斐波那契堆(三)之 Java的实现
概要
前面分别通过C和C++实现了斐波那契堆,本章给出斐波那契堆的Java版本。还是那句老话,三种实现的原理一样,择其一了解即可。
目录
1. 斐波那契堆的介绍
2. 斐波那契堆的基本操作
3. 斐波那契堆的Java实现(完整源码)
4. 斐波那契堆的Java测试程序
转载请注明出处:
更多内容:数据结构与算法系列 目录
(01) 斐波那契堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
(02) 斐波那契堆(二)之 C++的实现
(03) 斐波那契堆(三)之 Java的实现
斐波那契堆的介绍
斐波那契堆(Fibonacci heap)是一种可合并堆,可用于实现合并优先队列。它比二项堆具有更好的平摊分析性能,它的合并操作的时间复杂度是O(1)。
与二项堆一样,它也是由一组堆最小有序树组成,并且是一种可合并堆。
与二项堆不同的是,斐波那契堆中的树不一定是二项树;而且二项堆中的树是有序排列的,但是斐波那契堆中的树都是有根而无序的。
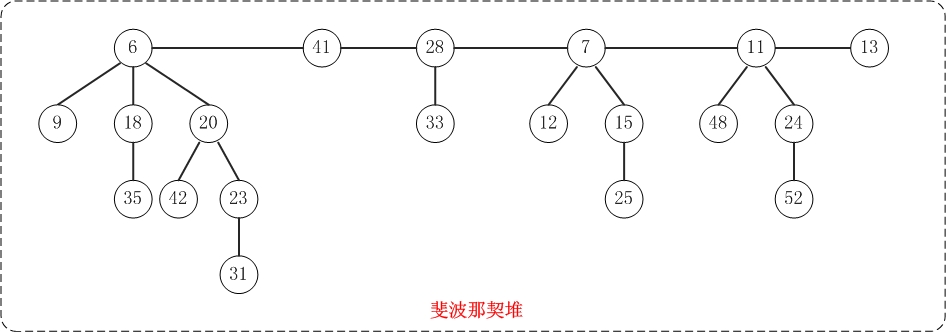
斐波那契堆的基本操作
1. 基本定义
public class FibHeap {
private int keyNum; // 堆中节点的总数
private FibNode min; // 最小节点(某个最小堆的根节点)
private class FibNode {
int key; // 关键字(键值)
int degree; // 度数
FibNode left; // 左兄弟
FibNode right; // 右兄弟
FibNode child; // 第一个孩子节点
FibNode parent; // 父节点
boolean marked; // 是否被删除第一个孩子
public FibNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
this.degree = 0;
this.marked = false;
this.left = this;
this.right = this;
this.parent = null;
this.child = null;
}
}
...
}
FibNode是斐波那契堆的节点类,它包含的信息较多。key是用于比较节点大小的,degree是记录节点的度,left和right分别是指向节点的左右兄弟,child是节点的第一个孩子,parent是节点的父节点,marked是记录该节点是否被删除第1个孩子(marked在删除节点时有用)。
FibHeap是斐波那契堆对应的类。min是保存当前堆的最小节点,keyNum用于记录堆中节点的总数,maxDegree用于记录堆中最大度,而cons在删除节点时来暂时保存堆数据的临时空间。

上面是斐波那契堆的两种不同结构图的对比。从中可以看出,斐波那契堆是由一组最小堆组成,这些最小堆的根节点组成了双向链表(后文称为"根链表");斐波那契堆中的最小节点就是"根链表中的最小节点"!
PS. 上面这幅图的结构和测试代码中的"基本信息"测试函数的结果是一致的;你可以通过测试程序来亲自验证!
