golang的interface剖析
- type MyInt int
- var i int
- var j MyInt
- var r io.Reader
- var r io.Reader
- tty, err := os.OpenFile("/dev/tty", os.O_RDWR, 0)
- if err != nil {
- return nil, err
- }
- r = tty
到这里,r的类型是什么?r的类型仍然是interface io.Reader,只是r = tty这一句,隐含了一个类型转换,将tty转成了io.Reader。
- type Binary uint64
- func (i Binary) String() string {
- return strconv.Uitob64(i.Get(), 2)
- }
- func (i Binary) Get() uint64 {
- return uint64(i)
- }
.png)
- var w io.Writer
- switch v := any.(type) {
- case int:
- return strconv.Itoa(v)
- case float:
- return strconv.Ftoa(v, 'g', -1)
- }
- 1 var any interface{} // initialized elsewhere
- 2 s := any.(Stringer) // dynamic conversion
- 3 for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
- 4 fmt.Println(s.String())
- 5 }
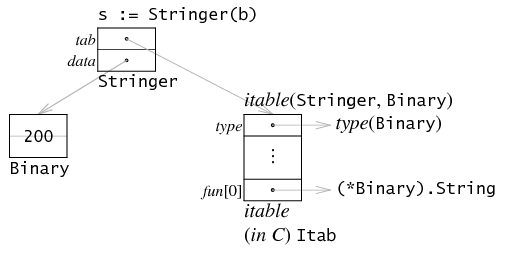
- 143 type iface struct {
- 144 tab *itab // 指南itable
- 145 data unsafe.Pointer // 指向真实数据
- 146 }
- 617 type itab struct {
- 618 inter *interfacetype
- 619 _type *_type
- 620 link *itab
- 621 bad int32
- 622 unused int32
- 623 fun [1]uintptr // variable sized
- 624 }
- 310 type imethod struct {
- 311 name nameOff
- 312 ityp typeOff
- 313 }
- 314
- 315 type interfacetype struct {
- 316 typ _type
- 317 pkgpath name
- 318 mhdr []imethod
- 319 }
- 320
- 28 type _type struct {
- 29 size uintptr
- 30 ptrdata uintptr // size of memory prefix holding all pointers
- 31 hash uint32
- 32 tflag tflag
- 33 align uint8
- 34 fieldalign uint8
- 35 kind uint8
- 36 alg *typeAlg
- 37 // gcdata stores the GC type data for the garbage collector.
- 38 // If the KindGCProg bit is set in kind, gcdata is a GC program.
- 39 // Otherwise it is a ptrmask bitmap. See mbitmap.go for details.
- 40 gcdata *byte
- 41 str nameOff
- 42 ptrToThis typeOff
- 43 }
- 22 func itabhash(inter *interfacetype, typ *_type) uint32 {
- 23 // compiler has provided some good hash codes for us.
- 24 h := inter.typ.hash
- 25 h += 17 * typ.hash
- 26 // TODO(rsc): h += 23 * x.mhash ?
- 27 return h % hashSize
- 28 }
- 44 h := itabhash(inter, typ)
- 45
- 46 // look twice - once without lock, once with.
- 47 // common case will be no lock contention.
- 48 var m *itab
- 49 var locked int
- 50 for locked = 0; locked < 2; locked++ {
- 51 if locked != 0 {
- 52 lock(&ifaceLock)
- 53 }
- 54 for m = (*itab)(atomic.Loadp(unsafe.Pointer(&hash[h]))); m != nil; m = m.link {
- 55 if m.inter == inter && m._type == typ {
- 71 return m // 找到了前面计算过的itab
- 72 }
- 73 }
- 74 }
- 75 // 没有找到,生成一个,并加入到itab的hash中。
- 76 m = (*itab)(persistentalloc(unsafe.Sizeof(itab{})+uintptr(len(inter.mhdr)-1)*sys.PtrSize, 0, &memstats.other_sys))
- 77 m.inter = inter
- 78 m._type = typ
- 79 additab(m, true, canfail)
- 13 const (
- 14 hashSize = 1009
- 15 )
- 16
- 17 var (
- 18 ifaceLock mutex // lock for accessing hash
- 19 hash [hashSize]*itab
- 20 )
- 92 // both inter and typ have method sorted by name,
- 93 // and interface names are unique,
- 94 // so can iterate over both in lock step;
- 95 // the loop is O(ni+nt) not O(ni*nt). // 按name排序过的,因此这里的匹配只需要O(ni+nt)
- 99 j := 0
- 100 for k := 0; k < ni; k++ {
- 101 i := &inter.mhdr[k]
- 102 itype := inter.typ.typeOff(i.ityp)
- 103 name := inter.typ.nameOff(i.name)
- 104 iname := name.name()
- 109 for ; j < nt; j++ {
- 110 t := &xmhdr[j]
- 111 tname := typ.nameOff(t.name)
- 112 if typ.typeOff(t.mtyp) == itype && tname.name() == iname {
- 118 if m != nil {
- 119 ifn := typ.textOff(t.ifn)
- 120 *(*unsafe.Pointer)(add(unsafe.Pointer(&m.fun[0]), uintptr(k)*sys.PtrSize)) = ifn // 找到匹配,将实际类型的方法填入itab的fun
- 121 }
- 122 goto nextimethod
- 123 }
- 124 }
- 125 }
- 135 nextimethod:
- 136 }
- 140 h := itabhash(inter, typ) //插入上面的全局hash
- 141 m.link = hash[h]
- 142 atomicstorep(unsafe.Pointer(&hash[h]), unsafe.Pointer(m))
- 143 }
到这里,interface的数据结构的框架。
golang的interface剖析的更多相关文章
- Golang 源码剖析:log 标准库
Golang 源码剖析:log 标准库 原文地址:Golang 源码剖析:log 标准库 日志 输出 2018/09/28 20:03:08 EDDYCJY Blog... 构成 [日期]<空格 ...
