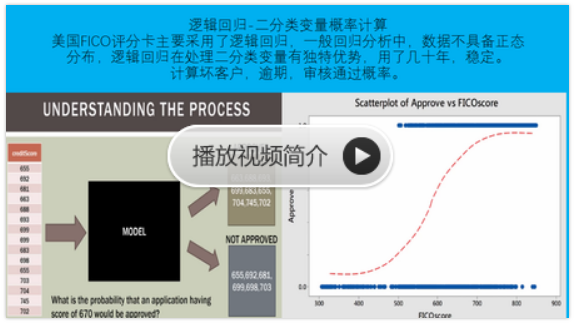
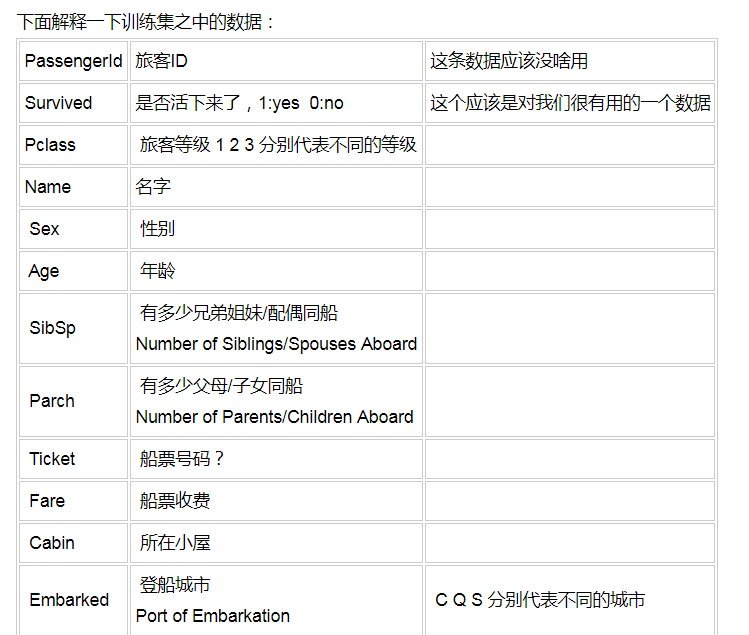
sklearn机器学习-泰坦尼克号
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博主亲自录制视频)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
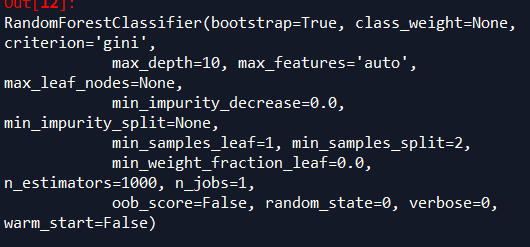
randomForest.py
调参后,预测最高准确性也达到了89%
随机森林的参数
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
#导入数据预处理,包括标准化处理或正则处理
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
#中文字体设置
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc",size=14) #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
names=features.columns trees=1000
max_depth=10
#n_estimators表示树的个数,测试中100颗树足够
forest=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=trees,random_state=0,max_depth=max_depth)
forest.fit(x_train,y_train) print("random forest with %d trees:"%trees)
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(forest.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(forest.score(x_test,y_test)))
#print('Feature importances:{}'.format(forest.feature_importances_)) names=features.columns
importance=forest.feature_importances_
zipped = zip(importance,names)
list1=list(zipped) list1.sort(reverse=True)
#print(list1) n_features=data_dummies.shape[1]
plt.barh(range(n_features),forest.feature_importances_,align='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(n_features),features)
plt.title("random forest with %d trees,%dmax_depth:"%(trees,max_depth))
plt.xlabel('Feature Importance')
plt.ylabel('Feature')
plt.show() '''
random forest with 1000 trees:
accuracy on the training subset:0.983
accuracy on the test subset:0.878 random forest with 1000 trees,max_depth=4:
accuracy on the training subset:0.854
accuracy on the test subset:0.884 random forest with 1000 trees,max_depth=5:
accuracy on the training subset:0.853
accuracy on the test subset:0.887 random forest with 1000 trees,max_depth=9
accuracy on the training subset:0.871
accuracy on the test subset:0.890
'''
去掉覆盖率低的变量后,随机森林准确性反而下降,看了随机森林不需要去计算变量覆盖率
训练数据准确性0.983
测试数据准确性0.878
'''
random forest with 1000 trees:
accuracy on the training subset:0.983
accuracy on the test subset:0.878
'''
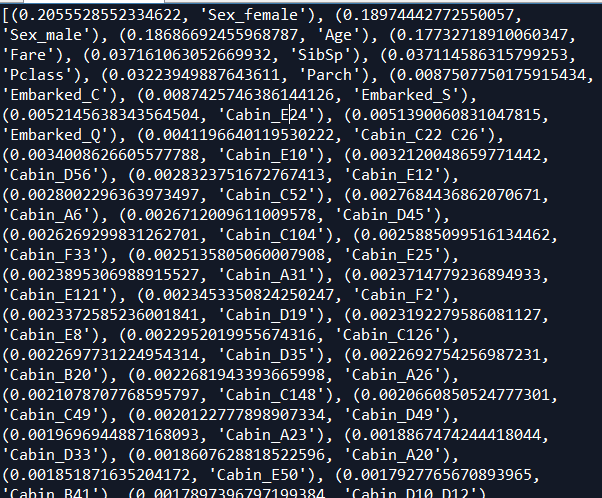
重要因子来看,性别第一,占据40%重要性,
年龄重要性18%左右,
票价重要性17%左右
logistic.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Apr 29 22:39:35 2018 @author: Administrator
""" # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
