ActiveMQ学习笔记(12)----ActiveMQ的集群
1. Queue consumer cluster
ActiveMQ支持Consumer对消息的高可靠性的负载均衡消费,如果一个Consumer死掉,该消息会转发到其他的Consumer消费的Queue。如果一个Consumer获得消息比其他Consumer快,那么他将获得更多的消息。因此推荐ActiveMQ的Broker和Client使用failover://transport的方式来配置连接
2. Broker clusters
大部分情况下是使用一系列的Broker和Client连接到一起。如果一个Broker死掉了,那么Client可以自动连接到其他的Broker上。实现以上行为需用failover协作Client.
如果启动了多个Broker,Client可以使用static discovery或者Dynamic discovery容易从一个broker到另一个broker直接连接。这样当一个broker上没有Consumer的话,那么它的消息不会被消费,然而该broker会通过存储和转发的策略来把该消息发送到其他broker上。
特别注意:ActiveMQ默认的两个Broker, static链接后是单方向的,broker-A可以访问消费Broker-b的消息,如果要支持双向通信,需要在networConnector配置的时候,设置duplex=true。
这里的集群使用的是静态网络连接,访问broker的时创建ConnectionFactory的路径应写为:
ConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("failover:(tcp://localhost:61616,tcp://localhost:61716)?randomize=false");
使用三个消费者,一个消费者连接端口61716,另外两个消费者连接61616端口。
三个消费者使用如下代码如下
package com.wangx.activemq.master;
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.*;
public class QR1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建链接工厂
ConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("failover:(tcp://localhost:61616,tcp://localhost:61716)?randomize=false");
Connection connection = null;
try{
//创建链接
connection = factory.createConnection();
//启动链接
connection.start();
//获取会话
final Session session = connection.createSession(Boolean.TRUE, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
//创建队列
Destination queue = session.createQueue("myQueue");
MessageConsumer consumer1 = session.createConsumer(queue);
MessageConsumer consumer2 = session.createConsumer(queue);
new Thread(new MasterRunnable(consumer1, session, "consumer1")).start();
new Thread(new MasterRunnable(consumer2, session, "consumer2")).start();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
线程任务类:开两个线程同时使用两个消费者同时监听61616端口
package com.wangx.activemq.master; import javax.jms.JMSException;
import javax.jms.MessageConsumer;
import javax.jms.Session; public class MasterRunnable implements Runnable { private MessageConsumer consumer; private Session session; private String name;
public MasterRunnable(MessageConsumer consumer, Session session, String name) {
this.consumer = consumer;
this.session = session;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
consumer.setMessageListener(new MyMessageListener(session, name));
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
消息监听类:
package com.wangx.activemq.master;
import javax.jms.*;
public class MyMessageListener implements MessageListener {
private Session session = null;
private String name;
public MyMessageListener(Session session, String name) {
this.session = session;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message) {
TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) message;
try {
System.out.println(name + "接受到消息:" + textMessage.getText());
session.commit();
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
连接61716端口的consumer
package com.wangx.activemq.master;
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.*;
public class QR2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建链接工厂
ConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("failover:(tcp://localhost:61616,tcp://localhost:61716)?randomize=false");
Connection connection = null;
try{
//创建链接
connection = factory.createConnection();
//启动链接
connection.start();
//获取会话
final Session session = connection.createSession(Boolean.TRUE, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
//创建队列
Destination queue = session.createQueue("myQueue");
//创建消费者
MessageConsumer messageConsumer = session.createConsumer(queue);
//监听消息
messageConsumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message) {
TextMessage textMessage = (TextMessage) message;
try {
System.out.println("QR2 接受到消息:" + textMessage.getText());
session.commit();
} catch (JMSException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
向端口61716发送消息
package com.wangx.activemq.master;
import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory; import javax.jms.*; public class MessageSender { public static void main(String[] args) throws JMSException {
//创建链接工厂
ConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://localhost:61716"); Connection connection = null;
Session session = null;
try{
//创建链接
connection = factory.createConnection();
//启动链接
connection.start();
//获取会话
session = connection.createSession(Boolean.TRUE, session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
//创建队列
Destination queue = session.createQueue("myQueue");
//创建生产者对象
MessageProducer messageProducer = session.createProducer(queue); for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
//创建消息对象
TextMessage textMessage = session.createTextMessage("hello:" + i);
//发送消息
messageProducer.send(textMessage);
System.out.println(textMessage.getText());
}
session.commit();
session.close();
connection.close();
}catch (Exception e) { }finally {
} }
}
分别启动两个消息监听类,可以发现,此时两个不同broker所连接的消费者所消费的消息是均分的,尽管此时有一个broker中有两个consumer,这是因为ActiveMQ默认的认为网络上的broker作为一个consumer,此时将conduitSubscriptions设置为false即可是整个集群上的所有consumer都有均分消费消息的可能。
2. Master Slave
在5.9的版本中,废除了Pure Master Slave的方式,目前支持
1. Shared File System Master Slave:基于共享存储的Master-Slave;多个broker实例使用一个存储文件,谁拿到文件锁谁就是master,其他处于待启动状态,如果master挂掉了,某个抢到文件锁的slave变成master
