SQLServer DMV Query
1.DMV Query to identify all active SQL Server Sessions
The query below identifies all currently active SQL Server user connections by their SQL Server Login name. It provides details of the IP address that the connection is sourced from, along with the number of sessions and connections that the SQL Server Login is currently responsible for.
SELECT
B.login_name,
A.client_net_address,
NoOfConnections = COUNT(*)
FROM
sys.dm_exec_connections A
INNER JOIN sys.dm_exec_sessions B ON A.session_id = B.session_id
GROUP BY login_name, client_net_address 2. How to find out how much memory used by sqlserver per database?
SELECT
(CASE WHEN ([is_modified] = 1) THEN 'Dirty' ELSE 'Clean' END) AS 'Page State',
(CASE WHEN ([database_id] = 32767) THEN 'Resource Database' ELSE DB_NAME (database_id) END) AS 'Database Name',
COUNT (*) AS 'Page Count'
FROM sys.dm_os_buffer_descriptors
GROUP BY [database_id], [is_modified]
ORDER BY [database_id], [is_modified];
GO
3. How to limit the amount of memory taken by SQL Server
Below is an example to limit the amount of memory taken by SQL Server to 2000 Mb.
--Enable advanced options:
USE master
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
--Set the maximum amount of memory to 2000 MB:
USE master
EXEC sp_configure 'max server memory (MB)', 2000 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
--Display the newly set configuration:
USE master
EXEC sp_configure 'max server memory (MB)'
--Set 'show advanced options' back to default:
USE master
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 0 RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
4. How to find out the most wait types for your SQL Server?
SELECT
wait_type,
waiting_tasks_count,
max_wait_time_ms,
(wait_time_ms - signal_wait_time_ms) resource_wait_time_ms,
(cast((wait_time_ms - signal_wait_time_ms) as decimal(19,2)) /
(select sum((wait_time_ms - signal_wait_time_ms)) from sys.dm_os_wait_stats))* 100 PercentOfAllResourceWaitTime