#导入数据预处理,包括标准化处理或正则处理
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
#中文字体设置
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc",size=14) #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
names=features.columns #n_estimators表示树的个数,测试中100颗树足够
logistic=LogisticRegression()
logistic.fit(x_train,y_train) print("logistic:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(logistic.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(logistic.score(x_test,y_test))) '''
logistic:
accuracy on the training subset:0.850
accuracy on the test subset:0.875
'''
目前效果最好的是去掉低覆盖率的变量后,SVM准确率最高0.89
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
from sklearn.svm import SVC
#导入数据预处理,包括标准化处理或正则处理
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
#中文字体设置
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc",size=14) #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
names=features.columns svm=SVC()
svm.fit(x_train,y_train)
print("svc:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm.score(x_test,y_test))) '''
svc:
accuracy on the training subset:0.900
accuracy on the test subset:0.726
''' #标准化数据
X_train_scaled = preprocessing.scale(x_train)
x_test_scaled = preprocessing.scale(x_test)
svm1=SVC()
svm1.fit(X_train_scaled,y_train)
#改变C参数,调优,kernel表示核函数,用于平面转换,probability表示是否需要计算概率
svm1=SVC()
svm1.fit(X_train_scaled,y_train)
print("accuracy on the scaled training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm1.score(X_train_scaled,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the scaled test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm1.score(x_test_scaled,y_test))) '''
accuracy on the scaled training subset:0.866
accuracy on the scaled test subset:0.881
'''
#改变C参数,调优,kernel表示核函数,用于平面转换,probability表示是否需要计算概率
svm2=SVC(C=10,gamma="auto",kernel='rbf',probability=True)
svm2.fit(X_train_scaled,y_train)
print("after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm2.score(X_train_scaled,y_train)))
print("after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm2.score(x_test_scaled,y_test))) '''
after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled training subset:0.878
after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled test subset:0.890
'''
xgboost1.py
效果也相当好
AUC: 0.9464
ACC: 0.8841
Recall: 0.8716
F1-score: 0.8716
Precesion: 0.8716
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
