java并发之线程执行器(Executor)
线程执行器和不使用线程执行器的对比(优缺点)
1.线程执行器分离了任务的创建和执行,通过使用执行器,只需要实现Runnable接口的对象,然后把这些对象发送给执行器即可。
2.使用线程池来提高程序的性能。当发送一个任务给执行器时,执行器会尝试使用线程池中的线程来执行这个任务。避免了不断创建和销毁线程导致的性能开销。
3.执行器可以处理实现了Callable接口的任务。Callable接口类似于Runnable接口,却提供了两方面的增强:
a.Callable主方法名称为call(),可以返回结果
b.当发送一个Callable对象给执行器时,将获得一个实现了Future接口的对象。可以使用这个对象来控制Callable对象的状态和结果。
4.提供了一些操作线程任务的功能
- 执行继承了Runnable接口的任务类
public class Task implements Runnable {
private String name;
public Task(String name){
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
}
}
public class Server {
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor;
public Server(){
executor=(ThreadPoolExecutor)Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
}
public void executeTask(Task task){
System.out.printf("Server: A new task has arrived\n");
executor.execute(task);
System.out.printf("Server: Active Count: %d\n",executor.getActiveCount());
System.out.printf("Server: Completed Tasks: %d\n",executor.getCompletedTaskCount());
}
public void endServer() {
executor.shutdown();
}
}
- 执行实现了Callable<T>接口的任务
public class FactorialCalculator implements Callable<Integer> {
private Integer number;
public FactorialCalculator(Integer number){
this.number=number;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int num, result;
num=number.intValue();
result=1;
// If the number is 0 or 1, return the 1 value
if ((num==0)||(num==1)) {
result=1;
} else {
// Else, calculate the factorial
for (int i=2; i<=number; i++) {
result*=i;
Thread.sleep(20);
}
}
System.out.printf("%s: %d\n",Thread.currentThread().getName(),result);
// Return the value
return result;
}
}
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = (ThreadPoolExecutor) Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);//实例化执行器
FactorialCalculator calculator = new FactorialCalculator(number);//实例化任务
Future<Integer> result = executor.submit(calculator);//执行任务,并返回Future<T>实例
public interface Callable<V> {
V call() throws Exception;
}


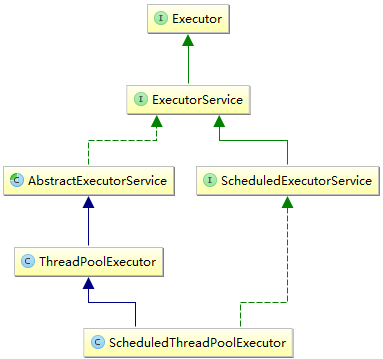
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
ScheduledExecutorService executor=(ScheduledExecutorService)Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
executor.schedule(task,i+1 , TimeUnit.SECONDS);
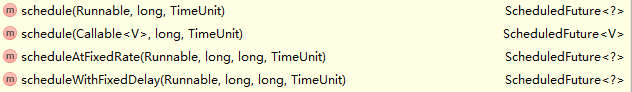
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,//即将执行的任务
long delay,//任务执行前需要等待的时间
TimeUnit unit)//时间单位
ScheduledExecutorService executor=(ScheduledExecutorService)Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
Task task=new Task("Task "+i);
executor.schedule(task,i+1 , TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
executor.shutdown();
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,//即将执行的任务
long delay, //任务执行前需要等待的时间
TimeUnit unit) //时间单位
ScheduledExecutorService executor=Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
Task task=new Task("Task");
ScheduledFuture<?> result=executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, 1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, //将被周期性执行的任务
long initialDelay,//任务第一次执行后的延后时间
long period, //两次执行的时间周期
TimeUnit unit) { //第二和第三个参数的时间单位
UserValidator ldapValidator=new UserValidator("LDAP");
UserValidator dbValidator=new UserValidator("DataBase");
// Create two tasks for the user validation objects
TaskValidator ldapTask=new TaskValidator(ldapValidator, username, password);
TaskValidator dbTask=new TaskValidator(dbValidator,username,password);
// Add the two tasks to a list of tasks
List<TaskValidator> taskList=new ArrayList<>();
taskList.add(ldapTask);
taskList.add(dbTask);
// Create a new Executor
ExecutorService executor=(ExecutorService)Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
String result;
try {
// Send the list of tasks to the executor and waits for the result of the first task
// that finish without throw and Exception. If all the tasks throw and Exception, the
// method throws and ExecutionException.
