jdk源码阅读笔记-AbstractStringBuilder
AbstractStringBuilder 在java.lang 包中,是一个抽象类,实现 Appendable 接口和 CharSequence 接口,这个类的诞生是为了解决 String 类在创建对象的时候总是创建新的对象的问题的。AbstractStringBuilder 有两个子类,分别是 StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer,这两个类的区别将会在下面说到。
从源码中可以看出来,AbstractStringBuilder类和String类是非常相似的,设计的思想可以说是一模一样,其内部维护的都是一个char类的数组。唯一的区别在于这个数组的修饰符不一样,String类维护的是一个不可变的数组,而后者维护的则是一个可变的数组。
AbstractStringBuilder源码:
String类源码:

AbstractStringBuilder 的应用场景
该类主要适用于在短时间内创建大量字符串的场景,比如在一个循环体中需要拼接一个非常长的字符串时,可以考虑 AbstractStringBuilder 的实现类来创建字符串,这样不管这个字符串有多长最终都只会生成一个对象,但是如果在循环体中使用String来创建字符串时,此时会创建出大量的对象,这样不仅影响性能,同时如果内存较小的情况下很容易发生oom异常。下面列举一下使用的建议:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 不建议这样做:
* 耗时:30726
*/
String str = "";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = ; i < ; i++) {
str += i;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时间:" + (end - start));
/**
* 推荐做法:
* 耗时:2
*/
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = ; i < ; i++) {
builder.append(i);
}
str = builder.tostring();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时间:" + (end - start));
}
}
上面的代码中分别将 100000 拼接成一个字符串,记录所需时间,总共运行了三次,第一种直接使用String来拼接三次耗时均在3000毫秒以上,第二种使用StringBuilder方式拼接字符串时三次最高的一次才为15毫秒,通过对比发现使用StringBuilder比String直接拼接性能高了非常多。
虽然在拼接大字符串是StringBuilder比String有着明显的优势,但是这并不意味这StringBuilder可以完全替代String,比如在创建比较小的字符串时使用String来创建就足够了,如果还是继续使用StringBuilder来创建,这样反而会对程序的性能有一定的影响,毕竟StringBuilder是一个对象,大量使用的话也会占内存。所以在使用字符串的时候要考虑清楚那种方式比较合理,这样才有助于提高程序的速度。
AbstractStringBuilder 常用api
AbstractStringBuilder的 常用api跟String常用的api几乎是一样的,而且其内部的实现方法也可以说是大同小异,所以就不再这里赘述了,只要了解了System类的静态方法 arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos,int length) 即可。里面的几乎所有的方法都用到了这个方法,是该类的核心。
1.getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)
该方法是将AbstractStringBuilder 的value数组 srcBegin 位置开始 srcEnd - srcBegin 长度的数组 复制到 dst 数组 dstBegin 开始的位置中;
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin)
{
if (srcBegin < )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcBegin);
if ((srcEnd < ) || (srcEnd > count))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(srcEnd);
if (srcBegin > srcEnd)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("srcBegin > srcEnd");
//value: AbstractStringBuilder 中维护的 char类型数组
System.arraycopy(value, srcBegin, dst, dstBegin, srcEnd - srcBegin);
}
大概流程是这样子的:

第一次画图有点难看,将就着看。。。
2、AbstractStringBuilder append(String str)
该方法是在当前的字符串的后面添加字符串 str。该方法有非常多重载的方法,方法体大都一样,所以其他的就不一一说明了。
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) {
if (str == null)
return appendNull();