import xgboost as xgb
#导入数据预处理,包括标准化处理或正则处理
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
#中文字体设置
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font=FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc",size=14) #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
names=features.columns dtrain=xgb.DMatrix(x_train,label=y_train)
dtest=xgb.DMatrix(x_test) params={'booster':'gbtree',
#'objective': 'reg:linear',
'objective': 'binary:logistic',
'eval_metric': 'auc',
'max_depth':4,
'lambda':10,
'subsample':0.75,
'colsample_bytree':0.75,
'min_child_weight':2,
'eta': 0.025,
'seed':0,
'nthread':8,
'silent':1} watchlist = [(dtrain,'train')] bst=xgb.train(params,dtrain,num_boost_round=100,evals=watchlist) ypred=bst.predict(dtest) # 设置阈值, 输出一些评价指标
y_pred = (ypred >= 0.5)*1 #模型校验
print ('AUC: %.4f' % metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test,ypred))
print ('ACC: %.4f' % metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred))
print ('Recall: %.4f' % metrics.recall_score(y_test,y_pred))
print ('F1-score: %.4f' %metrics.f1_score(y_test,y_pred))
print ('Precesion: %.4f' %metrics.precision_score(y_test,y_pred))
metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred) print("xgboost:")
print('Feature importances:{}'.format(bst.get_fscore())) '''
AUC: 0.9464
ACC: 0.8841
Recall: 0.8716
F1-score: 0.8716
Precesion: 0.8716
xgboost:
Feature importances:{'f5': 69, 'f1': 178, 'f2': 68, 'f4': 245, 'f6': 25, 'f0': 88, 'f3': 25, 'f194': 4, 'f193': 21, 'f195': 9}
'''
决策树
decisionTree.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Apr 30 19:04:10 2018 @author: Administrator
"""
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #读取变量名文件
varibleFileName="titantic.xlsx"
#读取目标文件
targetFileName="target.xlsx"
#读取excel
data=pd.read_excel(varibleFileName)
data_dummies=pd.get_dummies(data)
print('features after one-hot encoding:\n',list(data_dummies.columns))
features=data_dummies.ix[:,"Pclass":'Embarked_S']
x=features.values #数据预处理
imp = Imputer(missing_values='NaN', strategy='most_frequent', axis=0)
imp.fit(x)
x=imp.transform(x) target=pd.read_excel(targetFileName)
y=target.values
X_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
#变量名
names=features.columns #调参
list_average_accuracy=[]
depth=range(1,30)
for i in depth:
#max_depth=4限制决策树深度可以降低算法复杂度,获取更精确值