2. JDBC Master Slave: 基于JDBC的Master-Slave:使用同一个数据库,拿到LOCK表的写锁的broker成为master.
3. Replicated LeveDB Store:基于zookeeper复制LeveDB存储的Master-Slave机制,这个是5.9新家的机制。
具体的可以查看官方文档:
http://activemq.apache.org/masterslave.html
3. JDBC Master Slave方式
利用数据库作为数据源,采用Master/Slave模式,其中启动的时候Master首先获得独有锁,其他Slaves Broker等待获取独有锁。
推荐客户端使用Failover来连接Brokers.
具体如下图:
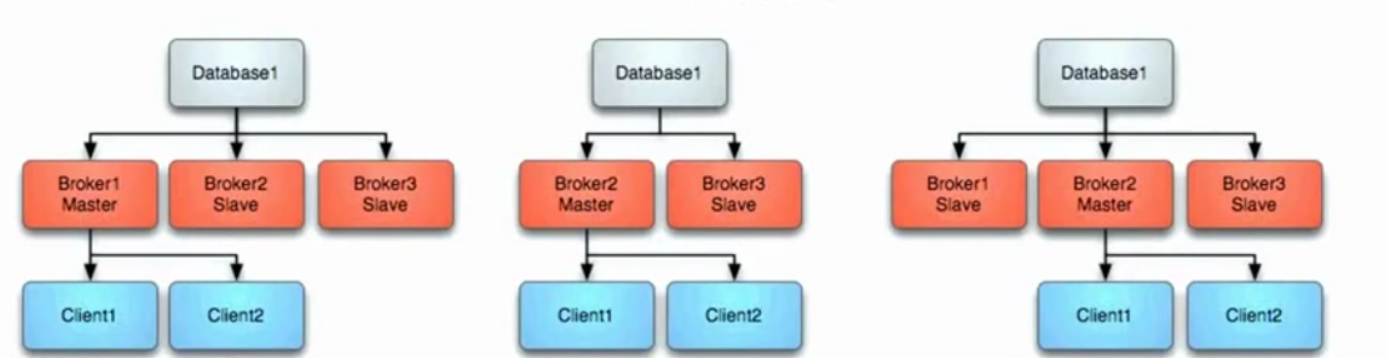
3.1. Master失败
如果master失败,则它释放独有锁,其他Slave获独有锁,其他Slave立即获得独有锁后它将变成Master,并且启动所有的传输连接。同时,Client将停止连接之前的Master并且它将会轮询其他可以利用到的Broker,即新的Master.如上中图所示。
3.2 Master重启
任何时候启动新的Broker,都会作为新的Slave来加入集群,如上右图所示。
3.3 JDBC Master Slave的配置
使用<jdbcPersistenceAdapter dataSource="#mysql-ds"/>来配置消息持久化,自动就会使用MasterSlave的方式。具体配置如下:
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
<!-- START SNIPPET: example -->
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core.xsd"> <!-- Allows us to use system properties as variables in this configuration file -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>file:${activemq.conf}/credentials.properties</value>
</property>
</bean> <!-- Allows accessing the server log -->
<bean id="logQuery" class="io.fabric8.insight.log.log4j.Log4jLogQuery"
lazy-init="false" scope="singleton"
init-method="start" destroy-method="stop">
</bean> <!--
The <broker> element is used to configure the ActiveMQ broker.
