PCA and Whitening on natural images
Step 0: Prepare data
Step 0a: Load data
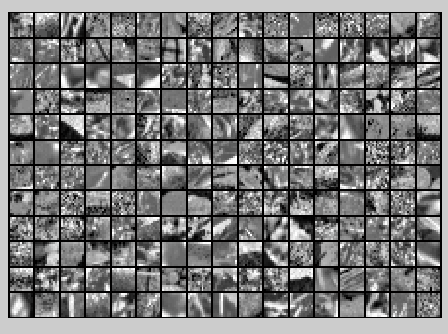
The starter code contains code to load a set of natural images and sample 12x12 patches from them. The raw patches will look something like this:
These patches are stored as column vectors
in the
matrix x.
Step 0b: Zero mean the data
First, for each image patch, compute the mean pixel value and subtract it from that image, this centering the image around zero. You should compute a different mean value for each image patch.
Step 1: Implement PCA
Step 1a: Implement PCA
In this step, you will implement PCA to obtain xrot, the matrix in which the data is "rotated" to the basis comprising the principal components
Step 1b: Check covariance
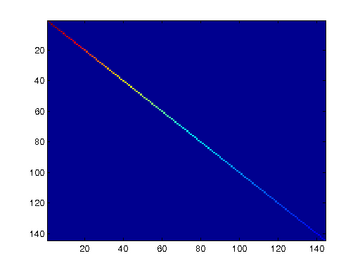
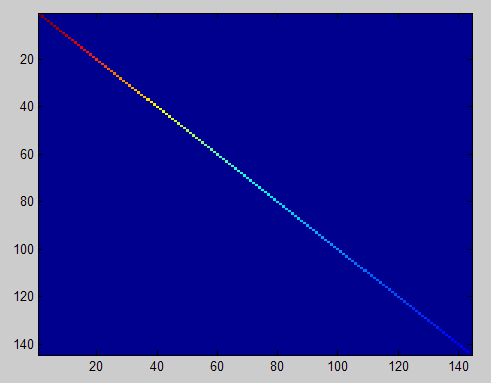
To verify that your implementation of PCA is correct, you should check the covariance matrix for the rotated data xrot. PCA guarantees that the covariance matrix for the rotated data is a diagonal matrix (a matrix with non-zero entries only along the main diagonal). Implement code to compute the covariance matrix and verify this property. One way to do this is to compute the covariance matrix, and visualise it using the MATLAB command imagesc.
Step 2: Find number of components to retain
Next, choose k, the number of principal components to retain. Pick k to be as small as possible, but so that at least 99% of the variance is retained.
Step 3: PCA with dimension reduction
Now that you have found k, compute
, the reduced-dimension representation of the data. This gives you a representation of each image patch as a k dimensional vector instead of a 144 dimensional vector.
Raw images
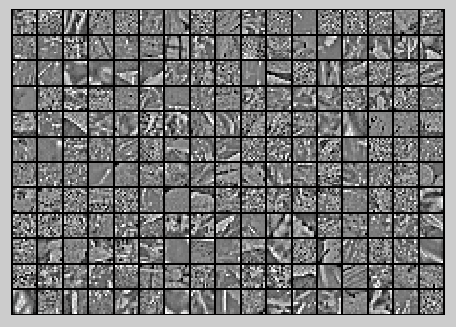
PCA dimension-reduced images
(99% variance)

PCA dimension-reduced images
(90% variance)
Step 4: PCA with whitening and regularization
Step 4a: Implement PCA with whitening and regularization
Step 4b: Check covariance
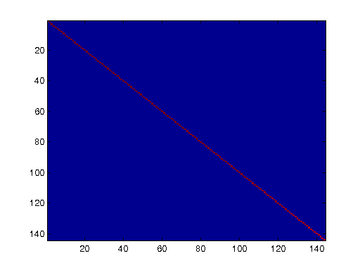
Similar to using PCA alone, PCA with whitening also results in processed data that has a diagonal covariance matrix. However, unlike PCA alone, whitening additionally ensures that the diagonal entries are equal to 1, i.e. that the covariance matrix is the identity matrix.That would be the case if you were doing whitening alone with no regularization. However, in this case you are whitening with regularization, to avoid numerical/etc. problems associated with small eigenvalues. As a result of this, some of the diagonal entries of the covariance of your xPCAwhite will be smaller than 1.
