扩容Linux文件系统
扩容Linux文件系统
腾讯云 云硬盘扩容
https://cloud.tencent.com/product/cbs
https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/362/6738
普通云硬盘(HDD Cloud Storage) 容量最大为16TB
高性能云硬盘(Premium Cloud Storage) 容量最大为4TB
SSD云硬盘(SSD Cloud Storage) 容量最大为4TB
单台虚拟机最多可挂载 10 块云盘,容量达 40TB。您可以轻松搭建大容量的文件系统,用于大数据、数据仓库、日志处理等业务。
请注意,由于MBR的限制,选择任何一种方式时,请保持任意分区的大小不超过2TB(若您扩容后的空间已经大于2TB则不可选择第二种方式。
一般系统分区方案
/boot 500M
/ 30G
SWAP 8G
/data 剩下空间
扩容分三步
1) 扩容实体云硬盘大小
2) 扩容分区
确定文件系统分区表形式
扩容分区
3) 扩容文件系统
GPT分区云硬盘扩容
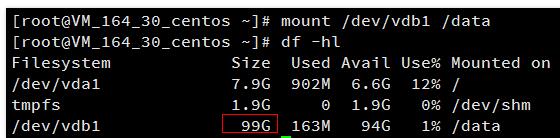
umount 挂载点
parted [磁盘路径]
e2fsck -f /dev/vdb1
resize2fs /dev/vdb1
mount 分区路径 挂载点
# 具体命令
umount -lf /data
parted /dev/vdb
e2fsck -f /dev/vdb1
resize2fs /dev/vdb1
mount /dev/vdb1 /data
或
echo "/dev/vdb /data ext4 defaults,noatime,nodiratime 0 0" >>/etc/fstab
mount -a
新空间增加到已有分区中(GPT分区格式)
查看数据盘信息
执行命令
parted 磁盘路径 print
确认云硬盘的容量变化。如在过程中收到如下提示,请输入Fix:
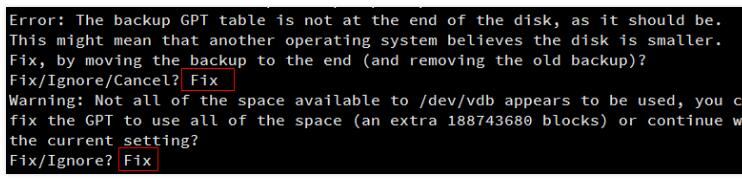
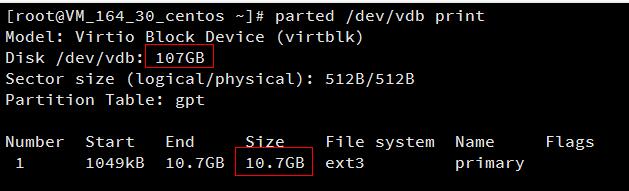
这里扩容后的云硬盘大小为107GB,已有分区的大小为10.7GB。
卸载已挂载数据盘
执行以下命令确认该云硬盘是否还有分区已挂载:
mount | grep '磁盘路径'
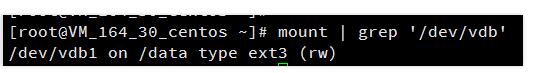
这里云硬盘上有一个分区(vdb1)挂载在/data上,需要将其解挂。
使用以下命令解挂:
umount 挂载点
本例中即执行umount /data进行卸载。
注:要将云硬盘上所有分区的文件系统都解挂,如vdb1、vdb2......
