Collection集合。
Collection集合。
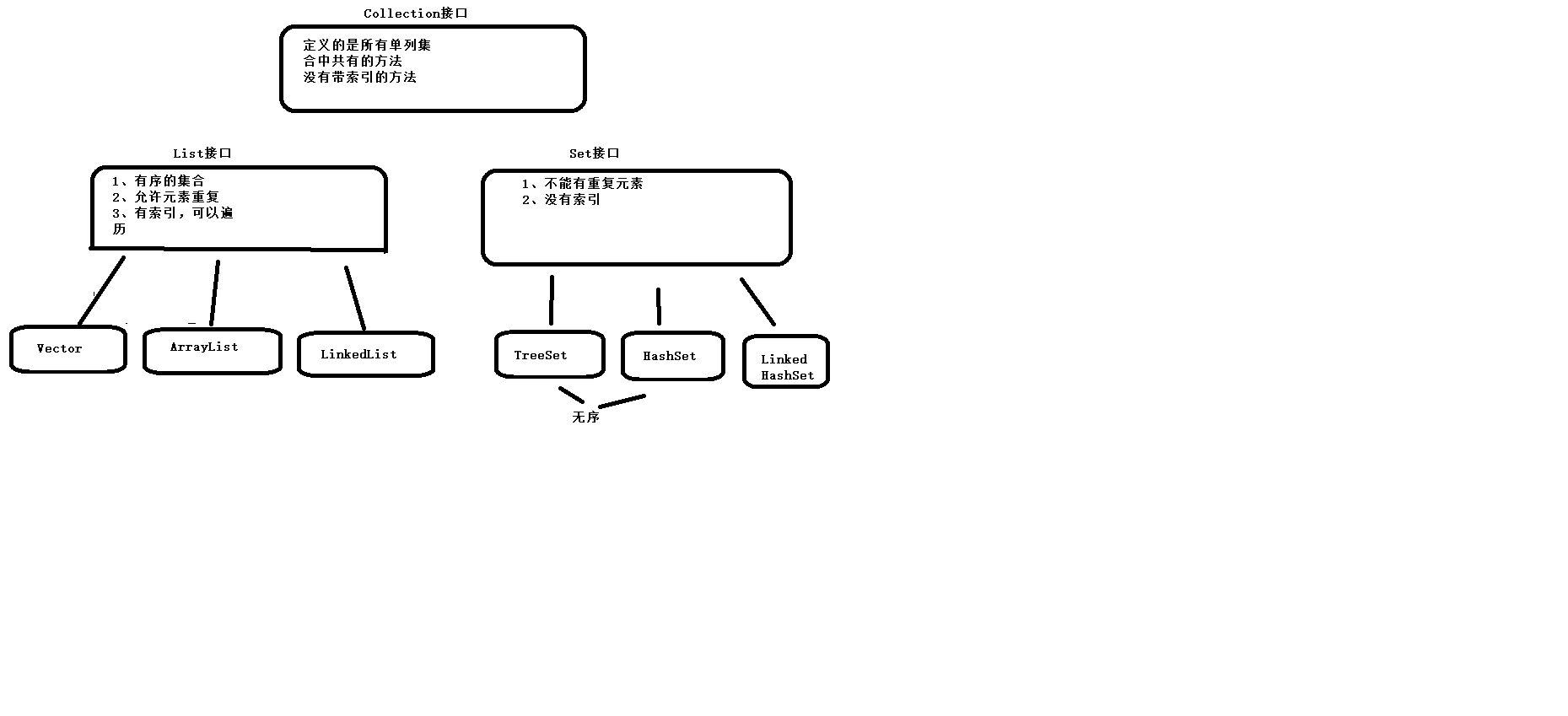
java.util.Collection 接口。 没有索引
是所有单列集合的最顶层的接口,里面定义了所有单列集合共性的方法。
任意的单列集合都可以使用Collecion接口中的方法。
共性的方法:
............................
