手把手教你写VueRouter
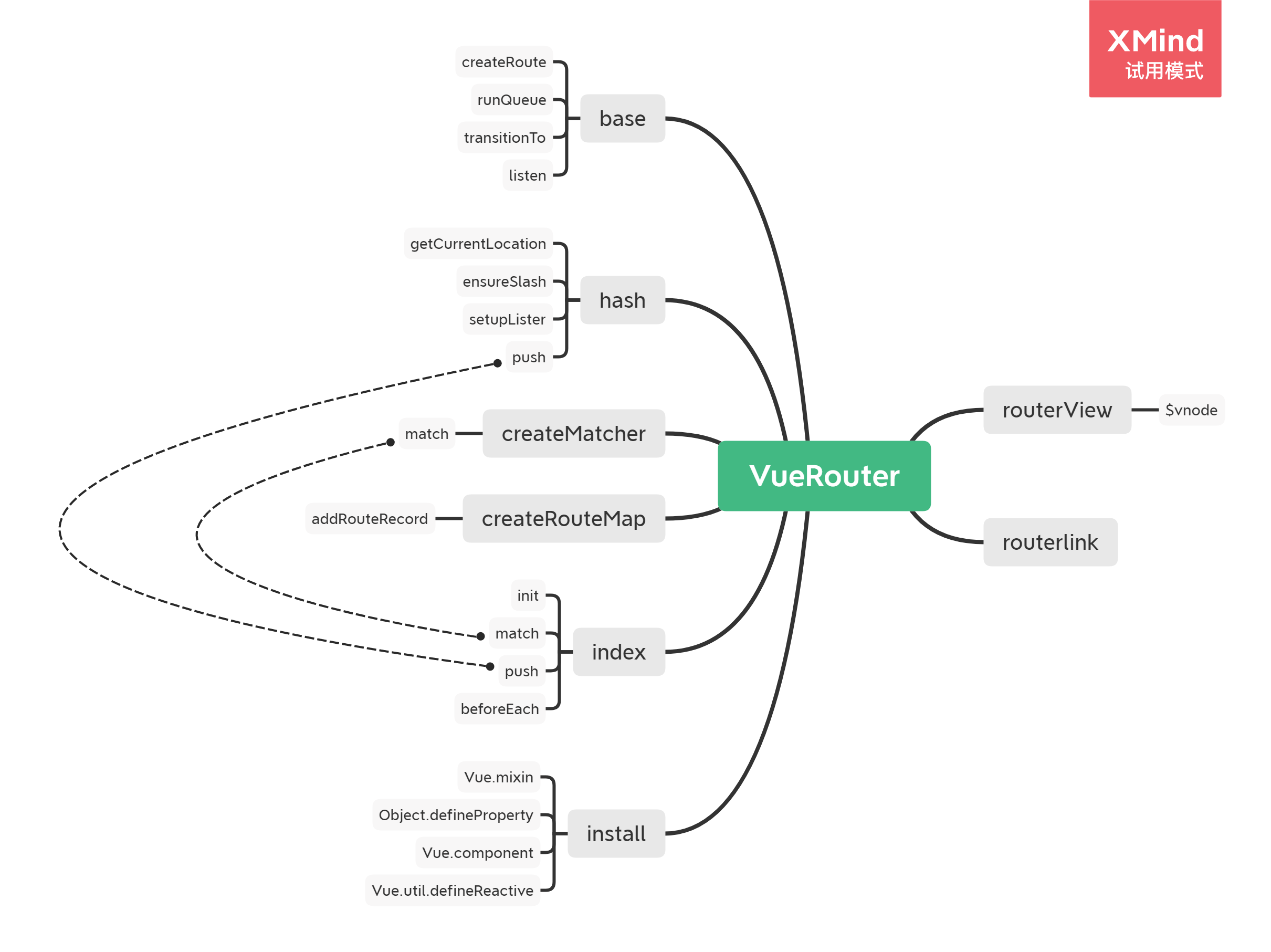
Vue-Router提供了俩个组件 `router-link` `router-view`, 提供了俩个原型上的属性`$route` `$router` ,我现在跟着源码来把它实现一下
开始
先看平时使用的 `Vue-Router` ,引入`Router` , `Vue.use` 注册插件。直接从这里开始入手
使用场景
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from "../vue-router"
import routes from './routes'
Vue.use(Router)
let router = new Router({
routes
})
index
先看`vue-router.js`文件,先生成一个`VueRouter`类,然后导入`install`方法,因为`Vue-Router`的`install`方法比`Vuex`复杂一些,所以将`install`单独作为一个文件。
import install from './install';
class VueRouter {
constructor(options) {
}
}
VueRouter.install = install;
export default VueRouter
Vue.use()
来先看 `Vue.use()`的源码中的一部分,这里面判断注册的插件里的`install`是不是一个函数,有就执行插件里的`install`函数。或者判断插件本身是不是一个函数,有就执行插件本身。这里本质上是没有区别,有没有`install`都可以。而`VueRouter`使用了`install`,目的是为了将`install`作为入口函数,方便封装,同时也将`install`和其他代码分开。
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') {
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args)
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') {
plugin.apply(null, args)
}
install
上述已经将`vue-router`的类构建好,现在`VueRouter`实例已经有了,然后执行`vue.use()`,然后会执行`VueRouter`类里的`install`函数,那来看`install.js`。
install里使用了`Vue.mixin`,混入代码,下面代码是在当前组件生命周期`beforeCreate`里混入代码,代码逻辑是判断当前组件是否为根组件,如果是则将`_routerRoot`作为键放入当前组件中,值为`Vue`实例。再将`_router`作为键放入当前组件中,值为`VueRouter`实例。然后执行初始化操作。
如果不为当前组件不是根组件,则该组件为根组件的子组件。将`_routerRoot`作为键放入当前组件中,值为父组件的`_routerRoot`,从父亲身上获取.
`$route`和`$router`是利用`Object.definePropert`代理`_routerRoot`里的`_router`和`_route`,访问到的。
接着注册全局组件`router-view`和`router-link`
import RouterView from '../components/router-view'
import RouterLink from '../components/router-link' const install = (_Vue, s) => {
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.router) { // 判断是不是根组件
this._routerRoot = this; // 把vue实例放在当前组件的——routerRoot属性上
this._router = this.$options.router // 这里直接获取根实例
this._router.init(this); // 初始化
_Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current) // 将属性_route成为响应式属性
} else {
this._routerRoot = this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot // 这里的是从父亲最顶层获取Router实例
}
}
})
Object.defineProperty(_Vue.prototype, '$route', { // 代理$route
get() {
return this._routerRoot._route
