Pandas与Matplotlib基础
.png)
pip install pandas
.png)
s = pd.Series([3, -5, 7, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
print(s) # result
a 3
b -5
c 7
d 4
dtype: int64
s.index = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']
print(s) # result
A 3
B -5
C 7
D 4
dtype: int64
data = {
'Country': ['Belgium', 'India', 'Brazil'],
'Capital': ['Brussels', 'New Delhi', 'Brasília'],
'Population': [11190846, 1303171035, 207847528]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['Country', 'Capital', 'Population'])
print(df)
# result
Country Capital Population
0 Belgium Brussels 11190846
1 India New Delhi 1303171035
2 Brazil Brasília 207847528
print(df.shape) # result
(260, 218)
print(df.columns)
print(df.index) # result
Index(['Life expectancy', '', '', '', '', '', '',
'', '', '',
...
'', '', '', '', '', '', '', '', '',
''],
dtype='object', length=218) Int64Index([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
...
250, 251, 252, 253, 254, 255, 256, 257, 258, 259],
dtype='int64', length=260)
print(df.info()) # result
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 260 entries, 0 to 259
Columns: 218 entries, Life expectancy to 2016
dtypes: float64(217), object(1)
memory usage: 444.8+ KB
print(df.head()) # result
Life expectancy 1800 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 \
0 Abkhazia NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 Afghanistan 28.21 28.20 28.19 28.18 28.17 28.16 28.15
2 Akrotiri and Dhekelia NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
3 Albania 35.40 35.40 35.40 35.40 35.40 35.40 35.40
4 Algeria 28.82 28.82 28.82 28.82 28.82 28.82 28.82 1807 1808 ... 2016
0 NaN NaN ... 0 NaN
1 28.14 28.13 ... 1 52.72
