Android Studio局部管理器
1、LinearLayout(线性布局)
该布局将其中的View子控件按照水平或者垂直方向排列。但是需要注意不管是水平还是竖直,对应的每一行或列都只能放一个控件。
线性布局两种排法:
从左到右:android:orientation="horizontal"
从上到下:android:orientation="vertical"
效果如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="250dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="96dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#b2dfdb" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="96dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#80cbc4" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="96dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#4db6ac" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="96dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#26a69a" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:background="#b2dfdb" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:background="#80cbc4" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:background="#4db6ac" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:background="#26a69a" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
一个竖向的大LinearLayout嵌套着两个小LinearLayout,第一个小LinearLayout为横向,第二个小LinearLayout为竖向。
2、RelativeLayout布局
参考其他控件进行布局,默认为父控件。
有三种类型的属性:
属性值是true或false
android:layout_centerHrizontal 水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical 垂直居中
android:layout_centerInparent 相对于父元素完全居中。
android:layout_alignParentBottom 位于父元素的下边缘
android:layout_alignParentTop 位于父元素的上边缘
android:layout_alignParentLeft 位于父元素的左边缘
android:layout_alignParentRight 位于父元素的右边缘
属性值是“@id/*”
android:layout_below 在某元素的下方
android:layout_above 在某元素的上方
andorid:layout_toRightOf 在某元素的右方
android:layout_toLeftOf 在某元素的左方
android:layout_alignBottom 和某元素下方对齐
android:layout_alignTop 和某元素上方对齐
android:layout_alignRight 和某元素右方对齐
android:layout_alignLeft 和某元素左方对齐
属性值是数值
android:layout_marginLeft 离某元素左边缘的距离
android:layout_marginRight 离某元素右边缘的距离
android:layout_marginTop 离某元素上边缘的距离
android:layout_marginBottom 离某元素下边缘的距离
注意:
如果没有定义左右,那么默认在左边,如果没有定义上下,默认在上边。
相同位置,新定义的元素会覆盖旧的元素。
只定义在父元素的下部,左右没有定义,默认在左边。
android:layout_below,在某元素的下部并不意味着就一定是紧随某元素,只是在下部的默认位置。
3、MyLayout布局(自定义ViewGroup)
自定义布局主要是重写两个方法:
onMeasure()写自定义容器的大小。
onLayout()写子元素的布局。
3.1、onMeasure()
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
/**
* 获得此ViewGroup上级容器为其推荐的宽和高,以及计算模式
*/
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); // 计算出所有的childView的宽和高
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
/**
* width和height是当wrap_content时使用的属性。
*/
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
int cCount = getChildCount();
int cWidth = 0;
int cHeight = 0;
/**
* 在这里计算当wrap_content时,布局的大小。
*/
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
cWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
cHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
width += cWidth;
height += cHeight;
}
/**
* 如果是wrap_content设置为我们计算的值
* 否则:直接设置为父容器计算的值
*/
setMeasuredDimension((widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeWidth
: width, (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeHeight
: height); }
布局计算模式,即最后的EXACTLY。共有三种计算模式:
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:精确尺寸,相当于具体数值和match_parent.
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:最大尺寸,相当于warp_content.
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:未指定尺寸,这种情况不多,一般用于AdapterView.
