java框架之Spring(3)-JDBC模板使用&事务管理
JDBC模板使用
入门
1、导包,如要导入 Spring 的基本开发包、数据库驱动包、Spring 提供的 JDBC 模板包,如下:
2、测试:
@Test
public void test(){
// 创建连接池对象
DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
driverManagerDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///test");
driverManagerDataSource.setUsername("root");
driverManagerDataSource.setPassword("root");
// 创建 JDBC 模板对象
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(driverManagerDataSource);
// 通过模板对象操作数据库
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user values(null,?,?)", "bob", 123);
}
将模板交给Spring
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean name="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
package com.zze.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void test() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update user set password=? where username=?", "345", "bob");
}
}
test
使用第三方连接池
DBCP配置
额外导入 jar 包:
配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--DBCP 配置-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
C3P0配置
额外导入 jar 包:
配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--C3P0连接池配置-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
抽取JDBC配置到属性文件
有如下属性文件:
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///test jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
jdbc.properties
方式一:
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
</bean>
方式二:
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
接下来就可以通过如下方式引用到属性文件中的属性,例:
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
CRUD操作
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.bean.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 保存
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user values (null,?,?)", "bob", "123");
}
/**
* 更新
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update user set password=? where username=?", "346", "bob");
}
/**
* 删除
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from user where username=?", "bob");
}
/**
* 查询首行首列
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
Integer integer = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select COUNT(1) from user", Integer.class);
System.out.println(integer);
}
/**
* 查询一条数据封装到单个对象
*/
@Test
public void test5() {
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from user where username=?", new RowMapper<User>() {
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
user.setUsername(rs.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
return user;
}
}, "bob");
System.out.println(user);
}
/**
* 查询多条记录封装到集合
*/
@Test
public void test6() {
List<User> userList = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from user", new RowMapper<User>() {
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
user.setUsername(rs.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
return user;
}
});
System.out.println(userList);
}
}
事务管理
事务回顾
参见【数据库事务了解一下】。
Spring事务管理API
- PlatformTransactionManager:平台事务管理器
接口,是 Spring 用于管理事务真正的对象。
DataSourceTransactionManager:底层使用JDBC管理事务。
HibernateTransactionManager:底层使用Hibernate管理事务。
- TransactionDefinition:事务定义信息
用于定义事务的相关的信息,隔离级别、超时信息、传播行为、是否只读。
- TransactionStatus:事务的状态
用于记录在事务管理过程中,事务的状态的对象。
Spring进行事务管理的时候,首先平台事务管理器根据事务定义信息进行事务的管理,在事务管理过程中,产生各种状态,将这些状态的信息记录到事务状态的对象中。
事务的传播行为
Spring 中提供了七种事务的传播行为,可分为如下三类:
- 保证多个操作在同一个事务中:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED :默认值,如果A中有事务,使用A中的事务,如果A没有,创建一个新的事务,将操作包含进来
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS :支持事务,如果A中有事务,使用A中的事务。如果A没有事务,不使用事务。
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY :如果A中有事务,使用A中的事务。如果A没有事务,抛出异常。
- 保证多个操作不在同一个事务中:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW :如果A中有事务,将A的事务挂起(暂停),创建新事务,只包含自身操作。如果A中没有事务,创建一个新事务,包含自身操作。
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED :如果A中有事务,将A的事务挂起。不使用事务管理。
PROPAGATION_NEVER :如果A中有事务,报异常。
- 嵌套式事务:
PROPAGATION_NESTED :嵌套事务,如果A中有事务,按照A的事务执行,执行完成后,设置一个保存点,执行B中的操作,如果没有异常,执行通过,如果有异常,可以选择回滚到最初始位置,也可以回滚到保存点。
搭建Spring的事务管理的环境
准备
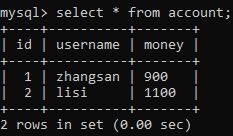
创建 account 表并初始化如下数据:

下面代码模拟一个转账场景:
package com.zze.dao;
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 转出
* @param username 转出账户的用户名
* @param money 转出金额
*/
void outMoney(String username,Double money);
/**
* 转入
* @param username 转入账户的用户名
* @param money 转入金额
*/
void inMoney(String username, Double money);
}
com.zze.dao.AccountDao
package com.zze.dao.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements AccountDao {
@Override
public void outMoney(String username, Double money) {
this.getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set money=money-? where username=?", money, username);
}
@Override
public void inMoney(String username, Double money) {
this.getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set money=money+? where username=?", money, username);
}
}
com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl
package com.zze.service;
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账
* @param usernameFrom 转账来源账户
* @param usernameTo 转账目标账户
* @param money 转账金额
*/
void transfer(String usernameFrom,String usernameTo,Double money);
}
com.zze.service.AccountService
