python3验证码机器学习
python3验证码机器学习
文档结构为
-- iconset
-- ...
-- jpg
-- captcha.gif
-- py
-- crack.py
需要的库
pip3 install pillow or easy_install Pillow
必须文件下载地址
1.读取图片,打印图片的结构直方图
# !/usr/bin/python3.4
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# From:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24222942
# 该知乎栏目为py2编写,这里改造成py3
im = Image.open("../jpg/captcha.gif")
his = im.histogram()
打印结果为
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 3, 1, 3, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 3, 2, 132, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 15, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 8, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 6, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 18, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 365, 115, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 135, 186, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 116, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 21, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 10, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 625]
该数组长度为255,每一个元素代表(0-255)颜色的多少,例如最后一个元素为625,即255(代表的是白色)最多,组合在一起
values = {}
for i in range(0, 256):
values[i] = his[i]
# 排序,x:x[1]是按照括号内第二个字段进行排序,x:x[0]是按照第一个字段
temp = sorted(values.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
# print(temp)
打印结果为
[(255, 625), (212, 365), (220, 186), (219, 135), (169, 132), (227, 116), (213, 115), (234, 21), (205, 18), (184, 15), (241, 10), (248, 10), (191, 8), (198, 6), (155, 3), (157, 3), (158, 3), (167, 3), (228, 3), (56, 2), (67, 2), (91, 2), (96, 2), (109, 2), (122, 2), (127, 2), (134, 2), (140, 2), (168, 2), (176, 2), (200, 2), (211, 2), (240, 2), (242, 2), (247, 2), (43, 1), (44, 1), (53, 1), (61, 1), (68, 1), (79, 1), (84, 1), (92, 1), (101, 1), (103, 1), (104, 1), (107, 1), (121, 1), (126, 1), (129, 1), (132, 1), (137, 1), (149, 1), (151, 1), (153, 1), (156, 1), (165, 1), (170, 1), (171, 1), (175, 1), (186, 1), (188, 1), (192, 1), (197, 1), (206, 1), (207, 1), (208, 1), (209, 1), (210, 1), (215, 1), (223, 1), (235, 1), (236, 1), (253, 1), (0, 0), (1, 0), (2, 0), (3, 0), (4, 0), (5, 0), (6, 0), (7, 0), (8, 0), (9, 0), (10, 0), (11, 0), (12, 0), (13, 0), (14, 0), (15, 0), (16, 0), (17, 0), (18, 0), (19, 0), (20, 0), (21, 0), (22, 0), (23, 0), (24, 0), (25, 0), (26, 0), (27, 0), (28, 0), (29, 0), (30, 0), (31, 0), (32, 0), (33, 0), (34, 0), (35, 0), (36, 0), (37, 0), (38, 0), (39, 0), (40, 0), (41, 0), (42, 0), (45, 0), (46, 0), (47, 0), (48, 0), (49, 0), (50, 0), (51, 0), (52, 0), (54, 0), (55, 0), (57, 0), (58, 0), (59, 0), (60, 0), (62, 0), (63, 0), (64, 0), (65, 0), (66, 0), (69, 0), (70, 0), (71, 0), (72, 0), (73, 0), (74, 0), (75, 0), (76, 0), (77, 0), (78, 0), (80, 0), (81, 0), (82, 0), (83, 0), (85, 0), (86, 0), (87, 0), (88, 0), (89, 0), (90, 0), (93, 0), (94, 0), (95, 0), (97, 0), (98, 0), (99, 0), (100, 0), (102, 0), (105, 0), (106, 0), (108, 0), (110, 0), (111, 0), (112, 0), (113, 0), (114, 0), (115, 0), (116, 0), (117, 0), (118, 0), (119, 0), (120, 0), (123, 0), (124, 0), (125, 0), (128, 