2. 插入操作
插入操作非常简单:插入一个节点到堆中,直接将该节点插入到"根链表的min节点"之前即可;若被插入节点比"min节点"小,则更新"min节点"为被插入节点。
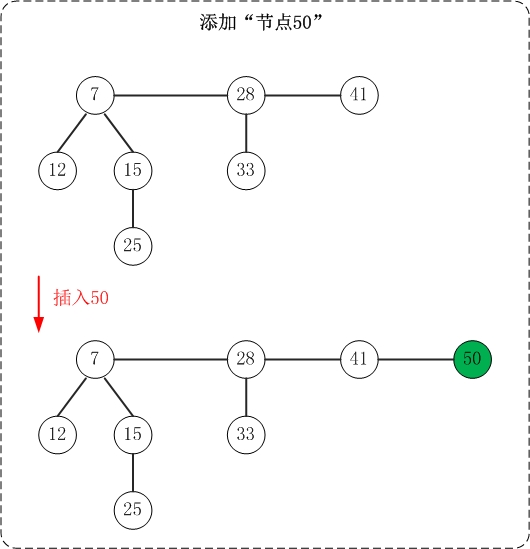
上面是插入操作的示意图。
斐波那契堆的根链表是"双向链表",这里将min节点看作双向联表的表头(后文也是如此)。在插入节点时,每次都是"将节点插入到min节点之前(即插入到双链表末尾)"。此外,对于根链表中最小堆都只有一个节点的情况,插入操作就很演化成双向链表的插入操作。
此外,插入操作示意图与测试程序中的"插入操作"相对应,感兴趣的可以亲自验证。
插入操作代码
/*
* 将node堆结点加入root结点之前(循环链表中)
* a …… root
* a …… node …… root
*/
private void addNode(FibNode node, FibNode root) {
node.left = root.left;
root.left.right = node;
node.right = root;
root.left = node;
} /*
* 将节点node插入到斐波那契堆中
*/
private void insert(FibNode node) {
if (keyNum == 0)
min = node;
else {
addNode(node, min);
if (node.key < min.key)
min = node;
} keyNum++;
} /*
* 新建键值为key的节点,并将其插入到斐波那契堆中
*/
public void insert(int key) {
FibNode node; node = new FibNode(key);
if (node == null)
return ; insert(node);
}
3. 合并操作
合并操作和插入操作的原理非常类似:将一个堆的根链表插入到另一个堆的根链表上即可。简单来说,就是将两个双链表拼接成一个双向链表。
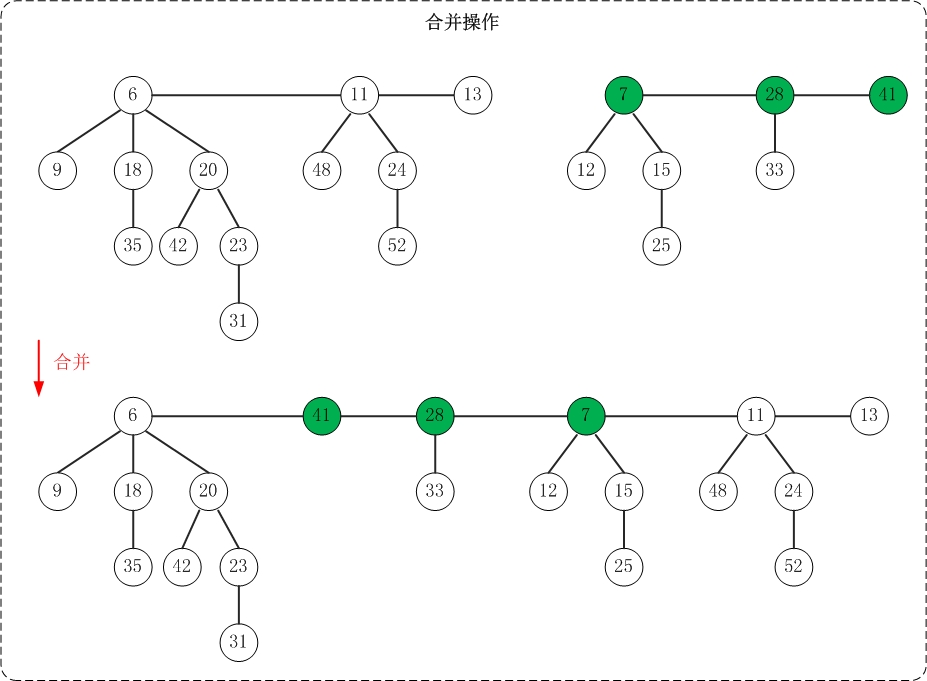
上面是合并操作的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"合并操作"相对应!
合并操作代码
/*
* 将双向链表b链接到双向链表a的后面
*/
private void catList(FibNode a, FibNode b) {
FibNode tmp; tmp = a.right;
a.right = b.right;
b.right.left = a;
b.right = tmp;
tmp.left = b;
} /*
* 将other合并到当前堆中
*/
public void union(FibHeap other) {
if (other==null)
return ; if((this.min) == null) { // this无"最小节点"
this.min = other.min;
this.keyNum = other.keyNum;
other = null;
} else if((other.min) == null) { // this有"最小节点" && other无"最小节点"
other = null;
} else { // this有"最小节点" && other有"最小节点"
// 将"other中根链表"添加到"this"中
catList(this.min, other.min) ; if (this.min.key > other.min.key)
this.min = other.min;
this.keyNum += other.keyNum;
other = null;;
}
}
4. 取出最小节点
抽取最小结点的操作是斐波那契堆中较复杂的操作。
(1)将要抽取最小结点的子树都直接串联在根表中;
(2)合并所有degree相等的树,直到没有相等的degree的树。

上面是取出最小节点的示意图。图中应该写的非常明白了,若有疑问,看代码。
此外,该操作示意图与测试程序中的"删除最小节点"相对应!有兴趣的可以亲自验证。
取出最小节点代码
/*
* 将node链接到root根结点
*/
private void link(FibNode node, FibNode root) {
// 将node从双链表中移除
removeNode(node);
// 将node设为root的孩子
if (root.child == null)
root.child = node;
else
addNode(node, root.child); node.parent = root;
root.degree++;
node.marked = false;
} /*
* 合并斐波那契堆的根链表中左右相同度数的树
*/
private void consolidate() {
// 计算log2(keyNum),floor意味着向上取整!
