【原创】大数据基础之Kerberos(1)简介、安装、使用
kerberos5-1.17

官方:https://kerberos.org/
一 简介
The Kerberos protocol is designed to provide reliable authentication over open and insecure networks where communications between the hosts belonging to it may be intercepted. However, one should be aware that Kerberos does not provide any guarantees if the computers being used are vulnerable: the authentication servers, application servers (imap, pop, smtp, telnet, ftp, ssh , AFS, lpr, ...) and clients must be kept constantly updated so that the authenticity of the requesting users and service providers can be guaranteed.
The above points justify the sentence: "Kerberos is an authentication protocol for trusted hosts on untrusted networks". By way of example, and to reiterate the concept: Kerberos' strategies are useless if someone who obtains privileged access to a server, can copy the file containing the secret key. Indeed, the intruder will put this key on another machine, and will only have to obtain a simple spoof DNS or IP address for that server to appear to clients as the authentic server.
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol. It is designed to provide strong authentication for client/server applications by using secret-key cryptography. A free implementation of this protocol is available from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Kerberos is available in many commercial products as well.
kerberos是一个网络身份认证协议,使用密钥加密算法为CS应用提供安全的身份认证;
The Internet is an insecure place. Many of the protocols used in the Internet do not provide any security. Tools to "sniff" passwords off of the network are in common use by malicious hackers. Thus, applications which send an unencrypted password over the network are extremely vulnerable. Worse yet, other client/server applications rely on the client program to be "honest" about the identity of the user who is using it. Other applications rely on the client to restrict its activities to those which it is allowed to do, with no other enforcement by the server.
互联网是非安全的,互联网的很多协议并没有提供任何安全机制,嗅探密码的工具在网络上被黑客广泛使用,因此,在网络上发送明文密码的应用是非常脆弱的;更糟糕的是,有些CS应用相信client的用户是honest的,有些应用依赖client来进行安全限制;
Some sites attempt to use firewalls to solve their network security problems. Unfortunately, firewalls assume that "the bad guys" are on the outside, which is often a very bad assumption. Most of the really damaging incidents of computer crime are carried out by insiders. Firewalls also have a significant disadvantage in that they restrict how your users can use the Internet. (After all, firewalls are simply a less extreme example of the dictum that there is nothing more secure than a computer which is not connected to the network --- and powered off!) In many places, these restrictions are simply unrealistic and unacceptable.
很多网站使用firewall来解决网络安全问题,不幸的是,firewall假设the bad guys在外部,这是一个非常不好的假设,绝大部分的计算机犯罪是从内部进行;
Kerberos was created by MIT as a solution to these network security problems. The Kerberos protocol uses strong cryptography so that a client can prove its identity to a server (and vice versa) across an insecure network connection. After a client and server has used Kerberos to prove their identity, they can also encrypt all of their communications to assure privacy and data integrity as they go about their business.
kerberos是MIT提出的一个应对网络安全问题的解决方案;kerberos协议使用强加密算法所以client可以通过不安全的网络连接来验证身份;当client和server使用kerberos来验证身份之后,他们可以加密所有的连接信息来保证数据隐私和完整性;
Kerberos is freely available from MIT, under copyright permissions very similar those used for the BSD operating system and the X Window System. MIT provides Kerberos in source form so that anyone who wishes to use it may look over the code for themselves and assure themselves that the code is trustworthy. In addition, for those who prefer to rely on a professionally supported product, Kerberos is available as a product from many different vendors.
kerberos是免费的开源的;
In summary, Kerberos is a solution to your network security problems. It provides the tools of authentication and strong cryptography over the network to help you secure your information systems across your entire enterprise. We hope you find Kerberos as useful as it has been to us. At MIT, Kerberos has been invaluable to our Information/Technology architecture.