}
})
Object.defineProperty(_Vue.prototype, '$router', { // 代理$router
get() {
return this._routerRoot._router
}
})
_Vue.component('router-view', RouterView) // 注册组件router-view
_Vue.component('router-link', RouterLink) // 注册组件router-view
}
export default install
init
vue-router 默认 hash 模式 —— 使用 URL 的 hash 来模拟一个完整的 URL,于是当 URL 改变时,页面不会重新加载。
然后回到`VueRouter`类中,此时多了个`init`函数。目前做的路由方式是`hash`方式,还有另外俩种方式,`history`,`abstract`。因为有三种方式,所以`Vue-Router`做了一个父类`base`执行同样的逻辑,子类三种方式继承父类`base`,再独自执行自己方式的代码。
通过`new HashHistory` 获取 `history`实例,初始化`init`执行`history`实例对应函数。将目光放到`history`实例上,这些函数来自于`base.js`和`hash.js`。
import install from './install';
class VueRouter {
constructor(options) {
this.history = new HashHistory(this);
}
init(app) {
const history = this.history;
const setupHashLister = () => {
history.setupLister(); // hash的跳转
}
history.transitionTo(
history.getCurrentLocation(),
setupHashLister
)
history.listen((route) => {
app._route = route
})
}
}
VueRouter.install = install;
export default VueRouter
base.js
先看构造函数`construcror`,将`router`作为键放在自身实例上,值为`VueRouter`实例,`curent`为当前导航正要离开的路由,也就是路由守卫的参数里的`from`<br/>
1.`transitionTo()`为跳转后立即执行的函数,传入当前路径和回调函数,`r`为`$route`,是扁平化后的配置,也就是即将要进入的目标 路由对象<br/>
2.`cb`是`History`的`listen()`函数,将`$route`放入当前组件上供用户使用。<br/>
3.`callback`是执行`HashHistory`的`setupHashLister()`函数,是给当前`window`添加监听事件`onhashChange`,`onhashChange`后续通过`hash`变化执行`transitionTo`进行更新。<br/>
4.最后将`r`赋值给`current`,更新路由信息。
class History {
constructor(router) {
this.router = router;
this.current = createRoute(null, {
path: '/'
})
}
transitionTo(location, callback) {
let r = this.router.match(location)
if (location == this.current.path && r.matched.length == this.current.matched.length) { // 防止重复跳转
return
}
this.cb && this.cb(r);
callback && callback();
this.current = r;
}
listen(cb) {
this.cb = cb;
}
}
hash.js
`hash`方式的函数就简单介绍一下,看构造函数`constructor`,跟父类一样赋值`router`。执行`ensureSlash`函数,因为`hash`相比其他函数,一进入页面就会多个#。所以就初始化的时候处理一下。`getCurrentLocation`函数是获取当前路径的,`push`是`hash`方式的跳转,`setupLister`函数是刚刚所述的监听函数`hashchange`。
import Histroy from './base';
function ensureSlash() {
if (window.location.hash) {
return
}
window.location.hash = '/';
}