- Golang的Interface是个什么鬼
问题概述 Golang的interface,和别的语言是不同的.它不需要显式的implements,只要某个struct实现了interface里的所有函数,编译器会自动认为它实现了这个interfa ...
- golang 关于 interface 的学习整理
Golang-interface(四 反射) go语言学习-reflect反射理解和简单使用 为什么在Go语言中要慎用interface{} golang将interface{}转换为struct g ...
- Golang 的 `[]interface{}` 类型
Golang 的 []interface{} 类型 我其实不太喜欢使用 Go 语言的 interface{} 类型,一般情况下我宁愿多写几个函数:XxxInt, XxxFloat, XxxString ...
- Golang接口(interface)三个特性(译文)
The Laws of Reflection 原文地址 第一次翻译文章,请各路人士多多指教! 类型和接口 因为映射建设在类型的基础之上,首先我们对类型进行全新的介绍. go是一个静态性语言,每个变量都 ...
- Golang-interface(四 反射)
github:https://github.com/ZhangzheBJUT/blog/blob/master/reflect.md 一 反射的规则 反射是程序执行时检查其所拥有的结构.尤其是类型的一 ...
- golang之interface
一.概述 接口类型是对 "其他类型行为" 的抽象和概况:因为接口类型不会和特定的实现细节绑定在一起:很多面向对象都有类似接口概念,但Golang语言中interface的独特之处在 ...
- golang将interface{}转换为struct
项目中需要用到golang的队列,container/list,需要放入的元素是struct,但是因为golang中list的设计,从list中取出时的类型为interface{},所以需要想办法把i ...
- Golang-interface(二 接口与nil)
github: https://github.com/ZhangzheBJUT/blog/blob/master/nil.md 一 接口与nil 前面解说了go语言中接口的基本用法,以下将说一说nil ...
随机推荐
- python 经典博客链接
1, 从文件的读取与输出: http://www.cnblogs.com/xuxn/archive/2011/07/27/read-a-file-with-python.html http://www ...
- LeetCode112:Path Sum
正常写法 bool HasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) { bool ret=false; if(root==null)return false; if(root.l ...
- 使用Windows API进行串口编程
使用Windows API进行串口编程 串口通信一般分为四大步:打开串口->配置串口->读写串口->关闭串口,还可以在串口上监听读写等事件.1.打开和关闭串口Windows中串口 ...
- pycharm shortcut
Alt+F12 is a shortcut to open/hide Terminal panel
- 阿里云ubuntu 16.04搭建odoo11服务器
ubuntu 16.04 具体如何搭建odoo11网站的具体步骤可以参考这一篇文章 按上面的文章配置环境后,自己网站的启动具体步骤如下: 1.登录阿里云 [远程连接],进入命令行界面1 2.cd到目录 ...
- React + js-xlsx构建Excel文件上传预览功能
首先要准备react开发环境以及js-xlsx插件 1. 此处省略安装react安装步骤 2.下载js-xlsx插件 yarn add xlsx 或者 npm install xlsx 在项目中引入 ...
- 通用漏洞评估方法CVSS3.0简表
CVSS3.0计算分值共有三种维度: 1. 基础度量. 分为 可利用性 及 影响度 两个子项,是漏洞评估的静态分值. 2. 时间度量. 基础维度之上结合受时间影响的三个动态分值,进而评估该漏洞的动态分 ...
- openhtmltopdf 支持自定义字体、粗体
一.支持自定义字体 private static void renderPDF(String html, OutputStream outputStream) throws Exception { t ...
- RSA公钥文件解密密文的原理分析
前言 最近在学习RSA加解密过程中遇到一个这样的难题:假设已知publickey公钥文件和加密后的密文flag,如何对其密文进行解密,转换成明文~~ 分析 对于rsa算法的公钥与私钥的产生,我们可以了 ...
- 开启C语言的学习之门
本人是一枚工业界的码农,为了职业道路越来越宽广决定向上位机方面进军,C语言曾经在大学里面学过点皮毛但是离应用远远不够,尽量每天在工作之余更新自己学习的进度,同时也希望有大神能给予在编程道路上的指导,话 ...
