Linux中断分层--软中断和tasklet
1. Linux中断分层

(1)上半部:当中断发生时,它进行相应的硬件读写,并“登记”该中断。通常由中断处理程序充当上半部。(一般情况下,上半部不可被打断)
(2)下半部:在系统空闲的时候,对上半部“登记”的中断进行后续处理(“延迟处理”)
2. 对于中断下半部的实现方式一共有三种
(1)软中断
(2)tasklet微线程
(3)工作队列
3. Linux内核软中断分析
(1)当中断发生时,Linux内核会跳转到中断总入口函数asm_do_IRQ(),根据传入的中断号,执行相应handle_irq()函数。做完这些工作之后,会调用函数irq_exit()(位于文件:kernal/softirq.c),该函数负责调用和处理待决的软中断。
void irq_exit(void)
{
account_system_vtime(current);
trace_hardirq_exit();
sub_preempt_count(IRQ_EXIT_OFFSET);
if (!in_interrupt() && local_softirq_pending())
invoke_softirq(); #ifdef CONFIG_NO_HZ
/* Make sure that timer wheel updates are propagated */
rcu_irq_exit();
if (idle_cpu(smp_processor_id()) && !in_interrupt() && !need_resched())
tick_nohz_stop_sched_tick();
#endif
preempt_enable_no_resched();
}
(2)invoke_softirq()是一个宏,等价于do_softirq()。调用do_softirq函数,就说明程序已经进入软中断环境了。与asm_do_IRQ所处的中断的上半部不同,处于软中断环境中,是可以被其他中断程序打断的,甚至是处于同一中断线的中断。也因为此,所以软中断可以执行一些稍微时间长一点的任务,也不会迟滞系统对中断的反应时间。
(3)软中断由一个softirq_action结构体表示,在该结构体中只定义了一个函数指针
struct softirq_action
{
void (*action)(struct softirq_action *);
};
(4)Linux内核中用一个数据项为softirq_action类型的数组softirq_vec来存储所支持的所有软中断
static struct softirq_action softirq_vec[NR_SOFTIRQS] __cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
(5)在驱动程序中,注册软中断使用函数open_softirq
void open_softirq(int nr, void (*action)(struct softirq_action *))
{
softirq_vec[nr].action = action;
}
(6)softirq_vec数组的下表代表不同类型的软中断,值越小,优先级越高,他们定义为一个枚举常量
enum
{
HI_SOFTIRQ=,
TIMER_SOFTIRQ,
NET_TX_SOFTIRQ,
NET_RX_SOFTIRQ,
BLOCK_SOFTIRQ,
TASKLET_SOFTIRQ,
SCHED_SOFTIRQ,
HRTIMER_SOFTIRQ,
RCU_SOFTIRQ, /* Preferable RCU should always be the last softirq */ NR_SOFTIRQS
};
(7)驱动程序所要做的工作是把软中断注册进去,而执行是do_softirq调用一个名为Ksoftirq的内核线程来完成。我们如果想要执行我们注册的软中断,还需要调用raise_softirq函数将我们想要执行的软中断处理程序挂起
void raise_softirq(unsigned int nr)
{
unsigned long flags; local_irq_save(flags);
raise_softirq_irqoff(nr);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
(8)相应类型的软中断被挂起之后,将会通过do_softirq得到执行
asmlinkage void do_softirq(void)
{
__u32 pending;
unsigned long flags; if (in_interrupt())
return; local_irq_save(flags); pending = local_softirq_pending(); if (pending)
__do_softirq(); local_irq_restore(flags);
}
(9)do_softirq调用函数__do_softirq来真正执行软中断
asmlinkage void __do_softirq(void)
{
struct softirq_action *h;
__u32 pending;
int max_restart = MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART;
int cpu; pending = local_softirq_pending();
account_system_vtime(current); __local_bh_disable((unsigned long)__builtin_return_address());
trace_softirq_enter(); cpu = smp_processor_id();
restart:
/* Reset the pending bitmask before enabling irqs */
