Codeforces Round #162 (Div. 2) A~D 题解
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
There is a sequence of colorful stones. The color of each stone is one of red, green, or blue. You are given a string s. The i-th (1-based) character of s represents the color of the i-th stone. If the character is "R", "G", or "B", the color of the corresponding stone is red, green, or blue, respectively.
Initially Squirrel Liss is standing on the first stone. You perform instructions one or more times.
Each instruction is one of the three types: "RED", "GREEN", or "BLUE". After an instruction c, if Liss is standing on a stone whose colors is c, Liss will move one stone forward, else she will not move.
You are given a string t. The number of instructions is equal to the length of t, and the i-th character of t represents the i-th instruction.
Calculate the final position of Liss (the number of the stone she is going to stand on in the end) after performing all the instructions, and print its 1-based position. It is guaranteed that Liss don't move out of the sequence.
The input contains two lines. The first line contains the string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 50). The second line contains the string t (1 ≤ |t| ≤ 50). The characters of each string will be one of "R", "G", or "B". It is guaranteed that Liss don't move out of the sequence.
Print the final 1-based position of Liss in a single line.
RGB
RRR
2
RRRBGBRBBB
BBBRR
3
BRRBGBRGRBGRGRRGGBGBGBRGBRGRGGGRBRRRBRBBBGRRRGGBBB
BBRBGGRGRGBBBRBGRBRBBBBRBRRRBGBBGBBRRBBGGRBRRBRGRB
15
模拟;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 200005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii; inline int rd() {
int x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/
string s, t; int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> s >> t;
int lens = s.length();
int lent = t.length();
int pos = 0;
int st = 0;
while (st < lent) {
if (t[st] == s[pos]) {
pos++; st++;
}
else st++;
}
printf("%d\n", pos + 1);
return 0;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Squirrel Liss loves nuts. There are n trees (numbered 1 to n from west to east) along a street and there is a delicious nut on the top of each tree. The height of the tree i is hi. Liss wants to eat all nuts.
Now Liss is on the root of the tree with the number 1. In one second Liss can perform one of the following actions:
- Walk up or down one unit on a tree.
- Eat a nut on the top of the current tree.
- Jump to the next tree. In this action the height of Liss doesn't change. More formally, when Liss is at height h of the tree i (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1), she jumps to height h of the tree i + 1. This action can't be performed if h > hi + 1.
Compute the minimal time (in seconds) required to eat all nuts.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of trees.
Next n lines contains the height of trees: i-th line contains an integer hi (1 ≤ hi ≤ 104) — the height of the tree with the number i.
Print a single integer — the minimal time required to eat all nuts in seconds.
2
1
2
5
5
2
1
2
1
1
14
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 200005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii; inline int rd() {
int x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/
int n;
int h[maxn];
int df[maxn];
int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
n = rd();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
h[i] = rd();
}
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)df[i] = h[i + 1] - h[i];
ans += 1ll*(h[1] + 1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (h[i] >= h[i - 1]) {
ans += 1ll*(1 + 1 + h[i] - h[i - 1]);
}
else {
ans += 1ll*(h[i - 1] - h[i] + 1 + 1);
}
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Squirrel Liss lived in a forest peacefully, but unexpected trouble happens. Stones fall from a mountain. Initially Squirrel Liss occupies an interval [0, 1]. Next, n stones will fall and Liss will escape from the stones. The stones are numbered from 1 to n in order.
The stones always fall to the center of Liss's interval. When Liss occupies the interval [k - d, k + d] and a stone falls to k, she will escape to the left or to the right. If she escapes to the left, her new interval will be [k - d, k]. If she escapes to the right, her new interval will be [k, k + d].
You are given a string s of length n. If the i-th character of s is "l" or "r", when the i-th stone falls Liss will escape to the left or to the right, respectively. Find the sequence of stones' numbers from left to right after all the n stones falls.
The input consists of only one line. The only line contains the string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 106). Each character in s will be either "l" or "r".
Output n lines — on the i-th line you should print the i-th stone's number from the left.
llrlr
3
5
4
2
1
rrlll
1
2
5
4
3
lrlrr
2
4
5
3
1
In the first example, the positions of stones 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 will be 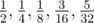 , respectively. So you should print the sequence: 3, 5, 4, 2, 1.
, respectively. So you should print the sequence: 3, 5, 4, 2, 1.
偏思维一点,找到规律就行了;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 1000005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii; inline int rd() {
int x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/ string s;
int pos[maxn];
int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> s;
int lens = s.length();
int ed = lens - 1;
int st = 0;
int tot = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
if (s[i] == 'l') {
pos[ed] = (i + 1); ed--;
}
else {
pos[st] = (i + 1); st++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
printf("%d\n", pos[i]);
}
return 0;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Squirrel Liss is interested in sequences. She also has preferences of integers. She thinks n integers a1, a2, ..., an are good.
Now she is interested in good sequences. A sequence x1, x2, ..., xk is called good if it satisfies the following three conditions:
- The sequence is strictly increasing, i.e. xi < xi + 1 for each i (1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1).
- No two adjacent elements are coprime, i.e. gcd(xi, xi + 1) > 1 for each i (1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1) (where gcd(p, q) denotes the greatest common divisor of the integers p and q).
- All elements of the sequence are good integers.
Find the length of the longest good sequence.
The input consists of two lines. The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of good integers. The second line contains a single-space separated list of good integers a1, a2, ..., an in strictly increasing order (1 ≤ ai ≤ 105; ai < ai + 1).