class HashHistory extends Histroy {
constructor(router) {
super();
this.router = router;
ensureSlash();
}
getCurrentLocation() {
return window.location.hash.slice(1);
}
push(location){
this.transitionTo(location,()=>{
window.location.hash = location
})
}
setupLister() {
window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => {
this.transitionTo(window.location.hash.slice(1));
})
}
}
export default HashHistory
扁平化
刚刚`base.js`里执行的`this.router.match(location)`以及`createRoute()`,都是需要建立在扁平化配置基础之上的。
平时配置的路由是这样的,需要将配置进行扁平化,才能用得上。
[
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
component: About,
children: [
{
path: 'add',
name: 'add',
component: Add
},
{
path: 'bull',
name: 'bull',
component: Bull
}
]
}
]
扁平化后是这样的
/: {path: "/", component: {…}, parnent: undefined}
/about: {path: "about", component: {…}, parnent: {…}}
/about/add: {path: "add", component: {…}, parnent: {…}}
/about/bull: {path: "bull", component: {…}, parnent: {…}}
接着看扁平化函数createMatcher以及createRouteMap
createMatcher
`createMatcher`返回一个`match`函数,`match`方法是匹配路径,根据路径拿扁平化对象里的配置,然后执行`createRoute`方法,将其转化为`route`,返回。`pathMap`由`createRouteMap`生成
import createRouteMap from './create-route-map'
import { createRoute } from './history/base'; export default function createMatcher(routes) {
let { pathList, pathMap } = createRouteMap(routes); function match(location) {
console.log(pathMap)
let record = pathMap[location]; return createRoute(record,{
path: location
})
} return {
match
}
}
createRouteMap
将`routes`配置传入`createRouteMap`中,遍历`routes`,进行扁平化操作
`pathMap`以路径为键名,值为一个对象包裹着路径,组件,父组件。
将路径匹配上父组件的路径和自身的路径
如果有子组件就进行递归,全部转为扁平化返回。
export default function createRouteMap(routes, oldPathList, oldpathMap) {
let pathList = oldPathList || [];
let pathMap = oldpathMap || Object.create(null);
routes.forEach(route => {
addRouteRecord(route, pathList, pathMap);
})
return {
pathList,
pathMap
}
}
function addRouteRecord(route, pathList, pathMap,parnent) {
let path = parnent ? `${parnent.path}/${route.path}`: route.path;
let record = {
path: route.path,
component: route.component,
parnent
}
if (!pathMap[path]) {
pathList.push(path);
pathMap[path] = record;
}
if(route.children){
