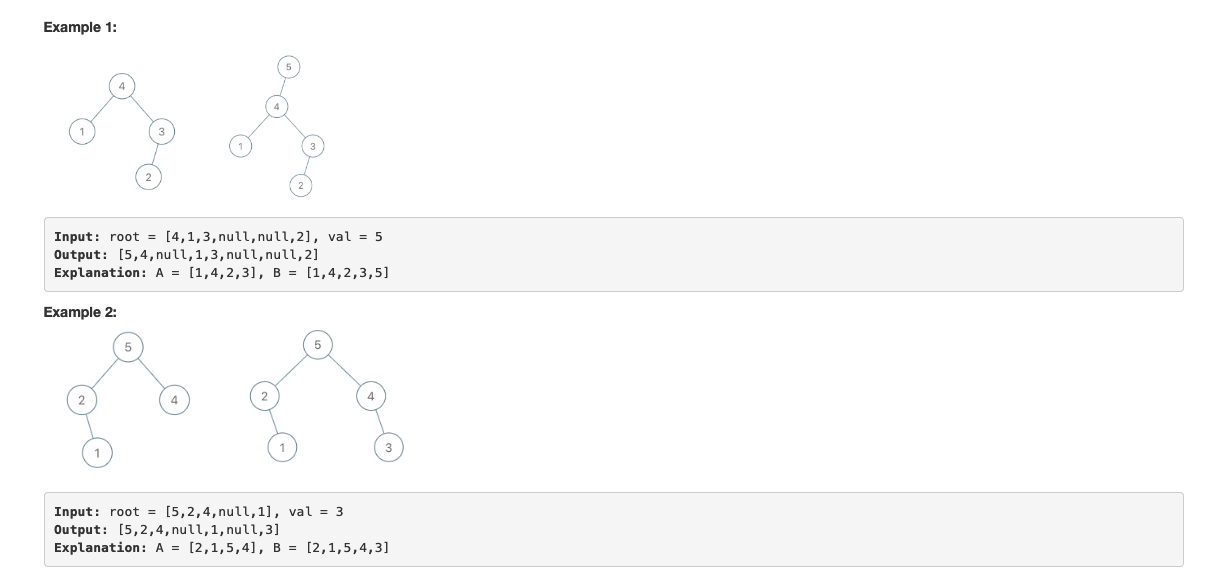
题解:看见树就递归,如果当前的根结点小于要插入的几点,那么新的结点就是根结点。否则要插入到当前根结点的右子树当中。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoMaxTree(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (!root) {
root = new TreeNode(val);
return root;
}
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(val);
if (val > root->val) {
node->left = root;
return node;
}
root->right = insertIntoMaxTree(root->right, val);
return root;
}
};
【1001】Grid Illumination(第四题 8分)(网格照明)
在 N x N 的网格上,每个单元格 (x, y) 上都有一盏灯,其中 0 <= x < N 且 0 <= y < N 。
最初,一定数量的灯是亮着的。lamps[i] 告诉我们亮着的第 i 盏灯的位置。每盏灯都照亮其所在 x 轴、y 轴和两条对角线上的每个正方形(类似于国际象棋中的皇后)
对于第 i 次查询 queries[i] = (x, y),如果单元格 (x, y) 是被照亮的,则查询结果为 1,否则为 0 。
在每个查询 (x, y) 之后 [按照查询的顺序],我们关闭位于单元格 (x, y) 上或其相邻 8 个方向上(与单元格 (x, y) 共享一个角或边)的任何灯。
返回答案数组 answer。每个值 answer[i] 应等于第 i 次查询 queries[i] 的结果。
题解:我们用四个map,分别表示 第 x 行,第 y 列, 坐标(x,y) 对应的正向对角线(key是 x-y)和反向对角线 (key 是 x+y)。然后对于每一个query,判断他的行,列,正反对角线是不是有灯照明,有的话,ans[i] = 1, 然后把 query 的坐标相邻的九个小格子的灯给关掉。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> gridIllumination(int N, vector<vector<int>>& lamps, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
unordered_map<int, int> rows, cols, dia, anti;
set<vector<int>> st(lamps.begin(), lamps.end());
for (auto& l : lamps) {
int x = l[], y = l[];
rows[x]++, cols[y]++;
dia[x+y]++, anti[x-y]++;
}
const int size = queries.size();
const int dirx[] = {-, -, -, , , , , , };
const int diry[] = {-, , , -, ,, -, , };
vector<int> res(size, );
for (int i = ; i < size; ++i) {
int x = queries[i][], y = queries[i][];
if (rows.find(x) != rows.end() && rows[x] > || cols.find(y) != cols.end() && cols[y] >
|| dia.find(x+y) != dia.end() && dia[x+y] > || anti.find(x-y) != anti.end() && anti[x-y] > ) {
res[i] = ;
}
for (int k = ; k <= ; ++k) {
int newx = x + dirx[k], newy = y + diry[k];
if (newx < || newx >= N || newy < || newy >= N) {continue;}
if (st.find({newx, newy}) == st.end()) {continue;}
rows[newx]--;
cols[newy]--;
dia[newx + newy]--;
anti[newx - newy]--;
}
}
return res;
}
};
Contest 126(题号1000,1002~1004)(2019年3月3日)
链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-126
总结:结果:3/4,rank:333/4564,这周怎么说,第一题愣住了,第二题用了一个错误的解法AC了,第三题 sliding window 快忘完了,第四题不会做。第四题合并石子,两堆会合并,k 堆不会合并。
【1002】Find Common Characters(第一题 3分)