0), (130, 0), (131, 0), (133, 0), (135, 0), (136, 0), (138, 0), (139, 0), (141, 0), (142, 0), (143, 0), (144, 0), (145, 0), (146, 0), (147, 0), (148, 0), (150, 0), (152, 0), (154, 0), (159, 0), (160, 0), (161, 0), (162, 0), (163, 0), (164, 0), (166, 0), (172, 0), (173, 0), (174, 0), (177, 0), (178, 0), (179, 0), (180, 0), (181, 0), (182, 0), (183, 0), (185, 0), (187, 0), (189, 0), (190, 0), (193, 0), (194, 0), (195, 0), (196, 0), (199, 0), (201, 0), (202, 0), (203, 0), (204, 0), (214, 0), (216, 0), (217, 0), (218, 0), (221, 0), (222, 0), (224, 0), (225, 0), (226, 0), (229, 0), (230, 0), (231, 0), (232, 0), (233, 0), (237, 0), (238, 0), (239, 0), (243, 0), (244, 0), (245, 0), (246, 0), (249, 0), (250, 0), (251, 0), (252, 0), (254, 0)]
将占比最多的10个颜色筛选出来
# 占比最多的10种颜色
# for j, k in temp[:10]:
# print(j, k)
# 255 625
# 212 365
# 220 186
# 219 135
# 169 132
# 227 116
# 213 115
# 234 21
# 205 18
# 184 15
2.构造新的无杂质图片
生成一张白底啥都没有的图片
# 获取图片大小,生成一张白底255的图片
im2 = Image.new("P", im.size, 255)
# print(im2.size[1])
# (84, 22)
原作者自己观察得到代表数字的颜色为220灰色和227红色

将这些颜色根据宽和高的坐标以此写入新生成的白底照片中
# (84, 22)=(宽,高)=(size[0],size[1])
# 获得y坐标
for y in range(im.size[1]):
# 获得y坐标
for x in range(im.size[0]):
# 获得坐标(x,y)的RGB值
pix = im.getpixel((x, y))
# 这些是要得到的数字
# 220灰色,227红色
if pix == 220 or pix == 227:
# 将黑色0填充到im2中
im2.putpixel((x, y), 0)
# 生成了一张黑白二值照片
# im2.show()
黑白二值照片

3.切割图片
x代表图片的宽,y代表图片的高
对图片进行纵向切割
# 纵向切割
# 找到切割的起始和结束的横坐标
inletter = False
foundletter = False
start = 0
end = 0
letters = []
for x in range(im2.size[0]):
for y in range(im2.size[1]):
pix = im2.getpixel((x, y))
if pix != 255:
inletter = True
if foundletter == False and inletter == True:
foundletter = True
start = x
if foundletter == True and inletter == False:
foundletter = False
end = x
letters.append((start, end))
inletter = False
打印结果为
# [(6, 14), (15, 25), (27, 35), (37, 46), (48, 56), (57, 67)]
(6, 14)代表从x=6到x=14纵向切割成一条状
保存字段到本地观察,这一步没有什么用,只是保存下来看看而已
# 保存切割下来的字段
import time
count = 0
for letter in letters:
# (切割的起始横坐标,起始纵坐标,切割的宽度,切割的高度)
im3 = im2.crop((letter[0], 0, letter[1], im2.size[1]))
# 更改成用时间命名
# im3.save("../jpg/%s.gif" % (time.strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S', time.localtime())))
count += 1
# 可以看到保存下来的6个字段
字段样式

4.训练识别
使用的是 AI与向量空间图像识别
将标准图片转换成向量坐标a,需要识别的图片字段为向量坐标b,cos(a,b)值越大说明夹角越小,越接近重合
空间两向量计算公式
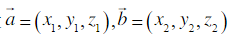
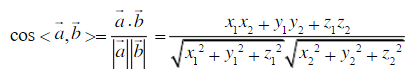
编写的夹角公式为
# 夹角公式
import math
class VectorCompare:
# 计算矢量大小
# 计算平方和
def magnitude(self, concordance):
total = 0
# concordance.iteritems:报错'dict' object has no attribute 'iteritems'
# concordance.items()
for word, count in concordance.items():
total += count ** 2
return math.sqrt(total)
# 计算矢量之间的 cos 值
def relation(self, concordance1, concordance2):
topvalue = 0
# concordance1.iteritems:报错'dict' object has no attribute 'iteritems'
# concordance1.items()
for word, count in concordance1.items():
# if concordance2.has_key(word):报错'dict' object has no attribute 'has_key'
# 改成word in concordance2
if word in concordance2:
# 计算相乘的和
topvalue += count * concordance2[word]