再次使用mount | grep '/dev/vdb'命令来确认此硬盘上所有分区的文件系统都已解挂。
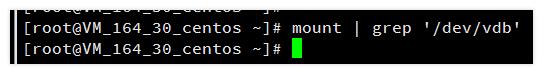
数据盘分区
确认云硬盘所有分区均已卸载后,执行以下命令,将原分区删除并以同样的起始偏移新建一个分区:
parted [磁盘路径]
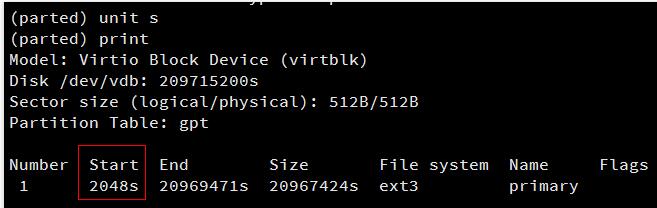
接下来输入unit s,将显示和操纵单位变成sector(默认为GB),输入print来查看分区信息,记住已有分区的Start值。
删除分区并新建后,Start值必须与这个相同,否则数据将会丢失。
执行以下命令删除原有分区:
rm [分区Number]
由上图可知云硬盘上有一个分区,Number号为“1”,执行rm 1,结果如下图:

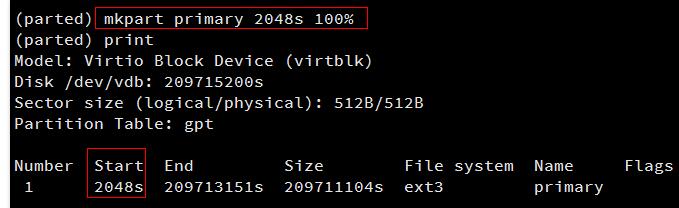
输入mkpart primary [原分区起始扇区] 100%
新建一个主分区。
本例中使用mkpart primary 2048s 100%,此主分区从第2048个扇区开始(必须与删除之前的分区一致),100%表示此分区到磁盘的最末尾。
如果出现如图状态请输入Ignore:

再次输入print可发现新分区已经新建成功,输入quit,即可退出parted工具:
检查扩容后分区的文件系统
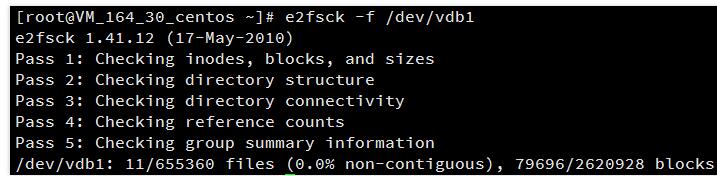
使用以下命令检查扩容后的分区:
e2fsck -f 分区路径
前述步骤中本例已新建了分区1,使用e2fsck -f /dev/vdb1进行操作。结果如下:
扩容文件系统
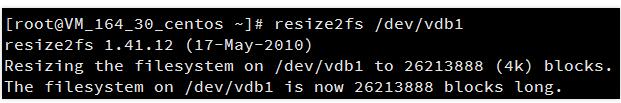
执行以下命令进行分区上文件系统的扩容操作:
resize2fs 分区路径
挂载新分区
执行以下命令挂载分区:
mount 分区路径 挂载点
这里通过mount /dev/vdb1 /data
手动挂载新分区,并使用df -h命令查看,出现以下信息说明挂载成功,即可以查看到数据盘了。
MBR分区云硬盘扩容
下面两种情况都可以选择使用自动扩容工具(devresize.py)进行扩容
1、原有的硬盘(数据盘)只有一个MBR主分区并制作了文件系统
2、原有的硬盘(数据盘)没有分区,直接在此硬盘上制作了文件系统
自动扩容工具适用于Linux操作系统,用于将扩容时新扩的云硬盘存储空间添加到已存在的文件系统中,扩容能够成功必须满足下面3个条件:
1、文件系统是ext2/ext3/ext4,并且只有一个主分区没有其他主分区和扩展分区
2、当前文件系统不能有错误
3、扩容后的磁盘大小不超过2TB
umount 挂载点
wget -O /tmp/devresize.py http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/install/virts/devresize.py 下载一键扩容工具
