caffe-mnist别手写数字
【来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/denny402/p/5685909.html】
整个工作目录建在:/home/ubunt16041/caffe/examples/abc_mnist/
再建一个mnist目录,所有的都放在mnist目录下。
(/home/ubuntu16041/caffe/examples/abc_mnist/mnist/)
图片下载好,test.txt,train.txt都有了。
mnist.py用来生成训练需要的文件:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import caffe
from caffe import layers as L,params as P,proto,to_proto
#设定文件的保存路径
root='/home/ubuntu16041/caffe/examples/abc_mnist/' #根目录
train_list=root+'mnist/train/train.txt' #训练图片列表
test_list=root+'mnist/test/test.txt' #测试图片列表
train_proto=root+'mnist/train.prototxt' #训练配置文件
test_proto=root+'mnist/test.prototxt' #测试配置文件
solver_proto=root+'mnist/solver.prototxt' #参数文件 #编写一个函数,生成配置文件prototxt
def Lenet(img_list,batch_size,include_acc=False):
#第一层,数据输入层,以ImageData格式输入
data, label = L.ImageData(source=img_list, batch_size=batch_size, ntop=2,root_folder=root,
transform_param=dict(scale= 0.00390625))
#第二层:卷积层
conv1=L.Convolution(data, kernel_size=5, stride=1,num_output=20, pad=0,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
#池化层
pool1=L.Pooling(conv1, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
#卷积层
conv2=L.Convolution(pool1, kernel_size=5, stride=1,num_output=50, pad=0,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
#池化层
pool2=L.Pooling(conv2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
#全连接层
fc3=L.InnerProduct(pool2, num_output=500,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
#激活函数层
relu3=L.ReLU(fc3, in_place=True)
#全连接层
fc4 = L.InnerProduct(relu3, num_output=10,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
#softmax层
loss = L.SoftmaxWithLoss(fc4, label) if include_acc: # test阶段需要有accuracy层
acc = L.Accuracy(fc4, label)
return to_proto(loss, acc)
else:
return to_proto(loss) def write_net():
#写入train.prototxt
with open(train_proto, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(Lenet(train_list,batch_size=64))) #写入test.prototxt
with open(test_proto, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(Lenet(test_list,batch_size=100, include_acc=True))) #编写一个函数,生成参数文件
def gen_solver(solver_file,train_net,test_net):
s=proto.caffe_pb2.SolverParameter()
s.train_net =train_net
s.test_net.append(test_net)
s.test_interval = 938 #60000/64,测试间隔参数:训练完一次所有的图片,进行一次测试
s.test_iter.append(500) #50000/100 测试迭代次数,需要迭代500次,才完成一次所有数据的测试
s.max_iter = 9380 #10 epochs , 938*10,最大训练次数
s.base_lr = 0.01 #基础学习率
s.momentum = 0.9 #动量
s.weight_decay = 5e-4 #权值衰减项
s.lr_policy = 'step' #学习率变化规则
s.stepsize=3000 #学习率变化频率
s.gamma = 0.1 #学习率变化指数
s.display = 20 #屏幕显示间隔
s.snapshot = 938 #保存caffemodel的间隔
s.snapshot_prefix = root+'mnist/lenet' #caffemodel前缀
s.type ='SGD' #优化算法
s.solver_mode = proto.caffe_pb2.SolverParameter.CPU #加速
#写入solver.prototxt
with open(solver_file, 'w') as f:
f.write(str(s)) #开始训练
def training(solver_proto):
solver = caffe.SGDSolver(solver_proto)
solver.solve()
#
if __name__ == '__main__':
write_net()
gen_solver(solver_proto,train_proto,test_proto)
training(solver_proto)
运行:python mnist.py
接下来就是生成deploy.prototxt文件:
deploy.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from caffe import layers as L,params as P,to_proto
root='/home/ubuntu16041/caffe/examples/abc_mnist/'
deploy=root+'mnist/deploy.prototxt' #文件保存路径 def create_deploy():
#少了第一层,data层
conv1=L.Convolution(bottom='data', kernel_size=5, stride=1,num_output=20, pad=0,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
pool1=L.Pooling(conv1, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
conv2=L.Convolution(pool1, kernel_size=5, stride=1,num_output=50, pad=0,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
pool2=L.Pooling(conv2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
fc3=L.InnerProduct(pool2, num_output=500,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
relu3=L.ReLU(fc3, in_place=True)
fc4 = L.InnerProduct(relu3, num_output=10,weight_filler=dict(type='xavier'))
#最后没有accuracy层,但有一个Softmax层
prob=L.Softmax(fc4)
return to_proto(prob)
def write_deploy():
with open(deploy, 'w') as f:
f.write('name:"Lenet"\n')
f.write('input:"data"\n')
f.write('input_dim:1\n')
f.write('input_dim:3\n')
f.write('input_dim:28\n')
f.write('input_dim:28\n')
f.write(str(create_deploy()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
write_deploy()
照样运行,就可以生成了。
最后就是测试:test.py
#coding=utf-8 import caffe
import numpy as np
root='/home/ubuntu16041/caffe/examples/abc_mnist/' #根目录
deploy=root + 'mnist/deploy.prototxt' #deploy文件
caffe_model=root + 'mnist/lenet_iter_9380.caffemodel' #训练好的 caffemodel
img=root+'mnist/test/8/00061.png' #随机找的一张待测图片
labels_filename = root + 'mnist/test/labels.txt' #类别名称文件,将数字标签转换回类别名称 net = caffe.Net(deploy,caffe_model,caffe.TEST) #加载model和network #图片预处理设置
transformer = caffe.io.Transformer({'data': net.blobs['data'].data.shape}) #设定图片的shape格式(1,3,28,28)
transformer.set_transpose('data', (2,0,1)) #改变维度的顺序,由原始图片(28,28,3)变为(3,28,28)
#transformer.set_mean('data', np.load(mean_file).mean(1).mean(1)) #减去均值,前面训练模型时没有减均值,这儿就不用
transformer.set_raw_scale('data', 255) # 缩放到【0,255】之间
transformer.set_channel_swap('data', (2,1,0)) #交换通道,将图片由RGB变为BGR im=caffe.io.load_image(img) #加载图片
net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformer.preprocess('data',im) #执行上面设置的图片预处理操作,并将图片载入到blob中 #执行测试
out = net.forward() labels = np.loadtxt(labels_filename, str, delimiter='\t') #读取类别名称文件
prob= net.blobs['Softmax1'].data[0].flatten() #取出最后一层(Softmax)属于某个类别的概率值,并打印
print prob
order=prob.argsort()[-1] #将概率值排序,取出最大值所在的序号
print 'the class is:',labels[order] #将该序号转换成对应的类别名称,并打印
至此,完成对某个手写字的识别。要想识别另外的手写字,就在test.py里面改!