FROM sys.dm_os_wait_stats
ORDER BY PercentOfAllResourceWaitTime DESC
5. How to identify the most costly SQL in Average for SQL Server queries
SELECT TOP 20
qs.sql_handle,
qs.execution_count,
qs.total_worker_time AS Total_CPU,
total_CPU_inSeconds = --Converted from microseconds
cast(qs.total_worker_time as decimal)/1000000 ,
average_CPU_inSeconds = --Converted from microseconds
cast(qs.total_worker_time as decimal) /1000000/ qs.execution_count,
qs.total_elapsed_time,
total_elapsed_time_inSeconds = --Converted from microseconds
cast(qs.total_elapsed_time as decimal) /1000000,
average_elapsed_inSeconds = --Converted from microseconds
cast(qs.total_elapsed_time as decimal) /1000000/qs.execution_count,
st.text,
qp.query_plan
FROM
sys.dm_exec_query_stats AS qs
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(qs.sql_handle) AS st
CROSS apply sys.dm_exec_query_plan (qs.plan_handle) AS qp
ORDER BY average_elapsed_inSeconds DESC
6. How to find out the implicit column convertion in the Plan Cache?
SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ UNCOMMITTED
DECLARE @dbname SYSNAME
SET @dbname = QUOTENAME(DB_NAME());
WITH XMLNAMESPACES
(DEFAULT 'http://schemas.microsoft.com/sqlserver/2004/07/showplan')
SELECT
stmt.value('(@StatementText)[1]', 'varchar(max)'),
t.value('(ScalarOperator/Identifier/ColumnReference/@Schema)[1]', 'varchar(128)'),
t.value('(ScalarOperator/Identifier/ColumnReference/@Table)[1]', 'varchar(128)'),
t.value('(ScalarOperator/Identifier/ColumnReference/@Column)[1]', 'varchar(128)'),
ic.DATA_TYPE AS ConvertFrom,
ic.CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH AS ConvertFromLength,
t.value('(@DataType)[1]', 'varchar(128)') AS ConvertTo,
t.value('(@Length)[1]', 'int') AS ConvertToLength,
query_plan
FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans AS cp
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan(plan_handle) AS qp
CROSS APPLY query_plan.nodes('/ShowPlanXML/BatchSequence/Batch/Statements/StmtSimple') AS batch(stmt)
CROSS APPLY stmt.nodes('.//Convert[@Implicit="1"]') AS n(t)
JOIN INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS AS ic
ON QUOTENAME(ic.TABLE_SCHEMA) = t.value('(ScalarOperator/Identifier/ColumnReference/@Schema)[1]', 'varchar(128)')
AND QUOTENAME(ic.TABLE_NAME) = t.value('(ScalarOperator/Identifier/ColumnReference/@Table)[1]', 'varchar(128)')
AND ic.COLUMN_NAME = t.value('(ScalarOperator/Identifier/ColumnReference/@Column)[1]', 'varchar(128)')
WHERE t.exist('ScalarOperator/Identifier/ColumnReference[@Database=sql:variable("@dbname")][@Schema!="[sys]"]') = 1
7. How to view the partitions table in SQLServer inlcude the which file it is in , how many rows each partition, what's the first page of each partition.
DECLARE @TableName NVARCHAR(200) = N'Facts.Credit'
SELECT SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id) + '.' + OBJECT_NAME(i.object_id) AS [object]
, p.partition_number AS [p#]
, fg.name AS [filegroup]
, p.rows
, au.total_pages AS pages
, CASE boundary_value_on_right
WHEN 1 THEN 'less than'
ELSE 'less than or equal to' END as comparison
, rv.value
, CONVERT (VARCHAR(6), CONVERT (INT, SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 6, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 5, 1))) + ':' + CONVERT (VARCHAR(20),
CONVERT (INT, SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 4, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 3, 1) + SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 2, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 1, 1))) AS first_page
FROM sys.partitions p
INNER JOIN sys.indexes i
ON p.object_id = i.object_id
AND p.index_id = i.index_id
INNER JOIN sys.objects o
ON p.object_id = o.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.system_internals_allocation_units au
ON p.partition_id = au.container_id
INNER JOIN sys.partition_schemes ps
ON ps.data_space_id = i.data_space_id
INNER JOIN sys.partition_functions f
ON f.function_id = ps.function_id
INNER JOIN sys.destination_data_spaces dds
ON dds.partition_scheme_id = ps.data_space_id
AND dds.destination_id = p.partition_number
INNER JOIN sys.filegroups fg
ON dds.data_space_id = fg.data_space_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.partition_range_values rv
ON f.function_id = rv.function_id
AND p.partition_number = rv.boundary_id
WHERE i.index_id < 2
AND o.object_id = OBJECT_ID(@TableName);
Second SQL:
DECLARE @TableName NVARCHAR(200) = N'HumanResources.Department'
SELECT SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id) + '.' + OBJECT_NAME(i.object_id) AS [object]
, p.partition_number AS [p#]
, FILEGROUP_NAME(au.filegroup_id) [filegroup]
, p.rows
, au.total_pages AS pages
, CASE boundary_value_on_right
WHEN 1 THEN 'less than'
ELSE 'less than or equal to' END as comparison
, rv.value
, CONVERT (VARCHAR(6), CONVERT (INT, SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 6, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 5, 1))) + ':' + CONVERT (VARCHAR(20),
CONVERT (INT, SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 4, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 3, 1) + SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 2, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 1, 1))) AS first_page
FROM sys.partitions p
INNER JOIN sys.indexes i
ON p.object_id = i.object_id
AND p.index_id = i.index_id
INNER JOIN sys.objects o
ON p.object_id = o.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.system_internals_allocation_units au
ON p.partition_id = au.container_id
INNER JOIN sys.partition_schemes ps
ON ps.data_space_id = i.data_space_id
INNER JOIN sys.partition_functions f
ON f.function_id = ps.function_id
INNER JOIN sys.destination_data_spaces dds
ON dds.partition_scheme_id = ps.data_space_id
AND dds.destination_id = p.partition_number
LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.partition_range_values rv
ON f.function_id = rv.function_id
AND p.partition_number = rv.boundary_id
WHERE i.index_id < 2
AND o.object_id = OBJECT_ID(@TableName);
Above query will only return information for partitioned table, for non-partition table, we can use below query to the total rows,total pages and first pages.
