opencv之dlib库人脸识别
基础知识
python知识:
import os,shutil
shutil.rmtree("C:\\Users\\yangwj\\Desktop\\test") #删除目录
os.remove("C:\\Users\\yangwj\\Desktop\\replay_pid28076.log") # 删除文件
os.path.isfile() # 判断是否为文件
os.listdir() # 列出路径下的目录
1、从摄像头获取人脸图片
import dlib # 人脸处理的库 Dlib
import numpy as np # 数据处理的库 Numpy
import cv2 # 图像处理的库 OpenCv import os # 读写文件
import shutil # 读写文件 # Dlib 正向人脸检测器 / frontal face detector
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector() # Dlib 68 点特征预测器 / 68 points features predictor
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('data/data_dlib/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat') # OpenCv 调用摄像头 use camera
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 设置视频参数 set camera
cap.set(3, 480) # 人脸截图的计数器 the counter for screen shoot
cnt_ss = 0 # 存储人脸的文件夹 the folder to save faces
current_face_dir = "" # 保存 faces images 的路径 the directory to save images of faces
path_photos_from_camera = "data/data_faces_from_camera/" # 新建保存人脸图像文件和数据CSV文件夹
# mkdir for saving photos and csv
def pre_work_mkdir(): # 新建文件夹 / make folders to save faces images and csv
if os.path.isdir(path_photos_from_camera):
pass
else:
os.mkdir(path_photos_from_camera) pre_work_mkdir() ##### optional/可选, 默认关闭 #####
# 删除之前存的人脸数据文件夹
# delete the old data of faces
def pre_work_del_old_face_folders():
# 删除之前存的人脸数据文件夹
# 删除 "/data_faces_from_camera/person_x/"...
folders_rd = os.listdir(path_photos_from_camera)
for i in range(len(folders_rd)):
shutil.rmtree(path_photos_from_camera+folders_rd[i]) if os.path.isfile("data/features_all.csv"):
os.remove("data/features_all.csv") # 这里在每次程序录入之前, 删掉之前存的人脸数据
# 如果这里打开,每次进行人脸录入的时候都会删掉之前的人脸图像文件夹 person_1/,person_2/,person_3/...
# If enable this function, it will delete all the old data in dir person_1/,person_2/,/person_3/...
# pre_work_del_old_face_folders()
################################## # 如果有之前录入的人脸 / if the old folders exists
# 在之前 person_x 的序号按照 person_x+1 开始录入 / start from person_x+1
if os.listdir(path_photos_from_camera):
# 获取已录入的最后一个人脸序号 / get the num of latest person
person_list = os.listdir(path_photos_from_camera)
person_num_list = []
for person in person_list:
person_num_list.append(int(person.split('_')[-1]))
person_cnt = max(person_num_list) # 如果第一次存储或者没有之前录入的人脸, 按照 person_1 开始录入
# start from person_1
else:
person_cnt = 0 # 之后用来控制是否保存图像的 flag / the flag to control if save
save_flag = 1 # 之后用来检查是否先按 'n' 再按 's' / the flag to check if press 'n' before 's'
press_n_flag = 0 while cap.isOpened():
flag, img_rd = cap.read()
# print(img_rd.shape)
# It should be 480 height * 640 width kk = cv2.waitKey(1) img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY) # 人脸数 faces
faces = detector(img_gray, 0) # 待会要写的字体 / font to write
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX # 按下 'n' 新建存储人脸的文件夹 / press 'n' to create the folders for saving faces
if kk == ord('n'):
person_cnt += 1
print("请输入名字")
person_name = input()
current_face_dir = path_photos_from_camera + "person_" + str(person_cnt)
os.makedirs(current_face_dir)
print('\n')
print("新建的人脸文件夹 / Create folders: ", current_face_dir) cnt_ss = 0 # 将人脸计数器清零 / clear the cnt of faces
press_n_flag = 1 # 已经按下 'n' / have pressed 'n' # 检测到人脸 / if face detected
if len(faces) != 0:
# 矩形框 / show the rectangle box
for k, d in enumerate(faces):
# 计算矩形大小
# we need to compute the width and height of the box
# (x,y), (宽度width, 高度height)
pos_start = tuple([d.left(), d.top()])
pos_end = tuple([d.right(), d.bottom()]) # 计算矩形框大小 / compute the size of rectangle box