-----
显示曲线效果的:【http://www.cnblogs.com/denny402/p/5686067.html】
look.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Jul 19 16:22:22 2016 @author: root
""" import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import caffe #caffe.set_device(0)
#caffe.set_mode_gpu() # 使用SGDSolver,即随机梯度下降算法
solver = caffe.SGDSolver('/home/ubuntu16041/caffe/examples/abc_mnist/mnist/solver.prototxt') # 等价于solver文件中的max_iter,即最大解算次数
niter = 9380
# 每隔100次收集一次数据
display= 100 # 每次测试进行100次解算,10000/100
test_iter = 100
# 每500次训练进行一次测试(100次解算),60000/64
test_interval =938 #初始化
train_loss = np.zeros(np.ceil(niter * 1.0 / display))
test_loss = np.zeros(np.ceil(niter * 1.0 / test_interval))
test_acc = np.zeros(np.ceil(niter * 1.0 / test_interval)) # iteration 0,不计入
solver.step(1) # 辅助变量
_train_loss = 0; _test_loss = 0; _accuracy = 0
# 进行解算
for it in range(niter):
# 进行一次解算
solver.step(1)
# 每迭代一次,训练batch_size张图片
_train_loss += solver.net.blobs['SoftmaxWithLoss1'].data
if it % display == 0:
# 计算平均train loss
train_loss[it // display] = _train_loss / display
_train_loss = 0 if it % test_interval == 0:
for test_it in range(test_iter):
# 进行一次测试
solver.test_nets[0].forward()
# 计算test loss
_test_loss += solver.test_nets[0].blobs['SoftmaxWithLoss1'].data
# 计算test accuracy
_accuracy += solver.test_nets[0].blobs['Accuracy1'].data
# 计算平均test loss
test_loss[it / test_interval] = _test_loss / test_iter
# 计算平均test accuracy
test_acc[it / test_interval] = _accuracy / test_iter
_test_loss = 0
_accuracy = 0 # 绘制train loss、test loss和accuracy曲线
print '\nplot the train loss and test accuracy\n'
_, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax2 = ax1.twinx() # train loss -> 绿色
ax1.plot(display * np.arange(len(train_loss)), train_loss, 'g')
# test loss -> 黄色
ax1.plot(test_interval * np.arange(len(test_loss)), test_loss, 'y')
# test accuracy -> 红色
ax2.plot(test_interval * np.arange(len(test_acc)), test_acc, 'r') ax1.set_xlabel('iteration')
ax1.set_ylabel('loss')
ax2.set_ylabel('accuracy')
plt.show()
就会出现一个:
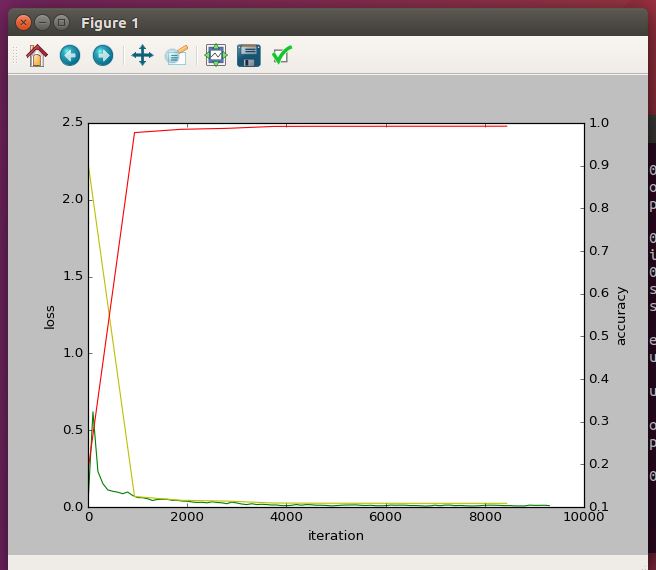
ok,接下来就要读读代码啦,今天我叫搬运工:)。。。
【windows可以参考这个:http://blog.csdn.net/zb1165048017/article/details/52217772
http://www.cnblogs.com/yixuan-xu/p/5862657.html
】
caffe-mnist别手写数字的更多相关文章
- keras实现mnist数据集手写数字识别
一. Tensorflow环境的安装 这里我们只讲CPU版本,使用 Anaconda 进行安装 a.首先我们要安装 Anaconda 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1AxdGi ...
- caffe的python接口学习(4):mnist实例---手写数字识别
深度学习的第一个实例一般都是mnist,只要这个例子完全弄懂了,其它的就是举一反三的事了.由于篇幅原因,本文不具体介绍配置文件里面每个参数的具体函义,如果想弄明白的,请参看我以前的博文: 数据层及参数 ...