2 NaN NaN ... 2 NaN
3 35.40 35.40 ... 3 78.10
4 28.82 28.82 ... 4 76.50 [5 rows x 218 columns]
print(df.tail()) # result
Life expectancy 1800 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 \
255 Yugoslavia NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
256 Zambia 32.60 32.60 32.60 32.60 32.60 32.60 32.60 32.60
257 Zimbabwe 33.70 33.70 33.70 33.70 33.70 33.70 33.70 33.70
258 ?land NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
259 South Sudan 26.67 26.67 26.67 26.67 26.67 26.67 26.67 26.67 1808 ... 2016
255 NaN ... NaN
256 32.60 ... 57.10
257 33.70 ... 61.69
258 NaN ... NaN
259 26.67 ... 56.10 [5 rows x 218 columns]
selected_cols = ['', '', '']
date_df = df[selected_cols]
print(date_df.head()) # result
2010 2011 2012
0 NaN NaN NaN
1 53.6 54.0 54.4
2 NaN NaN NaN
3 77.2 77.4 77.5
4 76.0 76.1 76.2
print(df.loc[250, 'Life expectancy']) # result
250 Vietnam Name: Life expectancy, dtype: object
df.iloc[:10, -2:] # result
2015 2016
0 NaN NaN
1 53.8 52.72
2 NaN NaN
3 78.0 78.10
4 76.4 76.50
5 72.9 73.00
6 84.8 84.80
7 59.6 60.00
8 NaN NaN
9 76.4 76.50
mask = df > 50
print(df[mask].head()) #result
Life expectancy 1800 1801 1802 1803 1804 1805 1806 1807 \
0 Abkhazia NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 Afghanistan NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2 Akrotiri and Dhekelia NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
3 Albania NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
4 Algeria NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN 1808 ... 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016
0 NaN ... NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 NaN ... 52.4 52.8 53.3 53.6 54.0 54.4 54.8 54.9 53.8 52.72