Covariance for PCA whitening with regularization
Covariance for PCA whitening without regularization
Step 5: ZCA whitening
Now implement ZCA whitening to produce the matrix xZCAWhite. Visualize xZCAWhite and compare it to the raw data
实验过程及结果
随机选取10000个patch,并显示其中204个patch,如下图所示:
然后对这些patch做均值为0化操作得到如下图:
对选取出的patch做PCA变换得到新的样本数据,其新样本数据的协方差矩阵如下图所示:
保留99%的方差后的PCA还原原始数据,如下所示:
PCA Whitening后的图像如下:
此时样本patch的协方差矩阵如下:
ZCA Whitening的结果如下:
Code
%%================================================================
%% Step 0a: Load data
% Here we provide the code to load natural image data into x.
% x will be a * matrix, where the kth column x(:, k) corresponds to
% the raw image data from the kth 12x12 image patch sampled.
% You do not need to change the code below. x = sampleIMAGESRAW();
figure('name','Raw images');
randsel = randi(size(x,),,); % A random selection of samples for visualization
display_network(x(:,randsel));%为什么x有负数还可以显示? %%================================================================
%% Step 0b: Zero-mean the data (by row)
% You can make use of the mean and repmat/bsxfun functions. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
x = x-repmat(mean(x,),size(x,),);%求的是每一列的均值
%x = x-repmat(mean(x,),,size(x,)); %%================================================================
%% Step 1a: Implement PCA to obtain xRot
% Implement PCA to obtain xRot, the matrix in which the data is expressed
% with respect to the eigenbasis of sigma, which is the matrix U. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xRot = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
[n m] = size(x);
sigma = (1.0/m)*x*x';
[u s v] = svd(sigma);
xRot = u'*x; %%================================================================
%% Step 1b: Check your implementation of PCA
% The covariance matrix for the data expressed with respect to the basis U
% should be a diagonal matrix with non-zero entries only along the main
% diagonal. We will verify this here.
% Write code to compute the covariance matrix, covar.
% When visualised as an image, you should see a straight line across the
% diagonal (non-zero entries) against a blue background (zero entries). % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
covar = zeros(size(x, )); % You need to compute this
covar = (./m)*xRot*xRot'; % Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a line across the
% diagonal against a blue background.
figure('name','Visualisation of covariance matrix');
imagesc(covar); %%================================================================
%% Step : Find k, the number of components to retain
% Write code to determine k, the number of components to retain in order
% to retain at least % of the variance. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
k = ; % Set k accordingly
ss = diag(s);
% for k=:m
% if sum(s(:k))./sum(ss) < 0.99
% continue;
% end
%其中cumsum(ss)求出的是一个累积向量,也就是说ss向量值的累加值
%并且(cumsum(ss)/sum(ss))<=.99是一个向量,值为0或者1的向量,为1表示满足那个条件
k = length(ss((cumsum(ss)/sum(ss))<=0.99)); %%================================================================
%% Step : Implement PCA with dimension reduction
% Now that you have found k, you can reduce the dimension of the data by
% discarding the remaining dimensions. In this way, you can represent the
% data in k dimensions instead of the original , which will save you
% computational time when running learning algorithms on the reduced
% representation.
%
% Following the dimension reduction, invert the PCA transformation to produce
% the matrix xHat, the dimension-reduced data with respect to the original basis.