- caffe的python接口学习(4)mnist实例手写数字识别
以下主要是摘抄denny博文的内容,更多内容大家去看原作者吧 一 数据准备 准备训练集和测试集图片的列表清单; 二 导入caffe库,设定文件路径 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- im ...
- 分类-MNIST(手写数字识别)
这是学习<Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow>的笔记,如果此笔记对该书有侵权内容,请联系我,将其删除. 这 ...
- CNN完成mnist数据集手写数字识别
# coding: utf-8 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data d ...
- MNIST手写数字数据库
手写数字库很容易建立,但是总会很浪费时间.Google实验室的Corinna Cortes和纽约大学柯朗研究所的Yann LeCun建有一个手写数字数据库,训练库有60,000张手写数字图像,测试库有 ...
- keras—多层感知器MLP—MNIST手写数字识别
一.手写数字识别 现在就来说说如何使用神经网络实现手写数字识别. 在这里我使用mind manager工具绘制了要实现手写数字识别需要的模块以及模块的功能: 其中隐含层节点数量(即神经细胞数量)计算 ...
- mnist手写数字识别——深度学习入门项目(tensorflow+keras+Sequential模型)
前言 今天记录一下深度学习的另外一个入门项目——<mnist数据集手写数字识别>,这是一个入门必备的学习案例,主要使用了tensorflow下的keras网络结构的Sequential模型 ...
- 用Keras搭建神经网络 简单模版(三)—— CNN 卷积神经网络(手写数字图片识别)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np np.random.seed(1337) #for reproducibility再现性 from keras.d ...
- 用Keras搭建神经网络 简单模版(二)——Classifier分类(手写数字识别)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np np.random.seed(1337) #for reproducibility再现性 from keras.d ...
随机推荐
- 谈谈pooling?
使用pooling的目的之一是获取一定的特征不变性,目前用的比较多的是Max..,非线性对于Deep的重要性不用多说,pooling是主要贡献之一,当然少不了relu类的激活函数.pooling还有一 ...
- MSSQL—字符串分离(Split函数)
前面提到了记录合并,有了合并需求肯定也会有分离需求,说到字符串分离,大家肯定会想到SPLIT函数,这个在.NET,Java和JS中都有函数,很可惜在SQL SERVER中没有,我们只能自己来写这么一个 ...
- gdb 调试出现 ImportError: No module named 'libstdcxx'
在emacs使用gdb调试程序,出现错误 , in <module> from libstdcxx.v6.printers import register_libstdcxx_printe ...
- PHP 输入流 php://input
在使用xml-rpc的时候,server端获取client数据,主要是通过php输入流input,而不是$_POST数组.所以,这里主要探讨php输入流php://input 对一php://in ...
- 矩阵分解ALS方法
目标函数 优化目标函数 利用坐标下降法,依次更新u和v的值.u和v的先后顺序无所谓,只要保证两者是交替更新的就好.这种方法又称为alternating least squares(ALS). 增加偏置 ...
- VMware卸载出现“the msi failed”解决办法
最近被VMware卸载搞烦死掉,最后通过这个帖子解决. http://www.cnblogs.com/noble/p/4144267.html 总结:有啥软件使用问题最好找官方的FAQ找答案,不然百度 ...
- CentOS7 搭建python3 Django环境
yum install gcc yum install make yum install openssl-devel -y yum install sqlite-devel -y wget https ...
- wordpress(三)wordpress手动更新
第一:备份数据库还有文件 第二:从WP中文官网下载最新版WordPress,下载完毕解压到你电脑上. 第三:删除博客主机上的wp-includes和wp-admin目录. 第四:将解压在本地电脑的wo ...
- chosen组件实现下拉框
chosen组件用于增强原生的select控件,使之有更好的用户体验.官方demo https://harvesthq.github.io/chosen/ 目前项目中碰到的使用,比如一个页面中有两个不 ...
- ZTOOLS HTTP®EXTEST&JSONS 工具包
下载地址:点击下载
