第十三节,使用带有全局平均池化层的CNN对CIFAR10数据集分类
这里使用的数据集仍然是CIFAR-10,由于之前写过一篇使用AlexNet对CIFAR数据集进行分类的文章,已经详细介绍了这个数据集,当时我们是直接把这些图片的数据文件下载下来,然后使用pickle进行反序列化获取数据的,具体内容可以参考这里:第十六节,卷积神经网络之AlexNet网络实现(六)
与MNIST类似,TensorFlow中也有一个下载和导入CIFAR数据集的代码文件,不同的是,自从TensorFlow1.0之后,将里面的Models模块分离了出来,分离和导入CIFAR数据集的代码在models中,所以要先去TensorFlow的GitHub网站将其下载下来。点击下载地址开始下载。

一 描述
在该例子中,使用了全局平均池化层来代替传统的全连接层,使用了3个卷积层的同卷积网络,滤波器为5x5,每个卷积层后面跟有一个步长2x2的池化层,滤波器大小为2x2,最后一个池化层为全局平均池化层,输出后为batch_sizex1x1x10,我们对其进行形状变换为batch_sizex10,得到10个特征,再对这10个特征进行softmax计算,其结果代表最终分类。
- 输入图片大小为24x24x3
- 经过5x5的同卷积操作(步长为1),输出64个通道,得到24x24x64的输出
- 经过f=2,s=2的池化层,得到大小为12x12x24的输出
- 经过5x5的同卷积操作(步长为1),输出64个通道,得到12x12x64的输出
- 经过f=2,s=2的池化层,得到大小为6x6x64的输出
- 经过5x5的同卷积操作(步长为1),输出10个通道,得到6x6x10的输出
- 经过一个全局平均池化层f=6,s=6,得到1x1x10的输出
- 展开成1x10的形状,经过softmax函数计算,进行分类
二 导入数据集
'''
一 引入数据集
'''
batch_size = 128
learning_rate = 1e-4
training_step = 15000
display_step = 200
#数据集目录
data_dir = './cifar10_data/cifar-10-batches-bin'
print('begin')
#获取训练集数据
images_train,labels_train = cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data=False,data_dir = data_dir,batch_size=batch_size)
print('begin data')
注意这里调用了cifar10_input.inputs()函数,这个函数是专门获取数据的函数,返回数据集合对应的标签,但是这个函数会将图片裁切好,由原来的32x32x3变成24x24x3,该函数默认使用测试数据集,如果使用训练数据集,可以将第一个参数传入eval_data=False。另外再将batch_size和dir传入,就可以得到dir下面的batch_size个数据了。我们可以查看一下这个函数的实现:
def inputs(eval_data, data_dir, batch_size):
"""Construct input for CIFAR evaluation using the Reader ops. Args:
eval_data: bool, indicating if one should use the train or eval data set.
data_dir: Path to the CIFAR-10 data directory.
batch_size: Number of images per batch. Returns:
images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size.
labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size.
"""
if not eval_data:
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'data_batch_%d.bin' % i)
for i in xrange(1, 6)]
num_examples_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN
else:
filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'test_batch.bin')]
num_examples_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL for f in filenames:
if not tf.gfile.Exists(f):
raise ValueError('Failed to find file: ' + f) with tf.name_scope('input'):
# Create a queue that produces the filenames to read.
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames) # Read examples from files in the filename queue.
read_input = read_cifar10(filename_queue)
reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32) height = IMAGE_SIZE
width = IMAGE_SIZE # Image processing for evaluation.
# Crop the central [height, width] of the image.
resized_image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(reshaped_image,
height, width) # Subtract off the mean and divide by the variance of the pixels.
float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(resized_image) # Set the shapes of tensors.
float_image.set_shape([height, width, 3])
read_input.label.set_shape([1]) # Ensure that the random shuffling has good mixing properties.
