Deep Learning Tutorial - Convolutional Neural Networks(LENET)
CNN很多概述和要点在CS231n、Neural Networks and Deep Learning中有详细阐述,这里补充Deep Learning Tutorial中的内容。本节前提是前两节的内容,因为要用到全连接层、logistic regression层等。关于Theano:掌握共享变量,下采样,conv2d,dimshuffle的应用等。
1.卷积操作
在Theano中,ConvOp是提供卷积操作的主力。ConvOp来自theano.tensor.signal.conv.conv2d,有两个参数输入[input, W]:
1)input:对应于小批量输入图像的4维张量。尺寸为[小批量尺寸,特征映射数量(滤波器数量),图像高度,图像宽度]
2)W:对应于权重W的4维张量。尺寸为[第m层滤波器数量,m-1层滤波器数量,滤波器高度,滤波器宽度]
但是下面这段代码没有使用这个函数,而是另一个theano.tensor.nnet.conv2d,后面再做解释。
# coding=utf-8
import theano
from theano import tensor as T
from theano.tensor.nnet import conv
import numpy
import numpy
import pylab
from PIL import Image rng = numpy.random.RandomState(23455)
input = T.tensor4(name='input') #初始化4维张量类型!
w_shp = (2, 3, 9, 9) #2个滤波器,3通道,9*9滤波窗口(感受野)
w_bound = numpy.sqrt(3 * 9 * 9)
W = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(rng.uniform(low=-1.0 / w_bound,high=1.0 / w_bound,size=w_shp),dtype=input.dtype), name ='W')
b_shp = (2,)
b = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(rng.uniform(low=-.5, high=.5, size=b_shp),dtype=input.dtype), name ='b')
conv_out = conv.conv2d(input, W) #求卷积
output = T.nnet.sigmoid(conv_out + b.dimshuffle('x', 0, 'x', 'x'))
f = theano.function([input], output) #卷积操作函数 img = Image.open('3wolfmoon.jpg') #文档中给出的3狼图像(639,516,3)
img = numpy.asarray(img, dtype='float64') / 256.
img_ = img.transpose(2, 0, 1).reshape(1, 3, 639, 516) #图像变形为(1,3,639,516)
filtered_img = f(img_) #求卷积
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 1); pylab.axis('off'); pylab.imshow(img)
pylab.gray();
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 2); pylab.axis('off'); pylab.imshow(filtered_img[0, 0, :, :]) #第一滤波器结果
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 3); pylab.axis('off'); pylab.imshow(filtered_img[0, 1, :, :]) #第二滤波器结果
pylab.show()
代码结果: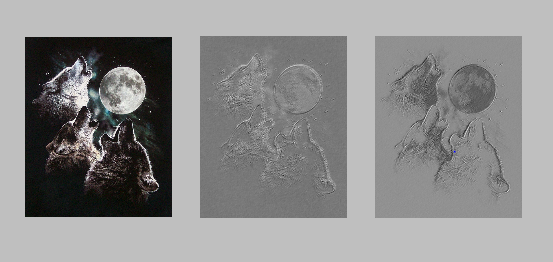
由图中可以看出,随机初始化形成的滤波器经过卷积操作类似于边缘描述子
2.池化(pooling)
Cnn的一个重要步骤是池化,是一种非线性的下采样。比较重要和常见的是最大值采样。在Theano中用 theano.tensor.signal.downsample.max_pool_2d来进行。输入为N维张量(tensor)N>2。下面有一个应用例子,分别是忽略边界和不忽略边界:
from theano.tensor.signal import downsample
input = T.dtensor4(’input’)
maxpool_shape = (2, 2) #2*2的一个池化窗口
pool_out = downsample.max_pool_2d(input, maxpool_shape, ignore_border=True) #忽略边界的池化
f = theano.function([input],pool_out)
invals = numpy.random.RandomState(1).rand(3, 2, 5, 5)
print ’With ignore_border set to True:’
print ’invals[0, 0, :, :] =\n’, invals[0, 0, :, :]
print ’output[0, 0, :, :] =\n’, f(invals)[0, 0, :, :]
pool_out = downsample.max_pool_2d(input, maxpool_shape, ignore_border=False) #保留边界的池化
f = theano.function([input],pool_out)
print ’With ignore_border set to False:’
print ’invals[1, 0, :, :] =\n ’, invals[1, 0, :, :]
print ’output[1, 0, :, :] =\n ’, f(invals)[1, 0, :, :]
3.完整模型:LeNet
Sparse(稀疏连接),convolutional layers(卷积层)和max-pooling(最大值池化)是LeNet家族模型的核心。虽然细节差别很大,下图展示了LeNet几何模型:

上图结构很明了,(卷积+池化)*2+全连接层(MLP),这个全连接层是很传统的一种,包含隐层+logsitic regression,这俩前两节都有介绍。现在讨论theano.tensor.nnet.conv2d和theano.tensor.signal.conv.conv.2d.前者在目前几乎所有模型中使用最多,在这个操作中,每个输出的特征映射与输入的特征映射通过2维滤波器相联系,其值为通过对应滤波器进行卷积操作的和。在原始LeNet中,输出特征映射只与输入特征映射的子集有关系。那么后者只用在信号处理中。
4.主代码
# coding=UTF-8
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import sys