package com.zze.service.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String usernameFrom, String usernameTo, Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(usernameFrom, money);
accountDao.inMoney(usernameTo,money);
}
}
com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///test jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root
jdbc.properties
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--
<bean name="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
-->
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/>-->
</bean>
<bean name="accountService" class="com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void test(){
// zhangsan 给 lisi 转账 100
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",100d);
}
}
执行结果如下:
test
编程式事务管理
1、修改配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置 C3p0 连接池-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务的管理的模板类-->
<bean name="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>
</bean>
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean name="accountService" class="com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
<!--注入事务管理模板-->
<property name="transactionTemplate" ref="transactionTemplate"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
2、修改代码模拟异常并使用事务:
package com.zze.service.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionCallbackWithoutResult;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void setTransactionTemplate(TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate) {
this.transactionTemplate = transactionTemplate;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String usernameFrom, String usernameTo, Double money) {
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
accountDao.outMoney(usernameFrom, money);
// 模拟过程中异常
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.inMoney(usernameTo, money);
}
});
}
}
com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
3、测试:
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void test(){
// zhangsan 给 lisi 转账 100
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",100d);
// 此时表数据将不会发生变化
}
}
test
声明式事务管理-XML
1、修改配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置 C3p0 连接池-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务的通知/增强-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!--事务管理规则-->
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<!--
name : 匹配方法名
read-only : 为 true 时表示只做只读操作
propagation : 事务的传播行为
timeout : 事务过期时间,为 -1 时不会过期
isolation : 事务的隔离级别
-->
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT" timeout="-1"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--AOP 配置-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pc_account" expression="execution(* com.zze.service.AccountService.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pc_account"/>
</aop:config>
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean name="accountService" class="com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
2、修改代码模拟异常:
package com.zze.service.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String usernameFrom, String usernameTo, Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(usernameFrom, money);
// 模拟过程中异常
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.inMoney(usernameTo, money);
}
}
com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
3、测试:
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void test(){
// zhangsan 给 lisi 转账 100
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",100d);
// 此时表数据将不会发生变化
}
}
test
声明式事务管理-注解
1、修改配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置 C3p0 连接池-->
<bean name="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean name="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--开启注解事务-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<bean name="accountDao" class="com.zze.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean name="accountService" class="com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
applicationContext.xml
2、修改代码模拟异常并添加事务注解:
package com.zze.service.impl;
import com.zze.dao.AccountDao;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
// 业务类上添加注解使用事务
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String usernameFrom, String usernameTo, Double money) {
accountDao.outMoney(usernameFrom, money);
// 模拟过程中异常
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.inMoney(usernameTo, money);
}
}
com.zze.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
3、测试:
package com.zze.test;
import com.zze.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Demo {
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void test(){
// zhangsan 给 lisi 转账 100
accountService.transfer("zhangsan","lisi",100d);
// 此时表数据将不会发生变化
}
}
test
java框架之Spring(3)-JDBC模板使用&事务管理的更多相关文章
- 四、spring的JDBC模板和事务管理
Spring的JDBC模板 Spring是JavaEE开发的一站式框架,对各种持久化技术都提供了简单的模板 ORM持久化技术 模板类 JDBC org.springframework.jdbc.cor ...
- Java学习笔记43(Spring的jdbc模板)
在之前的学习中,我们执行sql语句,需要频繁的开流,关流比较麻烦,为了更加的简化代码,我们使用Spring 的jdbc模板jdbcTemplate来简化我们的代码量:需要导入的包有: 我们在之前的dr ...
- Java - 框架之 Spring
一. IOC 和 DI IOC : 控制反转,将对象的创建权反转给了 Spring.DI : 依赖注入,前提是必须要有 IOC 的环境,Spring 管理这个类的时候将类的依赖的属性注入(设置)进来 ...