// ex. log2(13) = 3,向上取整为4。
int maxDegree = (int) Math.floor(Math.log(keyNum) / Math.log(2.0));
int D = maxDegree + 1;
FibNode[] cons = new FibNode[D+1]; for (int i = 0; i < D; i++)
cons[i] = null; // 合并相同度的根节点,使每个度数的树唯一
while (min != null) {
FibNode x = extractMin(); // 取出堆中的最小树(最小节点所在的树)
int d = x.degree; // 获取最小树的度数
// cons[d] != null,意味着有两棵树(x和y)的"度数"相同。
while (cons[d] != null) {
FibNode y = cons[d]; // y是"与x的度数相同的树"
if (x.key > y.key) { // 保证x的键值比y小
FibNode tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
} link(y, x); // 将y链接到x中
cons[d] = null;
d++;
}
cons[d] = x;
}
min = null; // 将cons中的结点重新加到根表中
for (int i=0; i<D; i++) { if (cons[i] != null) {
if (min == null)
min = cons[i];
else {
addNode(cons[i], min);
if ((cons[i]).key < min.key)
min = cons[i];
}
}
}
} /*
* 移除最小节点
*/
public void removeMin() {
if (min==null)
return ; FibNode m = min;
// 将min每一个儿子(儿子和儿子的兄弟)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中
while (m.child != null) {
FibNode child = m.child; removeNode(child);
if (child.right == child)
m.child = null;
else
m.child = child.right; addNode(child, min);
child.parent = null;
} // 将m从根链表中移除
removeNode(m);
// 若m是堆中唯一节点,则设置堆的最小节点为null;
// 否则,设置堆的最小节点为一个非空节点(m.right),然后再进行调节。
if (m.right == m)
min = null;
else {
min = m.right;
consolidate();
}
keyNum--; m = null;
}
5. 减小节点值
减少斐波那契堆中的节点的键值,这个操作的难点是:如果减少节点后破坏了"最小堆"性质,如何去维护呢?下面对一般性情况进行分析。
(1) 首先,将"被减小节点"从"它所在的最小堆"剥离出来;然后将"该节点"关联到"根链表"中。 倘若被减小的节点不是单独一个节点,而是包含子树的树根。则是将以"被减小节点"为根的子树从"最小堆"中剥离出来,然后将该树关联到根链表中。
(2) 接着,对"被减少节点"的原父节点进行"级联剪切"。所谓"级联剪切",就是在被减小节点破坏了最小堆性质,并被切下来之后;再从"它的父节点"进行递归级联剪切操作。
而级联操作的具体动作则是:若父节点(被减小节点的父节点)的marked标记为false,则将其设为true,然后退出。
否则,将父节点从最小堆中切下来(方式和"切被减小节点的方式"一样);然后递归对祖父节点进行"级联剪切"。
marked标记的作用就是用来标记"该节点的子节点是否有被删除过",它的作用是来实现级联剪切。而级联剪切的真正目的是为了防止"最小堆"由二叉树演化成链表。
(3) 最后,别忘了对根链表的最小节点进行更新。
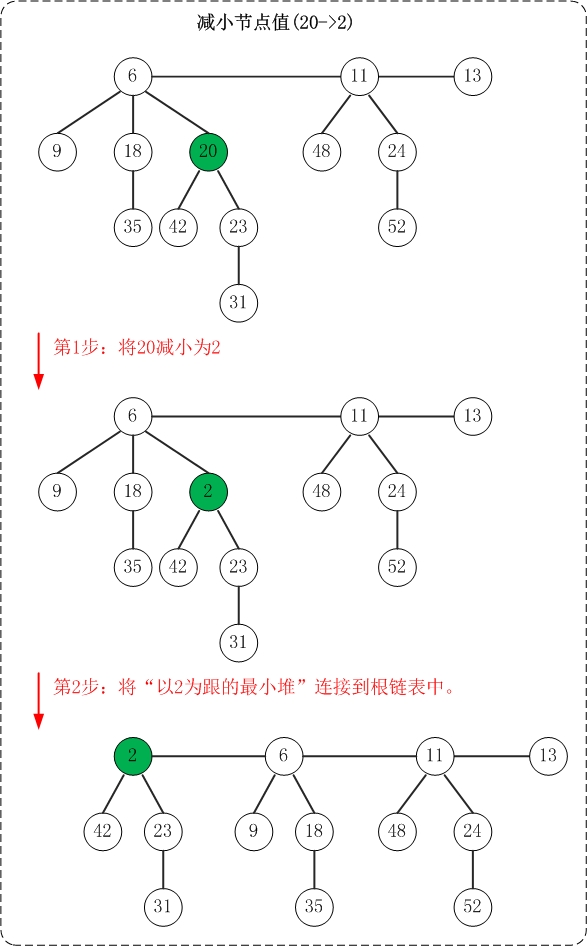
上面是减小节点值的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"减小节点"相对应!
