机器学习之决策树熵&信息增量求解算法实现
此文不对理论做相关阐述,仅涉及代码实现:
1.熵计算公式:
P为正例,Q为反例
Entropy(S) = -PLog2(P) - QLog2(Q);
2.信息增量计算:
Gain(S,Sv) = Entropy(S) - (|Sv|/|S|)ΣEntropy(Sv);
举例:
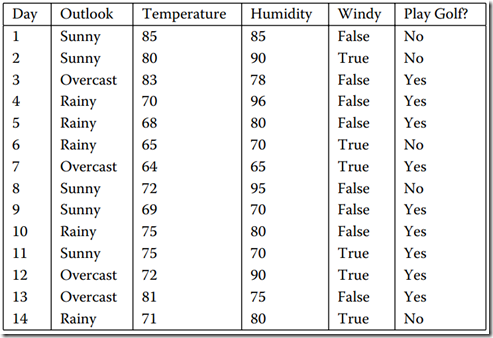
转化数据输入:
5 14
Outlook Sunny Sunny Overcast Rain Rain Rain Overcast Sunny Sunny Rain Sunny Overcast Overcast Rain
Temperature Hot Hot Hot Mild Cool Cool Cool Mild Cool Mild Mild Mild Hot Mild
Humidity High High High High Normal Normal Normal High Normal Normal Normal High Normal High
Wind Weak Strong Weak Weak Weak Strong Strong Weak Weak Weak Strong Strong Weak Strong
PlayTennis No No Yes Yes Yes No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
package com.qunar.data.tree; /**
* *********************************************************
* <p/>
* Author: XiJun.Gong
* Date: 2016-09-02 15:28
* Version: default 1.0.0
* Class description:
* <p>统计该类型出现的次数</p>
* <p/>
* *********************************************************
*/
public class CountMap<T> { private T key; //类型
private int value; //出现的次数 public CountMap() {
this(null, 0);
} public CountMap(T key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
} public T getKey() {
return key;
} public void setKey(T key) {
this.key = key;
} public int getValue() {
return value;
} public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
package com.qunar.data.tree; import com.google.common.collect.ArrayListMultimap;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
import com.google.common.collect.Multimap;
import com.google.common.collect.Sets; import java.util.*; /**
* *********************************************************
* <p/>
* Author: XiJun.Gong
* Date: 2016-09-02 14:24
* Version: default 1.0.0
* Class description:
* <p>决策树</p>
* <p/>
* *********************************************************
*/ public class DecisionTree<T, K> { private static String positiveExampleType = "Yes";
private static String counterExampleType = "No"; public double pLog2(final double p) {
if (0 == p) return 0;
return p * (Math.log(p) / Math.log(2));
} /**
* 熵计算
*
* @param positiveExample 正例个数
* @param counterExample 反例个数
* @return 熵值
*/
public double entropy(final double positiveExample, final double counterExample) { double total = positiveExample + counterExample;
double positiveP = positiveExample / total;
double counterP = counterExample / total;
return -1d * (pLog2(positiveP) + pLog2(counterP));
} /**
* @param features 特征列表
* @param results 对应结果
* @return 将信息整合成新的格式
*/
public Multimap<T, CountMap<K>> merge(final List<T> features, final List<T> results) {
//数据转化
Multimap<T, CountMap<K>> InfoMap = ArrayListMultimap.create();
Iterator result = results.iterator();
for (T feature : features) {
K res = (K) result.next();
boolean tag = false;
Collection<CountMap<K>> countMaps = InfoMap.get(feature);
for (CountMap countMap : countMaps) {
if (countMap.getKey().equals(res)) {
/*修改值*/
int num = countMap.getValue() + 1;
InfoMap.remove(feature, countMap);
InfoMap.put(feature, new CountMap<K>(res, num));
tag = true;
break;
}
}
if (!tag)
InfoMap.put(feature, new CountMap<K>(res, 1));
} return InfoMap;
} /**
* 信息增益
*
* @param infoMap 因素(Outlook,Temperature,Humidity,Wind)对应的结果
* @param dataTable 输入的数据表
* @param type 因素中的类型(Outlook{Sunny,Overcast,Rain})
* @param entropyS 总的熵值
* @param totalSize 总的样本数
* @return 信息增益
*/
public double gain(Multimap<T, CountMap<K>> infoMap,
Map<K, List<T>> dataTable,
final String type,
double entropyS,
final int totalSize) {
//去重
Set<T> subTypes = Sets.newHashSet();
subTypes.addAll(dataTable.get(type));
/*计算*/
for (T subType : subTypes) {
Collection<CountMap<K>> countMaps = infoMap.get(subType);
