C#版 - LeetCode 148. Sort List 解题报告(归并排序小结)
二路归并排序其实要做两件事,:
(1)“分解”——将序列每次折半划分。
(2)“合并”——将划分后的序列段两两合并后排序。
1) If head == NULL or 只有一个元素
return head.
2) else 将链表分为两个部分,
pSlow是中点; /* pFast, pSlow指针找到中点 */
3) 分别对front,back排序
sortList(head); // 前半段
sortList(pSlow->next); // 后半段
4) 合并已排序的front, back
merge(*pFront, *pBack);
单链表递归实现 自顶向下
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *pFast, *pSlow,*pFront,*pBack;
pFast=head;
pSlow=head;
if(head==NULL || head->next==NULL) return head;
else {
while(pFast->next!=NULL && pFast->next->next!=NULL)
{
pFast=pFast->next->next;
pSlow=pSlow->next; //快慢指针找到中间节点,当快指针到末尾,慢指针恰好到中点
}
// 从中间结点断开,中间结点的next域置为NULL,中间结点及其以前的部分为前半段,中间结点后一个节点到最后为后半段
pFast=pSlow;
pSlow=pSlow->next;
pFast->next=NULL;
pFront=sortList(head); // 递归地排序前半段
pBack=sortList(pSlow); // 递归地排序后半段
return merge(pFront,pBack); // 合并前后两段序列
}
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* head1, ListNode *head2) // 将两个已经有序的序列进行合并
{
ListNode *res, *p;
if(head1==NULL) return head2;
if(head2==NULL) return head1;
if(head1->val < head2->val)
{
res=head1; // 结点需要整体赋值,不能只给val属性赋值
head1=head1->next;
}
else {
res=head2;
head2=head2->next;
}
p=res;
while(head1!=NULL && head2!=NULL)
{
if(head1->val < head2->val)
{
p->next=head1;
head1=head1->next;
}
else {
p->next=head2;
head2=head2->next;
}
p=p->next;
}
if(head1!=NULL) p->next=head1; // 挂接上去
else if(head2!=NULL) p->next=head2;
return res;
}
};
// 以下为测试部分
/*
int main()
{
ListNode *pOut;
ListNode *head=new ListNode(5);
head->next=new ListNode(8);
head->next->next=new ListNode(7);
head->next->next->next=new ListNode(12);
head->next->next->next->next=new ListNode(4);
Solution sol;
pOut=sol.sortList(head);
while(pOut!=NULL)
{
cout<<pOut->val<<" ";
pOut=pOut->next;
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
*/链表 非递归实现 自底向上
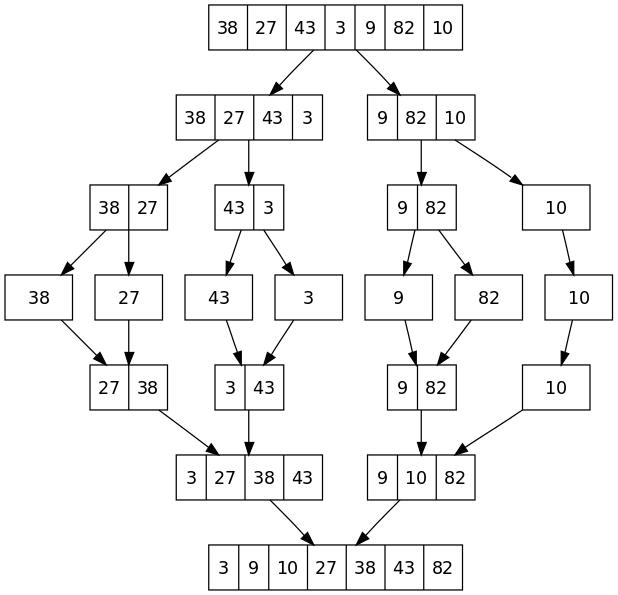
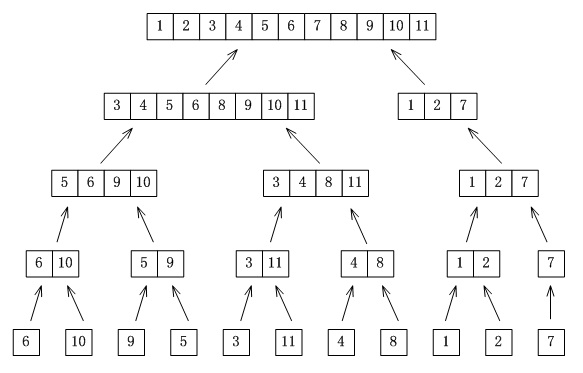
非递归实现的思想和递归正好相反,原来的递归过程是将待排序集合一分为二,直至排序集合就剩下一个元素位置,然后不断的合并两个排好序的数组。所以非递归思想为,将数组中的相邻元素两两配对。用merge函数将他们排序,构成n/2组长度gap为2的排序好的子数组段,然后再将他们排序成长度为4的子数组段,如此继续下去,直至整个数组排好序。
先将1+1(gap=1)个只有1个结点的链表按二路归并的方法加到tail结点的后面,然后更新tail;接着将2+2(gap=2)个分别有序的链表按二路归并的方式加到当前tail结点的后面,然后更新tail;gap每次扩大2倍,直到从split()函数(从head结点开始分离出长度为gap的链表)的返回值为NULL时结束外层循环。
例如: 下图是6 10 9 5 3 11 4 8 1 2 7的自底向上的归并过程...
链表 非递归
AC代码:
// To-Do: 链表非递归实现,自底向上
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode{
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x): val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *split(ListNode *head, int size) // 从head结点开始分离出长度为size的链表,并将第size-1个结点的next置为NULL,返回剩下的链表
{
for(int i = 1; i < size; i++)
{
if(head != NULL) head=head->next; // 从head结点开始分离出长度为size的链表,分离前总长度>size时,可以顺利到结尾,如果不足size,剩下的链表为NULL,分离到的长度为实际长度(<size的某值)
}
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode *p = head->next;
head->next = NULL;