int len = str.length();
//将value数组长度增加 len 个长度,以便后面将字符串放入到数组中
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
//将字符串 str 放入到 数组 value 中,从数组后面添加
//count:当前 字符串长度
str.getChars(, len, value, count);
//字符串长度增加 len
count += len;
return this;
}
3、public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end)
该方法是从当前字符串中的 start位置开始删除字符串删到 end 位置;
public AbstractStringBuilder delete(int start, int end) {
/**
* 删除边界检查
*/
if (start < )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
end = count;
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException();
//删除的长度
int len = end - start;
if (len > ) {
//注意:删除方法并不会重新创建一个新的数组,而是在原来的数组中将
//需要删除的字符移动数组的最后面,然后将字符串的长度减少 len 个长度
//从而达到删除的效果,这一点需要的注意,我在看代码的花了一点时间才弄明白
System.arraycopy(value, start+len, value, start, count-end);
//字符串长度减少 len 个长度
count -= len;
}
return this;
}
举个例子,加入当前的字符串为 abcdefg , 然后执行删除操作,开始位置start为1,结束为止end为3,count为7,len为2,数组复制的大致流程如下: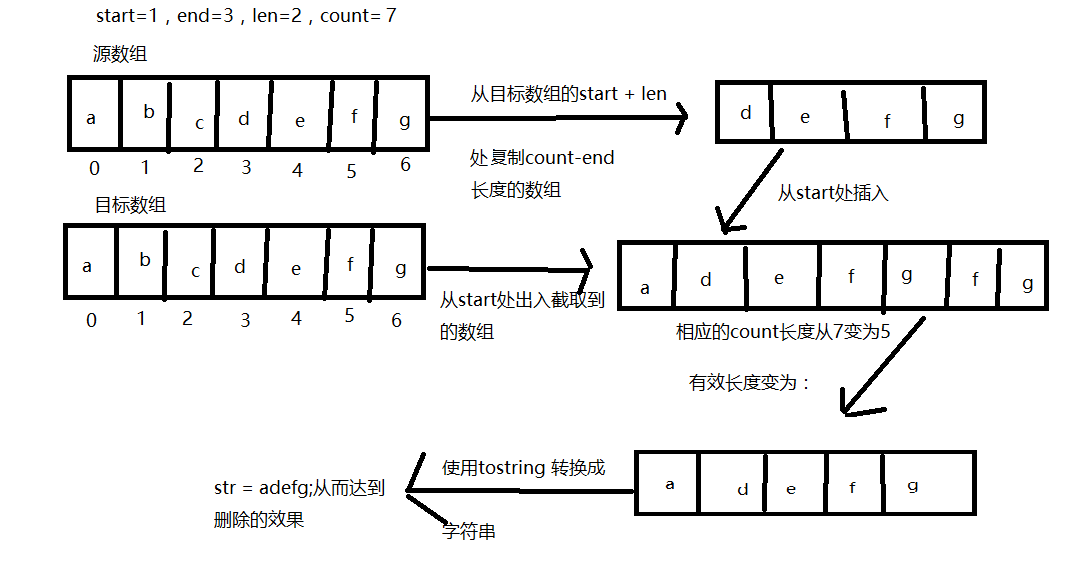
值得注意的是,在删除时数组长度并不会减少,这个跟我之前想的有很大的出入,减少的是count的值,即字符串的长度。
4、public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str)
该方法是指当前字符串start 到 end 区间的字符串替换成 str 字符串。
public AbstractStringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) {
if (start < )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (start > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > length()");
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException("start > end");
if (end > count)
end = count;
//替换字符串长度
int len = str.length();
//替换后当前字符串长度
int newCount = count + len - (end - start);
//根据替换后字符串长度调整 char 数组的大小,避免数组下标溢出异常
ensureCapacityInternal(newCount);
//对扩容后的char数组元素进行移动
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end);
//将替换字符串添加到char数组中
str.getChars(value, start);
//修改有效字符串的长度
count = newCount;
return this;
}
大致的执行流程如下:
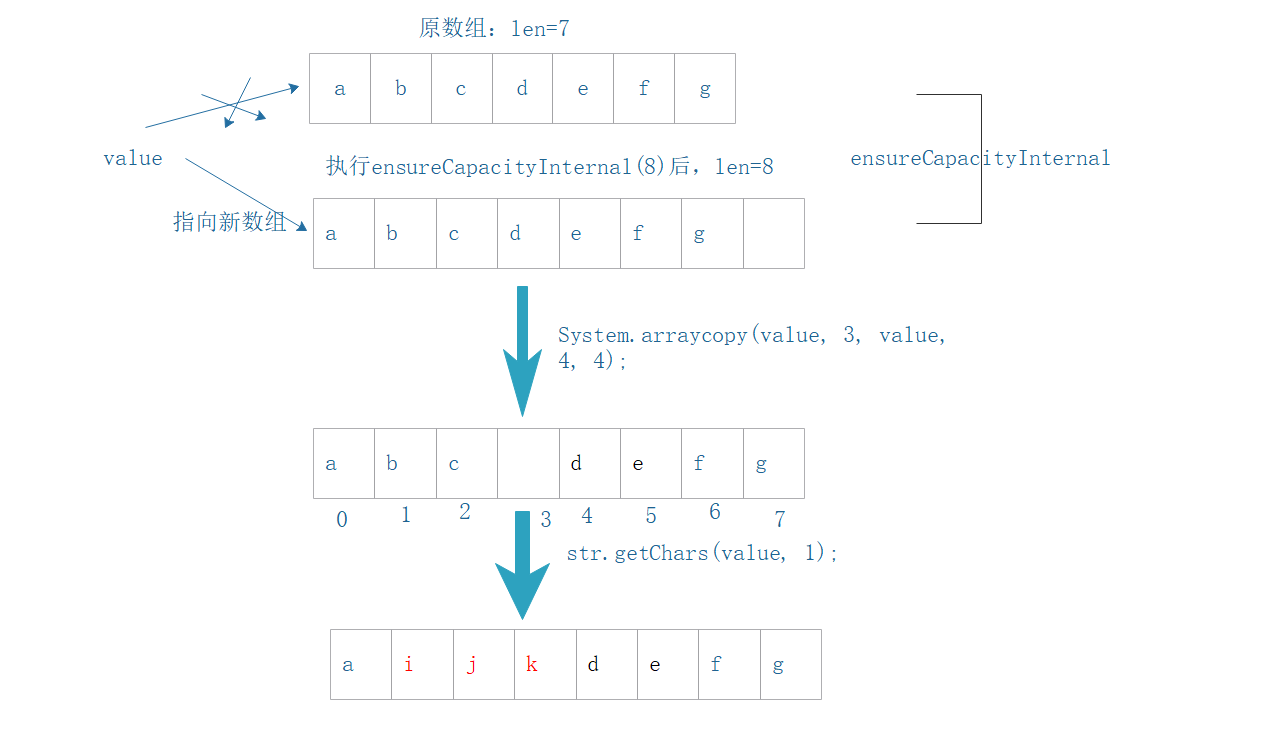
加入当前的字符串为 abcdefg,start=1,end=3,替换字符串str为 ijk,则,
第一步:计算出替换字符串后的长度:int newCount = 7 + 3 - (3-1)= 8;
第二步:创建一个newCount 大小的数组,将原数组数据放入到新数组中,新数组多出来的元素默认为 null;
上面两个步骤是在 ensureCapacityInternal(newCount) 方法中完成的。
第三步:执行System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start + len, count - end)方法,该方法是将替换区间的后段数据移到最后面,顺序保持不变;
第四步:将替换字符串放入到新的数组中;
第五步:更新count 变量,该变量使用来记录字符串的长度。
执行流程图:
5、public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int index, char[] str, int offset,int len)
该方法是用来向字符串中插入字符串,index:插入位置;str:插入字符数组;offset字符数组开始开始插入位置;len:插入长度。该方法有非常多的重载的方法,操作流程基本一致,无非是传入是数组的话就调用 arraycopy,是字符串则调用String 的 getChars 方法给数组赋值。
public AbstractStringBuilder insert(int index, char[] str, int offset,
int len)