- Spring的jdbc模板1
Spring是EE开发的一站式框架,有EE开发的每一层解决方案.Spring对持久层也提供了解决方案:ORM模块和jdbc模块,ORM模块在整合其他框架的时候使用 Spring提供了很多的模板用于简化 ...
- 创建JDBC模板简化代码、JDBC应用的事务管理以及连接池的作用
一.创建JDBC模板简化代码 一个简单的查询.要做这么一大堆事情,并且还要处理异常,我们不防来梳理一下: 1.获取connection 2.获取statement 3.获取resultset 4 ...
- 【Spring实战】—— 16 基于JDBC持久化的事务管理
前面讲解了基于JDBC驱动的Spring的持久化管理,本篇开始则着重介绍下与事务相关的操作. 通过本文你可以了解到: 1 Spring 事务管理的机制 2 基于JDBC持久化的事务管理 Spring的 ...
- Spring 简单而强大的事务管理功能
开始之前 关于本教程 本教程将深入讲解 Spring 简单而强大的事务管理功能,包括编程式事务和声明式事务.通过对本教程的学习,您将能够理解 Spring 事务管理的本质,并灵活运用之. 先决条件 本 ...
- 事务隔离级别与传播机制,spring+mybatis+atomikos实现分布式事务管理
1.事务的定义:事务是指多个操作单元组成的合集,多个单元操作是整体不可分割的,要么都操作不成功,要么都成功.其必须遵循四个原则(ACID). 原子性(Atomicity):即事务是不可分割的最小工作单 ...
- Spring事务隔离级别与传播机制详解,spring+mybatis+atomikos实现分布式事务管理
原创说明:本文为本人原创作品,绝非他处转载,转账请注明出处 1.事务的定义:事务是指多个操作单元组成的合集,多个单元操作是整体不可分割的,要么都操作不成功,要么都成功.其必须遵循四个原则(ACID). ...
随机推荐
- 使用PIP扩展BTARN
下载安装部署 从GS1 US RosettaNet下载相应的PIP文件  新建BizTalk解决方案并设置签名 添加->现有项(C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft ...
- Redis 的事务到底是不是原子性的
ACID 中关于原子性的定义: 原子性:一个事务(transaction)中的所有操作,要么全部完成,要么全部不完成,不会结束在中间某个环节.事务在执行过程中发生错误,会被恢复(Rollback)到事 ...
- [HBase Manual]CH5 HBase运行模式:单实例和分布式
HBase运行模式:单实例和分布式 HBase运行模式:单实例和分布式 1.单实例模式 1.1 单实例在HDFS下 2.分布式 2.1 伪分布式 3完全分布式 HBase有2种运行模式,单实例和分布式 ...
- shell 十进制数字转十六进制字符串并将结果保存到变量
. . . . . 今天写测试脚本的时候需要将生成的十六进制值作为参数传递给某个命令,而循环生成的数值都是十进制的.在网上查了好久也没有找到如何将一个变量中的值进行进制转换,并保存到变量中,网上的办法 ...
- 从一次线上故障思考Java问题定位思路
问题出现:现网CPU飙高,Full GC告警 CGI 服务发布到现网后,现网机器出现了Full GC告警,同时CPU飙高99%.在优先恢复现网服务正常后,开始着手定位Full GC的问题.在现场只能够 ...
- Cookie的简单实用
作用域: 一个域名下的所有网页共用一套cookie. 几个封装好的工具方法: // 添加一个cookie function setCookie(name, value, iDay) { var oDa ...
- ubuntu开机后弹出System program problem detected的解决办法
sudo gedit /etc/default/apport 将enabled=1改为enabled=0保存退出重启后就可以了
- Hystrix入门与分析(二):依赖隔离之线程池隔离
1.依赖隔离概述 依赖隔离是Hystrix的核心目的.依赖隔离其实就是资源隔离,把对依赖使用的资源隔离起来,统一控制和调度.那为什么需要把资源隔离起来呢?主要有以下几点: 1.合理分配资源,把给资源分 ...
- 公司中springcloud项目遇到的问题
1.更改maven的.m2下的settings.xml文件,程序就可以运行,是不是很神奇?
- dll注入遇到CreateRemoteThread()返回错误代码5
在进行dll注入的时候,发现触发了CreateRemoteThread()的错误并返回错误代码5,刚开始以为权限不够,用了管理员权限和加了SetPrivilege()函数提权和用NtCreateThr ...