减小节点值的代码
/*
* 修改度数
*/
private void renewDegree(FibNode parent, int degree) {
parent.degree -= degree;
if (parent. parent != null)
renewDegree(parent.parent, degree);
} /*
* 将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,
* 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员。
*/
private void cut(FibNode node, FibNode parent) {
removeNode(node);
renewDegree(parent, node.degree);
// node没有兄弟
if (node == node.right)
parent.child = null;
else
parent.child = node.right; node.parent = null;
node.left = node.right = node;
node.marked = false;
// 将"node所在树"添加到"根链表"中
addNode(node, min);
} /*
* 对节点node进行"级联剪切"
*
* 级联剪切:如果减小后的结点破坏了最小堆性质,
* 则把它切下来(即从所在双向链表中删除,并将
* 其插入到由最小树根节点形成的双向链表中),
* 然后再从"被切节点的父节点"到所在树根节点递归执行级联剪枝
*/
private void cascadingCut(FibNode node) {
FibNode parent = node.parent; if (parent != null) {
if (node.marked == false)
node.marked = true;
else {
cut(node, parent);
cascadingCut(parent);
}
}
} /*
* 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值减少为key
*/
private void decrease(FibNode node, int key) {
if (min==null ||node==null)
return ; if (key > node.key) {
System.out.printf("decrease failed: the new key(%d) is no smaller than current key(%d)\n", key, node.key);
return ;
} FibNode parent = node.parent;
node.key = key;
if (parent!=null && (node.key < parent.key)) {
// 将node从父节点parent中剥离出来,并将node添加到根链表中
cut(node, parent);
cascadingCut(parent);
} // 更新最小节点
if (node.key < min.key)
min = node;
}
6. 增加节点值
增加节点值和减少节点值类似,这个操作的难点也是如何维护"最小堆"性质。思路如下:
(1) 将"被增加节点"的"左孩子和左孩子的所有兄弟"都链接到根链表中。
(2) 接下来,把"被增加节点"添加到根链表;但是别忘了对其进行级联剪切。

上面是增加节点值的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"增大节点"相对应!
增加节点值的代码
/*
* 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值增加为key
*/
private void increase(FibNode node, int key) {
if (min==null ||node==null)
return ; if ( key <= node.key) {
System.out.printf("increase failed: the new key(%d) is no greater than current key(%d)\n", key, node.key);
return ;
} // 将node每一个儿子(不包括孙子,重孙,...)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中
while (node.child != null) {
FibNode child = node.child;
removeNode(child); // 将child从node的子链表中删除
if (child.right == child)
node.child = null;
else
node.child = child.right; addNode(child, min); // 将child添加到根链表中
child.parent = null;
}
node.degree = 0;
node.key = key; // 如果node不在根链表中,
// 则将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,
// 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员,
// 然后进行"级联剪切"
// 否则,则判断是否需要更新堆的最小节点
FibNode parent = node.parent;
if(parent != null) {
cut(node, parent);
cascadingCut(parent);
} else if(min == node) {
FibNode right = node.right;
while(right != node) {
if(node.key > right.key)
min = right;
right = right.right;
}
}
}
7. 删除节点
删除节点,本文采用了操作是:"取出最小节点"和"减小节点值"的组合。
(1) 先将被删除节点的键值减少。减少后的值要比"原最小节点的值"即可。
(2) 接着,取出最小节点即可。
删除节点值的代码
/*
* 删除结点node
*/
private void remove(FibNode node) {
int m = min.key;
decrease(node, m-1);
removeMin();
}
注意:关于斐波那契堆的"更新"、"打印"、"销毁"等接口就不再单独介绍了。后文的源码中有给出它们的实现代码,Please RTFSC(Read The Fucking Source Code)!