2 NaN ... NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
3 NaN ... 76.6 76.8 77.0 77.2 77.4 77.5 77.7 77.9 78.0 78.10
4 NaN ... 75.3 75.5 75.7 76.0 76.1 76.2 76.3 76.3 76.4 76.50 [5 rows x 218 columns]
heights = [59.0, 65.2, 62.9, 65.4, 63.7]
data = {
'height': heights, 'sex': 'Male',
}
df_heights = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df_heights) # result
height sex
0 59.0 Male
1 65.2 Male
2 62.9 Male
3 65.4 Male
4 63.7 Male
df_heights.columns = ['HEIGHT', 'SEX']
df_heights.index = ['david', 'bob', 'lily', 'sara', 'tim']
print(df_heights) # result
HEIGHT SEX
david 59.0 Male
bob 65.2 Male
lily 62.9 Male
sara 65.4 Male
tim 63.7 Male
print(df_heights.sum()) # result
HEIGHT 316.2
SEX MaleMaleMaleMaleMale
dtype: object
print(df_heights.cumsum()) # result
HEIGHT SEX
david 59 Male
bob 124.2 MaleMale
lily 187.1 MaleMaleMale
sara 252.5 MaleMaleMaleMale
tim 316.2 MaleMaleMaleMaleMale
print(df_heights.max()) # result
HEIGHT 65.4
SEX Male
dtype: object
print(df_heights.min()) # result
HEIGHT 59
SEX Male
dtype: object
print(df_heights.mean()) # result
HEIGHT 63.24
dtype: float64
print(df_heights.median()) # result
HEIGHT 63.7
dtype: float64
print(df_heights.describe()) # result
HEIGHT
count 5.000000
mean 63.240000
std 2.589015
min 59.000000
25% 62.900000
50% 63.700000
75% 65.200000
max 65.400000
df_heights.drop(['david', 'tim'])
print(df_heights) # result
df_heights = df_heights.drop(['david', 'tim'])
print(df_heights) # result
HEIGHT SEX
bob 65.2 Male
lily 62.9 Male
sara 65.4 Male
print(df_heights.drop('SEX', axis=1))
# result
HEIGHT
david 177.0
bob 195.6
lily 188.7
sara 196.2
tim 191.1
print(df_heights.sort_index()) # result
HEIGHT SEX