Print a single integer — the length of the longest good sequence.
5
2 3 4 6 9
4
9
1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10
4
In the first example, the following sequences are examples of good sequences: [2; 4; 6; 9], [2; 4; 6], [3; 9], [6]. The length of the longest good sequence is 4.
有趣的dp题目;
考虑枚举因数;
用dp[i]表示以因数i结尾时的最大值;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 1000005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-5
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii; inline int rd() {
int x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
} ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; } /*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/ int n;
int a[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
int ans; void sol(int x) {
int maxx = -inf;
for (int i = 2; i <= sqrt(x); i++) {
if (x%i == 0) {
maxx = max(max(maxx, dp[i]), dp[x / i]);
}
}
maxx = max(maxx, dp[x]);
for (int i = 2; i <= sqrt(x); i++) {
if (x%i == 0) {
dp[i] = maxx + 1; dp[x / i] = maxx + 1;
while (x%i == 0)x /= i;
}
}
dp[x] = maxx + 1; ans = max(ans, maxx + 1);
} int main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
n = rd();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = rd();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)sol(a[i]);
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #162 (Div. 2) A~D 题解的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #612 (Div. 2) 前四题题解
这场比赛的出题人挺有意思,全部magic成了青色. 还有题目中的图片特别有趣. 晚上没打,开virtual contest打的,就会前三道,我太菜了. 最后看着题解补了第四道. 比赛传送门 A. An ...
- Codeforces Round #198 (Div. 2)A,B题解
Codeforces Round #198 (Div. 2) 昨天看到奋斗群的群赛,好奇的去做了一下, 大概花了3个小时Ak,我大概可以退役了吧 那下面来稍微总结一下 A. The Wall Iahu ...
- Codeforces Round #672 (Div. 2) A - C1题解
[Codeforces Round #672 (Div. 2) A - C1 ] 题目链接# A. Cubes Sorting 思路: " If Wheatley needs more th ...
- Codeforces Round #614 (Div. 2) A-E简要题解
链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1293 A. ConneR and the A.R.C. Markland-N 题意:略 思路:上下枚举1000次扫一遍,比较一下 ...
- Codeforces Round #610 (Div. 2) A-E简要题解
contest链接: https://codeforces.com/contest/1282 A. Temporarily unavailable 题意: 给一个区间L,R通有网络,有个点x,在x+r ...
- Codeforces Round #611 (Div. 3) A-F简要题解
contest链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1283 A. Minutes Before the New Year 题意:给一个当前时间,输出离第二天差多少分钟 ...
- Codeforces Round #162 (Div. 1) B. Good Sequences (dp+分解素数)
题目:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/264/B 题意:给你一个递增序列,然后找出满足两点要求的最长子序列 第一点是a[i]>a[i-1] 第二 ...
- Codeforces Round #499 (Div. 2) D. Rocket题解
题目: http://codeforces.com/contest/1011/problem/D This is an interactive problem. Natasha is going to ...
- Codeforces Round #499 (Div. 2) C Fly题解
题目 http://codeforces.com/contest/1011/problem/C Natasha is going to fly on a rocket to Mars and retu ...
随机推荐
- Educational Codeforces Round 45 (Rated for Div. 2)
A bracket sequence is a string containing only characters "(" and ")". A regular ...
- Hadoop编码解码【压缩解压缩】机制详解(1)
想想一下,当你需要处理500TB的数据的时候,你最先要做的是存储下来.你是选择源文件存储呢?还是处理压缩再存储?很显然,压缩编码处理是必须的.一段刚刚捕获的60分钟原始视屏可能达到2G,经过压缩处理可 ...
- Gym - 101128C:Canvas Painting
这个就是哈夫曼树哇~ 我们仨英语太差了,跟榜时候才看出来是哈夫曼树雾 一个优先队列就可以搞定 #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #i ...
- mfs教程(三)
mfs文件系统(三) 使用 MooseFS 一.挂载文件系统 启动管理服务器(master server)和数据服务器(chunkservers) (chunkservers一个是必需的,但至少两个 ...
- js,javascript生成 UUID的四种方法
全局唯一标识符(GUID,Globally Unique Identifier)也称作 UUID(Universally Unique IDentifier) . GUID是一种由算法生成的二进制长度 ...
- Python05 函数
待更新... 2018-4-16 09:00:30
- Luogu 2597 [ZJOI2012]灾难
BZOJ 2815. 解法还是挺巧妙的. 放上写得很详细很好懂的题解链接 戳这里. 一个物种$x$如果要灭绝,那么沿着它的入边反向走走走,一定可以走到一个点$y$,如果这个点$y$的物种灭绝了,那么 ...
- 利用osmosis导出osm城市数据
转载(未测试) 方法核心就是利用osmosis的导出指定功能,即是从大范围导出小范围的基本用例. 我们只需要知道我们所需要提取的城市的经纬度范围, 例如广州市的经纬度范围是北纬22.26~23.56度 ...
- IIS 身份验证
IIS 支持以下身份验证模式: 匿名.如果不需要对客户端进行身份验证(或者使用自定义身份验证机制,如窗体身份验证),则可将 IIS 配置为允许匿名访问.在该事件中,IIS 创建一个 Windows 令 ...
- Deep Visual-Semantic Alignments for Generating Image Descriptions(深度视觉-语义对应对于生成图像描述)
https://cs.stanford.edu/people/karpathy/deepimagesent/ Abstract We present a model that generates na ...