DECLARE @TableName NVARCHAR(200) = N'Production.Culture';
SELECT SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id) + '.' + OBJECT_NAME(i.object_id) AS [object]
, p.partition_number AS [p#]
, fg.name AS [filegroup]
, p.rows
, au.total_pages AS pages
, CONVERT (VARCHAR(6), CONVERT (INT, SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 6, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 5, 1))) + ':' + CONVERT (VARCHAR(20),
CONVERT (INT, SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 4, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 3, 1) + SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 2, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 1, 1))) AS first_page
FROM sys.partitions p
INNER JOIN sys.indexes i
ON p.object_id = i.object_id
AND p.index_id = i.index_id
INNER JOIN sys.objects o
ON p.object_id = o.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.system_internals_allocation_units au
ON p.partition_id = au.container_id
INNER JOIN sys.data_spaces ds
ON i.data_space_id = ds.data_space_id
INNER JOIN sys.filegroups fg
ON ds.data_space_id = fg.data_space_id
WHERE i.index_id < 2
AND o.object_id = OBJECT_ID(@TableName);
Second SQL:
DECLARE @TableName NVARCHAR(200) = N'Production.Culture';
SELECT SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id) + '.' + OBJECT_NAME(o.object_id) AS [object]
, p.partition_number AS [p#]
, FILEGROUP_NAME(au.filegroup_id) AS [filegroup]
, p.rows
, au.total_pages AS pages
, CONVERT (VARCHAR(6), CONVERT (INT, SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 6, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 5, 1))) + ':' + CONVERT (VARCHAR(20),
CONVERT (INT, SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 4, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 3, 1) + SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 2, 1) +
SUBSTRING (au.first_page, 1, 1))) AS first_page
FROM sys.partitions p
INNER JOIN sys.objects o
ON p.object_id = o.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.system_internals_allocation_units au
ON p.partition_id = au.container_id
WHERE p.index_id < 2 and o.object_id = OBJECT_ID(@TableName);
8. How to Query partitions detail information
--Just about everything here, including Total_page count for indexes.
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(i.OBJECT_ID) AS TableName, pf.name AS PFName, ps.name AS PSName, ds.name AS FGName, pv.value
,CASE WHEN pf.boundary_value_on_right = 1 THEN 'Range Right' ELSE 'Range Left' END AS Type
,t.name AS DataType, pp.max_length, pp.PRECISION, pp.scale
,ps.is_default
,pv.parameter_id, pf.fanout AS PartitionCount
,i.index_id AS Index_ID,
p.partition_number,
rows AS ApproxRowCount,
au.total_pages
--select *
FROM sys.partitions p
JOIN sys.indexes i ON p.OBJECT_ID = i.OBJECT_ID AND p.index_id = i.index_id
JOIN sys.partition_schemes ps ON ps.data_space_id = i.data_space_id
JOIN sys.partition_functions pf ON pf.function_id = ps.function_id
LEFT JOIN sys.partition_range_values pv ON pf.function_id = pv.function_id
AND p.partition_number = pv.boundary_id
JOIN sys.destination_data_spaces dds ON dds.partition_scheme_id = ps.data_space_id
AND dds.destination_id = p.partition_number
JOIN sys.partition_parameters pp ON pf.function_id = pp.function_id
JOIN sys.types t ON t.system_type_id = pp.system_type_id
JOIN sys.data_spaces ds ON ds.data_space_id=dds.data_space_id