bob 65.2 Male
david 59.0 Male
lily 62.9 Male
sara 65.4 Male
tim 63.7 Male
print(df_heights.sort_values(by='HEIGHT')) # result
HEIGHT SEX
david 59.0 Male
lily 62.9 Male
tim 63.7 Male
bob 65.2 Male
sara 65.4 Male
print(df_heights.rank()) # result
HEIGHT SEX
david 1.0 3.0
bob 4.0 3.0
lily 2.0 3.0
sara 5.0 3.0
tim 3.0 3.0
df_heights = df_heights.apply(lambda height: height*3)
print(df_heights) # result
HEIGHT SEX
david 177.0 MaleMaleMale
bob 195.6 MaleMaleMale
lily 188.7 MaleMaleMale
sara 196.2 MaleMaleMale
tim 191.1 MaleMaleMale
df = pd.read_csv("tips.csv")
print(df.info())
# result
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 244 entries, 0 to 243
Data columns (total 8 columns):
total_bill 244 non-null float64
tip 244 non-null float64
sex 244 non-null object
smoker 244 non-null object
day 244 non-null object
time 244 non-null object
size 244 non-null int64
fraction 244 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(1), object(4)
memory usage: 15.3+ KB
df = pd.read_csv('tips.csv', header=None, names=column_names)
df = pd.read_csv('tips.csv', header=None, names=column_names, na_values={'DAY': '-1'})
date_df = pd.read_csv('created_date.csv', parse_dates=[[3, 4, 5]])
.png)
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt df = pd.read_csv('percent-bachelors-degrees-women-usa.csv', index_col='Year')
print(df.info())
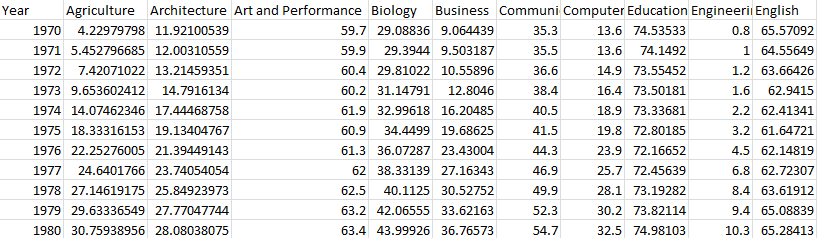
print(df.head()) # result
Agriculture Architecture Art and Performance Biology Business \ ... ... Social Sciences and History
Year ... ... Year
1970 4.229798 11.921005 59.7 29.088363 9.064439 ... ... 1970 36.8
1971 5.452797 12.003106 59.9 29.394403 9.503187 ... ... 1971 36.2