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue = 0.4
min_queue_examples = int(num_examples_per_epoch *
min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue) # Generate a batch of images and labels by building up a queue of examples.
return _generate_image_and_label_batch(float_image, read_input.label,
min_queue_examples, batch_size,
shuffle=False)
这个函数主要包含以下几步:
- 读取测试集文件名或者训练集文件名,并创建文件名队列。
- 使用文件读取器读取一张图像的数据和标签,并返回一个存放这些张量数据的类对象。
- 对图像进行裁切处理。
- 归一化输入。
- 读取batch_size个图像和标签。(返回的是一个张量,必须要在会话中执行才能得到数据)
三 定义网络结构
'''
二 定义网络结构
'''
def weight_variable(shape):
'''
初始化权重 args:
shape:权重shape
'''
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape=shape,mean=0.0,stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape):
'''
初始化偏置 args:
shape:偏置shape
'''
initial =tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial) def conv2d(x,W):
'''
卷积运算 ,使用SAME填充方式 卷积层后
out_height = in_hight / strides_height(向上取整)
out_width = in_width / strides_width(向上取整) args:
x:输入图像 形状为[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
W:权重 形状为[filter_height,filter_width,in_channels,out_channels]
'''
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') def max_pool_2x2(x):
'''
最大池化层,滤波器大小为2x2,'SAME'填充方式 池化层后
out_height = in_hight / strides_height(向上取整)
out_width = in_width / strides_width(向上取整) args:
x:输入图像 形状为[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
'''
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME') def avg_pool_6x6(x):
'''
全局平均池化层,使用一个与原有输入同样尺寸的filter进行池化,'SAME'填充方式 池化层后
out_height = in_hight / strides_height(向上取整)
out_width = in_width / strides_width(向上取整) args;
x:输入图像 形状为[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
'''
return tf.nn.avg_pool(x,ksize=[1,6,6,1],strides=[1,6,6,1],padding='SAME') def print_op_shape(t):
'''
输出一个操作op节点的形状
'''
print(t.op.name,'',t.get_shape().as_list()) #定义占位符
input_x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,24,24,3]) #图像大小24x24x
input_y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,10]) #0-9类别 x_image = tf.reshape(input_x,[-1,24,24,3]) #1.卷积层 ->池化层
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,3,64])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1) + b_conv1) #输出为[-1,24,24,64]
print_op_shape(h_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) #输出为[-1,12,12,64]
print_op_shape(h_pool1) #2.卷积层 ->池化层
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,64,64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2) + b_conv2) #输出为[-1,12,12,64]
print_op_shape(h_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) #输出为[-1,6,6,64]
print_op_shape(h_pool2) #3.卷积层 ->全局平均池化层
W_conv3 = weight_variable([5,5,64,10])
b_conv3 = bias_variable([10]) h_conv3 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool2,W_conv3) + b_conv3) #输出为[-1,6,6,10]
print_op_shape(h_conv3) nt_hpool3 = avg_pool_6x6(h_conv3) #输出为[-1,1,1,10]
print_op_shape(nt_hpool3)
nt_hpool3_flat = tf.reshape(nt_hpool3,[-1,10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(nt_hpool3_flat)