Iterator接口
java.util.Iterator
迭代器,Collection集合元素的通用取出方式。对集合遍历。 也是有泛型的,跟着集合走
常用方法: boolean hasNext() 还有没有元素可以迭代。
next()取出集合的下一个元素。
获取实现类的方式比较特殊:
在Collection接口中有一个方法叫 Iterator,这个方法的返回就是迭代器的实现类对象。
使用步骤:重点
1、使用集合中的方法,Iterator()获取迭代器的实现类对象,使用Iterator接口接收(多态)
2、使用hasnext方法,判断是否还有下一个
3、使用next,取出下一个元素
代码实现:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> collection=new ArrayList<>();
collection.add("科比");
collection.add("姚明");
collection.add("乔丹");
Iterator<String> iterator =collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
Java的foreach:
内部也是迭代器,简化迭代器的使用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3,4};
for(int i : arr){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
List接口。
List 接口 extends Collection类。
List接口的特点:
1、有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的。
2、有索引,包含了一些索引的方法。
3、允许重复元素。
List接口特有的方法:
注意:操作索引要注意越界问题。
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 创建一个List集合对象,多态。 */
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
//add 添加元素。
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("a"); //可重复
System.out.println(list); //重写了tostring方法。
// public void add(int index, E elemet);
list.add(2,"c");
System.out.println(list);
//public E remove (int index) 移除指定位置元素,
//并返回该元素。
String remove=list.remove(3);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(remove);
//public E set(int index, E element)
//替换指定位置的元素,并返回被替换的值。
String update=list.set(2,"update");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(update);
//List集合遍历有三种方式。
//1、for
//2、迭代器。
//3、foreach
}
LinkedList 集合:
java.util.LinkedList 集合 implements List 接口。
特有特点:
链表结构,查询慢,但增删快。
有大量操作首位元素的方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Public void addFirst(E e) =public void push(E e)
LinkedList<String> linkedList=new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("b");
linkedList.add("c");
linkedList.addFirst("a");
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.push("push an element");
System.out.println(linkedList);
//public void addLast(E e) = add()
linkedList.addLast("d");
System.out.println(linkedList);
//获取元素。
//getFirst getLast
//移除
// removeFirst = pop removeLast
}
Set接口:
特点:
java.util.Set extends Collection
不允许重复
没有索引,不能用普通的for遍历
java.util.HashSet 集合 implement Set 接口
HashSet特点:
1、无序集合,存元素和取元素的顺序有可能不一致。
2、底层是哈希表结构 查询速度快。
哈希表:
哈希值:是一个十进制的整数,由系统随机给出(就是对象的地址值,是一个逻辑
地址,是模拟出来的地址看,不是数据实际存储的物理地址)
Object类有一个方法能获取对象的哈希值。
int hashCode() 返回该对象的哈希值。