3.2、onLayout()
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int cCount = getChildCount(); /**
* 遍历所有childView根据其宽和高,以及margin进行布局
*/
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
r = l + childView.getMeasuredWidth();
b = t + childView.getMeasuredHeight();
childView.layout(l, t, r, b);
l += childView.getMeasuredWidth();
t += childView.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
这个方法的作用是设置摆放子元素的位置。其中onLayout()传入的l、t、分别是对应子元素左上角的left,top坐标。r、b分别是对应子元素右下角的right,bottom坐标。
可以使用childview.getMeasureWidth()和childView.getMeasureHeight()得到子元素的宽和高。
xml代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.example.layoutdemo.MyLayout.MyLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
> <TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#b2dfdb" /> <TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#80cbc4" /> <TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#4db6ac" /> <TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#26a69a" /> </com.example.layoutdemo.MyLayout.MyLayout>
4、FrameLayout布局
帧布局,这个布局的特点是从左上角开始,后面的会覆盖前面的控件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="100dp"
android:textColor="#9c27b0"
android:text="第一层"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="80dp"
android:textColor="#e91e63"
android:text="第二层"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="60dp"
android:textColor="#e51c23"
android:text="第三层"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="40dp"
android:textColor="#5677fc"
android:text="第四层"/>
</FrameLayout>
效果图如下:

5、TableLayout布局
表格布局,应遵循以下布局结构。
<TableLayout>
<TableRow>
<!-在这里填充第一行的元素->
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<!-在这里填充第二行的元素->
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
几个重要属性:
写在TableLayout中的属性
android:stretchColumns 设置第几列为伸展(0表示第一列)
android:shrinkColumns 设置第几列为收缩
android:collapseColumns 设置第几列为隐藏
写在TableRow里的控件里的属性
android:layout_column 设置控件在第几列
android:layout_span 设置控件能跨多少列
代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:collapseColumns="2"
android:shrinkColumns="1"
android:stretchColumns="0"> <TableRow
>
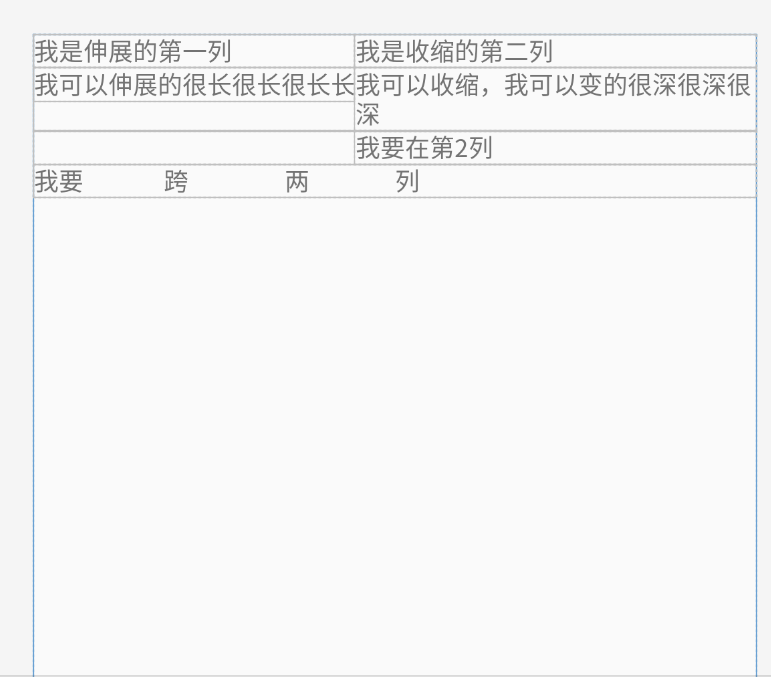
<TextView android:text="我是伸展的第一列" /> <TextView android:text="我是收缩的第二列" /> <TextView android:text="我被隐藏了" />
</TableRow> <TableRow>
<TextView android:text="我可以伸展的很长很长很长长" /> <TextView android:text="我可以收缩,我可以变的很深很深很深" /> <TextView android:text="我被隐藏了T_T" />
</TableRow> <TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_column="1"
android:text="我要在第2列" />
</TableRow> <TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_span="2"
android:text="我要 跨 两 列" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
效果图如下:
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/u013254061/article/details/52512146
Android Studio局部管理器的更多相关文章
- Android TelephonyManager电话管理器
今天介绍一下Android的电话管理器--TelephonyManager,TelephonyManager管理手机通话状态.电话网络信息的服务类,获取TelephonyManager: Teleph ...