tree= DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=i,random_state=0)
tree.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy_training=tree.score(X_train,y_train)
accuracy_test=tree.score(x_test,y_test)
average_accuracy=(accuracy_training+accuracy_test)/2.0
#print("average_accuracy:",average_accuracy)
list_average_accuracy.append(average_accuracy) max_value=max(list_average_accuracy)
#索引是0开头,结果要加1
best_depth=list_average_accuracy.index(max_value)+1
print("best_depth:",best_depth) best_tree= DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=best_depth,random_state=0)
best_tree.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy_training=best_tree.score(X_train,y_train)
accuracy_test=best_tree.score(x_test,y_test) print("decision tree:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(best_tree.score(X_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(best_tree.score(x_test,y_test))) '''
best_depth: 19
decision tree:
accuracy on the training subset:0.976
accuracy on the test subset:0.860
''' #绘图,显示因子重要性
n_features=x.shape[1]
plt.barh(range(n_features),best_tree.feature_importances_,align='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(n_features),features)
plt.title("Decision Tree:")
plt.xlabel('Feature Importance')
plt.ylabel('Feature')
plt.show() #生成一个dot文件,以后用cmd形式生成图片
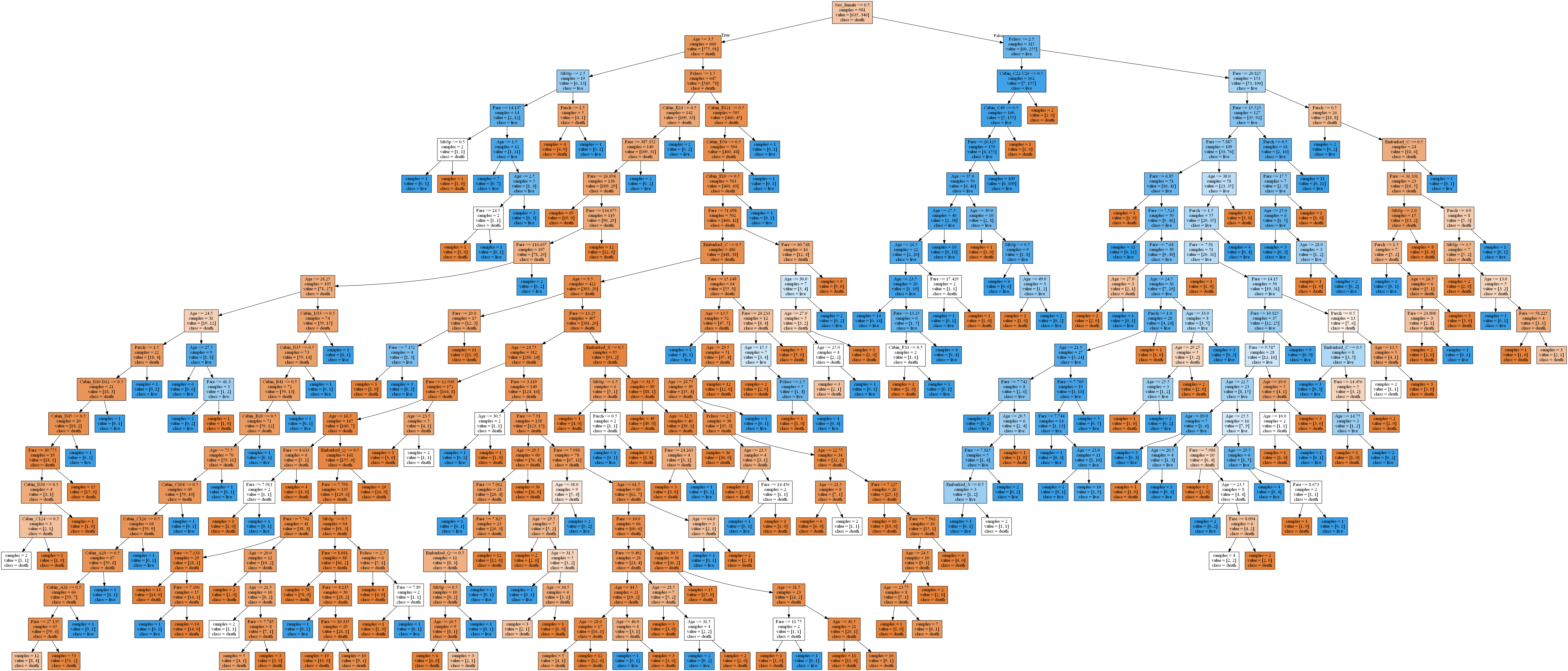
export_graphviz(best_tree,out_file="Titanic.dot",class_names=['death','live'],feature_names=names,impurity=False,filled=True)
python风控评分卡建模和风控常识
sklearn机器学习-泰坦尼克号的更多相关文章
- Python 3 利用 Dlib 19.7 和 sklearn机器学习模型 实现人脸微笑检测
0.引言 利用机器学习的方法训练微笑检测模型,给一张人脸照片,判断是否微笑: 使用的数据集中69张没笑脸,65张有笑脸,训练结果识别精度在95%附近: 效果: 图1 示例效果 工程利用pytho ...
- 使用sklearn机器学习库实现线性回归
import numpy as np # 导入科学技术框架import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 导入画图工具from sklearn.linear_model imp ...
- Python线性回归算法【解析解,sklearn机器学习库】
一.概述 参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yszd/p/8529704.html 二.代码实现[解析解] import numpy as np import matplotl ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报数据 模型和使用
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 模型和使用 项目地址 系列教程 0.前言 1.建立模型 a.准备 引入所需要的头文件 选择模型 选择评估方法 获取数据集 b.建立模型 c.获取模型 ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报数据 数据
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 数据 项目地址 系列教程 勘误表 0.前言 1.爬虫 a.确认要被爬取的网页网址 b.爬虫部分 c.网页内容匹配取出部分 d.写入csv文件格式化 ...