python /tmp/devresize.py 硬盘路径 云硬盘,而不是分区名
mount 分区路径 挂载点
# 具体命令
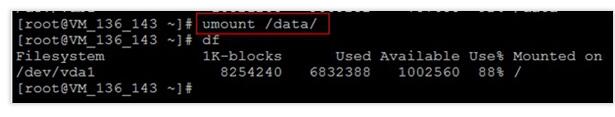
umount -lf /data
wget -O /tmp/devresize.py http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/install/virts/devresize.py
python /tmp/devresize.py /dev/vdb
mount /dev/vdb1 /data
或
echo "/dev/vdb /data ext4 defaults,noatime,nodiratime 0 0" >>/etc/fstab
mount -a
新空间增加到已有分区中(MBR分区格式)
卸载正在使用的硬盘分区
执行以下命令卸载分区:
umount 挂载点
下载一键扩容工具
执行以下命令下载工具:
wget -O /tmp/devresize.py http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/install/virts/devresize.py
执行扩容工具
执行以下命令进行扩容:
python /tmp/devresize.py 硬盘路径
请注意,这里硬盘路径是需要扩容的云硬盘,而不是分区名。若您的文件系统在vdb1上,则应执行
python /tmp/devresize.py /dev/vdb
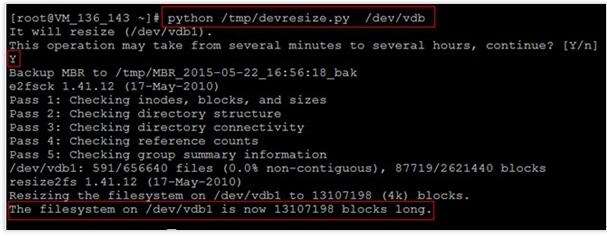
若输出“The filesystem on /dev/vdb1 is now XXXXX blocks long.“则表示扩容成功。
重新挂载扩容后的分区
执行以下命令挂载扩容后的分区:
mount 分区路径 挂载点
并通过以下命令查看扩容后的分区容量:
df -h
这里通过mount /dev/vdb1 /data命令手动挂载扩容后的分区(如果原先是没有分区的,执行mount /dev/vdb /data),
用df -h命令查看,出现以下信息说明挂载成功,即可以查看到数据盘了:
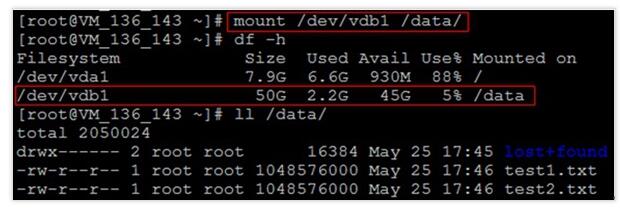
再执行ll /data命令,可以查看到,扩容后原分区的数据没有丢失,新增加的存储空间已经扩容到文件系统中。
devresize.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
# FileName: devresize.py
"""
It only handle the following two situations:
1. There is only one primary partiion in the disk with a format of ext2/3/4;
2. The disk is raw with a file system whose format is ext2/3/4.
""" import struct
import array
import fcntl
import time
import sys
import os
import glob
import logging BLKSSZGET = 0x1268
BLKGETSIZE = 0x1260
BLKRRPART = 0x125f
BLKGETSIZE64 = 0x80041272 logger = None def read_ub(data):
return struct.unpack('B', data[0])[0] def read_us(data):
return struct.unpack('<H', data[0:2])[0] def read_ui(data):
return struct.unpack('<I', data[0:4])[0] def read_ul(data):
return struct.unpack('<Q', data[0:8])[0] def init_log():
global logger
log_file = 'devresize.log'
fmt_file = '%(asctime)s - [%(levelname)-5.5s]- %(filename)s:%(lineno)s - %(message)s'
fmt_stream = '[%(levelname)s] - %(message)s'
logger = logging.getLogger('devresize')
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) file_handler = logging.FileHandler(log_file)
file_handler.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
file_handler.setFormatter(logging.Formatter(fmt_file))
logger.addHandler(file_handler) stream_handler = logging.StreamHandler()
stream_handler.setLevel(logging.INFO)
stream_handler.setFormatter(logging.Formatter(fmt_stream))
logger.addHandler(stream_handler) class PartitionEntry(object):
PartitionTypes = {
0x05: "Microsoft Extended",
0x83: "Linux",
0x85: "Linux Extended"
} def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.boot_sig = data[0] self.start_head, self.start_sector, self.start_cylinder = (
PartitionEntry.get_hsc(data[1:1 + 3])) self.partition_type = read_ub(data[4]) self.end_head, self.end_sector, self.end_cylinder = (
PartitionEntry.get_hsc(data[5:5 + 3])) self.start_lba = read_ui(data[8:8 + 4])
self.sector_num = read_ui(data[12:12 + 4]) self.partition_type_name = PartitionEntry.PartitionTypes.get(self.partition_type, "other") @staticmethod
def get_hsc(data):
h, s, c = struct.unpack('BBB', data[0:3])
c = (c | ((s & 0xC0) << 2))
s = (s & 0x3F)
return h, s, c @staticmethod
def cal_hsc(sector, hh, ss):
s = sector % ss + 1
sector /= ss
h = sector % hh
sector /= hh
c = sector & 0xFF
s |= (sector >> 2) & 0xC0
return h, s, c def vaild_type(self):
return self.partition_type in self.PartitionTypes def isprimary(self):
return self.partition_type == 0x83 def __str__(self):
if not self.vaild_type():
print "%x" % self.partition_type
return "This isn't a Linux Partition!"
return """
Start h,s,c: %u %u %u
End h,s,c: %u %u %u
Partition Type Name:%s
Start LBA: %u
Sector Number: %u
""" % (self.start_head, self.start_sector, self.start_cylinder,
self.end_head, self.end_sector, self.end_cylinder,
self.partition_type_name, self.start_lba, self.sector_num) class MBR(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.boot_code = data[:446]
self.mbr_sig = data[510:512] if self.check_mbr_sig():
self.partitions = ([PartitionEntry(data[446 + 16 * i:446 + 16 * (i + 1)])
for i in range(0, 4)])
else:
self.partitions = None if self.partitions is not None:
self.vaild_part_num = len(filter(lambda x: x.vaild_type(), self.partitions))
else:
self.vaild_part_num = 0 self.device_heads = 0
self.device_sectors = 0 self.cal_device_hs() def cal_device_hs(self):
if self.partitions is not None and self.vaild_part_num == 1:
self.device_heads = self.partitions[0].end_head + 1
self.device_sectors = self.partitions[0].end_sector & 0x3F def check_mbr_sig(self):
mbr_sig = read_us(self.mbr_sig)
if mbr_sig == 0xAA55:
return True
else:
return False def get_device_size(fd):
buf = array.array('c', [chr(0)] * 8)
fcntl.ioctl(fd, BLKSSZGET, buf, True)
logical_sector_size = read_ul(buf) buf = array.array('c', [chr(0)] * 8)
try:
fcntl.ioctl(fd, BLKGETSIZE, buf, True)
device_size = read_ul(buf) * 512
except IOError:
fcntl.ioctl(fd, BLKGETSIZE64, buf, True)
device_size = read_ul(buf)
device_sector_number = device_size / logical_sector_size
logger.debug(
'''device_size:%d
device_sector_number:%d
logical_sector_size:%d''' % (device_size, device_sector_number, logical_sector_size))
return device_size, device_sector_number, logical_sector_size def backup_mbr(data):