-->
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" brokerName="localhost" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}"> <destinationPolicy>
<policyMap>
<policyEntries>
<!--<policyEntry topic=">" >
The constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy is used to prevent
slow topic consumers to block producers and affect other consumers
by limiting the number of messages that are retained
For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/slow-consumer-handling.html <pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
<constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy limit="1000"/>
</pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
</policyEntry>-->
<policyEntry queue=">" enableAudit="false">
<networkBridgeFilterFactory>
<conditionalNetworkBridgeFilterFactory replayWhenNoConsumers="true"/>
</networkBridgeFilterFactory>
</policyEntry>
</policyEntries>
</policyMap>
</destinationPolicy> <!--
The managementContext is used to configure how ActiveMQ is exposed in
JMX. By default, ActiveMQ uses the MBean server that is started by
the JVM. For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/jmx.html
-->
<managementContext>
<managementContext createConnector="false"/>
</managementContext> <!--
Configure message persistence for the broker. The default persistence
mechanism is the KahaDB store (identified by the kahaDB tag).
For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/persistence.html
-->
<persistenceAdapter>
<!--<kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb_2"/>-->
<jdbcPersistenceAdapter dataSource="#mysql-ds"/>
</persistenceAdapter> <!--
The systemUsage controls the maximum amount of space the broker will
use before disabling caching and/or slowing down producers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html
-->
<systemUsage>
<systemUsage>
<memoryUsage>
<memoryUsage percentOfJvmHeap="70" />
</memoryUsage>
<storeUsage>
<storeUsage limit="100 gb"/>
</storeUsage>
<tempUsage>
<tempUsage limit="50 gb"/>
</tempUsage>
</systemUsage>
</systemUsage> <!--
The transport connectors expose ActiveMQ over a given protocol to
clients and other brokers. For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/configuring-transports.html
-->
<transportConnectors>
<!-- DOS protection, limit concurrent connections to 1000 and frame size to 100MB -->
<transportConnector name="openwire" uri="tcp://0.0.0.0:61616?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="amqp" uri="amqp://0.0.0.0:9999?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="stomp" uri="stomp://0.0.0.0:61613?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="mqtt" uri="mqtt://0.0.0.0:1883?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="ws" uri="ws://0.0.0.0:61614?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
</transportConnectors> <!-- destroy the spring context on shutdown to stop jetty -->
<shutdownHooks>
<bean xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" class="org.apache.activemq.hooks.SpringContextHook" />
</shutdownHooks> </broker>
<bean id="mysql-ds" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/activemq?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="username" value="wangx"/>
<property name="password" value="wangx"/>
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!--
Enable web consoles, REST and Ajax APIs and demos
The web consoles requires by default login, you can disable this in the jetty.xml file Take a look at ${ACTIVEMQ_HOME}/conf/jetty.xml for more details
-->
<import resource="jetty.xml"/> </beans>
<!-- END SNIPPET: example -->
去掉静态网络连接配置,将持久化方式改为jdbc数据的方式,去掉消息回流的配置。这里每个Broker都需要如此配置,只需要端口不一致即可,启动两个broker,使用如上连接61716端口的Client像Broker发送消息,此时停掉端口为61716的Broker,启动消费者接受消息,使用了容错配置,此时仍然可以接收到前面一个Broker存活时接收到的消息并进行消费。其实这是由于当61716接受到消息之后做了持久化,所以当它死掉后,61616升级为Master,它会获取到前一个master存活时未被消费的消息,所以我们在访问61616端口的broker时仍然可以消费消息。
说明:使用了failover协议之后,当61716死掉后,client会停止与61716的连接。自动轮询集群中可用的broker,即新的master(61616端口的broker)
ActiveMQ学习笔记(12)----ActiveMQ的集群的更多相关文章
- Spark学习笔记--Linux安装Spark集群详解
本文主要讲解如何在Linux环境下安装Spark集群,安装之前我们需要Linux已经安装了JDK和Scala,因为Spark集群依赖这些.下面就如何安装Spark进行讲解说明. 一.安装环境 操作系统 ...
- DOCKER 学习笔记8 Docker Swarm 集群搭建
前言 在前面的文章中,已经介绍如何在本地通过Docker Machine 创建虚拟Docker 主机,以及也可以在本地Windows 创建虚拟主机,也是可以使用的.这一节,我们将继续学习 Docker ...