- 用python+sklearn(机器学习)实现天气预报 准备
用python+sklearn机器学习实现天气预报 准备 项目地址 系列教程 0.流程介绍 1. 环境搭建 a.python b.涉及到的机器学习相关库 sklearn panda seaborn j ...
- 5分钟教你玩转 sklearn 机器学习(上)
假期结束,你的状态有没有回归?那么,放空脑袋后,先来学习学习,欢迎大家继续关注腾讯云技术社区. 作者:赵成龙 这是一篇很难写的文章,因为我希望这篇文章能对大家有所帮助.我不会给大家介绍机器学习,数据挖 ...
- 编程作业1.1——sklearn机器学习算法系列之LinearRegression线性回归
知识点 scikit-learn 对于线性回归提供了比较多的类库,这些类库都可以用来做线性回归分析. 我们也可以使用scikit-learn的线性回归函数,而不是从头开始实现这些算法. 我们将scik ...
- sklearn机器学习-特征提取1
scikit-learn机器学习的特征提取部分较多nlp内容,故学到一半学不下去,看完nltk再来补上 scikit-learn机器学习的特征提取这一章感觉讲的不是特别好,所以会结合着来看 首先是Di ...
随机推荐
- Nginx 反向代理如何连接上游服务器
L:92 想上游服务器先建立TCP连接 如三次握手 下面指令可以控制握手时间 proxy_next_upstream 指令当出现502可以换个上游服务器 Tcp keepalive 一般都是由进程在 ...
- The Cow Lexicon POJ - 3267 dp
题意 给出一个母串 和一个字典 问母串最少删去几个字母 删去后的母串是由字典里面的单词拼起来的 思路:dp[i]表示从i到母串结尾最少需要删除多少个字母 初始化dp[length]=0 ...
- BZOJ 4326 运输计划
二分答案+树链剖分+树上差分 我们假设x是最小的花费,可以想到给定x,所有运输计划中花费大于x的计划必须经过虫洞,且最长的一条的花费减去虫洞所在边的花费要小于等于x 那么对于x,虫洞所在的位置肯定是确 ...
- python中的split()方法的使用
Python split()方法:通过指定分隔符对字符串进行分割并返回一个列表,默认分隔符为所有空字符,包括空格.换行(\n).制表符(\t)等. l Str.split()默认以空格,换行\n,制 ...
- ALGO-19 审美课
算法训练 审美课 时间限制:1.0s 内存限制:256.0MB 问题描述 <审美的历程>课上有n位学生,帅老师展示了m幅画,其中有些是梵高的作品,另外的都出自五岁小朋 ...
- 洛谷2754 [CTSC1999]家园
题目链接:[CTSC1999]家园 这个题目我们不是很好在做网络流的时候判断是否有解,因此我们考虑分开来做 对于是否有解的判断,我们唯一需要解决的是飞船的周期停泊问题,对于这个问题,我们可以用并查集解 ...
- (转)最短路径算法-Dijkstra算法分析及实践
原地址:http://www.wutianqi.com/?p=1890 这篇博客写的非常简洁易懂,其中各个函数的定义也很清晰,配合图表很容易理解这里只选取了 其中一部分(插不来图片). Dijkstr ...
- Java 枚举(enum) 详解7种常见的用法
Java 枚举(enum) 详解7种常见的用法 来源 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27093465/article/details/52180865 JDK1.5引入了新的类型— ...
- BM算法
BM算法 用来求解一个数列的递推式. 即给定\(\{x_i\}\)求解一个\(\{a_i\}\),满足\(|a|=m,x_n=\sum_{i=1}^ma_i*x_{n-i}\). 考虑增量法构造. 假 ...
- 【BZOJ2324】[ZJOI2011]营救皮卡丘(网络流,费用流)
[BZOJ2324][ZJOI2011]营救皮卡丘(网络流,费用流) 题面 BZOJ 洛谷 题解 如果考虑每个人走的路径,就会很麻烦. 转过来考虑每个人破坏的点集,这样子每个人可以得到一个上升的序列. ...