pthread小结
参考1 https://computing.llnl.gov/tutorials/pthreads/
参考2 http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/pthreads.7.html
join
int pthread_join(pthread_t, void**);阻塞调用线程,直至指定pthread_t线程终止- 在同一个线程中重复调用join会导致错误
- 在创建线程的时候可以指定要创建的线程是否joinable,如果是,则可以join,否则(即detached)不可以。一般默认都是joinable
- POSIX指出线程should指定为joinable
- 如果确定一个线程需要join,那么最好明确指定该线程joinable,通过如下四步:
- Declare a pthread attribute variable of the
pthread_attr_t datatype - Initialize the attribute variable with
pthread_attr_init() - Set the attribute detached status with
pthread_attr_setdetachstate() - When done, free library resources used by the attribute with
pthread_attr_destroy()
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE);
for(t=0; t<NUM_THREADS; t++) {
printf("Main: creating thread %ld\n", t);
rc = pthread_create(&thread[t], &attr, BusyWork, (void *)t); //一个attr可以给多个线程使用
if (rc) {
printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_create() is %d\n", rc);
exit(-1);
}
}
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr); //记得释放资源。create执行完之后就可以释放,而不用等待线程结束
- 如果确定一个线程不需要joinable,那么应该明确考虑设置属性为detached
- 通过
pthread_detach()来设置线程为不可join,即使它被创建的时候被设置为joinable。这个动作不可逆
stack
- POSIX没有规定创建的线程的stack大小是多少,这是由implementation决定的
pthread_attr_setstacksize可以用来设置需要的stack大小pthread_attr_getstackaddr和pthread_attr_setstackaddr可以用来设置stack需要放置到特定的内存区域
size_t stacksize;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_getstacksize (&attr, &stacksize);
printf("Default stack size = %li\n", stacksize);
size = 10000; //设置为10000bytes
pthread_attr_setstacksize (&attr, stacksize);
printf("set stack size = %li\n", stacksize);
pthread_create(&threads[t], &attr, dowork, (void *)t);
mutex
Creating and Destroying Mutexes
//destroy,成功则返回0
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
//动态初始化,成功则返回0. 如果attr为NULL,那么将使用默认属性,相当于PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
//使用默认参数静态初始化
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
//mutex属性
int pthread_mutexattr_destroy(pthread_mutexattr_t *attr);
int pthread_mutexattr_init(pthread_mutexattr_t *attr);
- 被destroy的mutex可以使用
pthread_mutex_init重新初始化 - destroy一个处于lock状态的mutex,将会导致undefined行为
- 只有mutex可以用来执行synchronization,用它的copies来执行lock,unlock和trylock将导致undefined
- 不可以重复初始化已经初始化了的mutex
Locking and Unlocking Mutexes
//如果别的线程已经lock,那会一直阻塞当前线程直至获得锁
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
| mutex类型 | 性质 |
|---|---|
| PTHREAD_MUTEX_NORMAL | 对mutex的重复lock,即本线程已经lock了mutex,在没有unlock之前又尝试lock,将导致死锁行为;unlock一个没有被本线程lock或者没有被任何线程lock的mutex,将导致未定义行为 |
| PTHREAD_MUTEX_ERRORCHECK | 尝试重复lock一个mutex将不会死锁,而是返回一个错误值;unlock一个没有被本线程lock或者没有被任何线程lock的mutex,也会返回错误值 |
| PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE | mutex可以被重复lock。每次lock会增加相关计数,直至通过unlock使计数达到0时,才可以被别的线程lock;unlock一个没有被本线程lock或者没有被任何线程lock的mutex,也会返回错误值 |
| PTHREAD_MUTEX_DEFAULT | 重复lock会导致未定义行为(NORMAL中会导致死锁);unlock一个没有被本线程lock或者没有被任何线程lock的mutex,也将导致未定义行为。 不过,在NDK的定义中,直接把PTHREAD_MUTEX_DEFAULT = PTHREAD_MUTEX_NORMAL |
pthread_mutex_trylock与pthread_mutex_lock只有一点区别:如果当前mutex被任意线程lock,pthread_mutex_trylock都将会立刻返回。如果mutex是PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE的,且mutex已经被当前调用线程lock,pthread_mutex_trylock也同样会导致计数增一,并返回success。- 如果正在等待lock的线程收到了一个signal,当其从signal handler返回之后,会继续等待lock,就和signal没有发生一样
- 除非使用了 thread priority scheduling,否则多个正在等待lock的线程获得lock的情况可能多少有点random
- 如果成功,这三个函数都是返回0,否则返回相应的error
Condition Variables
- mutex通过控制对数据的访问权限来达到同步;而condition variables则基于数据的值来控制同步
- 如果不使用condition variable,线程想要检查某个条件则只能通过轮询的方式,这将非常resource consuming,因为这期间线程将一直active。而使用condition variable则将在不使用轮询的情况下实现此目标
- condition variable 经常和mutex一起使用
Creating and Destroying Condition Variables
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
int pthread_condattr_destroy(pthread_condattr_t *attr);
int pthread_condattr_init(pthread_condattr_t *attr);
- destory正由某个线程用于block的cv将导致未定义行为
- 只有cv自己能够用于同步,任何基于它的copies调用
pthread_cond_wait(), pthread_cond_timedwait(), pthread_cond_signal(), pthread_cond_broadcast(), pthread_cond_destroy()都会产生未定义行为 - 初始化一个已经初始化的cv会导致未定义行为;已经destory的cv可以再次初始化;
Waiting and Signaling on Condition Variables
一般使用流程:
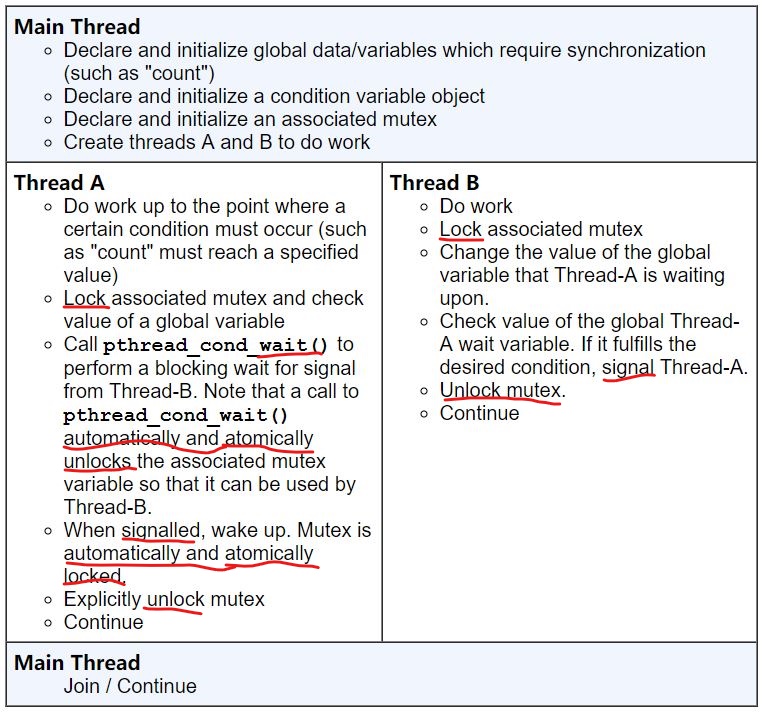
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const struct timespec *restrict abstime);
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
- 这两个函数将导致调用线程block on the condition variable, 并且需要传入一个由调用线程lock了的mutex,否则导致未定义行为
- 如果在wait之前,没有明确lock对应mutex,可能并不会导致block
- 这两个函数会原子的unlock the mutex,并且导致调用线程block on the condition variable。这里的原子的意味着:只要其他线程lock了这个mutex,那么这个线程对
pthread_cond_broadcast()或pthread_cond_signal()的调用都会产生调用wait的线程已经blocked on the condition variable的效果。 - 只要这两个函数返回,那么调用线程就已经lock了这个mutex
- 虚假唤醒Spurious wakeups 可能会产生,而且这并不违反标准,所以,即使调用线程被唤醒,也不意味着对某个值做出某种保证,应该再次确认条件是否真的满足了。同时,考虑到线程之间的竞争,
pthread_cond_timedwait由于超时返回之后,条件也可能已经满足。总之。任何时候wait返回,都需要重新评估条件是否满足,这点非常重要 - 一旦线程waits on the condition variable,那么这个cv就和相应的mutex绑定了,在wait返回之前,不能再使用另外的mutex来调用wait,这会导致未定义行为
- condition wait是一个cancellation point。未明白
- 假设一个由于wait调用而block线程由于被canceled而unblocked,这个不会consume任何condition signal。
pthread_cond_timedwait()和pthread_cond_wait()是equivalent的,除了:当signaled或者broadcasted超过指定时间,pthread_cond_timedwait()就会返回返回error。同时,cv还可以支持 Clock Selection,选择不同的Clock来measure指定的时间- 当cv wait期间,一个signal产生了,那么cv可能会继续wait就像没有中断一样,或者这会形成一个spurious wakeup,返回0.
