AI-IBM-cognitive class --Liner Regression
Liner Regression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import pylab as pl
import numpy as np
%matplotlib inline
%motib inline
%matplotlib作用
- 是在使用jupyter notebook 或者 jupyter qtconsole的时候,才会经常用到%matplotlib,
- 而%matplotlib具体作用是当你调用matplotlib.pyplot的绘图函数plot()进行绘图的时候,或者生成一个figure画布的时候,可以直接在你的python console里面生成图像。
在spyder或者pycharm实际运行代码的时候,可以注释掉这一句
下载数据包
!wget -O FuelConsumption.csv https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/ML0101ENv3/labs/FuelConsumptionCo2.csv
df = pd.read_csv("./FuelConsumptionCo2.csv") # use pandas to read csv file.
# take a look at the dataset, show top 10 lines.
df.head(10)
out:

# summarize the data
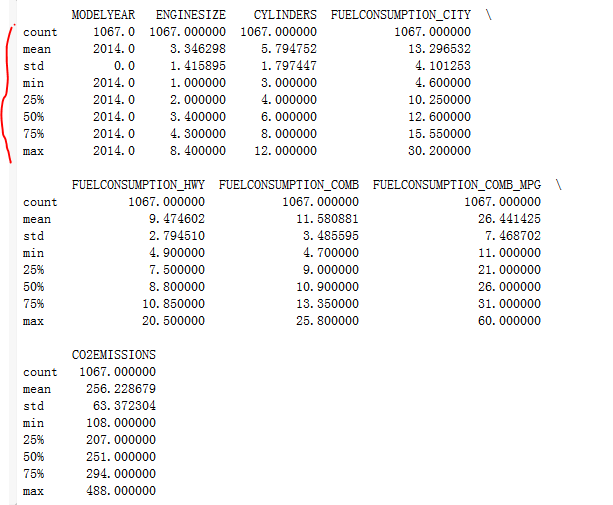
print(df.describe())
使用describe函数进行表格的预处理,求出最大最小值,已经分比例的数据。
out:
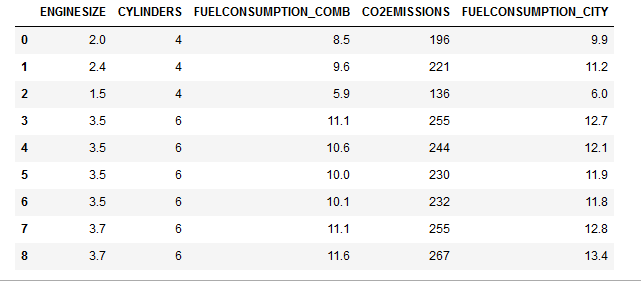
进行表格的重新组合, 提取出我们关心的数据类型。
out:
cdf = df[['ENGINESIZE','CYLINDERS','FUELCONSUMPTION_COMB','CO2EMISSIONS','FUELCONSUMPTION_CITY']]
cdf.head(9)
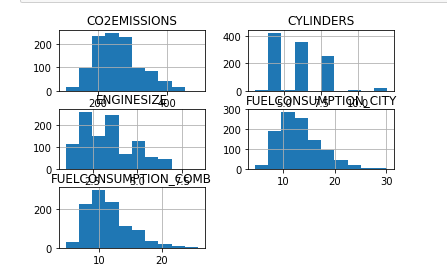
每一列数据可生成hist(直方图)
viz = cdf[['CYLINDERS','ENGINESIZE','CO2EMISSIONS','FUELCONSUMPTION_COMB','FUELCONSUMPTION_CITY']]
viz.hist()
plt.show()
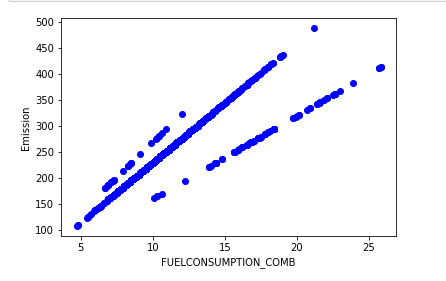
使用scatter生成散列图, 定义散列图的参数, 颜色
具体使用可参考连接:https://blog.csdn.net/qiu931110/article/details/68130199
plt.scatter(cdf.FUELCONSUMPTION_COMB, cdf.CO2EMISSIONS, color='blue')
plt.xlabel("FUELCONSUMPTION_COMB")
plt.ylabel("Emission")
plt.show()
选择表中len长度小于8的数据, 创建训练集合测试集,并生成散列图
Creating train and test dataset
Train/Test Split involves splitting the dataset into training and testing sets respectively, which are mutually exclusive. After which, you train with the training set and test with the testing set. This will provide a more accurate evaluation on out-of-sample accuracy because the testing dataset is not part of the dataset that have been used to train the data. It is more realistic for real world problems.
This means that we know the outcome of each data point in this dataset, making it great to test with! And since this data has not been used to train the model, the model has no knowledge of the outcome of these data points. So, in essence, it is truly an out-of-sample testing.
msk = np.random.rand(len(df)) < 0.8
train = cdf[msk]
test = cdf[~msk]
print(train)
print(test)
plt.scatter(train.ENGINESIZE, train.CO2EMISSIONS, color='blue')
plt.xlabel("Engine size")
plt.ylabel("Emission")
plt.show()

Modeling: Using sklearn package to model data.
from sklearn import linear_model
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
train_x = np.asanyarray(train[['ENGINESIZE']])
train_y = np.asanyarray(train[['CO2EMISSIONS']])
regr.fit (train_x, train_y)
# The coefficients
print ('Coefficients: ', regr.coef_)
print ('Intercept: ',regr.intercept_)
out:
Coefficients: [[39.64984954]]
Intercept: [124.08949291] As mentioned before, Coefficient and Intercept in the simple linear regression, are the parameters of the fit line. Given that it is a simple linear regression,
with only 2 parameters, and knowing that the parameters are the intercept and slope of the line, sklearn can estimate them directly from our data.
