Comparable与Comparator源码分析
- package java.lang;
- import java.util.*;
- /**
- * This interface imposes a total ordering on the objects of each class that
- * implements it. This ordering is referred to as the class's <i>natural
- * ordering</i>, and the class's <tt>compareTo</tt> method is referred to as
- * its <i>natural comparison method</i>.<p>
- *
- * Lists (and arrays) of objects that implement this interface can be sorted
- * automatically by {@link Collections#sort(List) Collections.sort} (and
- * {@link Arrays#sort(Object[]) Arrays.sort}). Objects that implement this
- * interface can be used as keys in a {@linkplain SortedMap sorted map} or as
- * elements in a {@linkplain SortedSet sorted set}, without the need to
- * specify a {@linkplain Comparator comparator}.<p>
- *
- * The natural ordering for a class <tt>C</tt> is said to be <i>consistent
- * with equals</i> if and only if <tt>e1.compareTo(e2) == 0</tt> has
- * the same boolean value as <tt>e1.equals(e2)</tt> for every
- * <tt>e1</tt> and <tt>e2</tt> of class <tt>C</tt>. Note that <tt>null</tt>
- * is not an instance of any class, and <tt>e.compareTo(null)</tt> should
- * throw a <tt>NullPointerException</tt> even though <tt>e.equals(null)</tt>
- * returns <tt>false</tt>.<p>
- *
- * It is strongly recommended (though not required) that natural orderings be
- * consistent with equals. This is so because sorted sets (and sorted maps)
- * without explicit comparators behave "strangely" when they are used with
- * elements (or keys) whose natural ordering is inconsistent with equals. In
- * particular, such a sorted set (or sorted map) violates the general contract
- * for set (or map), which is defined in terms of the <tt>equals</tt>
- * method.<p>
- *
- * For example, if one adds two keys <tt>a</tt> and <tt>b</tt> such that
- * {@code (!a.equals(b) && a.compareTo(b) == 0)} to a sorted
- * set that does not use an explicit comparator, the second <tt>add</tt>
- * operation returns false (and the size of the sorted set does not increase)
- * because <tt>a</tt> and <tt>b</tt> are equivalent from the sorted set's
- * perspective.<p>
- *
- * Virtually all Java core classes that implement <tt>Comparable</tt> have natural
- * orderings that are consistent with equals. One exception is
- * <tt>java.math.BigDecimal</tt>, whose natural ordering equates
- * <tt>BigDecimal</tt> objects with equal values and different precisions
- * (such as 4.0 and 4.00).<p>
- *
- * For the mathematically inclined, the <i>relation</i> that defines
- * the natural ordering on a given class C is:<pre>
- * {(x, y) such that x.compareTo(y) <= 0}.
- * </pre> The <i>quotient</i> for this total order is: <pre>
- * {(x, y) such that x.compareTo(y) == 0}.
- * </pre>
- *
- * It follows immediately from the contract for <tt>compareTo</tt> that the
- * quotient is an <i>equivalence relation</i> on <tt>C</tt>, and that the
- * natural ordering is a <i>total order</i> on <tt>C</tt>. When we say that a
- * class's natural ordering is <i>consistent with equals</i>, we mean that the
- * quotient for the natural ordering is the equivalence relation defined by
- * the class's {@link Object#equals(Object) equals(Object)} method:<pre>
- * {(x, y) such that x.equals(y)}. </pre><p>
- *
- * This interface is a member of the
- * <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
- * Java Collections Framework</a>.
- *
- * @param <T> the type of objects that this object may be compared to
- *
- * @author Josh Bloch
- * @see java.util.Comparator
- * @since 1.2
- */
- public interface Comparable<T> {
- public int compareTo(T o);
- }
实现这个接口的类的集合或数组将会被自动排序通过Collections.sort或者Arrays.sort。同时,这个对象也可以被用来做Map或者Set的键值,而不需要另外制定一个比较器。
废话不多说了,直接举例子。
- package object;
- public class Person implements Comparable<Object>{
- private String name;
- private int age;
- Person(String name,int age){
- this.name=name;
- this.age=age;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "姓名:"+this.name +";年龄: " + this.age;
- }
- @Override
- public int compareTo(Object o) {
- Person temp =null;
- if(o instanceof Person )
- temp = (Person)(o);
- return this.age - temp.age;
- }
- }
测试类:
- public class Test{
- @org.junit.Test
- public void test(){
- Person[] people = {new Person("tom",21),new Person("jerry",18),new Person("dog",17)};
- System.out.println("排序前");
- for(Person p:people)
- System.out.println(p);
- System.out.println("排序后");
- java.util.Arrays.sort(people);
- for(Person p:people)
- System.out.println(p);
- }
- }
结果:
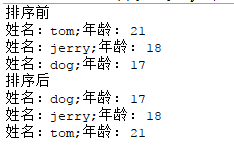
大家可以看到,这个排序方法是放到排序的对象类里面的,但是如果我们已经设计好了某类,而且不想改变其数据结构,就这可以用到比较器Comparator。用 Comparator 是策略模式,就是不改变对象自身,而用一个策略对象来改变它的行为。
- package java.util;
- import java.io.Serializable;
- import java.util.function.Function;
- import java.util.function.ToIntFunction;
- import java.util.function.ToLongFunction;
- import java.util.function.ToDoubleFunction;
- import java.util.Comparators;
- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface Comparator<T> {
- int compare(T o1, T o2);
- boolean equals(Object obj);
- }
Comparator里面只有两个无实现体的接口方法,其它的方法有实现体,好像是新特性,暂时未用到。这里的equals与Object的equals方法类似。所以对于实现这个接口的类不必实现equals方法,也不会报错。
下面的例子我用的是匿名函数。
- package object;
- public class Person{
- private String name;
- private int age;
- Person(String name,int age){
- this.name=name;
- this.age=age;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "姓名:"+this.name +";年龄: " + this.age;
- }
- }
测试类:
- public class Test{
- @org.junit.Test
- public void test(){
- Person[] people = {new Person("tom",21),new Person("jerry",18),new Person("dog",17)};
- System.out.println("排序前");
- for(Person p:people)
- System.out.println(p);
- System.out.println("排序后");
- Arrays.sort(people, new Comparator<Person>() {
- public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
- return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();};
- });
- for(Person p:people)
- System.out.println(p);
- }
- }
结果:

总结:
用Comparable 简单, 只要实现Comparable 接口的对象直接就成为一个可以比较的对象,但是需要修改源代码,用Comparator 的好处是不需要修改源代码,而是另外实现一个比较器,当某个自定义的对象需要作比较的时候,把比较器和对象一起传递过去就可以比大小了,并且在Comparator 里面用户可以自己实现复杂的可以通用的逻辑,使其可以匹配一些比较简单的对象,那样就可以节省很多重复劳动了。
Comparable与Comparator源码分析的更多相关文章
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之Comparable && Comparator(九)
一.前言 在Java集合框架里面,各种集合的操作很大程度上都离不开Comparable和Comparator,虽然它们与集合没有显示的关系,但是它们只有在集合里面的时候才能发挥最大的威力.下面是开始我 ...