源码: public native int hashCode()
native 代表该方法调用的是本地操作系统的方法。
String类的哈希值:
重写了Object类的hashCode方法。
哈希表:
jdk1.8之前,哈希表=数组+链表 jdk1.8之后, 哈希表还=数组+红黑树(查询快)
Set不允许重复元素的原理:
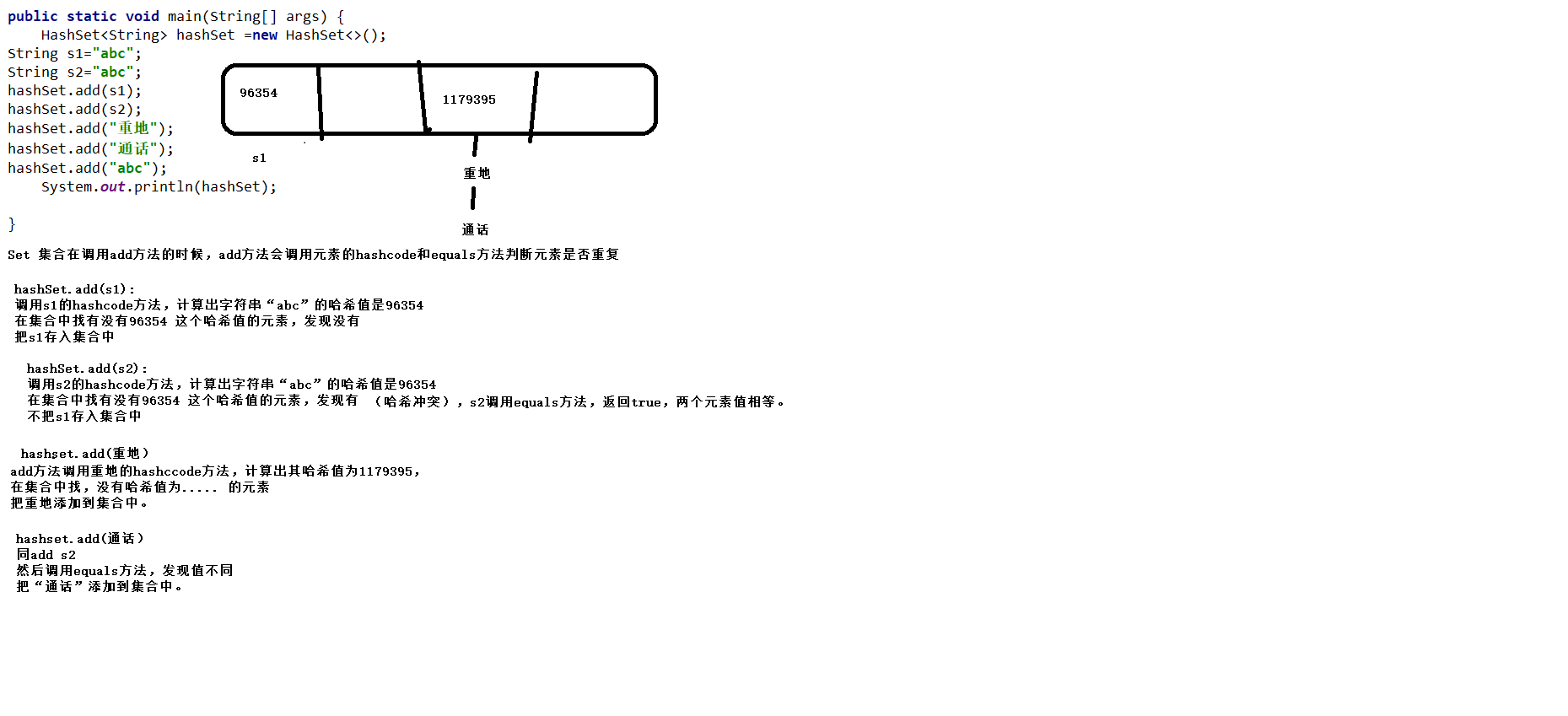
Hash Set存储自定义类型元素:
需要重写对象中的hashcode 和 equals方法,建立自己的比较方式,
才能保证 HashSet中的对象唯一。
//需求:
//同名同龄的人,视为同一个人,只能存储一次。
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Person> set=new HashSet<>();
Person p1=new Person("Sam",18);
Person p2=new Person("Sam",18);
Person p3=new Person("Penny",19);
set.add(p1);
set.add(p2);
set.add(p3);
System.out.println(set);
//[Person{name='Sam', age=18}, Person{name='Penny', age=19}, Person{name='Sam', age=18}]
System.out.println(p1.hashCode());
System.out.println(p2.hashCode());
//1355531311
//
} }
重写方法后:
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Person> set=new HashSet<>();
Person p1=new Person("Sam",18);
Person p2=new Person("Sam",18);
Person p3=new Person("Penny",19);
set.add(p1);
set.add(p2);
set.add(p3);
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println(p1.hashCode());
System.out.println(p2.hashCode());
//[Person{name='Sam', age=18}, Person{name='Penny', age=19}]
//2570228
//
}
LinkedHashSet:
extends HashSet
特点:
底层是哈希表(数组+链表/红黑色) + 链表(用来记录元素的存储顺序)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> set=new HashSet<>();
set.add("c");
set.add("a");
set.add("b");
System.out.println(set);// 无序,不允许重复。
LinkedHashSet<String> linked=new LinkedHashSet<>();
linked.add("a");
linked.add("b");
linked.add("c");
System.out.println(linked);//有序,不允许重复
//[a, b, c]
//[a, b, c]
}
可变参数:
jdk 1.5 之后出现。
前提: 参数列表的数据类型已确定,但参数个数不确定时。
格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名 (数据类型...变量名){}
可变参数原理:
底层:数组,根据参数个数不同,来创建不同长度的数组,来存储参数。
参数个数: 0个-多个。
注意事项:
1、一个方法的参数列表,只能有一个可变参数。
2、如果参数有多个,可变参数放最后。
可变参数的终极写法 : method(Object...obj)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=add(10,20,30);//创建一个长度为三的数组
System.out.println(sum);
}
//计算多个整数的和。
public static int add(int...arr){
int sum=0;
for(int i:arr)
sum+=i;
return sum;
}
Collections 工具类:
java.utils.Collections 是集合工具类,用来对集合进行操作。
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<T> c,T...elements)
//往集合添加多个元素。
//public static void shuffle(List<T> list)
//打乱集合顺序。
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"a","b","c","d");
System.out.println(list);//[a, b, c, d]
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);//[c, d, b, a]