bak_name = '/tmp/MBR_%s_bak' % time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%X", time.localtime())
bak_file = open(bak_name, 'w')
bak_file.write(data)
bak_file.close()
logger.info("Backup MBR to %s" % bak_name)
return bak_name def is_first_start():
bak_file_list = glob.glob('/tmp/MBR_%s*bak' % time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", time.localtime()))
return len(bak_file_list) == 0 def cal_new_part(part_data, mbr, start_lab, new_end):
device_heads, device_sectors = mbr.device_heads, mbr.device_sectors new_partition_sector_num = new_end - start_lab + 1
begin_h, begin_s, begin_c = PartitionEntry.cal_hsc(start_lab, device_heads, device_sectors)
end_h, end_s, end_c = PartitionEntry.cal_hsc(new_end, device_heads, device_sectors) new_part_data = list(part_data[:])
new_part_data[1:1 + 3] = list(struct.pack('BBB', begin_h, begin_s, begin_c))
new_part_data[5:5 + 3] = list(struct.pack('BBB', end_h, end_s, end_c))
new_part_data[0xc:] = list(
struct.pack('BBBB', (new_partition_sector_num & 0xff), ((new_partition_sector_num >> 8) & 0xff),
((new_partition_sector_num >> 16) & 0xff), ((new_partition_sector_num >> 24) & 0xff))) logger.debug("""
Start h,s,c: %u %u %u
End h,s,c: %u %u %u
Partition Type Name:%s
Start LBA: %u
Sector Number: %u
""" % (begin_h, begin_s, begin_c,
end_h, end_s, end_c,
mbr.partitions[0].partition_type_name,
mbr.partitions[0].start_lba,
new_partition_sector_num))
return new_part_data # filesystem type must be ext2/3/4
def check_format(dev):
blkid_ret = os.popen('blkid %s' % dev)
s = blkid_ret.read()
if blkid_ret.close() is not None:
return False
return True in [i in s for i in ['ext2', 'ext3', 'ext4']] def part_probe(fd):
logger.debug('part_probe')
fd.flush()
fcntl.ioctl(fd, BLKRRPART) def resize2fs(dev):
ret = os.system('e2fsck -f %s' % dev)
logger.debug('e2fsck ret is %d' % ret)
if ret not in (0, 1):
raise RuntimeError('e2fsck failed!!')
if ret == 1:
logger.info('File system errors corrected') ret = os.system('resize2fs %s' % dev)
logger.debug('resize2fs ret is %d' % ret)
if ret != 0:
raise RuntimeError('resize2fs failed!!') def check_mount(target_dev): # target_dev is mounted!
return os.system('mount | grep "%s " > /dev/null' % target_dev) == 0 def write_mbr(fd, mbr_data):
fd.seek(0)
fd.write(mbr_data)
part_probe(fd)
fd.close()
time.sleep(1) def check_arg(device):
return not device[-1].isdigit() def get_disk_path(partation_name):
for i, ch in enumerate(os.path.basename(partation_name)[::-1]):
if not ch.isdigit():
return partation_name[::-1][i::][::-1]
logger.error("invalid para %s" % partation_name)
raise Exception("invalid para %s" % partation_name) def main():
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print "Usage: %s block_device" % sys.argv[0]
sys.exit(1) init_log()
logger.debug("user input:%s" % ' '.join(sys.argv))
device = sys.argv[1] if not check_arg(device):
logger.error("The argument should be a whole disk not a partation!like %s" % get_disk_path(device))
sys.exit(1) if not os.access(device, os.W_OK):
logger.error("Permission denied")
sys.exit(1) fd = open(device, 'r+') data = fd.read(512)
mbr = MBR(data) device_size, device_sector_number, logical_sector_size = get_device_size(fd) if mbr.vaild_part_num > 1:
logger.error("Disk %s have multi partition." % device)
sys.exit(1) target_partition = ''
resize_part_flag = True if mbr.vaild_part_num == 1: # only one partition, which is the primary partition
if not mbr.partitions[0].isprimary(): # and the filesystem type is ext2/3/4.
logger.error("Must be primary partition.")
resize_part_flag = True
if device[-1].isdigit():
target_partition = device + 'p1' # ex: /dev/nbd0 -> /dev/nbd0p1
else:
target_partition = device + '' # ex: /dev/vdb -> /dev/vdb1
logger.debug(mbr.partitions[0]) if mbr.vaild_part_num == 0: # no partition but whole disk is ext2/3/4
resize_part_flag = False
target_partition = device logger.debug('target_partition:%s' % target_partition) if not check_format(target_partition):
logger.error("Only can process ext2/3/4.")