set_softirq_pending(); local_irq_enable(); h = softirq_vec; do {
if (pending & ) {
int prev_count = preempt_count(); h->action(h); if (unlikely(prev_count != preempt_count())) {
printk(KERN_ERR "huh, entered softirq %td %p"
"with preempt_count %08x,"
" exited with %08x?\n", h - softirq_vec,
h->action, prev_count, preempt_count());
preempt_count() = prev_count;
} rcu_bh_qsctr_inc(cpu);
}
h++;
pending >>= ;
} while (pending); local_irq_disable(); pending = local_softirq_pending();
if (pending && --max_restart)
goto restart; if (pending)
wakeup_softirqd(); trace_softirq_exit(); account_system_vtime(current);
_local_bh_enable();
}
4. Linux内核tasklet分析
(1)软中断是将操作推迟到将来某一个时刻执行的最有效的方法。由于该延迟机制处理复杂,多个处理器可以同时并且独立得处理(即do_softirq函数可以被多个CPU同时执行),并且一个软中断的处理程序可以在多个CPU上同时执行,因此处理程序必须要被设计为完全可重入和线程安全的。此外临界区必须用自旋锁保护。软中断因为这些原因显得太过于麻烦,因此引入tasklet机制。
(2)tasklet是基于软中断实现的,确切的说应该是软中断的一个类型。所以根据软中断的性质,一个软中断类型对应一个软中断处理程序action。同理,也可以推出tasklet也会对应于一个唯一的action。
(3)每一个CPU都会有自己独立的tasklet队列,虽然一个tasklet类型的软中断只对应一个action处理程序,但是我们可以在该处理程序中轮询执行一个tasklet队列,队列里面的每一个tasklet_struct都会对应一个tasklet处理函数,这样当我们的驱动程序中需要使用到tasklet的时候,只要往这个tasklet队列加入我们自定义的tasklet_struct对象就可以了。同时,由于每一个CPU都会有一个tasklet队列,并且每一个CPU只会执行自己tasklet队列里面的tasklet_struct对象,因此tasklet并不需要自旋锁的保护(当然这只能是对同一个tasklet而言,如果多个不同的tasklet需要使用同一资源的话,仍需要自旋锁的保护)。
(4)Linux内核通过一个tasklet_struct结构体来描述一个tasklet对象,该结构体定义在include\linux\interrupt.h文件中
struct tasklet_struct
{
struct tasklet_struct *next;
unsigned long state;
atomic_t count;
void (*func)(unsigned long);
unsigned long data;
};
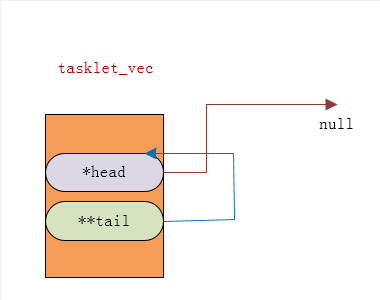
(5)tasklet的队列示意图
(5)Linux内核时通过名为tasklet_vec的tasklet_head结构体来组织tasklet对象的
struct tasklet_head
{
struct tasklet_struct *head;
struct tasklet_struct **tail;
};
head:指向第一个tasklet_struct结构体的指针
tail:指向tasklet队列最后一个tasklet_struct的next指针的地址
(6)如果tasklet队列没有元素,两个指针的指向是这样的
(7)向tasklet队列添加tasklet_struct对象,就是将最后一个tasklet_sturct的next指针指向新加的tasklet_struct对象,同时将列表头的tail指针的指针指向新加的tasklet_struct结构体的next指针的地址。代码如下
tasklet_struct * t;
* _get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).tail = t;
_get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).tail = &(t->next);
(8)tasklet类型的软中断唯一对应的action叫做tasklet_action(一般其他类型软中断的action都是由用户自己编写,但是tasklet不一样,Linux设计师已经帮我们实现了。所以也是因为这样,tasklet被广泛应用于驱动程序中)
static void tasklet_action(struct softirq_action *a)
{
struct tasklet_struct *list; local_irq_disable();
list = __get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).head;
__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).head = NULL;
__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).tail = &__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).head;
local_irq_enable(); while (list) {