height = (d.bottom() - d.top())
width = (d.right() - d.left()) hh = int(height/2)
ww = int(width/2) # 设置颜色 / the color of rectangle of faces detected
color_rectangle = (255, 255, 255) # 判断人脸矩形框是否超出 480x640
if (d.right()+ww) > 640 or (d.bottom()+hh > 480) or (d.left()-ww < 0) or (d.top()-hh < 0):
cv2.putText(img_rd, "OUT OF RANGE", (20, 300), font, 0.8, (0, 0, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
color_rectangle = (0, 0, 255)
save_flag = 0
if kk == ord('s'):
print("请调整位置 / Please adjust your position")
else:
color_rectangle = (255, 255, 255)
save_flag = 1 # TODO 可以考虑不减 ,看效果---->结果是只有脸部图像
cv2.rectangle(img_rd,
tuple([d.left() - ww, d.top() - hh]),
tuple([d.right() + ww, d.bottom() + hh]),
color_rectangle, 2) # 根据人脸大小生成空的图像 / create blank image according to the size of face detected
im_blank = np.zeros((int(height*2), width*2, 3), np.uint8) if save_flag:
# 按下 's' 保存摄像头中的人脸到本地 / press 's' to save faces into local images
if kk == ord('s'):
# 检查有没有先按'n'新建文件夹 / check if you have pressed 'n'
if press_n_flag:
cnt_ss += 1
for ii in range(height*2):
for jj in range(width*2):
# 将人脸图像填充到空图像中
im_blank[ii][jj] = img_rd[d.top()-hh + ii][d.left()-ww + jj]
cv2.imwrite(current_face_dir + "/img_face_" + str(cnt_ss) + ".jpg", im_blank)
print("写入本地 / Save into:", str(current_face_dir) + "/img_face_" + str(cnt_ss) + ".jpg")
else:
print("请在按 'S' 之前先按 'N' 来建文件夹 / Please press 'N' before 'S'") # 显示人脸数 / show the numbers of faces detected
cv2.putText(img_rd, "Faces: " + str(len(faces)), (20, 100), font, 0.8, (0, 255, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA) # 添加说明 / add some statements
cv2.putText(img_rd, "Face Register", (20, 40), font, 1, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_rd, "N: New face folder", (20, 350), font, 0.8, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_rd, "S: Save current face", (20, 400), font, 0.8, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_rd, "Q: Quit", (20, 450), font, 0.8, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA) # 按下 'q' 键退出 / press 'q' to exit
if kk == ord('q'):
break # 如果需要摄像头窗口大小可调 / uncomment this line if you want the camera window is resizeable
# cv2.namedWindow("camera", 0) cv2.imshow("camera", img_rd) # 释放摄像头 / release camera
cap.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
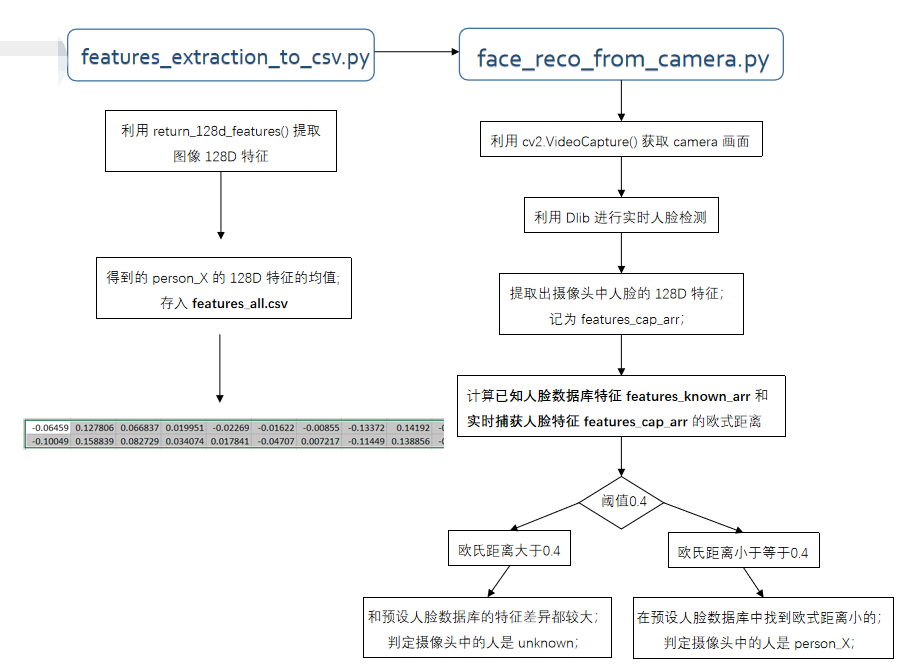
2、将获取的人脸图片转为csv文件
import cv2
import os
import dlib
from skimage import io
import csv
import numpy as np # 要读取人脸图像文件的路径q
path_images_from_camera = "data/data_faces_from_camera/" # Dlib 正向人脸检测器
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector() # Dlpredictorib 人脸预测器
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor("data/data_dlib/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat") # Dlib 人脸识别模型
# Face recognition model, the object maps human faces into 128D vectors
# shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat
face_rec = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1("data/data_dlib/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat") # 返回单张图像的 128D 特征
def return_128d_features(path_img):
img_rd = io.imread(path_img)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
faces = detector(img_gray, 1) print("%-40s %-20s" % ("检测到人脸的图像 / image with faces detected:", path_img), '\n') # 因为有可能截下来的人脸再去,检测不出检测来人脸了
# 所以要确保是 检测到人脸的人脸图像 拿去算特征
if len(faces) != 0:
shape = predictor(img_gray, faces[0])
face_descriptor = face_rec.compute_face_descriptor(img_gray, shape)
print("faces")
else:
face_descriptor = 0