斐波那契堆的Java实现(完整源码)
斐波那契堆的实现文件(FibHeap.java)
/**
* Java 语言: 斐波那契堆
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2014/04/07
*/ public class FibHeap { private int keyNum; // 堆中节点的总数
private FibNode min; // 最小节点(某个最小堆的根节点) private class FibNode {
int key; // 关键字(键值)
int degree; // 度数
FibNode left; // 左兄弟
FibNode right; // 右兄弟
FibNode child; // 第一个孩子节点
FibNode parent; // 父节点
boolean marked; // 是否被删除第一个孩子 public FibNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
this.degree = 0;
this.marked = false;
this.left = this;
this.right = this;
this.parent = null;
this.child = null;
}
} public FibHeap() {
this.keyNum = 0;
this.min = null;
} /*
* 将node从双链表移除
*/
private void removeNode(FibNode node) {
node.left.right = node.right;
node.right.left = node.left;
} /*
* 将node堆结点加入root结点之前(循环链表中)
* a …… root
* a …… node …… root
*/
private void addNode(FibNode node, FibNode root) {
node.left = root.left;
root.left.right = node;
node.right = root;
root.left = node;
} /*
* 将节点node插入到斐波那契堆中
*/
private void insert(FibNode node) {
if (keyNum == 0)
min = node;
else {
addNode(node, min);
if (node.key < min.key)
min = node;
} keyNum++;
} /*
* 新建键值为key的节点,并将其插入到斐波那契堆中
*/
public void insert(int key) {
FibNode node; node = new FibNode(key);
if (node == null)
return ; insert(node);
} /*
* 将双向链表b链接到双向链表a的后面
*/
private void catList(FibNode a, FibNode b) {
FibNode tmp; tmp = a.right;
a.right = b.right;
b.right.left = a;
b.right = tmp;
tmp.left = b;
} /*
* 将other合并到当前堆中
*/
public void union(FibHeap other) {
if (other==null)
return ; if((this.min) == null) { // this无"最小节点"
this.min = other.min;
this.keyNum = other.keyNum;
other = null;
} else if((other.min) == null) { // this有"最小节点" && other无"最小节点"
other = null;
} else { // this有"最小节点" && other有"最小节点"
// 将"other中根链表"添加到"this"中
catList(this.min, other.min) ; if (this.min.key > other.min.key)
this.min = other.min;
this.keyNum += other.keyNum;
other = null;;
}
} /*
* 将"堆的最小结点"从根链表中移除,
* 这意味着"将最小节点所属的树"从堆中移除!
*/
private FibNode extractMin() {
FibNode p = min; if (p == p.right)
min = null;
else {
removeNode(p);
min = p.right;
}
p.left = p.right = p; return p;
} /*
* 将node链接到root根结点
*/
private void link(FibNode node, FibNode root) {
// 将node从双链表中移除
removeNode(node);
// 将node设为root的孩子
if (root.child == null)
root.child = node;
else
addNode(node, root.child); node.parent = root;
root.degree++;
node.marked = false;
} /*
* 合并斐波那契堆的根链表中左右相同度数的树
*/
private void consolidate() {
// 计算log2(keyNum),floor意味着向上取整!
// ex. log2(13) = 3,向上取整为4。
int maxDegree = (int) Math.floor(Math.log(keyNum) / Math.log(2.0));
int D = maxDegree + 1;
FibNode[] cons = new FibNode[D+1]; for (int i = 0; i < D; i++)
cons[i] = null; // 合并相同度的根节点,使每个度数的树唯一
while (min != null) {
FibNode x = extractMin(); // 取出堆中的最小树(最小节点所在的树)
int d = x.degree; // 获取最小树的度数
// cons[d] != null,意味着有两棵树(x和y)的"度数"相同。
while (cons[d] != null) {
FibNode y = cons[d]; // y是"与x的度数相同的树"
if (x.key > y.key) { // 保证x的键值比y小
FibNode tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
} link(y, x); // 将y链接到x中
cons[d] = null;
d++;
}
cons[d] = x;
}
min = null; // 将cons中的结点重新加到根表中
for (int i=0; i<D; i++) { if (cons[i] != null) {
if (min == null)
min = cons[i];
else {
addNode(cons[i], min);
if ((cons[i]).key < min.key)
min = cons[i];
}
}
}
} /*
* 移除最小节点
*/
public void removeMin() {
if (min==null)
return ; FibNode m = min;
// 将min每一个儿子(儿子和儿子的兄弟)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中
while (m.child != null) {
FibNode child = m.child; removeNode(child);
if (child.right == child)
m.child = null;
else
m.child = child.right; addNode(child, min);
child.parent = null;
} // 将m从根链表中移除
removeNode(m);
// 若m是堆中唯一节点,则设置堆的最小节点为null;
// 否则,设置堆的最小节点为一个非空节点(m.right),然后再进行调节。
if (m.right == m)
min = null;
else {
min = m.right;
consolidate();
}
keyNum--; m = null;
} /*
* 获取斐波那契堆中最小键值;失败返回-1
*/
public int minimum() {
if (min==null)
return -1; return min.key;
} /*
* 修改度数
*/
private void renewDegree(FibNode parent, int degree) {
parent.degree -= degree;
if (parent. parent != null)
renewDegree(parent.parent, degree);
} /*
* 将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,
* 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员。
*/
private void cut(FibNode node, FibNode parent) {
removeNode(node);
renewDegree(parent, node.degree);
// node没有兄弟
if (node == node.right)