Notice that all of the data must be available to traverse and calculate the parameters.
plt.scatter(train.ENGINESIZE, train.CO2EMISSIONS, color='blue')
plt.plot(train_x, regr.coef_[0][0]*train_x + regr.intercept_[0], '-r')
# 通过斜率和截距画出线性回归曲线
plt.xlabel("Engine size")
plt.ylabel("Emission")
使用sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression进行线性回归 参考以下连接:
https://www.cnblogs.com/magle/p/5881170.html
AI-IBM-cognitive class --Liner Regression的更多相关文章
- (三)用Normal Equation拟合Liner Regression模型
继续考虑Liner Regression的问题,把它写成如下的矩阵形式,然后即可得到θ的Normal Equation. Normal Equation: θ=(XTX)-1XTy 当X可逆时,(XT ...
- CS229 3.用Normal Equation拟合Liner Regression模型
继续考虑Liner Regression的问题,把它写成如下的矩阵形式,然后即可得到θ的Normal Equation. Normal Equation: θ=(XTX)-1XTy 当X可逆时,(XT ...
- (线性回归)Liner Regression简单应用
警告:本文为小白入门学习笔记 数据连接: http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/DocumentPage.php?course=DeepLearni ...
- (转)A curated list of Artificial Intelligence (AI) courses, books, video lectures and papers
A curated list of Artificial Intelligence (AI) courses, books, video lectures and papers. Updated 20 ...
- (四)Logistic Regression
1 线性回归 回归就是对已知公式的未知参数进行估计.线性回归就是对于多维空间中的样本点,用特征的线性组合去拟合空间中点的分布和轨迹,比如已知公式是y=a∗x+b,未知参数是a和b,利用多真实的(x,y ...
- 广义线性模型 GLM
Logistic Regression 同 Liner Regression 均属于广义线性模型,Liner Regression 假设 $y|x ; \theta$ 服从 Gaussian 分布,而 ...
- 决策树之 CART
继上篇文章决策树之 ID3 与 C4.5,本文继续讨论另一种二分决策树 Classification And Regression Tree,CART 是 Breiman 等人在 1984 年提出的, ...
- [machine learning] Loss Function view
[machine learning] Loss Function view 有关Loss Function(LF),只想说,终于写了 一.Loss Function 什么是Loss Function? ...
- 【转】Loss Function View
感谢原文作者!原文地址:http://eletva.com/tower/?p=186 一.Loss Function 什么是Loss Function?wiki上有一句解释我觉得很到位,引用一下:Th ...
随机推荐
- 在子组件中触发事件,传值给父组件-vue
1.通过$emit触发事件 在子组件<x-test>中触发事件: <button @click="toSearchProduct()">搜索</but ...
- LinkedList与ArrayList的区别(内部实现)
ArrayList的内部实现是基于内部数组Object[],所以从概念上讲,它更像数组: LinkedList的内部实现是基于一组连接的记录,所以,它更像一个链表结构,所以,它们在性能上有很大的差别. ...
- JAVA泛型通配符T,E,K,V区别,T以及Class<T>,Class<?>的区别
1. 先解释下泛型概念 泛型是Java SE 1.5的新特性,泛型的本质是参数化类型,也就是说所操作的数据类型被指定为一个参数.这种参数类型可以用在类.接口和方法的创建中,分别称为泛型类.泛型接口.泛 ...
- 利用xcode Build生成模拟器运行包
真机只能运行.ipa包 模拟器上只能运行.app包 xcode中生成.app包步骤: 启动xcode IDE,打开gigold源码工程 [project]——[gigold]——[Basic]:修改V ...
- js执行上下文与执行上下文栈
一.什么是执行上下文 简单说就是代码运行时的执行环境,必须是在函数调用的时候才会产生,如果不调用就不会产生这个执行上下文.在这个环境中,所有变量会被事先提出来(变量提升),有的直接赋值,有的为默认值 ...
- [super class]和[self class]
参考: https://www.jianshu.com/p/3f2bcc588b44?utm_campaign=hugo&utm_medium=reader_share&utm_con ...
- 禁止input输入框输入指定内容
链接: http://blog.csdn.net/xiaoya_syt/article/details/52746598
- Queue2链队列
链队列 1 #include <iostream> using namespace std; template <class T> class Queue { private: ...
- 【HDOJ6681】Rikka with Cake(扫描线,线段树)
题意:给定一个n*m的平面,有k条垂直或平行的直线,问将平面分成了几个互不联通的部分 n,m<=1e9,k<=1e5 思路: 刻在DNA里的二维数点 #include<bits/st ...
- Nginx负载均衡与反向代理—《亿级流量网站架构核心技术》
当我们的应用单实例不能支撑用户请求时,此时就需要扩容,从一台服务器扩容到两台.几十台.几百台.然而,用户访问时是通过如http://www.XX.com的方式访问,在请求时,浏览器首先会查询DNS服务 ...