print("no face") return face_descriptor # 将文件夹中照片特征提取出来, 写入 CSV
def return_features_mean_personX(path_faces_personX):
features_list_personX = []
photos_list = os.listdir(path_faces_personX)
if photos_list:
for i in range(len(photos_list)):
# 调用return_128d_features()得到128d特征
print("%-40s %-20s" % ("正在读的人脸图像 / image to read:", path_faces_personX + "/" + photos_list[i]))
features_128d = return_128d_features(path_faces_personX + "/" + photos_list[i])
# print(features_128d)
# 遇到没有检测出人脸的图片跳过
if features_128d == 0:
continue
else:
features_list_personX.append(features_128d)
else:
print("文件夹内图像文件为空 / Warning: No images in " + path_faces_personX + '/', '\n') # 计算 128D 特征的均值
# personX 的 N 张图像 x 128D -> 1 x 128D
if features_list_personX:
features_mean_personX = np.array(features_list_personX).mean(axis=0)
else:
features_mean_personX = '' return features_mean_personX # 获取已录入的最后一个人脸序号 / get the num of latest person
person_list = os.listdir("data/data_faces_from_camera/")
person_num_list = []
for person in person_list:
person_num_list.append(int(person.split('_')[-1]))
person_cnt = max(person_num_list) with open("data/features_all.csv", "w", newline="") as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
for person in range(person_cnt):
# Get the mean/average features of face/personX, it will be a list with a length of 128D
print(path_images_from_camera + "person_"+str(person+1))
features_mean_personX = return_features_mean_personX(path_images_from_camera + "person_"+str(person+1))
writer.writerow(features_mean_personX)
print("特征均值 / The mean of features:", list(features_mean_personX))
print('\n')
print("所有录入人脸数据存入 / Save all the features of faces registered into: data/features_all.csv")
3、人脸识别
import dlib # 人脸处理的库 Dlib
import numpy as np # 数据处理的库 numpy
import cv2 # 图像处理的库 OpenCv
import pandas as pd # 数据处理的库 Pandas # 人脸识别模型,提取128D的特征矢量
# face recognition model, the object maps human faces into 128D vectors
# Refer this tutorial: http://dlib.net/python/index.html#dlib.face_recognition_model_v1
facerec = dlib.face_recognition_model_v1("data/data_dlib/dlib_face_recognition_resnet_model_v1.dat") # 计算两个128D向量间的欧式距离
# compute the e-distance between two 128D features
def return_euclidean_distance(feature_1, feature_2):
feature_1 = np.array(feature_1)
feature_2 = np.array(feature_2)
dist = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(feature_1 - feature_2)))
return dist # 处理存放所有人脸特征的 csv
path_features_known_csv = "data/features_all.csv"
csv_rd = pd.read_csv(path_features_known_csv, header=None) # 用来存放所有录入人脸特征的数组
# the array to save the features of faces in the database
features_known_arr = [] # 读取已知人脸数据
# print known faces
for i in range(csv_rd.shape[0]):
features_someone_arr = []
for j in range(0, len(csv_rd.ix[i, :])):
features_someone_arr.append(csv_rd.ix[i, :][j])
features_known_arr.append(features_someone_arr)
print("Faces in Database:", len(features_known_arr)) # Dlib 检测器和预测器
# The detector and predictor will be used
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('data/data_dlib/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat') # 创建 cv2 摄像头对象
# cv2.VideoCapture(0) to use the default camera of PC,
# and you can use local video name by use cv2.VideoCapture(filename)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # cap.set(propId, value)
# 设置视频参数,propId 设置的视频参数,value 设置的参数值
cap.set(3, 480) # cap.isOpened() 返回 true/false 检查初始化是否成功
# when the camera is open
while cap.isOpened(): flag, img_rd = cap.read()
kk = cv2.waitKey(1) # 取灰度