parent.child = null;
else
parent.child = node.right; node.parent = null;
node.left = node.right = node;
node.marked = false;
// 将"node所在树"添加到"根链表"中
addNode(node, min);
} /*
* 对节点node进行"级联剪切"
*
* 级联剪切:如果减小后的结点破坏了最小堆性质,
* 则把它切下来(即从所在双向链表中删除,并将
* 其插入到由最小树根节点形成的双向链表中),
* 然后再从"被切节点的父节点"到所在树根节点递归执行级联剪枝
*/
private void cascadingCut(FibNode node) {
FibNode parent = node.parent; if (parent != null) {
if (node.marked == false)
node.marked = true;
else {
cut(node, parent);
cascadingCut(parent);
}
}
} /*
* 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值减少为key
*/
private void decrease(FibNode node, int key) {
if (min==null ||node==null)
return ; if (key > node.key) {
System.out.printf("decrease failed: the new key(%d) is no smaller than current key(%d)\n", key, node.key);
return ;
} FibNode parent = node.parent;
node.key = key;
if (parent!=null && (node.key < parent.key)) {
// 将node从父节点parent中剥离出来,并将node添加到根链表中
cut(node, parent);
cascadingCut(parent);
} // 更新最小节点
if (node.key < min.key)
min = node;
} /*
* 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值增加为key
*/
private void increase(FibNode node, int key) {
if (min==null ||node==null)
return ; if ( key <= node.key) {
System.out.printf("increase failed: the new key(%d) is no greater than current key(%d)\n", key, node.key);
return ;
} // 将node每一个儿子(不包括孙子,重孙,...)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中
while (node.child != null) {
FibNode child = node.child;
removeNode(child); // 将child从node的子链表中删除
if (child.right == child)
node.child = null;
else
node.child = child.right; addNode(child, min); // 将child添加到根链表中
child.parent = null;
}
node.degree = 0;
node.key = key; // 如果node不在根链表中,
// 则将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,
// 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员,
// 然后进行"级联剪切"
// 否则,则判断是否需要更新堆的最小节点
FibNode parent = node.parent;
if(parent != null) {
cut(node, parent);
cascadingCut(parent);
} else if(min == node) {
FibNode right = node.right;
while(right != node) {
if(node.key > right.key)
min = right;
right = right.right;
}
}
} /*
* 更新斐波那契堆的节点node的键值为key
*/
private void update(FibNode node, int key) {
if(key < node.key)
decrease(node, key);
else if(key > node.key)
increase(node, key);
else
System.out.printf("No need to update!!!\n");
} public void update(int oldkey, int newkey) {
FibNode node; node = search(oldkey);
if (node!=null)
update(node, newkey);
} /*
* 在最小堆root中查找键值为key的节点
*/
private FibNode search(FibNode root, int key) {
FibNode t = root; // 临时节点
FibNode p = null; // 要查找的节点 if (root==null)
return root; do {
if (t.key == key) {
p = t;
break;
} else {
if ((p = search(t.child, key)) != null)
break;
}
t = t.right;
} while (t != root); return p;
} /*
* 在斐波那契堆中查找键值为key的节点
*/
private FibNode search(int key) {
if (min==null)
return null; return search(min, key);
} /*
* 在斐波那契堆中是否存在键值为key的节点。
* 存在返回true,否则返回false。
*/
public boolean contains(int key) {
return search(key)!=null ? true: false;
} /*
* 删除结点node
*/
private void remove(FibNode node) {
int m = min.key;
decrease(node, m-1);
removeMin();
} public void remove(int key) {
if (min==null)
return ; FibNode node = search(key);
if (node==null)
return ; remove(node);
} /*
* 销毁斐波那契堆
*/
private void destroyNode(FibNode node) {
if(node == null)
return; FibNode start = node;
do {
destroyNode(node.child);
// 销毁node,并将node指向下一个
node = node.right;
node.left = null;
} while(node != start);
} public void destroy() {
destroyNode(min);
} /*
* 打印"斐波那契堆"
*
* 参数说明:
* node -- 当前节点
* prev -- 当前节点的前一个节点(父节点or兄弟节点)
* direction -- 1,表示当前节点是一个左孩子;
* 2,表示当前节点是一个兄弟节点。
*/
private void print(FibNode node, FibNode prev, int direction) {
FibNode start=node; if (node==null)
return ;
do {
if (direction == 1)
System.out.printf("%8d(%d) is %2d's child\n", node.key, node.degree, prev.key);
else
System.out.printf("%8d(%d) is %2d's next\n", node.key, node.degree, prev.key); if (node.child != null)
print(node.child, node, 1); // 兄弟节点
prev = node;
node = node.right;
direction = 2;
} while(node != start);
} public void print() {
if (min==null)
return ; int i=0;
FibNode p = min;
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆的详细信息: ==\n");
do {
i++;
System.out.printf("%2d. %4d(%d) is root\n", i, p.key, p.degree); print(p.child, p, 1);
p = p.right;
} while (p != min);
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