{
//检查数组是否越界
if ((index < ) || (index > length()))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
if ((offset < ) || (len < ) || (offset > str.length - len))
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(
"offset " + offset + ", len " + len + ", str.length "
+ str.length);
//数组扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(count + len);
//插入点后段后移
System.arraycopy(value, index, value, index + len, count - index);
//将插入数组str放入到value中
System.arraycopy(str, offset, value, index, len);
//更新长度
count += len;
return this;
}
假如value数组为:a,b,c,d,e ,插入数组为:str=f,g,h,index=1,offset=0,len=str.length=3,则count=5,大概执行流程如下:

6、public String substring(int start, int end)
public String substring(int start, int end) {
if (start < )
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(start);
if (end > count)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end);
if (start > end)
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(end - start);
//调用String 构造方法截取
return new String(value, start, end - start);
}
StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer 的区别:
1.两者都继承了 AbstractStringBuilder 抽象类。
2.前者不是线程安全的,后者是线程安全的,后者在每个方法都添加了 synchronized 关键字,所以它是线程安全的。
3.两个都是维护一个可变的字符串;
4.在单线程或对安全性不高的程序中,建议使用前者,在多线程中建议使用后者。
总结:
1、AbstractStringBuilder 和 String 的使用方式如出一辙;
2、AbstractStringBuilder 的设计是为了解决String不可变的性质带来的问题的。
3、AbstractStringBuilder 不能完全替代String,具体场景具体分析。
jdk源码阅读笔记-AbstractStringBuilder的更多相关文章
- jdk源码阅读笔记-LinkedHashMap
Map是Java collection framework 中重要的组成部分,特别是HashMap是在我们在日常的开发的过程中使用的最多的一个集合.但是遗憾的是,存放在HashMap中元素都是无序的, ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-HashSet
通过阅读源码发现,HashSet底层的实现源码其实就是调用HashMap的方法实现的,所以如果你阅读过HashMap或对HashMap比较熟悉的话,那么阅读HashSet就很轻松,也很容易理解了.我之 ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-ArrayList
一.ArrayList概述 首先我们来说一下ArrayList是什么?它解决了什么问题?ArrayList其实是一个数组,但是有区别于一般的数组,它是一个可以动态改变大小的动态数组.ArrayList ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记
1.环境搭建 http://www.komorebishao.com/2020/idea-java-jdk-funyard/ 2. 好的源码阅读资源 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.co ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-Integer
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> Integer 由final修饰了,所以该 ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-HashMap
文章出处:[noblogs-it技术博客网站]的博客:jdk1.8源码分析 在Java语言中使用的最多的数据结构大概右两种,第一种是数组,比如Array,ArrayList,第二种链表,比如Array ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-LinkedList
一.LinkedList概述 LinkedList的底层数据结构为双向链表结构,与ArrayList相同的是LinkedList也可以存储相同或null的元素.相对于ArrayList来说,Linke ...