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_rd, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY) # 人脸数 faces
faces = detector(img_gray, 0) # 待会要写的字体 font to write later
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX # 存储当前摄像头中捕获到的所有人脸的坐标/名字
# the list to save the positions and names of current faces captured
pos_namelist = []
name_namelist = [] # 按下 q 键退出
# press 'q' to exit
if kk == ord('q'):
break
else:
# 检测到人脸 when face detected
if len(faces) != 0:
# 获取当前捕获到的图像的所有人脸的特征,存储到 features_cap_arr
# get the features captured and save into features_cap_arr
features_cap_arr = []
for i in range(len(faces)):
shape = predictor(img_rd, faces[i])
features_cap_arr.append(facerec.compute_face_descriptor(img_rd, shape)) # 遍历捕获到的图像中所有的人脸
# traversal all the faces in the database
for k in range(len(faces)):
print("##### camera person", k+1, "#####")
# 让人名跟随在矩形框的下方
# 确定人名的位置坐标
# 先默认所有人不认识,是 unknown
# set the default names of faces with "unknown"
name_namelist.append("unknown") # 每个捕获人脸的名字坐标 the positions of faces captured
pos_namelist.append(tuple([faces[k].left(), int(faces[k].bottom() + (faces[k].bottom() - faces[k].top())/4)])) # 对于某张人脸,遍历所有存储的人脸特征
# for every faces detected, compare the faces in the database
e_distance_list = []
for i in range(len(features_known_arr)):
# 如果 person_X 数据不为空
if str(features_known_arr[i][0]) != '0.0':
print("with person", str(i + 1), "the e distance: ", end='')
e_distance_tmp = return_euclidean_distance(features_cap_arr[k], features_known_arr[i])
print(e_distance_tmp)
e_distance_list.append(e_distance_tmp)
else:
# 空数据 person_X
e_distance_list.append(999999999)
# Find the one with minimum e distance
similar_person_num = e_distance_list.index(min(e_distance_list))
print("Minimum e distance with person", int(similar_person_num)+1) if min(e_distance_list) < 0.4:
# 在这里修改 person_1, person_2 ... 的名字
# 可以在这里改称 Jack, Tom and others
# Here you can modify the names shown on the camera
name_namelist[k] = "Person "+str(int(similar_person_num)+1)
print("May be person "+str(int(similar_person_num)+1))
else:
print("Unknown person") # 矩形框
# draw rectangle
for kk, d in enumerate(faces):
# 绘制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(img_rd, tuple([d.left(), d.top()]), tuple([d.right(), d.bottom()]), (0, 255, 255), 2)
print('\n') # 在人脸框下面写人脸名字
# write names under rectangle
for i in range(len(faces)):
cv2.putText(img_rd, name_namelist[i], pos_namelist[i], font, 0.8, (0, 255, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA) print("Faces in camera now:", name_namelist, "\n") cv2.putText(img_rd, "Press 'q': Quit", (20, 450), font, 0.8, (84, 255, 159), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_rd, "Face Recognition", (20, 40), font, 1, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img_rd, "Faces: " + str(len(faces)), (20, 100), font, 1, (0, 0, 255), 1, cv2.LINE_AA) # 窗口显示 show with opencv
cv2.imshow("camera", img_rd) # 释放摄像头 release camera
cap.release() # 删除建立的窗口 delete all the windows
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
完毕!
声明:代码是github以为博主的,本人只是拿着学习人脸识别,为了尊重博主,贴出其代码地址:https://github.com/coneypo/Dlib_face_recognition_from_camera
opencv之dlib库人脸识别的更多相关文章
- OpenCV 和 Dlib 人脸识别基础
00 环境配置 Anaconda 安装 1 下载 https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/ 考虑到兼容性问题,推荐下载Anaconda3-5.2.0版本. 2 安装 3 测 ...
- 写个神经网络,让她认得我`(๑•ᴗ•๑)(Tensorflow,opencv,dlib,cnn,人脸识别)
训练一个神经网络 能让她认得我 阅读原文 这段时间正在学习tensorflow的卷积神经网络部分,为了对卷积神经网络能够有一个更深的了解,自己动手实现一个例程是比较好的方式,所以就选了一个这样比较有点 ...