return p;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode *head1, ListNode *head2, ListNode *tail) // tail始终指向已合并链表的末尾,tail之后的结点值是有序的
{
while(head1 && head2) // head1、head2均不为NULL时
{
if(head1->val < head2->val) // 将值较小的结点挂到tail之后
{
tail->next = head1; // head1的值较小,将该结点挂到tail后
tail = tail->next;
head1 = head1->next;
}
else {
tail->next = head2; // head2的值较小,将该结点挂到tail后
tail = tail->next;
head2 = head2->next;
}
}
tail->next = (head1 == NULL) ? head2 : head1;
// 如果head1先为空,即head1对应的链表较短时,把head2剩下的那些结点挂到tail后面; 反之同理,同时为NULL时皆可
while(tail->next != NULL)
tail = tail->next;
return tail;
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head)
{
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
int len = 0;
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur)
{
len ++;
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode *front, *back;
ListNode *pTemp = new ListNode(0); //pTemp保存临时更小的那个节点
ListNode *tail = pTemp;
pTemp->next = head; // 将head挂到pTemp之后
for(int size = 1; size < len; size <<= 1) // 每次归并都分两路,链表的宽度的初始值为1,(2,4,8,....),size*2
{
cur = pTemp->next;
tail = pTemp;
while(cur) // 当前结点后面还有结点时继续循环
{
front = cur;
back = split(cur, size); //从当前结点向后分离出size长的链表front
cur = split(back, size); //从当前结点向后分离出size长的链表back
tail = merge(front, back, tail); // 将front链表、back链表以二路归并的方式加到tail后去
}
}
return pTemp->next;
}
};
// 以下为测试
int main()
{
Solution sol;
ListNode *pOut;
ListNode *head=new ListNode(5);
head->next=new ListNode(8);
head->next->next=new ListNode(7);
head->next->next->next=new ListNode(12);
head->next->next->next->next=new ListNode(-3);
pOut=sol.sortList(head);
while(pOut!=NULL)
{
cout<<pOut->val<<" ";
pOut=pOut->next;
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}数组 递归实现:
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
void Merge(int arr[], int left, int right, int mid) {
//归并操作
int length = right - left + 1;
int beginA = left, beginB = mid + 1; //设置两个标志,分别指向两个已排序序列的起始位置
int i, j = 0;
int *pArr = new int[length]; // 创建临时辅助数组
// if (pArr == NULL) { printf("Memory allocated error\n"); return; }
while(beginA <= mid)
{
if(arr[beginA] > arr[beginB]) pArr[j++] = arr[beginB++];
if(arr[beginA] < arr[beginB]) pArr[j++] = arr[beginA++];
if(beginB > right) break;
}
while(beginA <= mid) pArr[j++] = arr[beginA++]; //将小元素添加到辅助数组
while(beginB <= right) pArr[j++] = arr[beginB++]; //同上
for(i = 0; i < length; i++) arr[left++] = pArr[i]; //把排序好的部分移回arr数组中
delete[] pArr; // 释放辅助数组
}
void mergeSort(int arr[], int left, int right)
{
//对数组递归地进行二路归并
int mid =(left + right)/2;
if(left >= right) return;
mergeSort(arr,left, mid); //递归的归并排序左边
mergeSort(arr, mid+1, right); //递归的归并排序左边
Merge(arr,left,right,mid); //合并
}
int main()
{
int arr[]={5,2,6,3,9,10,8};
int len = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
mergeSort(arr,0,len-1);
for(int i = 0; i <= len-1; i++) {