kerberos提供了很多身份验证和强加密算法的工具;
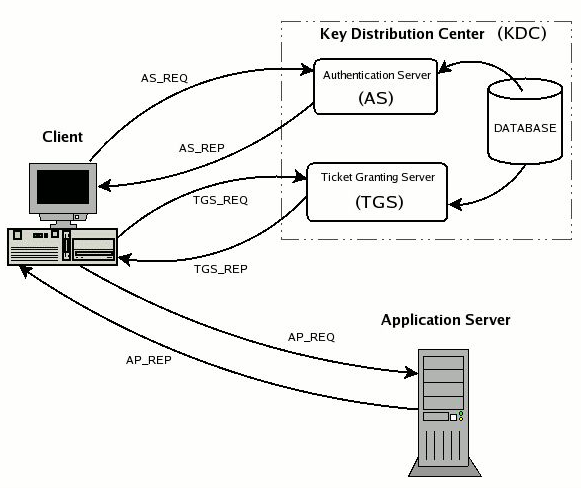
角色
Key Distribution Center (KDC)
The authentication server in a Kerberos environment, based on its ticket distribution function for access to the services, is called Key Distribution Center or more briefly KDC. Since it resides entirely on a single physical server (it often coincides with a single process) it can be logically considered divided into three parts: Database, Authentication Server (AS) and Ticket Granting Server (TGS).
1)Database
The database is the container for entries associated with users and services.
2)Authentication Server (AS)
The Authentication Server is the part of the KDC which replies to the initial authentication request from the client, when the user, not yet authenticated, must enter the password. In response to an authentication request, the AS issues a special ticket known as the Ticket Granting Ticket, or more briefly TGT, the principal associated with which is krbtgt/REALM@REALM. If the users are actually who they say they are (and we'll see later how they demonstrate this) they can use the TGT to obtain other service tickets, without having to re-enter their password.
3)Ticket Granting Server (TGS)
The Ticket Granting Server is the KDC component which distributes service tickets to clients with a valid TGT, guaranteeing the authenticity of the identity for obtaining the requested resource on the application servers. The TGS can be considered as an application server (given that to access it it is necessary to present the TGT) which provides the issuing of service tickets as a service. It is important not to confuse the abbreviations TGT and TGS: the first indicates a ticket and the second a service.
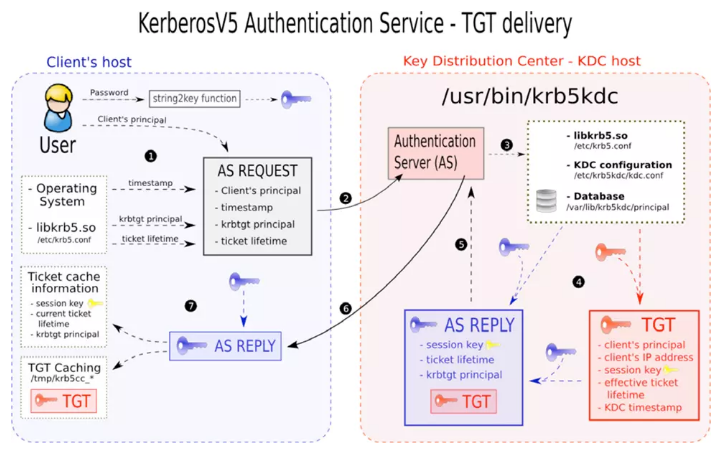
概念
realm
The term realm indicates an authentication administrative domain. Its intention is to establish the boundaries within which an authentication server has the authority to authenticate a user, host or service.
Basically, a user/service belongs to a realm if and only if he/it shares a secret (password/key) with the authentication server of that realm.
The name of a realm is case sensitive, i.e. there is a difference between upper and lower case letters, but normally realms always appear in upper case letters.
principal
A principal is the name used to refer to the entries in the authentication server database. A principal is associated with each user, host or service of a given realm. A principal in Kerberos 5 is of the following type:
component1/component2/.../componentN@REALM
However, in practice a maximum of two components are used. For an entry referring to a user the principal is the following type:
Name[/Instance]@REALM
The instance is optional and is normally used to better qualify the type of user. For example administrator users normally have the admin instance. The following are examples of principals referred to users:
pippo@EXAMPLE.COM admin/admin@EXAMPLE.COM pluto/admin@EXAMPLE.COM
Ticket
A ticket is something a client presents to an application server to demonstrate the authenticity of its identity. Tickets are issued by the authentication server and are encrypted using the secret key of the service they are intended for. Since this key is a secret shared only between the authentication server and the server providing the service, not even the client which requested the ticket can know it or change its contents. The main information contained in a ticket includes:
- The requesting user's principal (generally the username);
- The principal of the service it is intended for;
- The IP address of the client machine from which the ticket can be used. In Kerberos 5 this field is optional and may also be multiple in order to be able to run clients under NAT or multihomed.