return topvalue / (self.magnitude(concordance1) * self.magnitude(concordance2))
转换验证码图片为向量:
# 将图片转换为矢量
def buildvector(im):
d1 = {}
count = 0
for i in im.getdata():
d1[count] = i
count += 1
return d1
打印结果
{0: 255, 1: 255, 2: 255, 3: 255, 4: 255, 5: 255, 6: 255, 7: 255, 8: 255, 9: 255, 10: 255, 11: 255, 12: 255, 13: 255, 14: 255, 15: 255, 16: 255, 17: 255, 18: 255, 19: 255, 20: 255, 21: 255, 22: 255, 23: 255, 24: 255, 25: 255, 26: 255, 27: 255, 28: 255, 29: 255, 30: 255, 31: 255, 32: 255, 33: 255, 34: 255, 35: 255, 36: 255, 37: 255, 38: 255, 39: 255, 40: 255, 41: 255, 42: 255, 43: 255, 44: 255, 45: 255, 46: 255, 47: 255, 48: 255, 49: 255, 50: 255, 51: 255, 52: 255, 53: 255, 54: 255, 55: 255, 56: 255, 57: 255, 58: 255, 59: 255, 60: 255, 61: 255, 62: 255, 63: 255, 64: 255, 65: 255, 66: 255, 67: 0, 68: 0, 69: 0, 70: 255, 71: 255, 72: 255, 73: 255, 74: 0, 75: 0, 76: 0, 77: 255, 78: 0, 79: 255, 80: 255, 81: 0, 82: 0, 83: 0, 84: 0, 85: 0, 86: 0, 87: 255, 88: 255, 89: 0, 90: 255, 91: 255, 92: 255, 93: 0, 94: 0, 95: 255, 96: 0, 97: 255, 98: 0, 99: 255, 100: 255, 101: 0, 102: 0, 103: 0, 104: 0, 105: 0, 106: 0, 107: 255, 108: 255, 109: 0, 110: 0, 111: 0, 112: 0, 113: 0, 114: 255, 115: 255, 116: 255, 117: 0, 118: 0, 119: 0, 120: 255, 121: 0, 122: 255, 123: 255, 124: 255, 125: 0, 126: 0, 127: 0, 128: 255, 129: 0, 130: 0, 131: 255, 132: 255, 133: 0, 134: 0, 135: 0, 136: 255, 137: 0, 138: 0, 139: 0, 140: 0, 141: 0, 142: 0, 143: 255, 144: 255, 145: 0, 146: 0, 147: 0, 148: 0, 149: 0, 150: 0, 151: 255, 152: 255, 153: 255, 154: 255, 155: 0, 156: 0, 157: 0, 158: 255, 159: 255, 160: 255, 161: 255, 162: 255, 163: 255, 164: 255, 165: 255, 166: 255, 167: 255, 168: 255, 169: 255, 170: 255, 171: 255, 172: 255, 173: 255, 174: 255, 175: 255}
加载训练集,且把训练集也变成向量
v = VectorCompare()
iconset = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '0', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k',
'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
import os
imageset = []
for letter in iconset:
for img in os.listdir('../iconset/%s/' % (letter)):
temp = []
if img != "Thumbs.db" and img != ".DS_Store":
temp.append(buildvector(Image.open("../iconset/%s/%s" % (letter, img))))
imageset.append({letter: temp})
** 开始识别验证码 **
# 开始破解训练
count = 0
for letter in letters:
# (切割的起始横坐标,起始纵坐标,切割的宽度,切割的高度)
im3 = im2.crop((letter[0], 0, letter[1], im2.size[1]))
guess = []
# 将切割得到的验证码小片段与每个训练片段进行比较
for image in imageset:
# image.iteritems:报错'dict' object has no attribute 'iteritems'
# 改成image.items()
for x, y in image.items():
if len(y) != 0:
guess.append((v.relation(y[0], buildvector(im3)), x))
其中
y[0]为训练集里面的字母图片,即正确的图片-打印{0: 255, 1: 255, 2: 255, 3: 255, 4: 255, 5: 255, 6: 255, 7: 255, 8: 255, 9: 255, 10: 255, 11: 255, 12: 255, 13: 255, 14: 255, 15: 255, 16: 255, 17: 255, 18: 255, 19: 255, 20: 255, 21: 255, 22: 255, 23: 255, 24: 255, 25: 255, 26: 255, 27: 255, 28: 255, 29: 255, 30: 255, 31: 255, 32: 255, 33: 255, 34: 255, 35: 255, 36: 255, 37: 255, 38: 255, 39: 255, 40: 255, 41: 255, 42: 255, 43: 255, 44: 255, 45: 255, 46: 255, 47: 255, 48: 255, 49: 255, 50: 255, 51: 255, 52: 255, 53: 255, 54: 255, 55: 255, 56: 255, 57: 