推荐使用while循环替代if语句来检查当前条件是否真的满足,有如下三点好处:
- 如果有多个线程都是在wait相同过的wake up signal,那么当其他任意一个被waked up之后,他们都有可能更改条件值,而导致条件不满足
- 线程可能会因为程序bug而收到一个signal
- Pthreads library被容许产生虚假唤醒,而且这并不违反标准
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
- 当多于一个线程在wait的时候,应该使用
pthread_cond_broadcast() - 在signal之前,应该先lock对应mutex,然后在signal之后,应该unlock对应mutex。如果忘记了unlock,那么相应的wait线程会继续blocked,因为他们无法获得lock
结束线程
有:
- pthread_cancel
- pthread_exit
- pthread_kill
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/biyeymyhjob/archive/2012/10/11/2720377.html
其他函数
pthread_self
pthread_t pthread_self(void);返回调用线程的thread id
pthread_equal
int pthread_equal(pthread_t t1, pthread_t t2);比较两个ID是否相等,如果相等则返回not-zero value,不相等则返回0。由于pthread_t结果opaque,所以不应该用==来比较
pthread_once
int pthread_once(pthread_once_t *once_control, void (*init_routine)(void));:在进程中,任何首次调用这个函数的线程,在pthread_once_t once_control = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT的时候,会调用init_routine程序。并且当此函数返回的时候,init_routine已经执行完了(这里没有说init_routine会阻塞调用线程,可能考虑的是,当线程A已经调用init_routine,而另外一个线程B也调用了pthread_once,那么是否B也会等待A调用的init_routine执行完毕?)。如果成功完成,则pthread_once返回0。如果once_control参数不是PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT,那么行为将是undefined。在LinuxThreads中:
在LinuxThreads中,实际"一次性函数"的执行状态有三种:NEVER(0)、IN_PROGRESS(1)、DONE (2),如果once初值设为1,则由于所有pthread_once()都必须等待其中一个激发"已执行一次"信号,因此所有pthread_once ()都会陷入永久的等待中;如果设为2,则表示该函数已执行过一次,从而所有pthread_once()都会立即返回0。
这个函数在当无法编辑进程的main函数,比如写一个库的时候,就很有用。
TODO:如果多个线程使用的init_routine不相同怎么办?或者比如自己开发库,但是user的main中已经使用不同的init_routine调用了pthread_once,那么会是什么结果?
pthread小结的更多相关文章
- pthread多线程编程的学习小结
pthread多线程编程的学习小结 pthread 同步3种方法: 1 mutex 2 条件变量 3 读写锁:支持多个线程同时读,或者一个线程写 程序员必上的开发者服务平台 —— DevSt ...
- clone的fork与pthread_create创建线程有何不同&pthread多线程编程的学习小结(转)
进程是一个指令执行流及其执行环境,其执行环境是一个系统资源的集合,这些资源在Linux中被抽 象成各种数据对象:进程控制块.虚存空间.文件系统,文件I/O.信号处理函数.所以创建一个进程的 过程就是这 ...
- 4.1/4.2 多线程进阶篇<上>(Pthread & NSThread)
本文并非最终版本,如有更新或更正会第一时间置顶,联系方式详见文末 如果觉得本文内容过长,请前往本人 “简书” 本文源码 Demo 详见 Githubhttps://github.com/shorfng ...
- linux的<pthread.h>
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_66cc44d00100in5b.html Linux系统下的多线程遵循POSIX线程接口,称为pthread.编写Linux下的多 ...