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}数组 非递归实现:
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
// 将数组中连续的两个子序列合并为一个有序序列
void Merge(int* arr, int *tempArr, int bIndex, int mIndex, int eIndex)
{
int gap = eIndex - bIndex; //合并后的序列长度
int i = 0; //记录合并后序列插入数据的偏移
int j = bIndex; //记录子序列1插入数据的偏移
int k = mIndex; //记录子序列2插入数据的偏移
while(j < mIndex && k < eIndex)
{
if(arr[j] <= arr[k])
{
tempArr[i++] = arr[j];
j++;
}
else
{
tempArr[i++] = arr[k];
k++;
}
}
if(j == mIndex) //说明序列1已经插入完毕
{
while(k < eIndex)
tempArr[i++] = arr[k++];
}
else { //说明序列2已经插入完毕
while(j < mIndex)
tempArr[i++] = arr[j++];
}
for(i = 0; i < gap; i++) //将合并后序列重新放入arr
arr[bIndex + i] = tempArr[i];
}
// 自底向上的归并排序(非递归)
void mergeSort(int* arr, int len)
{
int *tempArr = new int[len]; //临时存放合并后的序列
int gap = 1; //初始有序子序列长度为1
while(gap < len)
{
int i = 0;
for(; i + 2*gap < len; i += 2*gap)
Merge(arr, tempArr, i, i + gap, i + 2*gap);
if(i + gap < len)
Merge(arr, tempArr, i, i + gap, len);
gap *= 2; //有序子序列长度*2
}
delete[] tempArr;
}
// 以下为测试
int main()
{
int arr[]={5,2,6,3,9,10,8};
int len = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
mergeSort(arr, len);
for(int i = 0; i <= len-1; i++) {
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}另外,如果要进行原址归并,不占用其他空间,编程珠玑上提出了一个很神奇的算法,代码如下:
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
//此函数用于一个反转数组
void reverse(int arr[], size_t size)
{
int left = 0,
right = size - 1,
tmp = 0;
while(left < right)
{
tmp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[right];
arr[right] = tmp;
left++;
right--;
}
}
//手摇法 通过三次反转操作交换两个子序列的位置,两个子序列内部的排序不变。
void swap_blocks(int arr[], size_t size, size_t lft_size) {
reverse(arr, lft_size);
reverse(arr + lft_size, size - lft_size);
reverse(arr, size);
}
void in_place_merge(int arr[], size_t size, size_t mid) //原地归并
{
size_t lft_s = 0, rit_s = mid, rmove;
while (lft_s < rit_s && rit_s < size)
{
while (lft_s < rit_s && arr[lft_s] <= arr[rit_s])
{
lft_s++;
}
rmove = 0;
while (rit_s < size && arr[lft_s] > arr[rit_s])
{
rmove++;
rit_s++;
}
swap_blocks(arr + lft_s, rit_s - lft_s, rit_s - lft_s - rmove);
lft_s += rmove;
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[]={5,2,6,3,9,10,8};
int len = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
in_place_merge(arr,0,len-1);
for(int i = 0; i <= len-1; i++) {
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}相关链接:
自顶向下的归并排序 - 太阳落雨 - CSDN http://blog.csdn.net/cjf_iceking/article/details/7921443
自底向上的归并排序 - 太阳落雨 - CSDN http://blog.csdn.net/cjf_iceking/article/details/7920153
归并排序(递归实现+非递归实现+自然合并排序) - geeker - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/liushang0419/archive/2011/09/19/2181476.html
C#版 - LeetCode 148. Sort List 解题报告(归并排序小结)的更多相关文章
- 【LeetCode】148. Sort List 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 日期 题目地址:https://leetcode.c ...