route.children.forEach(route=>{
addRouteRecord(route, pathList, pathMap,record)
})
}
}
createRoute
`createRoute`是生成`$route`的函数,传入参数为扁平化配置,路径。将`res`作为空数组,如果传进来的扁平化配置有值,则进行`while`循环,将自己从数组头部插入,取出父组件再从头部插入,如此反复,得到一个含着层次关系的数组。将`loaction`和数组包裹为对象返回。
export function createRoute(record, location) {
let res = [];
if (record) {
while (record) {
res.unshift(record)
record = record.parnent
}
}
return {
...location,
matched: res
}
}
router-view
然后在来看看`routerview`
是一个函数式组件,
返回`render`方法
进行`while`循环,遍历出嵌套的`routerview`
用`depth`作为深度,也是`matched`的`index`.
每遍历一次,就在`$vnode.data.rouView` 改为`true`,将深度加1
返回对应的组件即可
export default {
name:'routerView',
functional: true,
render(h,{parent,data}) {
let route = parent.$route
let depth = 0;
while (parent) {
if (parent.$vnode && parent.$vnode.data.routeView) {
depth++;
}
parent = parent.$parent;
}
data.routeView = true;
let record = route.matched[depth];
if (!record) {
return h();
}
return h(record.component, data);
}
}
router-link
再来看看`routerlink`
没什么东西就返回一个`a`标签,用插槽把对应的文本显示出来,在添加的跳转事件
调用`$router`的`push`方法,也就是`Router`类上的`push`
export default {
name: 'routerLink',
props: {
to: {
type: String,
required: true
},
tag: {
type: String,
default: 'a'
}
},
methods: {
handler(to) {
this.$router.push(to) // 路由跳转
}
},
render() {
return <a onClick={this.handler.bind(this,this.to)}>{this.$slots.default[0].text}</a>
}
}
vuerouter草稿:https://juejin.im/post/6862215979745673224
手把手教你写VueRouter的更多相关文章
- 手把手教你写Sublime中的Snippet
手把手教你写Sublime中的Snippet Sublime Text号称最性感的编辑器, 并且越来越多人使用, 美观, 高效 关于如何使用Sublime text可以参考我的另一篇文章, 相信你会喜 ...
- 手把手教你写LKM rookit! 之 第一个lkm程序及模块隐藏(一)
唉,一开始在纠结起个什么名字,感觉名字常常的很装逼,于是起了个这<手把手教你写LKM rookit> 我觉得: 你们觉得:...... 开始之前,我们先来理解一句话:一切的操作都是系统调用 ...
- 手把手教你写电商爬虫-第三课 实战尚妆网AJAX请求处理和内容提取
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 系列教程: 手把手教你写电商爬虫-第一课 找个软柿子捏捏 手把手教你写电商爬虫-第二课 实战尚妆网分页商品采集爬虫 看完两篇,相信大家已经从开始的 ...
- 手把手教你写电商爬虫-第四课 淘宝网商品爬虫自动JS渲染
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 系列教程: 手把手教你写电商爬虫-第一课 找个软柿子捏捏 手把手教你写电商爬虫-第二课 实战尚妆网分页商品采集爬虫 手把手教你写电商爬虫-第三课 ...
- 只有20行Javascript代码!手把手教你写一个页面模板引擎
http://www.toobug.net/article/how_to_design_front_end_template_engine.html http://barretlee.com/webs ...