1972 7.420710 13.214594 60.4 29.810221 10.558962 ... ... 1972 36.1
1973 9.653602 14.791613 60.2 31.147915 12.804602 ... ... 1973 36.4
1974 14.074623 17.444688 61.9 32.996183 16.204850 ... ... 1974 37.3 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 42 entries, 1970 to 2011
Data columns (total 17 columns):
Agriculture 42 non-null float64
Architecture 42 non-null float64
Art and Performance 42 non-null float64
Biology 42 non-null float64
Business 42 non-null float64
Communications and Journalism 42 non-null float64
Computer Science 42 non-null float64
Education 42 non-null float64
Engineering 42 non-null float64
English 42 non-null float64
Foreign Languages 42 non-null float64
Health Professions 42 non-null float64
Math and Statistics 42 non-null float64
Physical Sciences 42 non-null float64
Psychology 42 non-null float64
Public Administration 42 non-null float64
Social Sciences and History 42 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(17)
memory usage: 5.9 KB
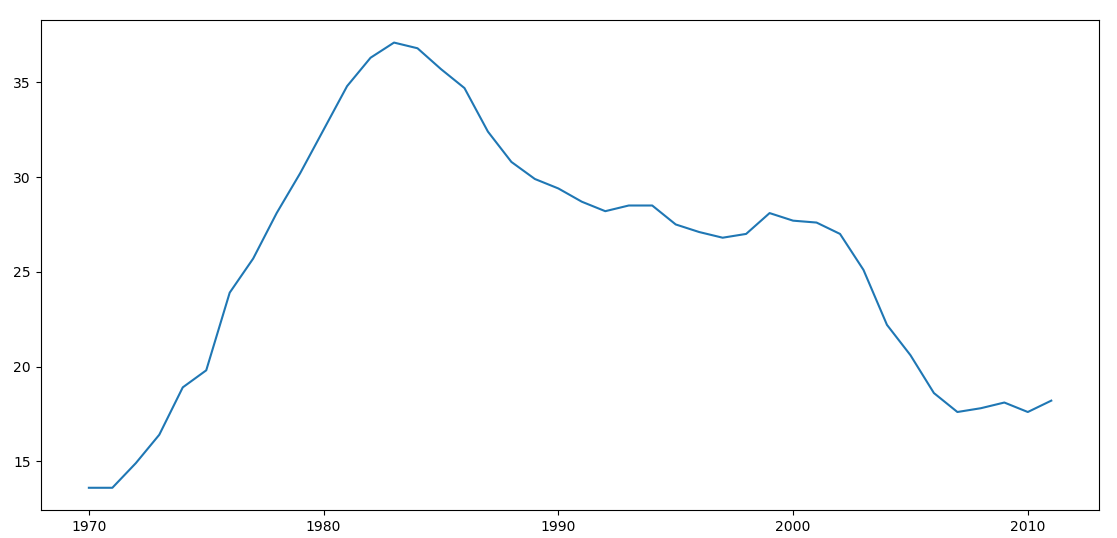
df_CS = df['Computer Science']
plt.plot(df_CS)
plt.show()
.png)
df_CS = df['Computer Science']
plt.plot(df_CS)
# 为图表添加标题
plt.title("Percentage of Computer Science's degrees awarded to women in the USA")
# 为X轴添加标签
plt.xlabel("Years")
# 为Y轴添加标签
plt.ylabel("Percentage")
plt.show()
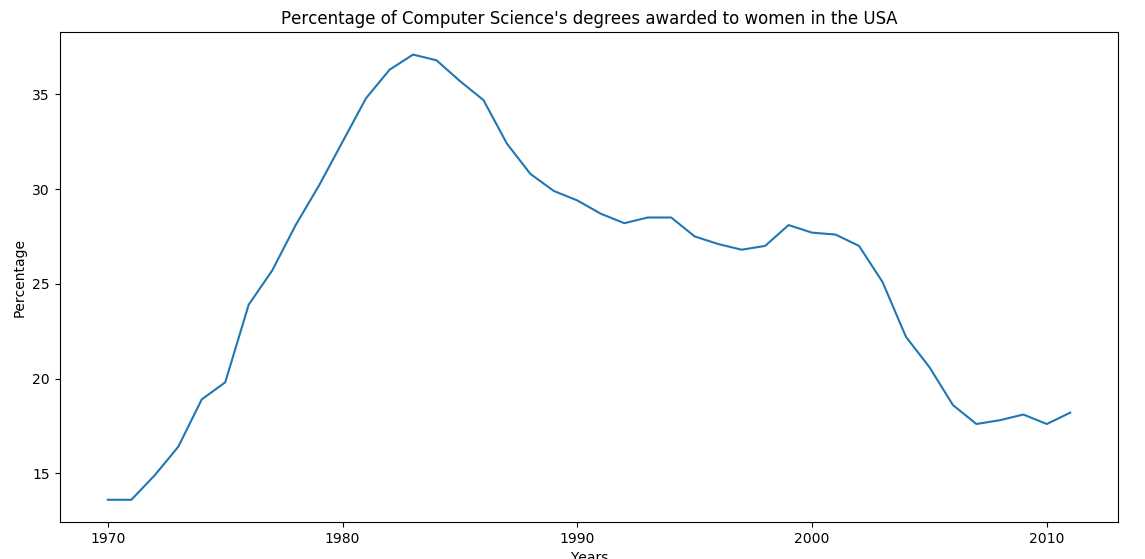
.png)
df_CS = df['Computer Science']
df_MS = df['Math and Statistics']
# 可以通过DataFrame的plot()方法直接绘制
# color指定线条的颜色
# style指定线条的样式
# legend指定是否使用标识区分
df_CS.plot(color='b', style='.-', legend=True)
df_MS.plot(color='r', style='-', legend=True)
plt.title("Percentage of Computer Science's degrees VS Math and Statistics's")
plt.xlabel("Years")
plt.ylabel("Percentage")