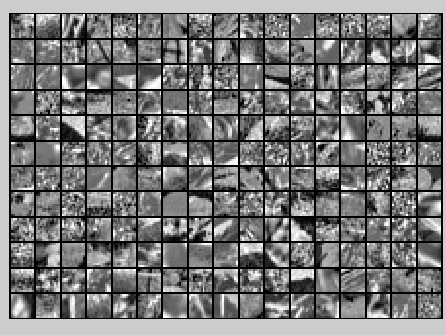
% Visualise the data and compare it to the raw data. You will observe that
% there is little loss due to throwing away the principal components that
% correspond to dimensions with low variation. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xHat = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xHat = u*[u(:,:k)'*x;zeros(n-k,m)]; % Visualise the data, and compare it to the raw data
% You should observe that the raw and processed data are of comparable quality.
% For comparison, you may wish to generate a PCA reduced image which
% retains only % of the variance. figure('name',['PCA processed images ',sprintf('(%d / %d dimensions)', k, size(x, )),'']);
display_network(xHat(:,randsel));
figure('name','Raw images');
display_network(x(:,randsel)); %%================================================================
%% Step 4a: Implement PCA with whitening and regularisation
% Implement PCA with whitening and regularisation to produce the matrix
% xPCAWhite. epsilon = 0.1;
xPCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xPCAWhite = diag(./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x;
figure('name','PCA whitened images');
display_network(xPCAWhite(:,randsel)); %%================================================================
%% Step 4b: Check your implementation of PCA whitening
% Check your implementation of PCA whitening with and without regularisation.
% PCA whitening without regularisation results a covariance matrix
% that is equal to the identity matrix. PCA whitening with regularisation
% results in a covariance matrix with diagonal entries starting close to
% and gradually becoming smaller. We will verify these properties here.
% Write code to compute the covariance matrix, covar.
%
% Without regularisation (set epsilon to or close to ),
% when visualised as an image, you should see a red line across the
% diagonal (one entries) against a blue background (zero entries).
% With regularisation, you should see a red line that slowly turns
% blue across the diagonal, corresponding to the one entries slowly
% becoming smaller. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
covar = (./m)*xPCAWhite*xPCAWhite'; % Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a red line across the
% diagonal against a blue background.
figure('name','Visualisation of covariance matrix');
imagesc(covar); %%================================================================
%% Step : Implement ZCA whitening
% Now implement ZCA whitening to produce the matrix xZCAWhite.
% Visualise the data and compare it to the raw data. You should observe
% that whitening results in, among other things, enhanced edges. xZCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xZCAWhite = u*xPCAWhite; % Visualise the data, and compare it to the raw data.
% You should observe that the whitened images have enhanced edges.
figure('name','ZCA whitened images');
display_network(xZCAWhite(:,randsel));
figure('name','Raw images');
display_network(x(:,randsel));
PCA and Whitening on natural images的更多相关文章
- UFLDL教程之(三)PCA and Whitening exercise
Exercise:PCA and Whitening 第0步:数据准备 UFLDL下载的文件中,包含数据集IMAGES_RAW,它是一个512*512*10的矩阵,也就是10幅512*512的图像 ( ...
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:PCA and Whitening
Exercise:PCA and Whitening 习题链接:Exercise:PCA and Whitening pca_gen.m %%============================= ...
- DL四(预处理:主成分分析与白化 Preprocessing PCA and Whitening )
预处理:主成分分析与白化 Preprocessing:PCA and Whitening 一主成分分析 PCA 1.1 基本术语 主成分分析 Principal Components Analysis ...
- Deep Learning学习随记(二)Vectorized、PCA和Whitening
接着上次的记,前面看了稀疏自编码.按照讲义,接下来是Vectorized, 翻译成向量化?暂且这么认为吧. Vectorized: 这节是老师教我们编程技巧了,这个向量化的意思说白了就是利用已经被优化 ...
- PCA和Whitening
PCA: PCA的具有2个功能,一是维数约简(可以加快算法的训练速度,减小内存消耗等),一是数据的可视化. PCA并不是线性回归,因为线性回归是保证得到的函数是y值方面误差最小,而PCA是保证得到的函 ...