sys.exit(1) if check_mount(target_partition):
logger.error("Target device %s must be unmounted." % target_partition)
sys.exit(1) logger.info("It will resize (%s).\n"
"This operation may take from several minutes to several hours, continue? [Y/n]"
% target_partition)
user_input = raw_input() if user_input.lower() != 'y' and user_input != '':
logger.warn("User input neither 'y' nor '[Enter]',exit.")
sys.exit(1) if not is_first_start():
logger.warn('We find some MBR backup file in /tmp,maybe the MBR is already changed,'
'do you want to just resize the filesystem? [Y/n]')
user_input = raw_input()
if user_input.lower() == 'y' or user_input == '':
resize_part_flag = False if resize_part_flag:
logger.debug("Begin to change the partation")
if (mbr.partitions[0].start_lba + mbr.partitions[0].sector_num) == device_sector_number:
logger.error("No free sectors available.")
sys.exit(1)
if mbr.partitions[0].sector_num > 0xFFFFFFFF * 512 / logical_sector_size:
logger.error("Can't process the partition which have exceeded 2TB.")
sys.exit(1)
new_start_sector = mbr.partitions[0].start_lba
new_end_sector = device_sector_number - 1
if (new_end_sector - new_start_sector + 1) * logical_sector_size > 0xFFFFFFFF * 512:
user_input = raw_input("The size of this disk is %.2fTB (%d bytes).\n"
"But DOS partition table format can not be used on drives for volumes larger than 2TB (2199023255040 bytes).\n"
"Do you want to resize (%s) to 2TB?[Y/n]"
% (round(device_size / 1024.0 / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 2), device_size,
target_partition))
if user_input.lower() != 'y' and user_input != '':
logger.warn("User input neither 'y' nor '[Enter]',exit.")
sys.exit(1)
new_end_sector = 0xFFFFFFFF * 512 / logical_sector_size + new_start_sector - 1 new_mbr_data = list(data)[:]
new_mbr_data[446:446 + 16] = cal_new_part(data[446:446 + 16], mbr,
new_start_sector, new_end_sector) backup_mbr(data)
try:
if resize_part_flag:
write_mbr(fd, ''.join(new_mbr_data))
resize2fs(target_partition)
except Exception, e:
logger.error(e)
logger.error('Some error occurred!!Maybe you should call the customer service staff.') if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
腾讯云主机做raid
https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/362/2932
都是系统层面的raid
windows主机
windows2012R2:使用系统自带磁盘管理器里的 ,新建镜像卷功能,把两个弹性云硬盘连接到云主机,然后新建镜像卷做raid1
Linux主机
centos6:Linux内核提供了md模块在底层管理RAID设备,我们可以使用mdadm工具来调用md模块。安装mdadm(以CentOS为例)
f
扩容Linux文件系统的更多相关文章
- 为Xen虚拟机扩容根文件系统(LVM)
===== 为Xen虚拟机扩容根文件系统(LVM) ===== 1. 增加1个4G的映像文件 # dd if=/dev/zero of=data.img bs=4k seek=1024k count= ...
- linux文件系统体系结构 和 虚拟文件系统(VFS)
图 1. Linux 文件系统组件的体系结构 用户空间包含一些应用程序(例如,文件系统的使用者)和 GNU C 库(glibc),它们为文件系统调用(打开.读取.写和关闭)提供用户接口.系统调用接口的 ...
- Linux文件系统
今天学习了Linux文件系统,现在来做个小总结. 首先Linux中一切都是文件,下面这个清单是Linux系统的顶层目录结构. 清单 1. Linux 系统的顶层目录结构 / 根目录 ├── bin 存 ...
- linux 文件系统简介
linux文件系统简介 文件系统是linux的一个十分基础的知识,同时也是学习linux的必备知识. 本文将站在一个较高的视图来了解linux的文件系统,主要包括了linux磁盘分区和目录.挂载基 ...