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public static <T> void sort(List<T> list)
//对集合排序,默认升序。
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
Collections.addAll(list, 1,3,2);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
sort方法的使用前提:
被排序的集合里边存储的元素,必须实现Comparable,重写接口中的compareTo
定义排序的规则。
Compareble 的排序规则:this - 参数 升序 反之。
public static void main(String[] args) {
//对Person类型的集合排序。
ArrayList<Person> personList=new ArrayList<>();
personList.add(new Person("张三",17));
personList.add(new Person("李四",19));
personList.add(new Person("王麻子",15));
Collections.sort(personList);
System.out.println(personList);
//[Person{name='王麻子', age=15}, Person{name='张三', age=17}, Person{name='李四', age=19}]
}
Person类:
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
//return 0; 认为元素都是相同的。
//自定义比较规则,比较两个人的年龄(this,参数Person)
return this.getAge()-o.getAge(); //年龄升序排序
}
Comparator 接口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public static <T> void sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T>)
//将集合中的元素按指定规则排序。
//Comparator和 Comparable的区别:
//Comparable : 自己 this 和别人(参数)比较,
//自己需要实现Comparable接口,重写compareto 方法
//Comparator:相当于找一个第三方裁判,来比较两个。
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,1,3,2);
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1-o2;//升序。
}
});
System.out.println(list);
// Person 类型的集合排序。
ArrayList<Person> personList=new ArrayList<>();
personList.add(new Person("张三",17));
personList.add(new Person("b李四",19));
personList.add(new Person("a王麻子",19));
//一个规则
// Collections.sort(personList, new Comparator<Person>() {
// @Override
// public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
// //年龄升序
// return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
// }
// });
//多个规则:
Collections.sort(personList, new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
int result=o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
if (result==0){
result=o1.getName().charAt(0)-o2.getName().charAt(0);
}
return result;
}
});
System.out.println(personList);
}
Collection集合。的更多相关文章
- 浅谈Collection集合
俗话说:一个东西,一件事都离不开三句话:"是什么,为什么,怎么办" 集合是什么: 集合简单的说一个数组集合的高级体现,用来存储数据或对象的容器: 集合为什么存在: 集合只是体现了对 ...
- Collection集合的功能及总结
Collection集合是集合顶层接口,不能实例化 功能 1.添加功能 boolean add(Object obj):添加一个元素 boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个 ...
- JAVA collection集合之 扑克牌游戏
主要内容:这里使用collection集合,模拟香港电影中大佬们玩的扑克牌游戏. 1.游戏规则:两个玩家每人手中发两张牌,进行比较.比较每个玩家手中牌最大的点数,大小由A-2,点数大者获胜.如果点数相 ...