- The date and time (in timestamp format) when the tickets validity commences;
- The ticket's maximum lifetime
- The session key (this has a fundamental role which is described below);
二 安装
kdc
# yum install krb5-libs krb5-server krb5-workstation
client
# yum install krb5-devel krb5-workstation
三 使用
kdc
1 修改配置:替换域名、修改ip、注释default_ccache_name
# vi /etc/krb5.conf
default_realm = ANYTHING.COM
#default_ccache_name = KEYRING:persistent:%{uid}
[realms]
ANYTHING.COM = {
kdc = 192.168.0.1
admin_server = 192.168.0.1
}
[domain_realm]
.anything.com = ANYTHING.COM
anything.com = ANYTHING.COM# vi /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf
ANYTHING.COM = {
#master_key_type = aes256-cts
max_renewable_life = 7d 0h 0m 0s
default_principal_flags = +renewable# vi /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl
*/admin@ANYTHING.COM *
2 创建数据库
# kdb5_util create -r ANYTHING.COM -s
3 创建管理员用户admin
# /usr/sbin/kadmin.local -q "addprinc admin/admin"
4 启动kdc
systemctl start krb5kdc
systemctl start kadminsystemctl enable krb5kdc
systemctl enable kadmin
5 本机ticket验证
# kinit admin/admin
# klist
7 本机admin验证(kdc上无需密码)
# kadmin.local
kadmin.local: ?
Available kadmin.local requests:add_principal, addprinc, ank
Add principal
delete_principal, delprinc
Delete principal
modify_principal, modprinc
Modify principal
rename_principal, renprinc
Rename principal
change_password, cpw Change password
get_principal, getprinc Get principal
list_principals, listprincs, get_principals, getprincs
List principals
add_policy, addpol Add policy
modify_policy, modpol Modify policy
delete_policy, delpol Delete policy
get_policy, getpol Get policy
list_policies, listpols, get_policies, getpols
List policies
get_privs, getprivs Get privileges
ktadd, xst Add entry(s) to a keytab
ktremove, ktrem Remove entry(s) from a keytab
lock Lock database exclusively (use with extreme caution!)
unlock Release exclusive database lock
purgekeys Purge previously retained old keys from a principal
get_strings, getstrs Show string attributes on a principal
set_string, setstr Set a string attribute on a principal
del_string, delstr Delete a string attribute on a principal
list_requests, lr, ? List available requests.
quit, exit, q Exit program.
也可以直接通过参数执行命令,比如
# kadmin.local -q 'listprincs'
非kdc服务器上使用kadmin
client
1 同步kdc上的/etc/krb5.conf
2 远程admin验证
# kadmin -p 'admin/admin'
3 远程ticket验证
# kinit admin/admin
# klist
其他常用命令
1)直接登录
# kinit admin/admin@ANYTHING.COM
2)查看
# klist
3)退出
# kdestroy
4)导出keytab
# kadmin.local -q 'ktadd -k /path/to/test.keytab -norandkey admin/admin@ANYTHING.COM'
5)查看keytab
# klist -k /path/to/test.keytab
6)使用keytab登录
# kinit -kt /path/to/test.keytab admin/admin@ANYTHING.COM
7)修改密码
# kadmin.local
kadmin.local: change_password admin/admin@ANYTHING.COM
也可以通过kpasswd修改,上边使用kadmin.local的方式相当于重置密码
8)添加principal
# kadmin.local -q 'addprinc $user/$host@$REALM'
增加参数-randkey则使用随机密码
参考:https://web.mit.edu/kerberos/
【原创】大数据基础之Kerberos(1)简介、安装、使用的更多相关文章
- 【原创】大数据基础之Kerberos(2)hive impala hdfs访问
1 hive # kadmin.local -q 'ktadd -k /tmp/hive3.keytab -norandkey hive/server03@TEST.COM'# kinit -kt / ...
- 大数据基础环境--jdk1.8环境安装部署
1.环境说明 1.1.机器配置说明 本次集群环境为三台linux系统机器,具体信息如下: 主机名称 IP地址 操作系统 hadoop1 10.0.0.20 CentOS Linux release 7 ...