double subSize = 0;
double positiveExample = 0;
double counterExample = 0;
for (CountMap<K> countMap : countMaps) {
subSize += countMap.getValue();
if (positiveExampleType.equals(countMap.getKey()))
positiveExample = countMap.getValue();
else
counterExample = countMap.getValue();
}
entropyS -= (subSize / totalSize) * entropy(positiveExample, counterExample);
}
return entropyS;
} /**
* 计算
*
* @param dataTable 数据表
* @param types 因素列表{Outlook,Temperature,Humidity,Wind}
* @param resultType 结果(PlayTennis)
* @return 返回信息增益集合
*/
public Map<String, Double> calculate(Map<K, List<T>> dataTable, List<K> types, K resultType) { Map<String, Double> answer = Maps.newHashMap();
List<T> results = dataTable.get(resultType);
int totalSize = results.size();
int positiveExample = 0;
int counterExample = 0;
double entropyS = 0d;
for (T ExampleType : results) {
if (positiveExampleType.equals(ExampleType)) {
++positiveExample;
continue;
}
++counterExample;
}
/*计算总的熵*/
entropyS = entropy(positiveExample, counterExample); Multimap<T, CountMap<K>> infoMap;
for (K type : types) {
infoMap = merge(dataTable.get(type), results);
double _gain = gain(infoMap, dataTable, (String) type, entropyS, totalSize);
answer.put((String) type, _gain);
}
return answer;
} } package com.qunar.data.tree;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps; import java.util.*; /**
* *********************************************************
* <p/>
* Author: XiJun.Gong
* Date: 2016-09-02 16:43
* Version: default 1.0.0
* Class description:
* <p/>
* *********************************************************
*/
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
DecisionTree<String, String> dt = new DecisionTree();
Map<String, List<String>> dataTable = Maps.newHashMap();
/*Map<String, List<String>> dataTable = Maps.newHashMap();*/
List<String> types = Lists.newArrayList();
String resultType;
int factorSize = scanner.nextInt();
int demoSize = scanner.nextInt();
String type; for (int i = 0; i < factorSize; i++) {
List<String> demos = Lists.newArrayList();
type = scanner.next();
for (int j = 0; j < demoSize; j++) {
demos.add(scanner.next());
}
dataTable.put(type, demos);
}
for (int i = 1; i < factorSize; i++) {
types.add(scanner.next());
}
resultType = scanner.next();
Map<String, Double> ans = dt.calculate(dataTable, types, resultType);
List<Map.Entry<String, Double>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Double>>(ans.entrySet());
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Double>>() { @Override
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Double> o1, Map.Entry<String, Double> o2) {
return (o2.getValue() > o1.getValue() ? 1 : -1);
}
}); for (Map.Entry<String, Double> iterator : list) {
System.out.println(iterator.getKey() + "= " + iterator.getValue());
}
}
} }
/**
*使用举例:*
5 14
Outlook Sunny Sunny Overcast Rain Rain Rain Overcast Sunny Sunny Rain Sunny Overcast Overcast Rain
Temperature Hot Hot Hot Mild Cool Cool Cool Mild Cool Mild Mild Mild Hot Mild
Humidity High High High High Normal Normal Normal High Normal Normal Normal High Normal High
Wind Weak Strong Weak Weak Weak Strong Strong Weak Weak Weak Strong Strong Weak Strong
PlayTennis No No Yes Yes Yes No Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Outlook Temperature Humidity Wind PlayTennis
*/
结果:
Outlook= 0.2467498197744391
Humidity= 0.15183550136234136
Wind= 0.04812703040826927
Temperature= 0.029222565658954647
机器学习之决策树熵&信息增量求解算法实现的更多相关文章
- 机器学习之决策树(ID3)算法与Python实现
机器学习之决策树(ID3)算法与Python实现 机器学习中,决策树是一个预测模型:他代表的是对象属性与对象值之间的一种映射关系.树中每个节点表示某个对象,而每个分叉路径则代表的某个可能的属性值,而每 ...