四 定义求解器
'''
三 定义求解器
''' #softmax交叉熵代价函数
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(input_y * tf.log(y_conv),axis=1)) #求解器
train = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) #返回一个准确度的数据
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_conv,1),tf.arg_max(input_y,1))
#准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,dtype=tf.float32))
五 开始测试
'''
四 开始训练
'''
sess = tf.Session();
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# 启动计算图中所有的队列线程 调用tf.train.start_queue_runners来将文件名填充到队列,否则read操作会被阻塞到文件名队列中有值为止。
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) for step in range(training_step):
#获取batch_size大小数据集
image_batch,label_batch = sess.run([images_train,labels_train]) #one hot编码
label_b = np.eye(10,dtype=np.float32)[label_batch] #开始训练
train.run(feed_dict={input_x:image_batch,input_y:label_b},session=sess) if step % display_step == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={input_x:image_batch,input_y:label_b},session=sess)
print('Step {0} tranining accuracy {1}'.format(step,train_accuracy))
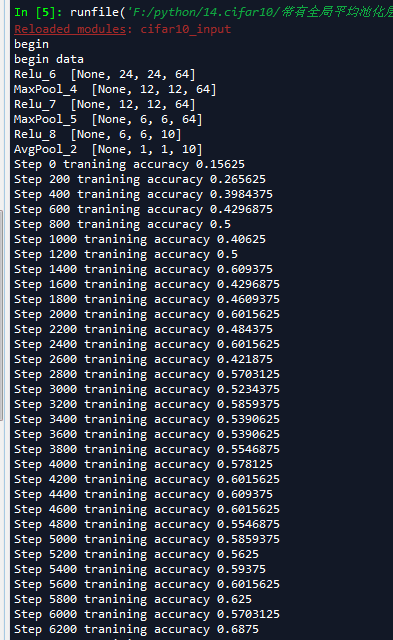
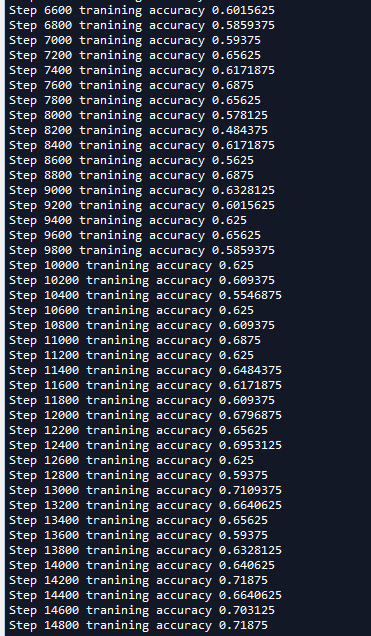
我们可以看到这个模型准确率接近70%,这主要是因为我们在图像预处理是进行了输入归一化处理,导致比我们在第十六节,卷积神经网络之AlexNet网络实现(六)文章中使用传统神经网络训练准确度52%要提高了不少,并且比AlexNet的60%高了一些(AlexNet我迭代的轮数比较少,因为太耗时)。
完整代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu May 3 12:29:16 2018 @author: zy
""" '''
建立一个带有全局平均池化层的卷积神经网络 并对CIFAR-10数据集进行分类
1.使用3个卷积层的同卷积操作,滤波器大小为5x5,每个卷积层后面都会跟一个步长为2x2的池化层,滤波器大小为2x2
2.对输出的10个feature map进行全局平均池化,得到10个特征
3.对得到的10个特征进行softmax计算,得到分类
''' import cifar10_input
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np '''
一 引入数据集
'''
batch_size = 128
learning_rate = 1e-4
training_step = 15000
display_step = 200
#数据集目录
data_dir = './cifar10_data/cifar-10-batches-bin'
print('begin')
#获取训练集数据
images_train,labels_train = cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data=False,data_dir = data_dir,batch_size=batch_size)
print('begin data') '''
二 定义网络结构
'''
def weight_variable(shape):
'''
初始化权重 args:
shape:权重shape
'''
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape=shape,mean=0.0,stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape):
'''
初始化偏置 args:
shape:偏置shape
'''
initial =tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial) def conv2d(x,W):
'''
卷积运算 ,使用SAME填充方式 池化层后
out_height = in_hight / strides_height(向上取整)
out_width = in_width / strides_width(向上取整) args:
x:输入图像 形状为[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
W:权重 形状为[filter_height,filter_width,in_channels,out_channels]
'''
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') def max_pool_2x2(x):
'''
最大池化层,滤波器大小为2x2,'SAME'填充方式 池化层后
out_height = in_hight / strides_height(向上取整)
out_width = in_width / strides_width(向上取整) args:
x:输入图像 形状为[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
'''
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME') def avg_pool_6x6(x):
'''
全局平均池化层,使用一个与原有输入同样尺寸的filter进行池化,'SAME'填充方式 池化层后