- android的布局管理器
理论上通过setContentView(view)能够把一个view设置到activity中,但当你有很多个view控件的时候,就需要用android的布局管理器来管理view控件了. android ...
- Android之声音管理器《AudioManager》的使用以及音量控制
以下为网上下载然后拼接-- Android声音管理AudioManager使用 手机都有声音模式,声音.静音还有震动,甚至震动加声音兼备,这些都是手机的基本功能.在Android手机中,我们同样可以通 ...
- 一步一步学android之布局管理器——LinearLayout
线性布局是最基本的一种布局,在基本控件篇幅中用到的都是LinearLayout,线性布局有两种方式,前面也有用到,一种是垂直的(vertical),一种是水平的(horizontal).我们同样来看下 ...
- Visual Studio 代码管理器svn插件下载
环境:Visual Studio 2010 Visual Studio的svn插件叫做VisualSVN,可自行到VisualSVN官网上下载相应版本,也可以通过vs中找到相关插件. ps:vs其他的 ...
- Android课程---布局管理器中的线性布局
线性布局实例: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout xmlns:andro ...
- 一步一步学android之布局管理器——RelativeLayout
今天开始学习RelativeLayout(相对布局),相对布局在平时布局的时候用的较多,因为Android适配方面的原因.相对布局可以控制组件摆放的位置(放在任一组件的上下左右等位置),下面来看看类的 ...
- android studio 统一管理版本号配置
1.在android 的根目录新建一个versions.gradle 2.在这里面声明 各个第三方库的版本,写法有两种,第一种,写ext 扩展, 引用的时候, 第二种: 然后在project级的bui ...
- Android课程---布局管理器
随机推荐
- DVWA学习记录 PartⅨ
XSS(DOM) 1. 题目 XSS,全称Cross Site Scripting,即跨站脚本攻击,某种意义上也是一种注入攻击,是指攻击者在页面中注入恶意的脚本代码,当受害者访问该页面时,恶意代码会在 ...
- java 数据结构(十一):Map接口
双列集合框架:Map1.常用实现类结构 |----Map:双列数据,存储key-value对的数据 ---类似于高中的函数:y = f(x) * |----HashMap:作为Map的主要实现类:线程 ...
- javascript基础(二): 操作BOM对象(重点)
浏览器介绍 javascript和浏览器关系?BOM:浏览器对象模型 IE6~11 Chrome Safari FireFox Opera 三方 QQ浏览器 360浏览器 window window代 ...
- AcWing 93. 递归实现组合型枚举
AcWing 93. 递归实现组合型枚举 原题链接 从 1~n 这 n 个整数中随机选出 m 个,输出所有可能的选择方案. 输入格式 两个整数 n,m ,在同一行用空格隔开. 输出格式 按照从小到大的 ...
- LeetCode第4题:寻找两个有序数组的中位数
double Solution::findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) ...
- TortoiseGit 解决冲突的两种方法
一.冲突发生原因: 用户A 有新提交 用户B 没有pull, 写新代码 ,pull , 提示有冲突 Solution: 1: stash save(把自己的代码隐藏存起来) -> 重新pul ...
- Cyber Security - Palo Alto Security Policies(2)
Task 3 The SOC(Security Operation Center) monitoring team dashboard reported more 1,000 requests to ...
- 题解 SP687 【REPEATS - Repeats】
考虑可以枚举字符串上的两个点,求出两个点所对应后缀的\(LCP\)和所对应前缀的\(LCS\),两点之间的距离为\(len\),则这两个点对答案的贡献为: \[ \frac{LCS+LCP+L-1}{ ...
- vue学习(十八)使用自定义指令 为字体渲染颜色
<div id="app"> //v-color 是自定义的 <input type="text" class="form-cont ...
- Object#wait()与Object#wait(long)的区别
例子 例1 最基础的等待-通知 下面一个例子,一个线程"waiting"在同步代码块调用了Object#wait()方法,另一个线程"timedWaiting" ...