import timeit import numpy import theano
import theano.tensor as T
from theano.tensor.signal import pool
from theano.tensor.nnet import conv2d from Logistic_sgd import LogisticRegression, load_data
from mlp import HiddenLayer class LeNetConvPoolLayer(object):
"""Pool Layer of a convolutional network """
def __init__(self, rng, input, filter_shape, image_shape, poolsize=(2, 2)):
assert image_shape[1] == filter_shape[1]
self.input = input
# there are "num input feature maps * filter height * filter width"
# inputs to each hidden unit
fan_in = numpy.prod(filter_shape[1:]) # 维度拉成列,每个元素都为一个像素,fan_out同理
# each unit in the lower layer receives a gradient from:
# "num output feature maps * filter height * filter width" / pooling size
fan_out = (filter_shape[0] * numpy.prod(filter_shape[2:]) /numpy.prod(poolsize))
W_bound = numpy.sqrt(6. / (fan_in + fan_out))
self.W = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(rng.uniform(low=-W_bound, high=W_bound, size=filter_shape),
dtype=theano.config.floatX),borrow=True)
b_values = numpy.zeros((filter_shape[0],), dtype=theano.config.floatX)
self.b = theano.shared(value=b_values, borrow=True) conv_out = conv2d( #利用滤波器进行卷积操作
input=input,
filters=self.W,
filter_shape=filter_shape,
input_shape=image_shape
) pooled_out = pool.pool_2d( #池化:最大值池化
input=conv_out,
ds=poolsize,
ignore_border=True
)
self.output = T.tanh(pooled_out + self.b.dimshuffle('x', 0, 'x', 'x')) #对阈值参数b维度进行调整
self.params = [self.W, self.b] #'x'看作1,0看作第零维度,这里调整后为b=(1,0维度,1,1)
self.input = input #若b本身为(5,1),则零维度为5,即b=(1,5,1,1) def evaluate_lenet5(learning_rate=0.1, n_epochs=200,dataset='mnist.pkl.gz',nkerns=[20, 50], batch_size=500):
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(23455) #nkerns:两次卷积的滤波器个数本别为20,50
datasets = load_data(dataset)
train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0]
valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1]
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2] n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size
n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size
n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size index = T.lscalar()
x = T.matrix('x')
y = T.ivector('y')
print('... building the model') layer0_input = x.reshape((batch_size, 1, 28, 28)) #mnist数据集图片尺寸28*28 # Construct the first convolutional pooling layer:
# filtering reduces the image size to (28-5+1 , 28-5+1) = (24, 24)
# maxpooling reduces this further to (24/2, 24/2) = (12, 12)
# 4D output tensor is thus of shape (batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12)
layer0 = LeNetConvPoolLayer( #输入(batch_size,1,28,28),输出(batch_size,20,12,12)
rng,
input=layer0_input,
image_shape=(batch_size, 1, 28, 28),
filter_shape=(nkerns[0], 1, 5, 5), #滤波器个数,灰度图像通道数为1,5*5的感受野
poolsize=(2, 2)
) # Construct the second convolutional pooling layer
# filtering reduces the image size to (12-5+1, 12-5+1) = (8, 8)
# maxpooling reduces this further to (8/2, 8/2) = (4, 4)
# 4D output tensor is thus of shape (batch_size, nkerns[1], 4, 4)
layer1 = LeNetConvPoolLayer( #输入(batch_size,20,12,12),输出(batch_size,1,4,4)
rng,
input=layer0.output,
image_shape=(batch_size, nkerns[0], 12, 12),
filter_shape=(nkerns[1], nkerns[0], 5, 5),
poolsize=(2, 2)