JOIN (SELECT container_id, SUM(total_pages) AS total_pages
FROM sys.allocation_units
GROUP BY container_id) AS au ON au.container_id = p.partition_id
ORDER BY partition_number
--Without the datapage information:
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(i.OBJECT_ID) AS TableName, pf.name AS PFName, ps.name AS PSName, ds.name AS FGName, pv.value
,CASE WHEN pf.boundary_value_on_right = 1 THEN 'Range Right' ELSE 'Range Left' END AS Type
,t.name AS DataType, pp.max_length, pp.PRECISION, pp.scale
,ps.is_default
,pv.parameter_id, pf.fanout AS PartitionCount
,p.partition_number
,rows AS ApproxRowCount
--select *
FROM sys.partitions p
JOIN sys.indexes i ON p.OBJECT_ID = i.OBJECT_ID AND p.index_id = i.index_id
JOIN sys.partition_schemes ps ON ps.data_space_id = i.data_space_id
JOIN sys.partition_functions pf ON pf.function_id = ps.function_id
LEFT JOIN sys.partition_range_values pv ON pf.function_id = pv.function_id
AND p.partition_number = pv.boundary_id
JOIN sys.destination_data_spaces dds ON dds.partition_scheme_id = ps.data_space_id
AND dds.destination_id = p.partition_number
JOIN sys.partition_parameters pp ON pf.function_id = pp.function_id
JOIN sys.types t ON t.system_type_id = pp.system_type_id
JOIN sys.data_spaces ds ON ds.data_space_id=dds.data_space_id
WHERE i.index_id = 1
ORDER BY partition_number
--Very simplified version of above. But if you haven't applied PF to a table yet, you need this.
SELECT
pf.name AS PFName, ps.name AS PSName, ds.name AS FGName, pv.value AS RangeValue
,CASE WHEN pf.boundary_value_on_right = 1 THEN 'Range Right' ELSE 'Range Left' END AS Type
,t.name AS DataType, pp.max_length, pp.PRECISION, pp.scale
,ps.is_default
,pf.fanout AS PartitionCount
--select *
FROM sys.partition_schemes ps
JOIN sys.destination_data_spaces dds ON dds.partition_scheme_id = ps.data_space_id
JOIN sys.data_spaces ds ON ds.data_space_id = dds.data_space_id
LEFT JOIN sys.partition_range_values pv ON pv.boundary_id = dds.destination_id
JOIN sys.partition_functions pf ON pf.function_id = ps.function_id
JOIN sys.partition_parameters pp ON pf.function_id = pp.function_id
JOIN sys.types t ON t.system_type_id = pp.system_type_id
9. How to check the cache hit ration and total cpu time percentage and other performace counter?
select sum(total_physical_reads) physical,
sum(total_logical_reads) logical,
sum(total_worker_time) total_cpu,
sum(total_elapsed_time) duration_time,
(1- CAST(sum(total_physical_reads) AS DECIMAL)/ CAST(sum(total_logical_reads) AS DECIMAL)) cache_hit,
(CAST(sum(total_worker_time) AS DECIMAL) / CAST(sum(total_elapsed_time) AS DECIMAL)) CPU_hit
from sys.dm_exec_query_Stats
select * from sys.dm_os_performance_counters
10. How to find out all the indexes under a special schema? SELECT
t.name as [Table Name],
i.name as [Index Name],
ic.index_column_id as[Column order],
c.name as [ColumnName],
ic.is_included_column as[IsIncluded],
c.is_nullable as [IsNullAble]
FROM sys.indexes i inner join sys.tables t on t.object_id = i.object_id
left outer join SYS.index_columns ic on i.object_id = ic.object_id and ic.index_id = i.index_id
left outer join sys.columns c on c.object_id = ic.object_id and c.column_id = ic.column_id
where t.schema_id = schema_id('GPCOMP1') and i.name is not null
order by [Table Name],[Index Name],[Column order]; 11. How to find those tables and indexes are using the most memory in the buffer cache?