- 【原创】大数据基础之Zookeeper(2)源代码解析
核心枚举 public enum ServerState { LOOKING, FOLLOWING, LEADING, OBSERVING; } zookeeper服务器状态:刚启动LOOKING,f ...
- CentOS6安装各种大数据软件 第八章:Hive安装和配置
相关文章链接 CentOS6安装各种大数据软件 第一章:各个软件版本介绍 CentOS6安装各种大数据软件 第二章:Linux各个软件启动命令 CentOS6安装各种大数据软件 第三章:Linux基础 ...
- 大数据应用日志采集之Scribe 安装配置指南
大数据应用日志采集之Scribe 安装配置指南 大数据应用日志采集之Scribe 安装配置指南 1.概述 Scribe是Facebook开源的日志收集系统,在Facebook内部已经得到大量的应用.它 ...
- 【原创】大数据基础之Impala(1)简介、安装、使用
impala2.12 官方:http://impala.apache.org/ 一 简介 Apache Impala is the open source, native analytic datab ...
- 【原创】大数据基础之Benchmark(2)TPC-DS
tpc 官方:http://www.tpc.org/ 一 简介 The TPC is a non-profit corporation founded to define transaction pr ...
- 【原创】大数据基础之词频统计Word Count
对文件进行词频统计,是一个大数据领域的hello word级别的应用,来看下实现有多简单: 1 Linux单机处理 egrep -o "\b[[:alpha:]]+\b" test ...
- 大数据基础知识:分布式计算、服务器集群[zz]
大数据中的数据量非常巨大,达到了PB级别.而且这庞大的数据之中,不仅仅包括结构化数据(如数字.符号等数据),还包括非结构化数据(如文本.图像.声音.视频等数据).这使得大数据的存储,管理和处理很难利用 ...
随机推荐
- 常用Java数据库连接池
概述 在这里所谓的数据库连接是指通过网络协议与数据库服务之间建立的TCP连接.通常,与数据库服务进行通信的网络协议无需由应用程序本身实现,原因有三: 实现复杂度大,需要充分理解和掌握相应的通信协议. ...
- MongoDB统计文档(Document)的数组(Array)中的各个元素出现的次数
一,问题描述 [使用 unwind 操作符 “解包” Document 里面的Array中的每个元素,然后使用 group 分组统计,最后使用 sort 对分组结果排序] 从 images.json ...
- electron-vue:Vue.js 开发 Electron 桌面应用
相信很多同学都知道 Electron 可以帮助开发人员使用前端技术开发桌面客户端应用,今天介绍的 electron-vue 框架是一套基于 Vue.js 开发 Electron 桌面应用的脚手架,该项 ...
- StarUML最新版2.8.1简单使用及代码生成
StarUML(简称SU)是一款开放源码的UML开发工具,由韩国公司主导开发出来的,可以直接到StarUML网站下载. 在这里直接超链接:http://staruml.io/download SU是一 ...
- Linux 文件大小查找排序
du -sh 文件大小查询: 1.当前目录的大小: du -sh | sort 2.当前 目录下的文件大小: ls -lsh 3.当前目录 下的文件大小排序: du -sh * |sort -n 4. ...
- service cloudera-scm-server restart报错 Unable to retrieve remote parcel repository manifest
Unable to retrieve remote parcel repository manifest 1 详细错误 ERROR ParcelUpdateService:com.cloudera.p ...
- 前端向服务器请求数据并渲染的方式(ajax/jQuery/axios/vue)
原理: jQuery的ajax请求:complete函数一般无论服务器有无数据返回都会显示(成功或者失败都显示数据): return result
- python3: print()函数:def,end关键字介绍
print()函数是最最普通常见的函数,我们常用的方式为类似这种的没有任何设置的“ print("今天是个好日子") ” 的简单输出. 其实print()函数中含有如下几个关键字, ...
- Maven项目配置logback
首先,在pom.xml中加入maven依赖 <!-- log start --> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</group ...
- AOP 横行切面编程和 纵向编程 介绍
1 aop:面向切面(方面)编程,扩展功能不修改源代码实现 2 AOP采取横向抽取机制,取代了传统纵向继承体系重复性代码3 aop底层使用动态代理实现(1)第一种情况,有接口情况,使用动态代理创建接口 ...