) # the HiddenLayer being fully-connected, it operates on 2D matrices of
# shape (batch_size, num_pixels) (i.e matrix of rasterized images).
# This will generate a matrix of shape (batch_size, nkerns[1] * 4 * 4),
# or (500, 50 * 4 * 4) = (500, 800) with the default values.
layer2_input = layer1.output.flatten(2) # 因为要进入全连接层,拉成一维向量即50*4*4 # construct a fully-connected sigmoidal layer
layer2 = HiddenLayer( #输入50*4*4,输出500
rng,
input=layer2_input,
n_in=nkerns[1] * 4 * 4,
n_out=500,
activation=T.tanh
) # classify the values of the fully-connected sigmoidal layer
layer3 = LogisticRegression(input=layer2.output, n_in=500, n_out=10) #输入500,输出10 # the cost we minimize during training is the NLL of the model
cost = layer3.negative_log_likelihood(y) # create a function to compute the mistakes that are made by the model
test_model = theano.function( #测试模型
[index],
layer3.errors(y),
givens={
x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
) validate_model = theano.function( #验证模型
[index],
layer3.errors(y),
givens={
x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
params = layer3.params + layer2.params + layer1.params + layer0.params #参数集
grads = T.grad(cost, params) #求梯度
updates = [(param_i, param_i - learning_rate * grad_i) for param_i, grad_i in zip(params, grads)]
# 参数太多,寻找更新方式太冗长,所以利用SGD更新(来自翻译)
train_model = theano.function( #训练模型
[index],
cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
print('... training')
# early-stopping 策略
patience = 10000 # look as this many examples regardless
patience_increase = 2 # wait this much longer when a new best is found
improvement_threshold = 0.995 # a relative improvement of this much is considered significant
validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience // 2)
# go through this many minibatche before checking the network on the validation set; in this case we check every epoch
best_validation_loss = numpy.inf
best_iter = 0
test_score = 0.
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
epoch = 0
done_looping = False while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping):
epoch = epoch + 1
for minibatch_index in range(n_train_batches): iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index if iter % 100 == 0:
print('training @ iter = ', iter)
cost_ij = train_model(minibatch_index) if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0:
# compute zero-one loss on validation set
validation_losses = [validate_model(i) for i in range(n_valid_batches)]
this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses)
print('epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, validation error %f %%' %(epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, this_validation_loss * 100.)) # if we got the best validation score until now
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss:
#improve patience if loss improvement is good enough
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * \
improvement_threshold:
patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase) # save best validation score and iteration number
best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss
best_iter = iter # test it on the test set
test_losses = [test_model(i)for i in range(n_test_batches)]
test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses)
print(('epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, test error of ''best model %f %%') %(epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, test_score * 100.)) if patience <= iter:
done_looping = True
break end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print('Optimization complete.')
print('Best validation score of %f %% obtained at iteration %i, '
'with test performance %f %%' %
(best_validation_loss * 100., best_iter + 1, test_score * 100.))
print(('The code for file ' +
os.path.split(__file__)[1] +
' ran for %.2fm' % ((end_time - start_time) / 60.)), file=sys.stderr) if __name__ == '__main__':
evaluate_lenet5() def experiment(state, channel):
evaluate_lenet5(state.learning_rate, dataset=state.dataset)
Deep Learning Tutorial - Convolutional Neural Networks(LENET)的更多相关文章
- Coursera, Deep Learning 4, Convolutional Neural Networks - week1
CNN 主要解决 computer vision 问题,同时解决input X 维度太大的问题. Edge detection 下面演示了convolution 的概念 下图的 vertical ed ...