返回一个wordlist里面所有word相同的字母,如果一个字母在这所有的单词里面都出现了至少m次,那么这个字母在结果的数组中也应该出现 m 次。
Example 1:
Input: ["bella","label","roller"]
Output: ["e","l","l"]
Example 2:
Input: ["cool","lock","cook"]
Output: ["c","o"]
题解:我先把每个单词都sort了一下,这样能方便统计每个字符出现的次数。然后对于每个字母a到z统计每个单词中出现的最小频次。
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> commonChars(vector<string>& A) {
for (auto & s : A) {
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
}
vector<string> res;
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; ++c) {
int times = INT_MAX;
for (auto& s: A) {
int pos1 = s.find_first_of(c);
if (pos1 == string::npos) {times = ; break;}
int pos2 = s.find_last_of(c);
times = min(times, pos2 - pos1 + );
}
if (times) {
for (int i = ; i < times; ++i) {
res.push_back(string(, c));
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
【1003】Check If Word Is Valid After Substitutions(第二题 5分)
给定的字符串"abc"是 valid的,把一个 valid 的字符串拆成两个部分 X + Y,那么在 X,Y之间放一个 valid 的字符串, X + valid + Y 也是 valid的。给定一个字符串 S,判断它是不是 valid 的。
Example 1:
Input: "aabcbc"
Output: true
Explanation:
We start with the valid string "abc".
Then we can insert another "abc" between "a" and "bc", resulting in "a" + "abc" + "bc" which is "aabcbc". Example 2:
Input: "abcabcababcc"
Output: true
Explanation:
"abcabcabc" is valid after consecutive insertings of "abc".
Then we can insert "abc" before the last letter, resulting in "abcabcab" + "abc" + "c" which is "abcabcababcc". Example 3:
Input: "abccba"
Output: false Example 4:
Input: "cababc"
Output: false
数据规模:
Note:
1 <= S.length <= 20000S[i]is'a','b', or'c'
题解:我比赛里面是用了三个变量 a,b,c 统计这三个字母出现的频次,如果不符合 cntA >= cntB >= cntC 就是 invalid 的字符串。但是如果输入是"aabbcc"这个条件是符合的,但是结果是这个字符串依旧是invalid的。
所以比赛之后的解法用了stack来做。
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string S) {
const int n = S.size();
string cur = "";
stack<string> stk;
for (auto& c : S) {
if (c == 'a') {
if (!cur.empty()) { stk.push(cur); }
cur = "a";
} else {
cur += c;
if (cur != "ab" && cur != "abc") {return false;}
}
if (cur == "abc") {
if (stk.empty()) {
cur = "";
} else {
cur = stk.top(); stk.pop();
}
}
}
return stk.empty() && cur.empty();
}
};
【1004】Max Consecutive Ones III(第三题 6分)
Given an array A of 0s and 1s, we may change up to K values from 0 to 1.
Return the length of the longest (contiguous) subarray that contains only 1s.