-- each buffer is 8K size
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(p.object_id) AS [ObjectName],
p.object_id,
p.index_id,
i.name,
COUNT(*) / 128 AS [buffer size(MB)],
COUNT(*) AS [buffer_count]
FROM sys.allocation_units AS a
INNER JOIN sys.dm_os_buffer_descriptors AS b ON a.allocation_unit_id = b.allocation_unit_id
INNER JOIN sys.partitions AS p ON a.container_id = p.hobt_id
INNER JOIN sys.indexes i on p.object_id = i.object_id and p.index_id = i.index_id
WHERE b.database_id = DB_ID() AND p.object_id > 100
GROUP BY p.object_id, p.index_id,i.name
ORDER BY buffer_count DESC;
12. How to find the most biggest table and indexes in current database?
-- the most biggest top 20 tables including cluster table or heap table.
SELECT top 20
OBJECT_NAME(p.object_id) as [Table Name],
au.total_pages * 8048/1024 as [DataPageSize In MB]
FROM sys.allocation_units au
INNER JOIN sys.partitions p on p.hobt_id = au.container_id
where p.index_id<=1 order by total_pages desc
-- the most biggest top 20 indexes.
SELECT top 20
OBJECT_NAME(p.object_id)as [Table Name],
p.index_id,
i.name,
au.total_pages/128 as [IndexPageSize In MB]
FROM sys.allocation_units au
INNER JOIN sys.partitions p on p.hobt_id = au.container_id
INNER JOIN sys.indexes i on p.object_id = i.object_id and p.index_id = i.index_id
where p.index_id>1 order by total_pages desc
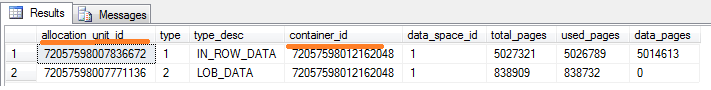
sys.dm_os_buffer_descriptors
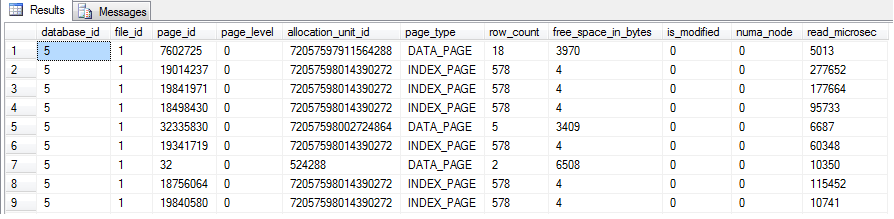
sys.allocation_units
13. how many pages of a table including indexes was loaded into the buffer cache?
-- all the indexes/tables size in memory divid all the indexes/tables storage in Disk.
SELECT
DB_NAME(a.database_id) AS [DataBaseName],
SCHEMA_NAME(t.schema_id) as [SchemaName],
t.name as [TableName],
sum(a.totalPagesNumbers) * 8 AS [MemorySpaceKB],
SUM(au.data_pages) * 8 AS [StorageSpaceKB],
CASE WHEN SUM(au.data_pages) <> 0 THEN
SUM(a.totalPagesNumbers)/CAST(SUM(au.data_pages) AS DECIMAL) END AS 'Percentage Of Object In Memory'
FROM
(
SELECT database_id, allocation_unit_id, COUNT(page_id) totalPagesNumbers
FROM sys.dm_os_buffer_descriptors WHERE database_id = DB_ID()
GROUP BY database_id, allocation_unit_id
) a
INNER JOIN sys.allocation_units au ON a.allocation_unit_id = au.allocation_unit_id
JOIN sys.partitions p ON (au.type IN (1,3) AND au.container_id = p.hobt_id) OR (au.type = 2 AND au.container_id = p.partition_id)
JOIN sys.tables t ON p.object_id = t.object_id AND t.is_ms_shipped = 0
GROUP BY database_id,t.schema_id,t.name
SQLServer DMV Query的更多相关文章
- BI测试工具之跨数据库数据对比,支持oracle,sqlserver
应用场景: 本周在进行SIT,我帮助仅有的一个测试妹妹对部分表进行数据质量验证,第一步需要做的就是比对source与stage表的table definition 与 数据内容的一致性. 本项目使用的 ...