- Coursera, Deep Learning 4, Convolutional Neural Networks - week4,
Face recognition One Shot Learning 只看一次图片,就能以后识别, 传统deep learning 很难做到这个. 而且如果要加一个人到数据库里面,就要重新train ...
- Coursera, Deep Learning 4, Convolutional Neural Networks - week2
Case Study (Note: 红色表示不重要) LeNet-5 起初用来识别手写数字灰度图片 AlexNet 输入的是227x227x3 的图片,输出1000 种类的结果 VGG VGG比Ale ...
- Coursera, Deep Learning 4, Convolutional Neural Networks, week3, Object detection
学习目标 Understand the challenges of Object Localization, Object Detection and Landmark Finding Underst ...
- 论文笔记之:Learning Multi-Domain Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Tracking
Learning Multi-Domain Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Tracking CVPR 2016 本文提出了一种新的CNN 框架来处理 ...
- [CVPR2015] Is object localization for free? – Weakly-supervised learning with convolutional neural networks论文笔记
p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 13.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 } p. ...
- 【论文阅读】Learning Dual Convolutional Neural Networks for Low-Level Vision
论文阅读([CVPR2018]Jinshan Pan - Learning Dual Convolutional Neural Networks for Low-Level Vision) 本文针对低 ...
- 卷积神经网络LeNet Convolutional Neural Networks (LeNet)
Note This section assumes the reader has already read through Classifying MNIST digits using Logisti ...
- 【DeepLearning学习笔记】Coursera课程《Neural Networks and Deep Learning》——Week2 Neural Networks Basics课堂笔记
Coursera课程<Neural Networks and Deep Learning> deeplearning.ai Week2 Neural Networks Basics 2.1 ...
随机推荐
- Maven 命令参数 整理
命令参数 备注 mvn -v --version 显示版本信息; mvn -V --show-version 显示版本信息后继续执行Maven其他目标; mvn -h --help 显示帮助信息; m ...
- 利用salt搭建hadoop集群
自动化工具有很多..今天总结一下salt安装hadoop 步骤,学习过程. 1,机器列表 hosts文件 只需要将namenode的两台机器上配置 ,不解释了. 2.salt-master在10 ...
- hibernate注解方式来处理映射关系
在hibernate中,通常配置对象关系映射关系有两种,一种是基于xml的方式,另一种是基于annotation的注解方式,熟话说,萝卜青菜,可有所爱,每个人都有自己喜欢的配置方式,我在试了这两种方式 ...
- Java动态代理之JDK实现和CGlib实现(简单易懂)
转载请注明原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ygj0930/p/6542259.html 一:代理模式(静态代理) 代理模式是常用设计模式的一种,我们在软件设计时常用的代理一般是 ...
- 2.抽象工厂(Abstract Factory)
常规的对象创建方法: //创建一个Road对象 Road road =new Road(); new 的问题: 实现依赖,不能应对“具体实例化类型”的变化.解决思路: 封装变化点-----哪里变 ...
- HTML5 离线缓存Appcache
创建一个和html同名的manifest文件,比如页面为index.html,那么可以建一个index.manifest的文件,然后给index.html的html标签添加如下属性即可: <ht ...
- SSRF漏洞分析与利用
转自:http://www.4o4notfound.org/index.php/archives/33/ 前言:总结了一些常见的姿势,以PHP为例,先上一张脑图,划√的是本文接下来实际操作的 0x01 ...
- Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization(第一周)深度学习的实践层面 (Practical aspects of Deep Learning)
1. Setting up your Machine Learning Application 1.1 训练,验证,测试集(Train / Dev / Test sets) 1.2 Bias/Vari ...
- MVC 5 Scaffolder + EntityFramework+UnitOfWork Pattern 代码生成工具
MVC 5 Scaffolder + EntityFramework+UnitOfWork Pattern 代码生成工具集成Visual Studio 2013 MVC 5 Scaffolder + ...
- Char类型与Sting类型的数字字符转换时的不同点
这是在一次编程时的bug里偶然发现的一个问题.在C#中,单引号默认是char类型字符,而双引号默认是string类型字符.对于char类型的数字字符,通过强制类型转换或者convert转换,转换成的整 ...