- [LeetCode] 148. Sort List 解题思路
Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space complexity. 问题:对一个单列表排序,要求时间复杂度为 O(n*logn ...
- C++版 - Leetcode 400. Nth Digit解题报告
leetcode 400. Nth Digit 在线提交网址: https://leetcode.com/problems/nth-digit/ Total Accepted: 4356 Total ...
- C++版 - Leetcode 69. Sqrt(x) 解题报告【C库函数sqrt(x)模拟-求平方根】
69. Sqrt(x) Total Accepted: 93296 Total Submissions: 368340 Difficulty: Medium 提交网址: https://leetcod ...
- LeetCode: Insertion Sort List 解题报告
Insertion Sort List Sort a linked list using insertion sort. SOLUTION: 使用一个dummynode 创建一个新的链,将旧的节点插入 ...
- 【LeetCode】Sort Colors 解题报告
[题目] Given an array with n objects colored red, white or blue, sort them so that objects of the same ...
- 【LeetCode】147. Insertion Sort List 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]147. Insertion Sort List 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): LeetCode 作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: h ...
- 【LeetCode】Permutations II 解题报告
[题目] Given a collection of numbers that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permuta ...
- 【LeetCode】Largest Number 解题报告
[LeetCode]Largest Number 解题报告 标签(空格分隔): LeetCode 题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-number/# ...
随机推荐
- ESP8266擦除工具完整安装
ESP8266擦除工具完整安装 一. ESP8266擦除工具路径:http://down.liangchan.net/ESP8266%B2%C1%B3%FD%B9%A4%BE%DF%CD%EA%D5 ...
- list常用方法
1.切片: ①.顾头不顾尾,从头开始取,但不包括最后一个. ②.从左向右数为正,从零开始,从右开始为负,从-1开始 如: names=['1','2','3'] ames[-1]与names[2]效果 ...
- clion中配置glfw和glew
clion中只能用cmake文件配置 最开始不清楚cmake语法走了不少弯路 如果遇到symbol(s) not found for architecture x86_64错误,百分百是cmake没配 ...
- version control
what 版本控制最主要的功能就是追踪文件的变更.它将什么时候.什么人更改了文件的什么内容等信息忠实地了已录下来.每一次文件的改变,文件的版本号都将增加.除了记录版本变更外,版本控制的另一个重要功能是 ...
- JQuery跳出each循环的方法
一.jquery each循环,要实现break和continue的功能: break----用return false; continue --用return ture; 二.jquery怎么跳出当 ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Lab 0 Warmup & Basic OCaml
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第1次大作业. 什么是编译 编译就是执行Program->Program'转换的过程,如下 ...
- 【adb】执行adb devices 设备offline
解决办法: 1.执行adb kill-server,在执行adb devices 2.重启手机 ---------------------------------------------------- ...
- 30.Iterator
迭代对于我们搞Java的来说绝对不陌生.我们常常使用JDK提供的迭代接口进行Java集合的迭代. Iterator iterator = list.iterator(); while(iterator ...
- 强大的jQGrid的傻瓜式使用方法。以及一些注意事项,备有相应的引入文件。
在介绍我的使用前,先按照国际惯例,列上网址http://blog.mn886.net/jqGrid/ 里面第一项就有相应的demo. 好,进入正题: 在学习到node.js的时候,需要使用到jQGri ...
- struts2 简单注解配置代替xml配置文件
1. 主要文件 LoginAction.javapackage com.edu.struts2.action;import org.apache.struts2.convention.annotati ...