- SQL Server 2008性能故障排查(三)——I/O
原文:SQL Server 2008性能故障排查(三)--I/O 接着上一章:CPU瓶颈 I/O瓶颈(I/O Bottlenecks): SQLServer的性能严重依赖I/O子系统.除非你的数据库完 ...
- DB SQL Monitor 会话状态及等待事件监控工具
DB SQL Monitor v1.7.6 Designed by Wang Zhaoguan 工具说明 --------------------------------------- ...
- Tempdb--monitoring and troubleshooting
TempDB用来存放临时表.全局临时表.表变量以及排序或HASH等操作引发的中间结果集 TempDB在每次实例重启时重新创建,TempDB数据库文件的初始化大小取决于Model数据库的文件大小或显示A ...
- DMV to track the temp file usage for SQLServer
There are three DMVs you can use to track tempdb usage: sys.dm_db_task_space_usagesys.dm_db_session_ ...
- 浅析SqlServer简单参数化模式下对sql语句自动参数化处理以及执行计划重用
我们知道,SqlServer执行sql语句的时候,有一步是对sql进行编译以生成执行计划, 在生成执行计划之前会去缓存中查找执行计划 如果执行计划缓存中有对应的执行计划缓存,那么SqlServer就会 ...
- [引用]SQLServer占CPU100%
程序猿是如何解决SQLServer占CPU100%的 文章目录 遇到的问题 使用SQLServer Profiler监控数据库 SQL1:查找最新的30条告警事件 SQL2:获取当前的总报警记录数 ...
- Inside TSQL Querying - Chapter 3. Query Tuning
Tuning Methodology When dealing with performance problems, database professionals tend to focus on t ...
- 带您理解SQLSERVER是如何执行一个查询的
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lyhabc/p/3367274.html 看这篇文章之前,阁下可以先看一下下面的文章 SQLSERVER独特的任务调度算法"SQLO ...
随机推荐
- JQuery获取和设置Select选项常用方法总结 (转)
1.获取select 选中的 text: $("#cusChildTypeId").find("option:selected").text(); $(&quo ...
- JAVA排序算法
]; ; i < ; i++){ sort[i] = ran.nextInt(); } System.out.print(;i<sort.length;i++){ ;j<sort ...
- ps命令交叉编译
busybox中的ps命令是针对于嵌入式的,其中一些选项并不完整.因此需要将源码下载下来,进行交叉编译 官方下载地址 github下载地址 含有configure,我在此使用的是这个源码包,官方的包在 ...
- 揪出Android流氓软件
揪出Android流氓软件 http://www.icpcw.com/Smartphone/Android/Android/1471/147142_all.htm http://www.william ...
- 简单排序算法 C++类实现
简单排序算法: 冒泡排序 插入排序 选择排序 .h代码: // // SortClass.h // sort and selection // // Created by wasdns on 16/1 ...
- Bootstrap页面布局9 - BS列表
列表: 无序列表(列表中项目内容没有固定的顺序), 有序列表(通常使用在一组有前后顺序的内容上), 描述列表(定义解释一组词汇) 无序列表: <ul> <li>Ueditor编 ...
- Java 获取类名,函数名,行数
C++下用宏来实现.分别是__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__分别代表,C++编译自动在每个文件中设定__FILE__类型是字符串常量 ,将__LINE__替换为当前行数,类型是数字常 ...
- java ReentrantReadWriteLock
// read and write lock is mutual exclusion lock //Listing 7-3. Using ReadWriteLock to Satisfy a Dict ...
- volatile in thread
public class TestCalc { public static void main(String[] args) { class StoppableThread extends Threa ...
- lisp分支
newLISP http://www.ituring.com.cn/article/110968 clojure http://clojure.org/ ...