斐波那契堆的测试程序(Main.java)
/**
* Java 语言: 斐波那契堆
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2014/04/07
*/ public class Main { private static final boolean DEBUG = false; // 共8个
private static int a[] = {12, 7, 25, 15, 28, 33, 41, 1};
// 共14个
private static int b[] = {18, 35, 20, 42, 9,
31, 23, 6, 48, 11,
24, 52, 13, 2 }; // 验证"基本信息(斐波那契堆的结构)"
public static void testBasic() {
FibHeap hb=new FibHeap(); // 斐波那契堆hb
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]);
hb.insert(b[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
hb.removeMin();
hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb
} // 验证"插入操作"
public static void testInsert() {
FibHeap ha=new FibHeap(); // 斐波那契堆ha
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]);
ha.insert(a[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");
ha.removeMin();
ha.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆ha System.out.printf("== 插入50\n");
ha.insert(50);
ha.print();
} // 验证"合并操作"
public static void testUnion() {
FibHeap ha=new FibHeap();
FibHeap hb=new FibHeap(); // 斐波那契堆ha
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]);
ha.insert(a[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");
ha.removeMin();
ha.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆ha // 斐波那契堆hb
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]);
hb.insert(b[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
hb.removeMin();
hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb // 将"斐波那契堆hb"合并到"斐波那契堆ha"中。
System.out.printf("== 合并ha和hb\n");
ha.union(hb);
ha.print();
} // 验证"删除最小节点"
public static void testRemoveMin() {
FibHeap ha=new FibHeap();
FibHeap hb=new FibHeap(); // 斐波那契堆ha
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i]);
ha.insert(a[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(ha)删除最小节点\n");
ha.removeMin();
//ha.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆ha // 斐波那契堆hb
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]);
hb.insert(b[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
hb.removeMin();
//hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb // 将"斐波那契堆hb"合并到"斐波那契堆ha"中。
System.out.printf("== 合并ha和hb\n");
ha.union(hb);
ha.print(); System.out.printf("== 删除最小节点\n");
ha.removeMin();
ha.print();
} // 验证"减小节点"
public static void testDecrease() {
FibHeap hb=new FibHeap(); // 斐波那契堆hb
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]);
hb.insert(b[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
hb.removeMin();
hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb System.out.printf("== 将20减小为2\n");
hb.update(20, 2);
hb.print();
} // 验证"增大节点"
public static void testIncrease() {
FibHeap hb=new FibHeap(); // 斐波那契堆hb
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]);
hb.insert(b[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
hb.removeMin();
hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb System.out.printf("== 将20增加为60\n");
hb.update(20, 60);
hb.print();
} // 验证"删除节点"
public static void testDelete() {
FibHeap hb=new FibHeap(); // 斐波那契堆hb
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: ");
for(int i=0; i<b.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", b[i]);
hb.insert(b[i]);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点\n");
hb.removeMin();
hb.print(); // 打印斐波那契堆hb System.out.printf("== 删除节点20\n");
hb.remove(20);
hb.print();
} public static void main(String[] args) {
// 验证"基本信息(斐波那契堆的结构)"
testBasic();
// 验证"插入操作"
//testInsert();
// 验证"合并操作"
//testUnion();
// 验证"删除最小节点"
//testRemoveMin();
// 验证"减小节点"
//testDecrease();
// 验证"增大节点"
//testIncrease();
// 验证"删除节点"
//testDelete();
}
}
斐波那契堆的Java测试程序
斐波那契堆的测试程序包括了"插入"、"合并"、"增大"、"减小"、"删除"、"基本信息"等几种功能的测试代码。默认是运行的"基本信息(验证斐波那契堆的结构)"测试代码,你可以根据自己的需要来对相应的功能进行验证!
下面是基本信息测试代码的运行结果:
== 斐波那契堆(hb)中依次添加: 18 35 20 42 9 31 23 6 48 11 24 52 13 2
== 斐波那契堆(hb)删除最小节点
== 斐波那契堆的详细信息: ==
1. 6(3) is root
9(0) is 6's child
18(1) is 9's next
35(0) is 18's child
20(2) is 18's next
42(0) is 20's child
23(1) is 42's next
31(0) is 23's child
2. 11(2) is root
48(0) is 11's child
24(1) is 48's next
52(0) is 24's child
3. 13(0) is root
斐波那契堆(三)之 Java的实现的更多相关文章
- 斐波那契堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
概要 本章介绍斐波那契堆.和以往一样,本文会先对斐波那契堆的理论知识进行简单介绍,然后给出C语言的实现.后续再分别给出C++和Java版本的实现:实现的语言虽不同,但是原理如出一辙,选择其中之一进行了 ...