- Redis学习笔记(十七) 集群(上)
Redis集群是Redis提供的分布式数据库方案,集群通过分片来进行数据共享,并提供复制和故障转移操作. 一个Redis集群通常由多个节点组成,在刚开始的时候每个节点都是相互独立的,他们处于一个只包含 ...
- Docker Swarm Mode 学习笔记(创建 Swarm 集群)
Swarm 集群由管理节点与工作节点组成. 初始化集群 使用命令:docker swarm init 如果你的 Docker 主机有多个网卡, 拥有多个 IP 地址, 必须使用 --advertise ...
- Spark学习笔记5:Spark集群架构
Spark的一大好处就是可以通过增加机器数量并使用集群模式运行,来扩展计算能力.Spark可以在各种各样的集群管理器(Hadoop YARN , Apache Mesos , 还有Spark自带的独立 ...
- Redis学习笔记(二):Redis集群
集群通过分片(sharding)来进行数据共享,并提供复制和故障转移功能. 1.节点 一个节点就是一个运行在集群模式下的Redis服务器.启动Redis服务器时,通过判断cluster-enabl ...
- ELK学习笔记之ElasticSearch的集群(Cluster),节点(Node),分片(Shard),Indices(索引),replicas(备份)之间关系
[Cluster]集群,一个ES集群由一个或多个节点(Node)组成,每个集群都有一个cluster name作为标识----------------------------------------- ...
- 王雅超的学习笔记-大数据hadoop集群部署(十)
Spark集群安装部署
- Redis学习笔记(九)——集群
一.概述 Redis Cluster与Redis3.0.0同时发布,以此结束了Redis无官方集群方案的时代. Redis Cluster是去中心化,去中间件,也就是说,集群中的每个节点都是平等的关 ...
- 王雅超的学习笔记-大数据hadoop集群部署(七)
MySQL的安装部署
随机推荐
- python包管理(distutils、easy_install、pip、setup.py/requirements.txt、wheel)
distutils.distutils2 distutils是 python 标准库的一部分,2000年发布.使用它能够进行 python 模块的 安装 和 发布. distutils2 被设计为 d ...
- Caffe CommonLayer分析
Caffe CommonLayer分析 \(Caffe\)中包含了很多通用的功能层,包含了\(concat\),\(slice\),\(split\),\(crop\),\(flip\),\(scal ...
- shell-6.环境变量配置文件
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
- C++下面关于字符串数组的一些操作
今天在写一个搜索引擎的分词系统,是很简单的那种,但是居然费了我一天的时间还没完成,晚上估计还得弄一会了,但是在这个过程中,遇到了集中关于字符串数组的操作,值得和大家分享一下. 首先是关于统计字符串数组 ...
- MySQL_索引原理与慢查询优化
索引原理与慢查询优化 创建/删除索引的语法 #方法一:创建表时 CREATE TABLE 表名 ( 字段名1 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…], 字段名2 数据类型 [完整性约束条件…], [UNIQU ...
- 第七章 Python之模块与包
模块介绍 一个模块就是包含了一组功能的python文件(例如module.py,模块名是module),它从文件级别组织程序,更方便管理,这时我们不仅仅可以把这些文件当作脚本执行,还可以把他们当作模块 ...
- hdu 1080 dp(最长公共子序列变形)
题意: 输入俩个字符串,怎样变换使其所有字符对和最大.(字符只有'A','C','G','T','-') 其中每对字符对应的值如下: 怎样配使和最大呢. 比如: A G T G A T G - G ...
- 路飞学城Python-Day37(practise)
#1.自行创建测试数据 create database homework; use homework; # 年级表->老师表->课程表->班级表->学生表->成绩表-&g ...
- STM32 HAL库使用中断实现串口接收不定长数据
以前用DMA实现接收不定长数据,DMA的方法接收串口助手的数据,全部没问题,不过如果接收模块返回的数据,而这些数据如果包含回车换行的话就会停止接收,例如接收:AT\r\nOK\r\n,就只能接收到AT ...
- where和having
where可以不能使用别名作为过滤条件,而having可以使用别名作为过滤条件. 在ORACLE中,select 语句的执行顺序是: 1. from语句 2. where语句(结合条件) 3. sta ...