struct tasklet_struct *t = list; list = list->next; if (tasklet_trylock(t)) {
if (!atomic_read(&t->count)) {
if (!test_and_clear_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))
BUG();
t->func(t->data);
tasklet_unlock(t);
continue;
}
tasklet_unlock(t);
} local_irq_disable();
t->next = NULL;
*__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).tail = t;
__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).tail = &(t->next);
__raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_enable();
}
}
(9)另一个tasklet非常重要的函数,就是tasklet_schedule,这个函数通常用于中断处理程序中,用于将tasklet_struct加入所在CPU的tasklet队列,同时将tasklet软中断挂起。
因为我们知道,在中断的上半部中的irq_exit函数中,会激活do_softirq函数,所以在中断处理程序中使用tasklet_schedule函数就显得特别必要。tasklet_schedule源代码如下,
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))
__tasklet_schedule(t);
}
test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state):这个函数的目的是设置t->state的第TASKLET_STATE_SCHED(0)位,并返回t->state的第TASKLET_STATE_SCHED位原来的值。
(10)_tasklet_schedule函数:
void __tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags; local_irq_save(flags);
t->next = NULL;
*__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).tail = t;
__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).tail = &(t->next);
raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
(11)我们驱动程序中若要使用tasklet,首先我们还必须要创建一个tasklet_struct对象,通常创建tasklet_struct对象一共有两种方式:
① 静态方式:
#define DECLARE_TASKLET(name, func, data) \
struct tasklet_struct name = { NULL, , ATOMIC_INIT(), func, data } #define DECLARE_TASKLET_DISABLED(name, func, data) \
struct tasklet_struct name = { NULL, , ATOMIC_INIT(), func, data }
② 动态方式:
static struct tasklet_struct my_tasklet;
tasklet_init(&my_tasklet, tasklet_handler, ); //count = 0,处于激活状态。
tasklet_init源码
void tasklet_init(struct tasklet_struct *t,
void (*func)(unsigned long), unsigned long data)
{
t->next = NULL;
t->state = ;
atomic_set(&t->count, );
t->func = func;
t->data = data;
}
然后,我们再调用tasklet_schedule函数将tasklet对象加入到tasklet队列中即可。
Linux中断分层--软中断和tasklet的更多相关文章
- Linux中断分层技术
一.中断嵌套 当系统正在执行某中断处理函数时,又产生了一个新的中断,这就叫做中断嵌套.当中断为慢速中断时,新的中断会取代当前中断,即当前中断没有执行完就结束 了:当中断为快速中断时,新的终端就不会产 ...
- Linux中断分层--工作队列
1. 工作队列是一种将任务推后执行的方式,它把推后的任务交由一个内核线程去执行.这样中断的下半部会在进程上下文执行,他允许重新调度甚至睡眠.每个被推后的任务叫做“工作”,由这些工作组成的队列称为工作队 ...
- linux内核--软中断与tasklet
硬件中断通常都需要在最短的时间内执行完毕,如果将所有硬件中断相关的处理都放在硬件中断处理程序中,那么就达不到这个目的. 通过linux提供的软中断和tasklet,可以将硬件中断处理程序中可以延迟处理 ...
- Linux中断底半部机制
参考: Linux下半部处理之软中断 linux中断底半部机制 <深入理解Linux内核>软中断/tasklet/工作队列 软中断和tasklet介绍 详解操作系统中断 Linux内核:中 ...