out_height = in_hight / strides_height(向上取整)
out_width = in_width / strides_width(向上取整) args;
x:输入图像 形状为[batch,in_height,in_width,in_channels]
'''
return tf.nn.avg_pool(x,ksize=[1,6,6,1],strides=[1,6,6,1],padding='SAME') def print_op_shape(t):
'''
输出一个操作op节点的形状
'''
print(t.op.name,'',t.get_shape().as_list()) #定义占位符
input_x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,24,24,3]) #图像大小24x24x
input_y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,shape=[None,10]) #0-9类别 x_image = tf.reshape(input_x,[-1,24,24,3]) #1.卷积层 ->池化层
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,3,64])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,W_conv1) + b_conv1) #输出为[-1,24,24,64]
print_op_shape(h_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) #输出为[-1,12,12,64]
print_op_shape(h_pool1) #2.卷积层 ->池化层
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,64,64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2) + b_conv2) #输出为[-1,12,12,64]
print_op_shape(h_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) #输出为[-1,6,6,64]
print_op_shape(h_pool2) #3.卷积层 ->全局平均池化层
W_conv3 = weight_variable([5,5,64,10])
b_conv3 = bias_variable([10]) h_conv3 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool2,W_conv3) + b_conv3) #输出为[-1,6,6,10]
print_op_shape(h_conv3) nt_hpool3 = avg_pool_6x6(h_conv3) #输出为[-1,1,1,10]
print_op_shape(nt_hpool3)
nt_hpool3_flat = tf.reshape(nt_hpool3,[-1,10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(nt_hpool3_flat) '''
三 定义求解器
''' #softmax交叉熵代价函数
cost = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(input_y * tf.log(y_conv),axis=1)) #求解器
train = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) #返回一个准确度的数据
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_conv,1),tf.arg_max(input_y,1))
#准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,dtype=tf.float32)) '''
四 开始训练
'''
sess = tf.Session();
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) for step in range(training_step):
image_batch,label_batch = sess.run([images_train,labels_train])
label_b = np.eye(10,dtype=np.float32)[label_batch] train.run(feed_dict={input_x:image_batch,input_y:label_b},session=sess) if step % display_step == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={input_x:image_batch,input_y:label_b},session=sess)
print('Step {0} tranining accuracy {1}'.format(step,train_accuracy))
第十三节,使用带有全局平均池化层的CNN对CIFAR10数据集分类的更多相关文章
- 全连接层(FC)与全局平均池化层(GAP)
在卷积神经网络的最后,往往会出现一两层全连接层,全连接一般会把卷积输出的二维特征图转化成一维的一个向量,全连接层的每一个节点都与上一层每个节点连接,是把前一层的输出特征都综合起来,所以该层的权值参数是 ...
- 【深度学习篇】--神经网络中的池化层和CNN架构模型
一.前述 本文讲述池化层和经典神经网络中的架构模型. 二.池化Pooling 1.目标 降采样subsample,shrink(浓缩),减少计算负荷,减少内存使用,参数数量减少(也可防止过拟合)减少输 ...
- 图像处理池化层pooling和卷积核
1.池化层的作用 在卷积神经网络中,卷积层之间往往会加上一个池化层.池化层可以非常有效地缩小参数矩阵的尺寸,从而减少最后全连层中的参数数量.使用池化层即可以加快计算速度也有防止过拟合的作用. 2.为什 ...
- 『TensorFlow』卷积层、池化层详解
一.前向计算和反向传播数学过程讲解
- CNN-卷积层和池化层学习
卷积神经网络(CNN)由输入层.卷积层.激活函数.池化层.全连接层组成,即INPUT-CONV-RELU-POOL-FC (1)卷积层:用它来进行特征提取,如下: 输入图像是32*32*3,3是它的深 ...