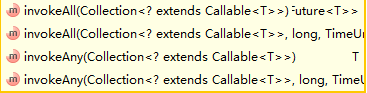
result = executor.invokeAny(taskList);
System.out.printf("Main: Result: %s\n",result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Shutdown the Executor
executor.shutdown();
public boolean validate(String name, String password) {
Random random=new Random();
try {
Long duration=(long)(Math.random()*10);
System.out.printf("Validator %s: Validating a user during %d seconds\n",this.name,duration);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(duration);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return false;
}
return random.nextBoolean();
}
List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Task task = new Task("Task-" + i);
taskList.add(task);
}
// Call the invokeAll() method
List<Future<Result>> resultList = null;
try {
resultList = executor.invokeAll(taskList);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Finish the executor
executor.shutdown();
Task task=new Task();
Future<String> result=executor.submit(task);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.printf("Main: Cancelling the Task\n");
result.cancel(true);
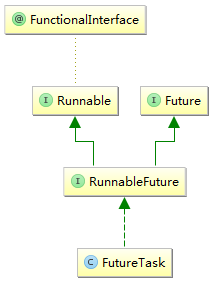
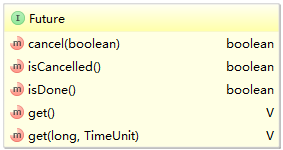
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}

public class ResultTask extends FutureTask<String> {
@Override
protected void done() {
if (isCancelled()) {
System.out.printf("%s: Has been cancelled\n",name);
} else {
System.out.printf("%s: Has finished\n",name);
}
}
}
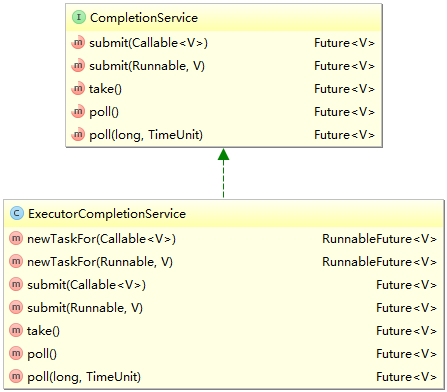
1.从list中遍历的每个Future对象并不一定处于完成状态,这时调用get()方法就会被阻塞住,如果系统是设计成每个线程完成后就能根据其结果继续做后面的事,这样对于处于list后面的但是先完成的线程就会增加了额外的等待时间。
2.而CompletionService的实现是维护一个保存Future对象的BlockingQueue。只有当这个Future对象状态是结束的时候,才会加入到这个Queue中,take()方法其实就是Producer-Consumer中的Consumer。它会从Queue中取出Future对象,如果Queue是空的,就会阻塞在那里,直到有完成的Future对象加入到Queue中。
public class RejectedTaskController implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.out.printf("RejectedTaskController: The task %s has been rejected\n",r.toString());
System.out.printf("RejectedTaskController: %s\n",executor.toString());
System.out.printf("RejectedTaskController: Terminating: %s\n",executor.isTerminating());
System.out.printf("RejectedTaksController: Terminated: %s\n",executor.isTerminated());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create the controller for the Rejected tasks
RejectedTaskController controller=new RejectedTaskController();
// Create the executor and establish the controller for the Rejected tasks
ThreadPoolExecutor executor=(ThreadPoolExecutor)Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(controller);
// Lauch three tasks
System.out.printf("Main: Starting.\n");
for (int i=0; i<3; i++) {
Task task=new Task("Task"+i);
executor.submit(task);
}
// Shutdown the executor
System.out.printf("Main: Shuting down the Executor.\n");
executor.shutdown();
// Send another task
System.out.printf("Main: Sending another Task.\n");
Task task=new Task("RejectedTask");
executor.submit(task);
// The program ends
System.out.printf("Main: End.\n");
}
Main: Starting.
Main: Shuting down the Executor.
Main: Sending another Task.
RejectedTaskController: The task java.util.concurrent.FutureTask@60e53b93 has been rejected
RejectedTaskController: java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@5e2de80c[Shutting down, pool size = 3, active threads = 3, queued tasks = 0, completed tasks = 0]
RejectedTaskController: Terminating: true
RejectedTaksController: Terminated: false
Main: End.
Task Task1: Starting
Task Task0: Starting
Task Task2: Starting
Task Task1: ReportGenerator: Generating a report during 4 seconds
Task Task0: ReportGenerator: Generating a report during 7 seconds
Task Task2: ReportGenerator: Generating a report during 6 seconds
Task Task1: Ending
Task Task2: Ending
Task Task0: Ending
java并发之线程执行器(Executor)的更多相关文章
- java并发之线程池的使用
背景 当系统并发的线程数量很多,并且每个线程都是执行一个时间很短的任务就结束了,这样频繁创建线程就会大大降低系统的效率,因为频繁创建线程和销毁线程需要消耗大量的系统资源. 所以需要一个办法使得线程可以 ...