Example 1:
Input: A = [1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0], K = 2
Output: 6
Explanation:
[1,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1]
Bolded numbers were flipped from 0 to 1. The longest subarray is underlined. Example 2:
Input: A = [0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1], K = 3
Output: 10
Explanation:
[0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1]
Bolded numbers were flipped from 0 to 1. The longest subarray is underlined. Note:
1 <= A.length <= 20000
0 <= K <= A.length
A[i] is 0 or 1
题解:这题用了 sliding window 标准模版,用一个变量统计已经 flip 之后的 0 的个数,如果 cnt > k 的时候,我们就尝试往前移动begin指针。
class Solution {
public:
int longestOnes(vector<int>& A, int K) {
const int n = A.size();
int start = , cnt = , res = ;
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
if (A[i] == ) {
cnt++;
}
while (cnt > K) {
if (A[start] == ) {--cnt;}
++start;
}
res = max(res, i - start + );
}
return res;
}
};
similar questions:
【1000】Minimum Cost to Merge Stones(第四题 9分)
Contest 126(题号1005~1008)(2019年3月10日)
https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-127/
结果:4/4,rank:476 / 4734 这次全做出来了,所以暂时不写题解,haha
【1005】Maximize Sum Of Array After K Negations(第一题 4分)
【1006】Clumsy Factorial(第二题 4分)
【1007】Minimum Domino Rotations For Equal Row(第三题 5分)(google tag)
【1008】Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal(第四题 6分)(水题)
【Leetcode周赛】从contest-121开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)的更多相关文章
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-91开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 91 (2018年10月24日,周三) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-91/ 模拟比赛情况记录:第一题柠檬摊的那题6分钟 ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest1开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
注意,以前的比赛我是自己开了 virtual contest.这个阶段的目标是加快手速,思考问题的能力和 bug-free 的能力. 前面已经有了100个contest.计划是每周做三个到五个cont ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-111开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 111 (题号941-944)(2019年1月19日,补充题解,主要是943题) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-111 ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-41开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 41 ()(题号) Contest 42 ()(题号) Contest 43 ()(题号) Contest 44 (2018年12月6日,周四上午)(题号653—656) 链接:htt ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-51开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 51 (2018年11月22日,周四早上)(题号681-684) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/leetcode-weekly-contest-51 ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-71开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 71 () Contest 72 () Contest 73 (2019年1月30日模拟) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-81开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 81 (2018年11月8日,周四,凌晨) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-81 比赛情况记录:结果:3/4, ranki ...
- 【LeetCode】从contest-21开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
[LeetCode Weekly Contest 29][2017/04/23] 第17周 Binary Tree Tilt (3) Array Partition I (6) Longest Lin ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】比赛目录索引
contest 1 ~ contest 10: contest 11 ~ contest 20: contest 21 ~ contest 30 : https://www.cnblogs.com/z ...
随机推荐
- re正则常用示例积累
2019-12-7 import re ''' 示例1: 提取网站的网址 ''' urls = ['https://blog.csdn.net/xxcupid/article/details/5199 ...
- linux运维、架构之路-Nginx服务
一.Nginx服务 1.介绍 Nginx软件常见的使用方式或架构为:LNMP(linux nginx mysql php),Nginx三大主要功能,web网站服务,反向代理负载均衡(n ...
- 检查电脑链接的网络是否支持ipv6
测试方法一:在浏览器地址栏输入网址“http://test-ipv6.com/”,在页面会给出您的ipv6网络测试结果 测试方法二:在浏览器地址栏输入网址“http://ipv6.jmu.edu.cn ...
- zabbix创建钉钉报警
https://juejin.im/post/5c8708eef265da2dd168a1c1 简介 家里搭建了zabbix去监控主机,邮件报警什么的都太麻烦了,所以直接使用钉钉机器人来提醒,下面是我 ...
- spring boot整合WebSocket示例
1.运行环境 开发工具:intellij idea JDK版本:1.8 项目管理工具:Maven 4.0.0 2.GITHUB地址 https://github.com/nbfujx/springBo ...
- JVM虚拟机运行机制
JVM虚拟机运行机制 什么是JVM?虚拟机是物理机器的软件实现.Java是用在VM上运行的WORA(Write Once Run Anywhere)概念而开发的.编译器将Java文件编译为Java . ...
- Harbor在安装前的几个注意点
由于Harbor有1.8后和前的配置不一样,决定先安装1.8,结果报错如下 [root@localhost harbor]# ./install.sh [Step 0]: checking insta ...
- (最小割)Path
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6582 思路:找到最短路核心边建图,跑一遍最小割,最短路核心边的定义为设起点到每个点的最短距离为d[i],每个点到 ...
- css中div垂直居中的方法。
利用绝对定位实现的居中 代码如下: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- Yii 1.1 常规框架部署和配置
<?php //index.php //入口文件配置操作 // change the following paths if necessary $yii=dirname(__FILE__).'/ ...