- 【转】PCA与Whitening
PCA: PCA的具有2个功能,一是维数约简(可以加快算法的训练速度,减小内存消耗等),一是数据的可视化. PCA并不是线性回归,因为线性回归是保证得到的函数是y值方面误差最小,而PCA是保证得到的函 ...
- (六)6.8 Neurons Networks implements of PCA ZCA and whitening
PCA 给定一组二维数据,每列十一组样本,共45个样本点 -6.7644914e-01 -6.3089308e-01 -4.8915202e-01 ... -4.4722050e-01 -7.4 ...
- CS229 6.8 Neurons Networks implements of PCA ZCA and whitening
PCA 给定一组二维数据,每列十一组样本,共45个样本点 -6.7644914e-01 -6.3089308e-01 -4.8915202e-01 ... -4.4722050e-01 -7.4 ...
- 数据预处理:PCA,SVD,whitening,normalization
数据预处理是为了让算法有更好的表现,whitening.PCA.SVD都是预处理的方式: whitening的目标是让特征向量中的特征之间不相关,PCA的目标是降低特征向量的维度,SVD的目标是提高稀 ...
随机推荐
- SQL Server在用户自定义函数(UDF)中使用临时表
SQL Server在用户自定义函数中UDF使用临时表,这是不允许的. 有时是为了某些特殊的场景, 我们可以这样的实现: CREATE TABLE #temp (id INT) GO INSERT I ...
- js文字的无缝滚动(上下)
使用scrolltop值的递增配合setInterval与setTimeout实现相关效果,左右无缝滚动使用scrollLeft即可 Dom内容 <div id="container& ...
- input的选中与否以及将input的value追加到一个数组里
html布局 <div class="mask"> //每一个弹层都有一个隐藏的input <label> <input hidden="& ...
- Git 内部原理 - (7)维护与数据恢复 (8) 环境变量 (9)总结
维护与数据恢复 有的时候,你需要对仓库进行清理 - 使它的结构变得更紧凑,或是对导入的仓库进行清理,或是恢复丢失的内容. 这个小节将会介绍这些情况中的一部分. 维护 Git 会不定时地自动运行一个叫做 ...
- 免费录屏软件之OBS Studio
好久没有再博客活动啦,今天给大家推荐一下录屏软件吧!首先我个人最喜欢的OBS Studio就说说它吧 1.免费.开源.功能强大.易上手 下面是下载地址: 官网下载 : https://ob ...
- MyBatis学习总结(17)——Mybatis分页插件PageHelper
如果你也在用Mybatis,建议尝试该分页插件,这一定是最方便使用的分页插件. 分页插件支持任何复杂的单表.多表分页,部分特殊情况请看重要提示. 想要使用分页插件?请看如何使用分页插件. 物理分页 该 ...
- SpringMVC拓展
### 原生SpringMVC有如下缺陷 参数的JSON反序列化只支持@RequestBody注解,这意味着不能在controller方法中写多个参数,如下代码是不对的 public Map test ...
- 新一代企业即时通信系统 -- 傲瑞通(OrayTalk)
傲瑞通(OrayTalk)是我们为企业专门打造的新一代企业即时通讯平台,功能强大丰富.像组织结构.文字/语音/视频会话.文件传送.远程协助.消息记录等功能都有,而且留有接口可与企业遗留系统进行集成. ...
- 使用Opencv2遇到error C2061: 语法错误: 标识符dest
在写代码是遇到了这样一个问题,error C2061: 语法错误: 标识符"dest": 1>d:\opencv\opencv\build\include\opencv2\f ...
- 查看SQLSERVER当前正在运行的sql信息
能够使用SQL Profiler捕捉在SQL Server实例上运行的活动.这种活动被称为Profiler跟踪.这个就不多说了,大家都知道,以下是使用代码为实现同样的效果. SET TRANSACTI ...