- Java并发之——线程池
一. 线程池介绍 1.1 简介 线程池是一种多线程处理形式,处理过程中将任务添加到队列,然后在创建线程后自动启动这些任务.线程池的基本思想还是一种对象池的思想,开辟一块内存空间,里面存放了众多(未死亡 ...
- Java并发之线程中断
前面的几篇文章主要介绍了线程的一些最基本的概念,包括线程的间的冲突及其解决办法,以及线程间的协作机制.本篇主要来学习下Java中对线程中断机制的实现.在我们的程序中经常会有一些不达到目的不会退出的线程 ...
- Java并发之线程管理(线程基础知识)
因为书中涵盖的知识点比较全,所以就以书中的目录来学习和记录.当然,学习书中知识的时候自己的思考和实践是最重要的.说到线程,脑子里大概知道是个什么东西,但很多东西都还是懵懵懂懂,这是最可怕的.所以想着细 ...
- Java并发之线程转储
一.java线程转储 java的线程转储可以被定义为JVM中在某一个给定的时刻运行的所有线程的快照.一个线程转储可能包含一个单独的线程或者多个线程.在多线程环境中,比如J2EE应用服务器,将会有许多线 ...
- Java 并发之线程安全
写线程安全的代码,说白了就是管理一个类的共享的.可变的状态.只要有多于 1 个线程对类的状态进行写入,那么就必须用同步来协调这多个线程对状态的访问.对于一个没有状态的类来说(简单的理解就是只有方法没有 ...
- Java并发之线程异常捕获
由于线程的本质特性,使得你不能捕获从线程中逃逸的异常,如: import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurre ...
- Java并发之线程
在前面我们介绍的一些内容中,我们的程序都是一条执行流,一步一步的执行.但其实这种程序对我们计算机的资源的使用上是低效的.例如:我们有一个用于计算的程序,主程序计算数据,在计算的过程中每得到一个结果就需 ...
- Java并发之线程间的协作
上篇文章我们介绍了synchronized关键字,使用它可以有效的解决我们多线程所带来的一些常见问题.例如:竞态条件,内存可见性等.并且,我们也说明了该关键字主要是一个加锁和释放锁的集成,所有为能获得 ...
随机推荐
- 【转载】十条jQuery代码片段助力Web开发效率提升
文章转载自 51CTO http://www.51cto.com/ 原文链接:http://developer.51cto.com/art/201604/509093.htm原文摘要:JQuery是继 ...
- 简易js模板引擎
前面 js 模板引擎有很多很多,我以前经常用 art-template ,有时候也会拿 vue 来当模板引擎用. 直到...... 年初的时候,我还在上个项目组,那时候代码规范是未经允许不能使用 [外 ...
- 【装逼利器效率软件】一张图问你想不想用Launchy
简述:Launchy博客园很多文章,长篇大论文字太多. 一张图问你想不想用? 长话多说: 一.设置Launchy扫描目录,安装后会默认,个人推荐自定义目录比较好 二.自行建立快捷方式别名文件夹,存放各 ...
- 关于scanf 与 cin gets(),getline()......输入输出字符串的区别
很对人对于字符串的输入输出一直是比较模糊的,今天总结一下几个常用的输入流符号对于输入字符串时的区别: 1.scanf(),首先 它遇到空格或回车键(\n)就会结束,并且会将回车符算入字符串中: 2.c ...
- 2017上海QCon之旅总结(上)
本来这个公众号的交流消息中间件相关的技术的.这周去上海参加了QCon,第一次参加这样的技术会议,感受挺多的,所以整理一下自己的一些想法接公众号和大家交流一下. 下面进入正题,从自己参加了的一些分享中挑 ...
- PyCharm 2017 免费 破解 注册 激活 教程(附 License Server 地址)(Python 编辑器 IDE 推荐)
许多朋友都在问如何破解 PyCharm 2017 Professional 专业版,咪博士对此是坚决反对的! 不到万不得已,请不要这样做.破解之前,请拖到文章末尾,思考几个问题,想明白你确实需要这样做 ...
- Linux.根据进程名关键字杀进程
先看例子, 假设系统中有以下2个进程 USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root ...
- LeetCode 405. Convert a Number to Hexadecimal (把一个数转化为16进制)
Given an integer, write an algorithm to convert it to hexadecimal. For negative integer, two’s compl ...
- Chrome 62 的大坑:修改密码后始终使用保存的旧密码登录
最近有用户向我们反馈,修改密码后,怎么也登录不了我们网站,总是提示密码错误.用户确认密码肯定没错,通过用户发给我们的操作截图看,用户修改密码的操作也没问题. 开始我们没能重现出这个问题,我们检查了相关 ...
- Asp.net Api中使用OAuth2.0实现“客户端验证”
一.实现继承自OAuthAuthorizationServerProvider的类,实现以"客户端验证"方式传入的相关认证和access_token发放. public class ...