- [DeeplearningAI笔记]卷积神经网络1.9-1.11池化层/卷积神经网络示例/优点
4.1卷积神经网络 觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~Follow Me 1.9池化层 优点 池化层可以缩减模型的大小,提高计算速度,同时提高所提取特征的鲁棒性. 池化层操作 池化操作与卷积操作类似 ...
- ubuntu之路——day17.3 简单的CNN和CNN的常用结构池化层
来看上图的简单CNN: 从39x39x3的原始图像 不填充且步长为1的情况下经过3x3的10个filter卷积后 得到了 37x37x10的数据 不填充且步长为2的情况下经过5x5的20个filter ...
- TensorFlow池化层-函数
池化层的作用如下-引用<TensorFlow实践>: 池化层的作用是减少过拟合,并通过减小输入的尺寸来提高性能.他们可以用来对输入进行降采样,但会为后续层保留重要的信息.只使用tf.nn. ...
- 学习笔记TF014:卷积层、激活函数、池化层、归一化层、高级层
CNN神经网络架构至少包含一个卷积层 (tf.nn.conv2d).单层CNN检测边缘.图像识别分类,使用不同层类型支持卷积层,减少过拟合,加速训练过程,降低内存占用率. TensorFlow加速所有 ...
随机推荐
- James 3.1服务器的安装与搭建
参考:1. ububtu下基于docker安装配置Apache James 3.1.0: https://blog.csdn.net/bonwei/article/details/83061372 2 ...
- 爬虫实战——Scrapy爬取伯乐在线所有文章
Scrapy简单介绍及爬取伯乐在线所有文章 一.简说安装相关环境及依赖包 1.安装Python(2或3都行,我这里用的是3) 2.虚拟环境搭建: 依赖包:virtualenv,virtualenvwr ...
- Centso7 简单优化(阿里云服务器)
##.下载常用包 # yum -y install wget net-tools screen lsof tcpdump nc mtr openssl-devel vim bash-completio ...
- java sort排序原理
事实上Collections.sort方法底层就是调用的Arrays.sort方法,而Arrays.sort使用了两种排序方法,快速排序和优化的归并排序. 快速排序主要是对那些基本类型数据(int,s ...
- Lodop控件NewPage();测试输出空白页
LODOP.NewPage();和LODOP.NewPageA();是强制分页语句,两者的区别可查看本博客的相关博文:Lodop强制分页LODOP.NewPage()和LODOP.NewPageA() ...
- 微服务 Micro services
微服务 (Microservices) 是一种软件架构风格,它是以专注于单一责任与功能的小型功能区块 (Small Building Blocks) 为基础,利用模组化的方式组合出复杂的大型应用程序, ...
- codeforces611C
New Year and Domino CodeForces - 611C 他们说:“每一年都像多米诺骨牌,一个接一个地倒下去”.但是,一年能够像多米诺骨牌那样放在网格中吗?我不这么认为. Zydsg ...
- 目前市场上有些什么样的数据库管理系统(DBMS),它们都有什么特点?它们之间的优缺点有什么?它们的使用场合分别是?
1 要求 目前市场上有些什么样的数据库管理系统(DBMS),它们都有什么特点?它们之间的优缺点有什么?它们的使用场合分别是? 1.1 目前市场上有些什么样的数据库管理系统(DBMS) 目前市场上的数据 ...
- Spring MVC 使用介绍(一)—— 概述
一.Web MVC简介 1.经典的MVC架构 存在的问题:1.控制器负责流程控制.请求数据整理与校验.模型与视图选择等功能,过于复杂.2.模型层没有进行分层设计 2.改进的MVC设计 1)控制器功能拆 ...
- 【XSY2744】信仰圣光 分治FFT 多项式exp 容斥原理
题目描述 有一个\(n\)个元素的置换,你要选择\(k\)个元素,问有多少种方案满足:对于每个轮换,你都选择了其中的一个元素. 对\(998244353\)取模. \(k\leq n\leq 1525 ...