- Linux文件系统层次结构标准
该标准的目的是定义Linux文件系统的标准路径,使得开发者和用户可以在合理的位置找到需要的东西. Linux的文件布局的大体想法是将文件和目录分为如下3组: 对运行Linux的某一特定系统唯一的文件和 ...
- linux文件系统节点详解
linux文件系统有两层结构,逻辑结构和物理结构.也就是inode和block. 每个文件都有一个inode, 记录文件属性:权限,时间还有最重要的block号码. block是实际存放文件内容的地方 ...
- Linux文件系统应用---系统数据备份和迁移(用户角度)
1 前言 首先承诺:对于从Windows系统迁移过来的用户,困扰大家的 “Linux系统下是否可以把系统文件和用户文件分开到C盘和D盘中” 的问题也可以得到完满解决. 之前的文章对Linux的文 ...
- linux 文件系统解析及相关命令
简介 文件系统就是分区或磁盘上的所有文件的逻辑集合. 文件系统不仅包含着文件中的数据而且还有文件系统的结构,所有Linux 用户和程序看到的文件.目录.软连接及文件保护信息等都存储在其中. 不同Lin ...
- 磁盘、分区及Linux文件系统 [Disk, Partition, Linux File System]
1.磁盘基础知识 1.1 物理结构 硬盘的物理结构一般由磁头与碟片.电动机.主控芯片与排线等部件组成:当主电动机带动碟片旋转时,副电动机带动一组(磁头)到相对应的碟片上并确定读取正面还是反面的碟面,磁 ...
随机推荐
- yaf项目将500错误打印到页面上
一般在yaf项目调试的时候,如果代码有错误,页面只会响应500错误,但看不到哪里报了什么错误,通过开启yaf的一个配置可以将错误信息显示在页面上. 打开项目的index.php入口文件,在开头加入如下 ...
- GPG
一.什么是GPG 要了解什么是GPG,就要先了解PGP. 1991年,程序员Phil Zimmermann为了避开政府监视,开发了加密软件PGP.这个软件非常好用,迅速流传开来,成了许多程序员的必备工 ...
- 使用python脚本实现iOS图片资源压缩
最近公司有一个新的需求,要把代码进行瘦身,这篇博客记录下如何对图片进行压缩的. 原理: 写一个脚本,把图片文件夹'.xcassets'的所有文件遍历出来,然后使用一个第三方的算法把图片压缩后再替换回去 ...
- idea创建maven SSM项目
maven配置 ➜ ~ cd /Applications/IntelliJ IDEA.app/Contents/plugins/maven/lib/maven3/conf ➜ conf vim set ...
- Python代码转换为exe可执行程序详解
1:安装pyinstaller pip install pyinstaller 2,制作exe 1,先写一个hello.py print('hello world!') input() 2.执行(在s ...
- Mysql Window 解压版 忘记密码
1. 首先检查mysql服务是否启动,若已启动则先将其停止服务,可在开始菜单的运行,使用命令: net stop mysql 打开第一个cmd1窗口,切换到mysql的bin目录,运行命令: mysq ...
- vscode切换界面布局
调整vscode的控制面板位置 鼠标操作 view>Appearance>Toggle Panel Position 调整控制面板在界面底部 或者界面右侧 2.编辑区分布 鼠标操作 v ...
- [转]Visual Studio 2015源文件编码问题(936)
在Visual Studio中,如果源文件中包含中文,那么当源文件编码为utf8时,会报“C4819 该文件包含不能在当前代码页(936)中表示的字符.请将该文件保存为 Unicode 格式以防止数据 ...
- 没钱买windows怎么办?
ReactOS是一个与 Windows 环境二进制兼容的操作系统. 同时,他是一款开源.免费的操作系统.
- 转载:VOC2007数据集制作
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/gaohuazhao/article/details/60871886 另外,可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/dcxhun3/a ...