plt.show()
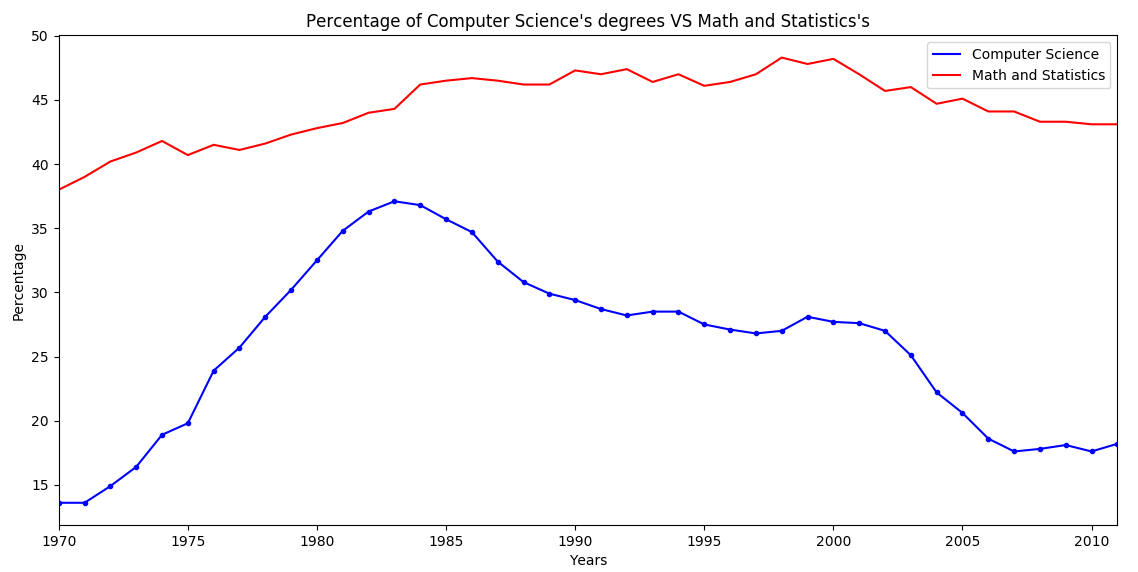
.png)
# alpha指定透明度(0~1)
df.plot(alpha=0.7)
plt.title("Percentage of bachelor's degrees awarded to women in the USA")
plt.xlabel("Years")
plt.ylabel("Percentage")
# axis指定X轴Y轴的取值范围
plt.axis((1970, 2000, 0, 200))
plt.show()

.png)
iris = pd.read_csv("iris.csv")
# 源数据中没有给column,所以需要手动指定一下
iris.columns = ['sepal_length', 'sepal_width', 'petal_length', 'petal_width', 'species']
# kind表示图形的类型
# x, y 分别指定X, Y 轴所指定的数据
iris.plot(kind='scatter', x='sepal_length', y='sepal_width')
plt.xlabel("sepal length in cm")
plt.ylabel("sepal width in cm")
plt.title("iris data analysis")
plt.show()

.png)
iris.plot(kind='box', y='sepal_length')
plt.ylabel("sepal length in cm")
plt.show()
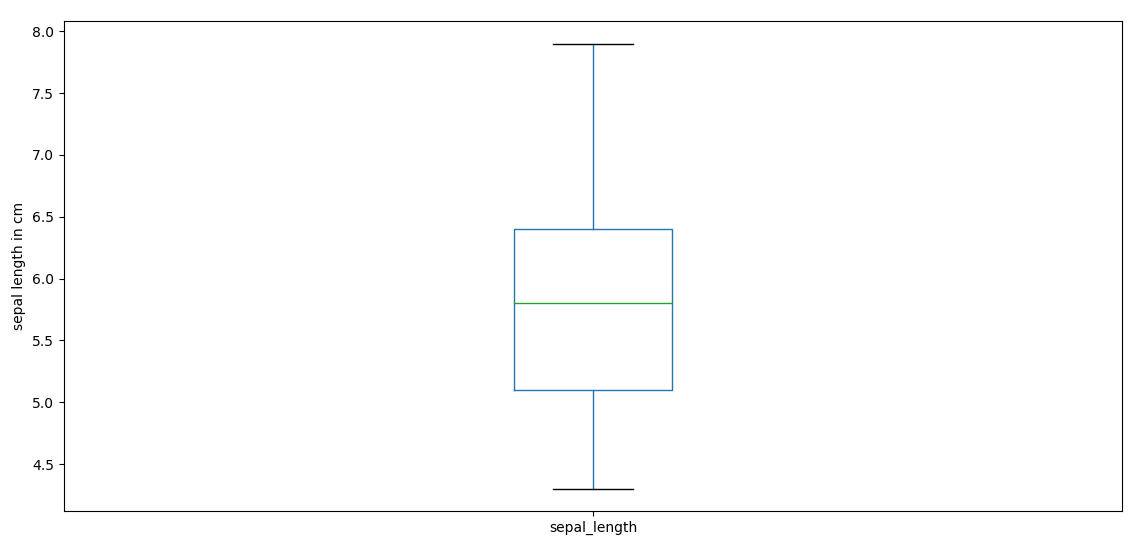
.png)
# 使用mask取出子集
mask = (iris.species == 'Iris-setosa')
setosa = iris[mask]
# bins指定柱状图的个数
# range指定X轴的取值范围
setosa.plot(kind='hist', bins=50, range=(0, 8), alpha=0.5)
plt.title("setosa in iris")
plt.xlabel("CM")
plt.show()
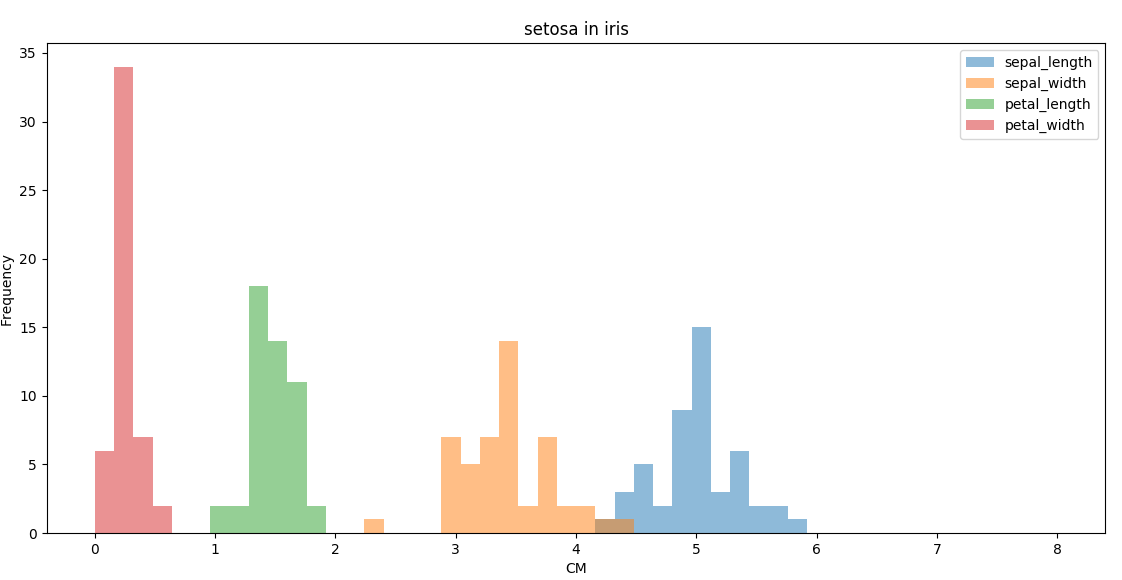
.png)
Pandas与Matplotlib基础的更多相关文章
- Pandas与Matplotlib
Pandas与Matplotlib基础 pandas是Python中开源的,高性能的用于数据分析的库.其中包含了很多可用的数据结构及功能,各种结构支持相互转换,并且支持读取.保存数据.结合matplo ...
- Matplotlib基础知识
Matplotlib基础知识 Matplotlib中的基本图表包括的元素 x轴和y轴 axis水平和垂直的轴线 x轴和y轴刻度 tick刻度标示坐标轴的分隔,包括最小刻度和最大刻度 x轴和y轴刻度标签 ...
- Matplotlib基础使用
matplotlib 一.Matplotlib基础知识 Matplotlib中的基本图表包括的元素 x轴和y轴 axis 水平和垂直的轴线 x轴和y轴刻度 tick 刻度标示坐标轴的分隔,包括最小刻度 ...
- 模块简介与matplotlib基础
模块简介与matplotlib基础 1.基本概念 1.1数据分析 对已知的数据进行分析,提取出一些有价值的信息. 1.2数据挖掘 对大量的数据进行分析与挖掘,得到一些未知的,有价值的信息. 1.3数据 ...
- 用Python的Pandas和Matplotlib绘制股票KDJ指标线
我最近出了一本书,<基于股票大数据分析的Python入门实战 视频教学版>,京东链接:https://item.jd.com/69241653952.html,在其中给出了MACD,KDJ ...