- Linux多线程编程小结
Linux多线程编程小结 前一段时间由于开题的事情一直耽搁了我搞Linux的进度,搞的我之前学的东西都遗忘了,非常烦躁的说,如今抽个时间把之前所学的做个小节.文章内容主要总结于<Linux程序 ...
- linux,pthread(转)
互斥量.条件变量与pthread_cond_wait()函数的使用,详解(二) 1.Linux“线程” 进程与线程之间是有区别的,不过linux内核只提供了轻量进程的支持,未实现线程模型.Linu ...
- 多线程本地图片载入演示样例【OpenCV】【Pthread】
Pthread barrier的简单使用演示样例: C++代码例如以下: // ThreadingLoadImages.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include "s ...
- ZT 为什么pthread_cond_t要和pthread_mutex_t同时使用 || pthread/Linux多线程编程
为什么线程同步的时候pthread_cond_t要和pthread_mutex_t同时使用 (2009-10-27 11:07:23) 转载▼ 标签: 杂谈 分类: 计算机 举一个例子(http:// ...
- 从零开始编写自己的C#框架(26)——小结
一直想写个总结,不过实在太忙了,所以一直拖啊拖啊,拖到现在,不过也好,有了这段时间的沉淀,发现自己又有了小小的进步.哈哈...... 原想框架开发的相关开发步骤.文档.代码.功能.部署等都简单的讲过了 ...
随机推荐
- Java进阶篇之十五 ----- JDK1.8的Lambda、Stream和日期的使用详解(很详细)
前言 本篇主要讲述是Java中JDK1.8的一些新语法特性使用,主要是Lambda.Stream和LocalDate日期的一些使用讲解. Lambda Lambda介绍 Lambda 表达式(lamb ...
- kubernetes实践之五:深入理解Service及内部DNS搭建
一.Service存在的意义: 防止Pod失联(服务发现) 定义一组Pod的访问策略(负载均衡) 支持ClusterIP,NodePort以及LoadBalancer三种类型 Service的底层实现 ...
- 【招聘】.NET高级开发、前端高级开发、测试工程师
.NET架构师 工作地点:厦门-湖里区 工作年限:5年及以上 学历要求:大专或以上 工资范围:15000元 - 25000元 福利待遇:五险一金,带薪年休假,年度旅游,丰富的员工团队活动:生日会.中秋 ...
- 安卓开发笔记(十二):SQLite数据库储存(上)
SQLite数据库存储(上) 创建数据库 Android专门提供了一个 SQLiteOpenHelper帮助类对数据库进行创建和升级 SQLiteOpenHelper需要创建一个自己的帮助类去继承它并 ...
- CI持续集成系列之(九)代码发布脚本模板书写
前言 前面我们介绍了Jenkins来发布项目通过nginx来展示流程,那里只是提供了一个简单的测试脚本,接下来呢介绍一下一个比较完善的发布脚本,该脚本可实现从gitlab服务器获取代码,打包,部署到W ...
- Vue应用框架整合与实战--Vue技术生态圈篇
实用框架以及工具 UI组件 开发框架 实用库 服务端 辅助工具 应用实例 Demo示例 UI组件 Element-UI ★13489 - 饿了么出品的Vue2的web UI工具套件 Vux ★8133 ...
- [LeetCode] 26. 删除排序数组中的重复项
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/ 题目描述: 给定一个排序数组,你需要在原地删除重复 ...
- ML.NET 发布0.11版本:.NET中的机器学习,为TensorFlow和ONNX添加了新功能
微软发布了其最新版本的机器学习框架:ML.NET 0.11带来了新功能和突破性变化. 新版本的机器学习开源框架为TensorFlow和ONNX添加了新功能,但也包括一些重大变化, 这也是发布RC版本之 ...
- F#正则表达式
此词法分析器允许您使用F#计算表达式以非常声明的方式定义基于正则表达式的规则. F# 打开 Lexer 让 定义= lexerDefinitions { 做!addNextlineDefinition ...
- 浏览器F12 waterfall性能检测详解详解
Queueing 是排队的意思 Stalled 是阻塞 请求访问该URL的主机是有并发和连接数限制的,必须要等之前的执行才能执行之后的,这段时间的耗时 DNS Lookup 是指域名解析所耗时间 I ...