- Linux中断管理 (2)软中断和tasklet
目录: <Linux中断管理> <Linux中断管理 (1)Linux中断管理机制> <Linux中断管理 (2)软中断和tasklet> <Linux中断管 ...
- linux中断源码分析 - 软中断(四)
本文为原创,转载请注明:http://www.cnblogs.com/tolimit/ 在上一篇文章中,我们看到中断实际分为了两个部分,俗称就是一部分是硬中断,一部分是软中断.软中断是专门用于处理中断 ...
- Linux内核中的软中断、tasklet和工作队列具体解释
[TOC] 本文基于Linux2.6.32内核版本号. 引言 软中断.tasklet和工作队列并非Linux内核中一直存在的机制,而是由更早版本号的内核中的"下半部"(bottom ...
- Linux软中断、tasklet和工作队列
Linux内核中的软中断.tasklet和工作队列详解 引言 软中断.tasklet和工作队列并不是Linux内核中一直存在的机制,而是由更早版本的内核中的“下半部”(bottom half)演变而来 ...
- Linux中断 - tasklet
一.前言 对于中断处理而言,linux将其分成了两个部分,一个叫做中断handler(top half),属于不那么紧急需要处理的事情被推迟执行,我们称之deferable task,或者叫做bott ...
随机推荐
- Django ——Timezone 处理
Django ——Timezone 处理 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37049781/article/details/79347278 2018年02月22日 14:50:24 ...
- Part10-C语言环境初始化-C与汇编混合编程lesson4
1.为什么要混合编程 汇编语言:执行效率高:编写繁琐: 执行效率高:能够更直接地控制处理器. c语言:可读性强,移植性好,调试方便. 1.汇编调用c函数 2.c调用汇编函数 汇编语言定义的函数(标号) ...
- 编写高质量代码改善C#程序的157个建议——建议4: TryParse比Parse好
建议4: TryParse比Parse好 如果注意观察除string外的所有基元类型,会发现它们都有两个将字符串转型为本身的方法:Parse和TryParse.以类型double为例,这两个方法最简单 ...
- IOS GPS跟踪备注
CLLocationManager还提供了如下类方法来判断当前设备的定位相关服务状态. Ø + locationServicesEnabled:返回当前定位服务是否可用. Ø + deferredLo ...
- laravel中firstOrCreate的使用
laravel - firstOrCreate(判断是否存在, 不存在则新增数据) 1, 判断goods_name是否存在YKQ003213_G这个参数 2, 不存在则添加数组的内容 3, 需要设置自 ...
- asp.net core 外部认证多站点模式实现
PS:之前因为需要扩展了微信和QQ的认证,使得网站是可以使用QQ和微信直接登录.github 传送门 .然后有小伙伴问,能否让这个配置信息(appid, appsecret)按需改变,而不是在 Con ...
- EFCore扩展Select方法(根据实体定制查询语句)
EFCore扩展Select方法(根据实体定制查询语句) 通常用操作数据库的时候查询返回的字段是跟 我们的定义的实体是不一致的,所以往往针对UI或者接口层创建大量的Model, 而且需要手动对应字段 ...
- 【python】10分钟教你用Python做个打飞机小游戏超详细教程
更多精彩尽在微信公众号[程序猿声] 我知道你们一定想先看效果如何 00 目录 整体框架 开始之前-精灵类Sprite 子弹类class Bullet 玩家飞机类class Player 敌机类clas ...
- 冒泡排序 思想 JAVA实现
已知一个数组78.75.91.36.72.94.43.64.93.46,使用冒泡排序将此数组有序. 冒泡排序是一个运行时间为O(N²)的排序算法. 算法思想:(已从小到大为例) 78.75.91.36 ...
- Linux常用的命令(3)
1 文件的内容显示 cat 显示全部 more: 分屏幕显示,只能向后翻 less: 分屏幕显示,可以向上翻 head:查看前n行 默认10行 tail:查看后n行 -n -f: 查看文件尾部,不退出 ...