- jdk源码阅读笔记-String
本人自学java两年,有幸初入这个行业,所以功力尚浅,本着学习与交流的态度写一些学习随笔,什么错误的地方,热烈地希望园友们提出来,我们共同进步!这是我入园写的第一篇文章,写得可能会很乱. 一.什么是S ...
- JDK源码阅读(三):ArraryList源码解析
今天来看一下ArrayList的源码 目录 介绍 继承结构 属性 构造方法 add方法 remove方法 修改方法 获取元素 size()方法 isEmpty方法 clear方法 循环数组 1.介绍 ...
随机推荐
- (linux虚拟机)克隆得到的虚拟机修改网卡信息和IP地址,以及DNS
克隆得到的虚拟机,与原先的系统是一模一样的包括MAC地址和IP地址.需要修改成信息. 克隆完事之后,首先在 点击生成一个新的MAC地址.然后启动,登陆. vim /etc/udev/rules.d/7 ...
- 【数据可视化之Flask】快速设计和部署Flask网站
Flask是Python应用于WEB开发的第三方开源框架,以设计简单高效著称.我也尝试过Django,相对于Flask显得更加全面同样也更加笨重,并且我也不需要它的后台管理功能,因此选择了Flask作 ...
- Cython入门Demo(Linux)
众所周知,Python语言是非常简单易用的,但是python程序在运行速度上还是有一些缺陷.于是,Cython就应运而生了,Cython作为Python的C扩展,保留了Python的语法特点,集成C语 ...
- 基于.net的爬虫应用-DotnetSpider
最近应朋友的邀请,帮忙做了个简单的爬虫程序,要求不高,主要是方便对不同网站的爬取进行扩展,获取到想要的数据信息即可.当然,基于数据的后期分析功能是后话,以后的随笔我会逐步的介绍. 开源的爬虫框架比较多 ...
- Runc 简介
RunC 是什么? RunC 是一个轻量级的工具,它是用来运行容器的,只用来做这一件事,并且这一件事要做好.我们可以认为它就是个命令行小工具,可以不用通过 docker 引擎,直接运行容器.事实上,r ...
- 第七章 mysql 事务索引以及触发器,视图等等,很重要又难一点点的部分
[索引] 帮助快速查询 MyISAM ,InnoDB支持btree索引 Memory 支持 btree和hash索引 存储引擎支持 每个表至少16个索引 总索引长度至少256字节 创建索引的优 ...
- laravel5.5 延时队列的使用
队列这个知识相对比较冷门,因为平时的CURD基本用不到这个知识,今天用到了,所以就写个博客记录一下吧. 首先你得清楚要用什么驱动,除了database队列驱动(选择database驱动要php art ...
- JS方法:数字转换为千分位字符
/** * 数字转为千分位字符 * @param {Number} num * @param {Number} point 保留几位小数,默认2位 */ function parseToThousan ...
- Vim手册
什么是 vim? Vim是从 vi 发展出来的一个文本编辑器.代码补完.编译及错误跳转等方便编程的功能特别丰富,在程序员中被广泛使用. 简单的来说, vi 是老式的字处理器,不过功能已经很齐全了,但是 ...
- Linux内核编程、调试技巧小集
1. 内核中通过lookup_symbol_name获取函数名称 内核中很多结构体成员是函数,有时可能比较复杂不知道具体使用哪一个函数.这是可以通过lookup_symbol_name来获取符号表名称 ...