- java中Comparator比较器顺序问题,源码分析
提示: 分析过程是个人的一些理解,如有不对的地方,还请大家见谅,指出错误,共同学习. 源码分析过程中由于我写的注释比较啰嗦.比较多,导致文中源代码不清晰,还请一遍参照源代码,一遍参照本文进行阅读. 原 ...
- HashMap与TreeMap源码分析
1. 引言 在红黑树--算法导论(15)中学习了红黑树的原理.本来打算自己来试着实现一下,然而在看了JDK(1.8.0)TreeMap的源码后恍然发现原来它就是利用红黑树实现的(很惭愧学了Ja ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之TreeMap(五)
一.前言 当我们需要把插入的元素进行排序的时候,就是时候考虑TreeMap了,从名字上来看,TreeMap肯定是和树是脱不了干系的,它是一个排序了的Map,下面我们来着重分析其源码,理解其底层如何实现 ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之Collections && Arrays(十)
一.前言 整个集合框架的常用类我们已经分析完成了,但是还有两个工具类我们还没有进行分析.可以说,这两个工具类对于我们操作集合时相当有用,下面进行分析. 二.Collections源码分析 2.1 类的 ...
- 【JUC】JDK1.8源码分析之ConcurrentSkipListMap(二)
一.前言 最近在做项目的同时也在修复之前项目的一些Bug,所以忙得没有时间看源代码,今天都完成得差不多了,所以又开始源码分析之路,也着笔记录下ConcurrentSkipListMap的源码的分析过程 ...
- Java中Comparable和Comparator接口区别分析
Java中Comparable和Comparator接口区别分析 来源:码农网 | 时间:2015-03-16 10:25:20 | 阅读数:8902 [导读] 本文要来详细分析一下Java中Comp ...
- Java集合源码分析(六)TreeSet<E>
TreeSet简介 TreeSet 是一个有序的集合,它的作用是提供有序的Set集合.它继承于AbstractSet抽象类,实现了NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, j ...
- Java集合类源码分析
常用类及源码分析 集合类 原理分析 Collection List Vector 扩充容量的方法 ensureCapacityHelper很多方法都加入了synchronized同步语句,来保 ...
随机推荐
- veket智能机器人
官方网站:http://www.lucky8k.com/forum.php veket儿童操作系统 希望工具超过小puppy linux系统 一个还在发展中的linux系统: Slax Linux : ...
- 【sqli-labs】 less23 Error based - strip comments (GET型基于错误的去除注释的注入)
. 加单引号报错 加# http://localhost/sqli-labs-master/Less-23/?id=1'%23 错误没有改变,推测过滤了# 查看源码发现# -- 都被替换掉了 那么可用 ...
- C# MVC 获得程序运行路径
string filePath = System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Request.MapPath("~/Upload"); //由虚拟路径指定的服务 ...
- eas中删除原来的监听事件添加新的监听事件
kdtEntrys.removeKDTEditListener(kdtEntrys.getListeners(KDTEditListener.class)[0]); kdtEntrys.addKDT ...
- npm命令及解释
npm是Node Package Manager,也就是长说的NPM包管理器. 一般安装node.js就会一起安装. npm install npm install XXX //表示安装模块, ...
- @dalao help!!!
- [luogu1090 SCOI2003] 字符串折叠(区间DP+hash)
传送门 Solution 区间DP,枚举断点,对于一个区间,枚举折叠长度,用hash暴力判断是否能折叠即可 Code #include <cstdio> #include <cstr ...
- [luogu 4886] 快递员
传送门 Solution 虽然不是点分治但用类似点分治的方法不断接近正确结果 Code // luogu-judger-enable-o2 #include <cstdio> #inclu ...
- 阿里云 LAMP 使用基础
产品亮点 1.基于阿里云CentOS7.2镜像 2.采用yum方式安装,软件安装均为默认目录,未作任何修改. 3.采用经典LAMP组合,拓展性强,资源丰富,解决方案较多 4.附带PhpMyadmin和 ...
- MySQL性能分析、及调优工具使用详解
本文汇总了MySQL DBA日常工作中用到的些工具,方便初学者,也便于自己查阅. 先介绍下基础设施(CPU.IO.网络等)检查的工具: vmstat.sar(sysstat工具包).mpstat.op ...