255, 58: 255, 59: 255, 60: 255, 61: 255, 62: 255, 63: 255, 64: 255, 65: 255, 66: 255, 67: 0, 68: 0, 69: 0, 70: 255, 71: 255, 72: 255, 73: 255, 74: 0, 75: 0, 76: 0, 77: 255, 78: 0, 79: 255, 80: 255, 81: 0, 82: 0, 83: 0, 84: 0, 85: 0, 86: 0, 87: 255, 88: 255, 89: 0, 90: 255, 91: 255, 92: 255, 93: 0, 94: 0, 95: 255, 96: 0, 97: 255, 98: 0, 99: 255, 100: 255, 101: 0, 102: 0, 103: 0, 104: 0, 105: 0, 106: 0, 107: 255, 108: 255, 109: 0, 110: 0, 111: 0, 112: 0, 113: 0, 114: 255, 115: 255, 116: 255, 117: 0, 118: 0, 119: 0, 120: 255, 121: 0, 122: 255, 123: 255, 124: 255, 125: 0, 126: 0, 127: 0, 128: 255, 129: 0, 130: 0, 131: 255, 132: 255, 133: 0, 134: 0, 135: 0, 136: 255, 137: 0, 138: 0, 139: 0, 140: 0, 141: 0, 142: 0, 143: 255, 144: 255, 145: 0, 146: 0, 147: 0, 148: 0, 149: 0, 150: 0, 151: 255, 152: 255, 153: 255, 154: 255, 155: 0, 156: 0, 157: 0, 158: 255, 159: 255, 160: 255, 161: 255, 162: 255, 163: 255, 164: 255, 165: 255, 166: 255, 167: 255, 168: 255, 169: 255, 170: 255, 171: 255, 172: 255, 173: 255, 174: 255, 175: 255}
buildvector(im3))为切割出来的字母切片,用来和y[0]进行夹角比对-打印{0: 255, 1: 255, 2: 255, 3: 255, 4: 255, 5: 255, 6: 255, 7: 255, 8: 255, 9: 255, 10: 255, 11: 255, 12: 255, 13: 255, 14: 255, 15: 255, 16: 255, 17: 255, 18: 255, 19: 255, 20: 255, 21: 255, 22: 255, 23: 255, 24: 255, 25: 255, 26: 255, 27: 255, 28: 255, 29: 255, 30: 255, 31: 255, 32: 255, 33: 255, 34: 255, 35: 255, 36: 255, 37: 255, 38: 255, 39: 255, 40: 255, 41: 255, 42: 255, 43: 255, 44: 255, 45: 255, 46: 255, 47: 255, 48: 255, 49: 255, 50: 255, 51: 255, 52: 255, 53: 255, 54: 255, 55: 255, 56: 255, 57: 255, 58: 255, 59: 255, 60: 255, 61: 255, 62: 255, 63: 255, 64: 255, 65: 0, 66: 0, 67: 0, 68: 0, 69: 0, 70: 0, 71: 255, 72: 0, 73: 0, 74: 0, 75: 0, 76: 0, 77: 0, 78: 0, 79: 0, 80: 255, 81: 0, 82: 0, 83: 0, 84: 0, 85: 0, 86: 0, 87: 0, 88: 255, 89: 255, 90: 255, 91: 255, 92: 255, 93: 255, 94: 0, 95: 255, 96: 255, 97: 255, 98: 255, 99: 255, 100: 255, 101: 0, 102: 0, 103: 255, 104: 255, 105: 255, 106: 255, 107: 255, 108: 255, 109: 255, 110: 0, 111: 255, 112: 255, 113: 255, 114: 255, 115: 255, 116: 0, 117: 0, 118: 255, 119: 255, 120: 255, 121: 255, 122: 255, 123: 255, 124: 0, 125: 0, 126: 255, 127: 255, 128: 255, 129: 255, 130: 255, 131: 0, 132: 0, 133: 0, 134: 255, 135: 255, 136: 255, 137: 255, 138: 255, 139: 0, 140: 0, 141: 255, 142: 255, 143: 255, 144: 255, 145: 255, 146: 0, 147: 0, 148: 0, 149: 255, 150: 255, 151: 255, 152: 255, 153: 255, 154: 255, 155: 255, 156: 0, 157: 255, 158: 255, 159: 255, 160: 255, 161: 255, 162: 255, 163: 255, 164: 255, 165: 255, 166: 255, 167: 255, 168: 255, 169: 255, 170: 255, 171: 255, 172: 255, 173: 255, 174: 255, 175: 255}
x为iconset-x打印依次显示为0,1,2,3,。。。,x,y,z
排序选出夹角最小的(即cos值最大)的向量,夹角越小则越接近重合,匹配越接近
guess.sort(reverse=True)
print("", guess[0])
count += 1
运行结果
(0.9637681159420289, '7')
(0.96234028545977, 's')
(0.9286884286888929, '9')
(0.9835037060984447, 't')
(0.9675116507250627, '9')
(0.9698971168877263, 'j')
完整源码在TTyb
python3验证码机器学习的更多相关文章
- Python3入门机器学习经典算法与应用
<Python3入门机器学习经典算法与应用> 章节第1章 欢迎来到 Python3 玩转机器学习1-1 什么是机器学习1-2 课程涵盖的内容和理念1-3 课程所使用的主要技术栈第2章 机器 ...