- 斐波那契堆(二)之 C++的实现
概要 上一章介绍了斐波那契堆的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了斐波那契堆.本章是斐波那契堆的C++实现. 目录1. 斐波那契堆的介绍2. 斐波那契堆的基本操作3. 斐波那契堆的C++实现(完整源码)4. ...
- 斐波那契堆(Fibonacci heap)原理详解(附java代码实现)
前言 斐波那契堆(Fibonacci heap)是计算机科学中最小堆有序树的集合.它和二项式堆有类似的性质,但比二项式堆有更好的均摊时间.堆的名字来源于斐波那契数,它常用于分析运行时间. 堆结构介绍 ...
- fibonacci-Heap(斐波那契堆)原理及C++代码实现
斐波那契堆是一种高级的堆结构,建议与二项堆一起食用效果更佳. 斐波那契堆是一个摊还性质的数据结构,很多堆操作在斐波那契堆上的摊还时间都很低,达到了θ(1)的程度,取最小值和删除操作的时间复杂度是O(l ...
- 基于visual Studio2013解决算法导论之045斐波那契堆
题目 斐波那契堆 解决代码及点评 // 斐波那契堆.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> ...
- 笔试算法题(46):简介 - 二叉堆 & 二项树 & 二项堆 & 斐波那契堆
二叉堆(Binary Heap) 二叉堆是完全二叉树(或者近似完全二叉树):其满足堆的特性:父节点的值>=(<=)任何一个子节点的键值,并且每个左子树或者右子树都是一 个二叉堆(最小堆或者 ...
- Java面试题:小白不得不懂的斐波那契数列
很长一段时间里,我都非常疑惑:“我写的技术文章不差啊,有内容的同时还很有趣,不至于每篇只有区区几十个人读啊?为什么有些内容简单到只有一行注册码的文章浏览量反而轻松破万?”这样的疑惑如鲠在喉啊!写技术博 ...
- 算法笔记_001:斐波那契数的多种解法(Java)
本篇文章解决的问题来源于算法设计与分析课程的课堂作业,主要是运用多种方法来计算斐波那契数.具体问题及解法如下: 一.问题1: 问题描述:利用迭代算法寻找不超过编程环境能够支持的最大整数的斐波那契数是第 ...
- 斐波那契数列【java实现】
java 实现斐波那契数列 以下是Java代码实现(递归与递推两种方式): import java.util.Scanner; /** * Fibonacci * * @author tongqian ...
随机推荐
- Leetcode-462 Minimum Moves to Equal Array Elements II
#462. Minimum Moves to Equal Array Elements II Given a non-empty integer array, find the minimum n ...
- android: SQLite添加数据
现在你已经掌握了创建和升级数据库的方法,接下来就该学习一下如何对表中的数据进 行操作了.其实我们可以对数据进行的操作也就无非四种,即 CRUD.其中 C 代表添加 (Create),R 代表查询(Re ...
- Java 命名空间的由来和引入
名字可视性(Name visibility) 名字管理对任何程序设计语言来说,都是一个重要问题.如果你在程序的某个模块里使用了 一个名字,而其他人在这个程序的另一个模块里也使用了相同的名字,那么怎样才 ...
- Maven - 项目结构
一个基础的Maven Java项目结构图如下所示: Project Name |__________ pom.xml |__________ src | |__ ...
- 每日英语:A New Way to Learn Chinese
Entrepreneur and author ShaoLan Hsueh thinks that English-speakers can start learning to read Chines ...
- iOS 日期处理 (Swift3.0 NSDate)
处理日期的常见情景 NSDate -> String & String -> NSDate 日期比较 日期计算(基于参考日期 +/- 一定时间) 计算日期间的差异 拆解NSDate ...
- 【转】mac/linux终端光标的快捷键操作
摘自网络:原标题是类似linux/unix命令行终端的光标及字符控制快捷键的东东. 常用的快捷键: Ctrl + d 删除一个字符,相当于通常的Delete键(命令行若无所有字符,则相当于exit:处 ...
- 初识WEB:输入URL之后的故事【转】
转载一篇文章,分析的是浏览器输入url后所执行的一系列操作!写得非常清晰易懂,分享给大家! 作者:Jesse 出处:http://jesse2013.cnblogs.com/ 本文版权归作者和博客园共 ...
- SQL语句转摘
http://www.cnblogs.com/Olive116/p/3271706.html 收藏没有用,来收到留链接
- ODAC(V9.5.15) 学习笔记(十七)主从模式
主从模式(Master/Detail mode)是指建立主表和从表关系的多个数据集集合模式. 1. 关系设置 要设置主从模式,必须有一个主表数据集(TDataSet)和一个从表数据集(TDataSet ...