- Collection集合List、Set
Collection集合,用来保存一组数据的数据结构. Collection是一个接口,定义了所有集合都应该包含的特征和行为 Collection派生出了两类集合 List和Set List接口:Li ...
- Collection集合之六大接口(Collection、Set、List、Map、Iterator和Comparable)
首先,我们先看一下Collection集合的基本结构: 1.Collection接口 Collection是最基本集合接口,它定义了一组允许重复的对象.Collection接口派生了两个子接口Set和 ...
- java.util.Map按照key值合并的value的Collection 集合中。
用java实现把多个map的内容合并的一个resultMap中 代码大致如下 /** * @author Shalf */ public class MapUtil { /** * 把partMa ...
- javad的Collection集合
集合框架:★★★★★,用于存储数据的容器. 特点: 1:对象封装数据,对象多了也需要存储.集合用于存储对象. 2:对象的个数确定可以使用数组,但是不确定怎么办?可以用集合.因为集合是可变长度的. 集合 ...
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记13:Collection集合存储学生对象并遍历
1. Collection集合存储学生对象并遍历: 需求:存储自定义对象并遍历Student(name,age) 分析: (1)创建学生类 (2)创建集合对象 (3)创建学生对象 (4)把学生对象添加 ...
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记12:Collection集合存储字符串并遍历
1. Collection集合存储字符串并遍历 分析: (1)创建集合对象 (2)创建字符串对象 (3)把字符串对象添加到集合中 (4)遍历集合 2. 代码示例: package cn.itcast ...
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记09:Collection集合迭代器使用的问题探讨
1.Collection集合迭代器使用的问题探讨: (1)问题1:能用while循环写这个程序,我能不能用for循环呢? 可以使用for循环替代. (2)问题2:不要 ...
随机推荐
- python d:\test.py File "<stdin>", line 1 python d:\test.py ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax
pyhton出错: python d:\test.py File "<stdin>", line 1 python d:\test.py ^SyntaxError: i ...
- Java_循环
遍历数组: 一个栗子: public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] aa = {19,92,12,03,4 ...
- vue简单指令笔记
v-once 执行一次性插值,数据改变插值处内容不会更新 <span v-once>这个将不会改变: {{ msg }}</span> v-text 插入文本 <!--两 ...
- selenium python 设置窗口打开大小
1. 窗口最大化 1 driver.maximize_window() 2. 设置窗口大小 1 driver.set_window_size(1920,1080) #分辨率1920 x 1080
- 如何实现文件上传 - JavaWeb
直接上代码 ( idea 开发,SpringBoot 框架 ): 首先是Controller的写法: package com.xxx.Controller; import com.xxx.Tools. ...
- JS DOM与BOM
DOM知识点 [DOM(文档对象模型)是 HTML 和 XML 的应用程序接口(API).DOM代表着被加载到浏览器窗口里的当前网页:浏览器向我们提供了当前网页的地图(或者说模型),而我们可以通过js ...
- ASP.NET 4.0验证请求 System.Web.HttpRequestValidationException: A potentially dangerous Request.F
System.Web.HttpRequestValidationException: A potentially dangerous Request.F 在使用类似eWebedtior 拷贝内容进去的 ...
- nova file injection的原理和调试过程
file injection代码 file injection原理来讲是比较简单的,在nova boot命令中,有参数--file,是将文件inject到image中 nova boot --flav ...
- LeetCode编程训练 - 拓扑排序(Topological Sort)
拓扑排序基础 拓扑排序用于解决有向无环图(DAG,Directed Acyclic Graph)按依赖关系排线性序列问题,直白地说解决这样的问题:有一组数据,其中一些数据依赖其他,问能否按依赖关系排序 ...
- NeuChar 平台使用及开发教程 索引
什么是 NeuChar? NeuChar 是由盛派(Senparc)团队发布的新一代跨平台服务系统,其中包含了开放的跨平台通讯标准及核心计算模块(Senparc.NeuChar.dll)以及配套的云管 ...