- 数据分析与展示——Matplotlib基础绘图函数示例
Matplotlib库入门 Matplotlib基础绘图函数示例 pyplot基础图表函数概述 函数 说明 plt.plot(x,y,fmt, ...) 绘制一个坐标图 plt.boxplot(dat ...
- Matplotlib基础图形之散点图
Matplotlib基础图形之散点图 散点图特点: 1.散点图显示两组数据的值,每个点的坐标位置由变量的值决定 2.由一组不连续的点组成,用于观察两种变量的相关性(正相关,负相关,不相关) 3.例如: ...
- numpy,scipy,pandas 和 matplotlib
numpy,scipy,pandas 和 matplotlib 本文会介绍numpy,scipy,pandas 和 matplotlib 的安装,环境为Windows10. 一般情况下,如果安装了Py ...
- linux下安装numpy,pandas,scipy,matplotlib,scikit-learn
python在数据科学方面需要用到的库: a.Numpy:科学计算库.提供矩阵运算的库. b.Pandas:数据分析处理库 c.scipy:数值计算库.提供数值积分和常微分方程组求解算法.提供了一个非 ...
随机推荐
- WEB服务器防盗链_HttpAccessKeyModule_Referer(Nginx&&PHP)
盗链的概念指在自己的页面上展示一些并不在自己服务器上的内容.也就是获得他人服务器上的资源地址,绕过别人的资源展示页面,直接在自己的页面上向最终用户提供此内容.如,小站盗用大站的图片.音乐.视频.软件等 ...
- JPA实体的常用注解
@Entity 标注于实体类上,通常和@Table是结合使用的,代表是该类是实体类@Table 标注于实体类上,表示该类映射到数据库中的表,没有指定名称的话就表示与数据库中表名为该类的简单类名的表名相 ...
- ubuntu追加磁盘空间
在用wubi安装的时候,按默认的是20G空间,明显不够用,从Windows上追加空间 首先用win7自带的磁盘分区工具,从任意一个空余空间较多的磁盘划出一块新分区(无损数据)(如NTFS),作为ubu ...
- 嵌入式Linux引导过程之1.2——Xloader的XLOADER_ENTRY
根据上文中获得的线索,本文分析init.S中的XLOADER_ENTRY. 在init.S中,定义了好多与平台相关的寄存器地址宏以及好多其他函数,我们在用到的时候再回过头来分析,这里,我们只看其中的一 ...
- 提升R代码运算效率的11个实用方法——并行、效率
转载于36大数据,原文作者:Selva Prabhakaran 译者:fibears 众所周知,当我们利用R语言处理大型数据集时,for循环语句的运算效率非常低.有许多种方法可以提升你的代码运算效率 ...
- dm642的中断定时器
TIMER_Handle TimerHandle0; void timer1() { ////////////定时器/////////////////////// TimerHandle0 = TI ...
- 九九乘法表的实现--JAVA基础
JAVA算法实现:输出九九乘法表 Jiujiu.java: package com.qkys.www; public class Jiujiu { public static void main(St ...
- ssm整合快速入门程序(二)
下面我们配置serivce层到项目中 1.service包中创建ItemsService.java接口,和service.imp包中创建一个service实现类ItemsServiceImpl.jav ...
- 【BZOJ1899】午餐(动态规划)
[BZOJ1899]午餐(动态规划) 题面 BZOJ 题解 我太弱了 这种\(dp\)完全做不动.. 首先,感性理解一些 如果所有人都要早点走, 那么,吃饭时间长的就先吃 吃饭时间短的就晚点吃 所以, ...
- [BZOJ4872][六省联考2017]分手是祝愿
BZOJ Luogu sol 首先发现肯定有解,又因为每个位置至多操作一次,所以最优解一定是在\([0,n]\)之间 有一种可以在\(O(\sum_{i=1}^{n}\lfloor\frac{n}{i ...