- [原创]手把手教你写网络爬虫(4):Scrapy入门
手把手教你写网络爬虫(4) 作者:拓海 摘要:从零开始写爬虫,初学者的速成指南! 封面: 上期我们理性的分析了为什么要学习Scrapy,理由只有一个,那就是免费,一分钱都不用花! 咦?怎么有人扔西红柿 ...
- [原创]手把手教你写网络爬虫(5):PhantomJS实战
手把手教你写网络爬虫(5) 作者:拓海 摘要:从零开始写爬虫,初学者的速成指南! 封面: 大家好!从今天开始,我要与大家一起打造一个属于我们自己的分布式爬虫平台,同时也会对涉及到的技术进行详细介绍.大 ...
- [原创]手把手教你写网络爬虫(7):URL去重
手把手教你写网络爬虫(7) 作者:拓海 摘要:从零开始写爬虫,初学者的速成指南! 封面: 本期我们来聊聊URL去重那些事儿.以前我们曾使用Python的字典来保存抓取过的URL,目的是将重复抓取的UR ...
- Android开发之手把手教你写ButterKnife框架(三)
欢迎转载,转载请标明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/johnny901114/article/details/52672188 本文出自:[余志强的博客] 一.概述 上一篇博客讲了, ...
随机推荐
- C语言学习笔记一---C语言概述
一.编程语言与解释语言 1.程序的执行 a.解释:借助一个能试图理解程序的程序,使计算机按要求执行你自己写的程序 b.编译:将所写程序翻译为机器语言写的程序,使计算机按要求执行你自己写的程序 2.两者 ...
- 动态页面技术(JSP)
JSP技术 jsp脚本和注释 jsp脚本: 1)<%java代码%> ----- 内部的java代码翻译到service方法的内部 2)<%=java变量或表达式> ----- ...
- AttributeError: module 'time' has no attribute 'clock'
在python3.8中flask项目运行报错: AttributeError: module 'time' has no attribute 'clock'解决方案 主要原因是因为python3.8中 ...
- python学习笔记1 -- 面向对象编程高级编程1
说起高级其实也就是些基础的东西,但是活用和熟用肯定会大幅度提升代码质量 首先要记录的是面向对象的灵活性,及如何去控制其灵活性,她允许你在实例中新增属性和方法,允许你给类新增属性和方法,也支持在定义类时 ...
- vector 赋初始值的问题
这个,输出为1 这个,啥都输不出来. 据说是因为没有初始化. 其实我搜了一下 vector<vector<int> > A;//正确的定义方式 vector<vector ...
- Nodejs同步和异步编程
同步API:只有当前API执行完成后,才能继续执行下一个API:异步API:当前API的执行不会阻塞后续代码的执行. 同步异步代码执行顺序 同步:从上到下依次执行,前面代码会阻塞后面代码的执行.异步: ...
- 3-Pandas之什么是Panel?
一.什么是Panel Series:包含一维索引的一组数据 DataFrame:包含index和columns两个轴 Panel(面板):一种三维数据容器 一个Panel对象由3个轴构成: items ...
- 笨办法学python 第四版 中文pdf高清版|网盘下载内附提取码
笨办法学 Python是Zed Shaw 编写的一本Python入门书籍.适合对计算机了解不多,没有学过编程,但对编程感兴趣的朋友学习使用.这本书以习题的方式引导读者一步一步学习编 程,从简单的打印一 ...
- Hibernate Validator校验参数全攻略
1. 前言 数据字段一般都要遵循业务要求和数据库设计,所以后端的参数校验是必须的,应用程序必须通过某种手段来确保输入进来的数据从语义上来讲是正确的. 2. 数据校验的痛点 为了保证数据语义的正确,我们 ...
- 用好这几个技巧,解决Maven Jar包冲突易如反掌
前言 大家在项目中肯定有碰到过Maven的Jar包冲突问题,经常出现的场景为: 本地运行报NoSuchMethodError,ClassNotFoundException.明明在依赖里有这个Jar包啊 ...