- 【Machine Learning·机器学习】决策树之ID3算法(Iterative Dichotomiser 3)
目录 1.什么是决策树 2.如何构造一棵决策树? 2.1.基本方法 2.2.评价标准是什么/如何量化评价一个特征的好坏? 2.3.信息熵.信息增益的计算 2.4.决策树构建方法 3.算法总结 @ 1. ...
- 决策树笔记:使用ID3算法
决策树笔记:使用ID3算法 决策树笔记:使用ID3算法 机器学习 先说一个偶然的想法:同样的一堆节点构成的二叉树,平衡树和非平衡树的区别,可以认为是"是否按照重要度逐渐降低"的顺序 ...
- 从决策树学习谈到贝叶斯分类算法、EM、HMM --别人的,拷来看看
从决策树学习谈到贝叶斯分类算法.EM.HMM 引言 最近在面试中,除了基础 & 算法 & 项目之外,经常被问到或被要求介绍和描述下自己所知道的几种分类或聚类算法(当然,这完全 ...
- 从决策树学习谈到贝叶斯分类算法、EM、HMM
从决策树学习谈到贝叶斯分类算法.EM.HMM (Machine Learning & Recommend Search交流新群:172114338) 引言 log ...
- 机器学习实战 -- 决策树(ID3)
机器学习实战 -- 决策树(ID3) ID3是什么我也不知道,不急,知道他是干什么的就行 ID3是最经典最基础的一种决策树算法,他会将每一个特征都设为决策节点,有时候,一个数据集中,某些特征属 ...
- pyhton机器学习入门基础(机器学习与决策树)
//2019.07.26#scikit-learn数据挖掘工具包1.Scikit learn是基于python的数据挖掘和机器学习的工具包,方便实现数据的数据分析与高级操作,是数据分析里面非常重要的工 ...
- 机器学习实战---决策树CART回归树实现
机器学习实战---决策树CART简介及分类树实现 一:对比分类树 CART回归树和CART分类树的建立算法大部分是类似的,所以这里我们只讨论CART回归树和CART分类树的建立算法不同的地方.首先,我 ...
- Python机器学习笔记:奇异值分解(SVD)算法
完整代码及其数据,请移步小编的GitHub 传送门:请点击我 如果点击有误:https://github.com/LeBron-Jian/MachineLearningNote 奇异值分解(Singu ...
随机推荐
- ORA-12537: TNS:connection closed
http://www.vitalsofttech.com/ora-12537-tnsconnection-closed/ Question: When trying to establish a sq ...
- Django进阶2
一.ORM操作进阶 ForeignKey关联 示例models from django.db import models # Create your models here. class User(m ...
- 基于webrtc的资源释放问题(二)
基于webrtc的资源释放问题(二) ——建立连接的过程中意外中断 应用背景: 我们在打电话的时候会不会遇到这种情况?打电话的时候未接通之前挂掉了电话,或者在接通之后建立的连接的过程中挂掉电话? 特别 ...
- php使用内置的mcrypt_encrypt和mcrypt_decrypt进行字符串加密解密
<?php /*****************************加密*******************************/$key = "miyao";// ...
- django系列--第一节
学习前准备 安装必须的学习环境环境(学习前提:python2.7) pip install django==1.8 pip install mysqldb(后面会用) pip install Pill ...
- js创建节点及其属性
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- js压缩图片base64长度
var myCanvas=$('.img-container > img').cropper('getCroppedCanvas'); (function (base64){ var image ...
- [Linux]cmd to use
0x01 Linux Perfermance Analysis in 60s 1> uptime ---load averages 2> dmesg -r | tail ---kernel ...
- Rails中的缓存
最近学习Rails. 看到如下代码: <% if notice %> <p id="notice"><%= notice %></p> ...
- X.509,RSA,PKCS 普及
X.509 X.509是一种非常通用的证书格式.所有的证书都符合ITU-T X.509国际标准,因此(理论上)为一种应用创建的证书可以用于任何其他符合X.509标准的应用. 在一份证书中,必须证明公钥 ...