- Opencv与dlib联合进行人脸关键点检测与识别
前言 依赖库:opencv 2.4.9 /dlib 19.0/libfacedetection 本篇不记录如何配置,重点在实现上.使用libfacedetection实现人脸区域检测,联合dlib标记 ...
- Python 实现的猫脸识别、人脸识别器。
代码地址如下:http://www.demodashi.com/demo/13071.html 前言: OpenCV是开源的跨平台计算机视觉库,提供了Python等语言的接口,实现了图像处理和计算机视 ...
- 05-人脸识别-FaceNet的感性认识
源码链接:https://github.com/davidsandberg/facenet 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.03832.pdf B站大神视频解读论文:h ...
- OpenCV/Python/dlib眨眼检测
今天我们来使用面部标志和OpenCV 检测和计算视频流中的眨眼次数. 为了构建我们的眨眼检测器,我们将计算一个称为眼睛纵横比(EAR)的指标,由Soukupová和Čech在其2016年的论文&quo ...
- 利用face_recognition,dlib与OpenCV调用摄像头进行人脸识别
用已经搭建好 face_recognition,dlib 环境来进行人脸识别 未搭建好环境请参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/guihua-pingting/p/12201077. ...
- OpenCV学习 物体检测 人脸识别 填充颜色
介绍 OpenCV是开源计算机视觉和机器学习库.包含成千上万优化过的算法.项目地址:http://opencv.org/about.html.官方文档:http://docs.opencv.org/m ...
- 基于QT和OpenCV的人脸检測识别系统(2)
紧接着上一篇博客的讲 第二步是识别部分 人脸识别 把上一阶段检測处理得到的人脸图像与数据库中的已知 人脸进行比对,判定人脸相应的人是谁(此处以白色文本显示). 人脸预处理 如今你已经得到一张人脸,你能 ...
随机推荐
- 关于MQ的几件小事(一)消息队列的用途、优缺点、技术选型
1.为什么使用消息队列? (1)解耦:可以在多个系统之间进行解耦,将原本通过网络之间的调用的方式改为使用MQ进行消息的异步通讯,只要该操作不是需要同步的,就可以改为使用MQ进行不同系统之间的联系,这样 ...
- linux网络编程之socket编程(七)
今天继续学习socket编程,北京在持续几天的雾霾天之后久违的太阳终于出来了,心情也特别特别的好,于是乎,在这美好的夜晚,该干点啥事吧,那当然就是继续坚持我的程序学习喽,闲话不多说,进入正题: 通过这 ...
- P1417 烹调方案[背包]
题目背景 由于你的帮助,火星只遭受了最小的损失.但gw懒得重建家园了,就造了一艘飞船飞向遥远的earth星.不过飞船飞到一半,gw发现了一个很严重的问题:肚子饿了~ gw还是会做饭的,于是拿出了储藏的 ...
- 【图文教程】CentOS 7配置静态IP地址
文档目标:帮助新手在刚刚安装好的CentOS 7上设置静态IP地址. 目标人群:本篇教程比较简单,针对的是初学者,专业人士请跳过,不喜勿喷.谢谢! 在vmware中安装好centos7(安装过程省略) ...
- H3C常见视图及命令
H3C常见视图及命令 H3C Comware的视图模式 1.用户视图:查看系统的硬件和系统的信息 2.系统视图(类似于Cisco的配置模式) 3.路由协议视图 4.接口视图 5.用户界面视图 各种视图 ...
- 1. let与const
1.ES6 新增了let命令,用来声明变量.它的用法类似于var,但是所声明的变量,只在let命令所在的代码块内有效. var a = []; for (var i = 0;i<10;i++) ...
- Selenium常用API的使用java语言之12-定位一组元素
在第(五)节我们已经学习了8种定位方法, 那8种定位方法是针对单个元素定位的, WebDriver还提供了另外8种用于定位一组元素的方法. import org.openqa.selenium.By; ...
- glog的安装使用
参考 :https://blog.csdn.net/Pig_Pig_Bang/article/details/81632962 https://blog.csdn.net/cywtd/article/ ...
- div 水平垂直居中
css <style> .main{ background: #999999; width: 600px; height: 400px; position: absolute; top: ...
- 论文笔记-Deep Affinity Network for Multiple Object Tracking
作者: ShijieSun, Naveed Akhtar, HuanShengSong, Ajmal Mian, Mubarak Shah 来源: arXiv:1810.11780v1 项目:http ...