- Python3实现机器学习经典算法(三)ID3决策树
一.ID3决策树概述 ID3决策树是另一种非常重要的用来处理分类问题的结构,它形似一个嵌套N层的IF…ELSE结构,但是它的判断标准不再是一个关系表达式,而是对应的模块的信息增益.它通过信息增益的大小 ...
- Python3实现机器学习经典算法(一)KNN
一.KNN概述 K-(最)近邻算法KNN(k-Nearest Neighbor)是数据挖掘分类技术中最简单的方法之一.它具有精度高.对异常值不敏感的优点,适合用来处理离散的数值型数据,但是它具有 非常 ...
- Python3实现机器学习经典算法(四)C4.5决策树
一.C4.5决策树概述 C4.5决策树是ID3决策树的改进算法,它解决了ID3决策树无法处理连续型数据的问题以及ID3决策树在使用信息增益划分数据集的时候倾向于选择属性分支更多的属性的问题.它的大部分 ...
- Python3入门机器学习经典算法与应用☝☝☝
Python3入门机器学习经典算法与应用 (一个人学习或许会很枯燥,但是寻找更多志同道合的朋友一起,学习将会变得更加有意义✌✌) 使用新版python3语言和流行的scikit-learn框架,算法与 ...
- Python3入门机器学习经典算法与应用✍✍✍
Python3入门机器学习经典算法与应用 整个课程都看完了,这个课程的分享可以往下看,下面有链接,之前做java开发也做了一些年头,也分享下自己看这个视频的感受,单论单个知识点课程本身没问题,大家看的 ...
- Python3入门机器学习 经典算法与应用
Python3入门机器学习 整个课程都看完了,这个课程的分享可以往下看,下面有链接,之前做java开发也做了一些年头,也分享下自己看这个视频的感受,单论单个知识点课程本身没问题,大家看的时候可以关注下 ...
- [转]Python3《机器学习实战》学习笔记(一):k-近邻算法(史诗级干货长文)
转自http://blog.csdn.net/c406495762/article/details/75172850 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 目录(?)[-] 一 简 ...
- Python3实现机器学习经典算法(二)KNN实现简单OCR
一.前言 1.ocr概述 OCR (Optical Character Recognition,光学字符识别)是指电子设备(例如扫描仪或数码相机)检查纸上打印的字符,通过检测暗.亮的模式确定其形状,然 ...
随机推荐
- linux-rpm
1. RPM本地安装 RPM包管理员(简称RPM,全称为The RPM Package Manager)是在Linux下广泛使用的软件包管理器.RPM此名词可能是指.rpm的文件格式的 ...
- Java第六次作业修改版
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Random; public class Draw ...
- php绘图问题
php绘图首先要确认gd库是否启用,到php.ini文件中,找到extension=php_gd2.dll将前面的:去掉,重新启动服务器. 如果在绘图中还是没有显示正常的图片,说明服务器在回复请求时, ...
- Spark的Straggler深入学习(2):思考Block和Partition的划分问题——以论文为参考
一.partition的划分问题 如何划分partition对block数据的收集有很大影响.如果需要根据block来加速task的执行,partition应该满足什么条件? 参考思路1:range ...
- sed用法
简介 sed 是一种在线编辑器,它一次处理一行内容.处理时,把当前处理的行存储在临时缓冲区中,称为“模式空间”(pattern space),接着用sed命令处理缓冲区中的内容,处理完成后,把缓冲区的 ...
- css中文乱码与替换字符
有时候,我们的css样式表中字体乱码,很诧异.百度谷歌是两个老师,有时jquery博客还上淘宝,那边有现成的代码,看看,发现里面定义全局字体是这样的font:12px/1.5 tahoma,arial ...
- MySQL中的information_schema数据库详解
information_schema数据库是MySQL自带的,它提供了访问数据库元数据的方式.什么是元数据呢?元数据是关于数据的数据,如数据库名或表名,列的数据类型,或访问权限等.有些时候用于表述该信 ...
- iOS 企业包碰到的问题
在这里 就不讲 iOS 企业包 怎么申请了 网上链接很多 也简单 真找不到靠谱的, 就用这个链接 教程 http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoc1314/p/5595312.html ...
- 使用Application对象简单完成网站总访问人数的统计
Global.asax文件: using System.IO; protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) { Fil ...
- CLR via C# 3rd - 01 - The CLR's Execution Model
1. Assemly A managed module is a standard 32-bit Microsoft Windoes portable executable (PE32) ...
