【原创】go语言学习(二十)并发编程
目录
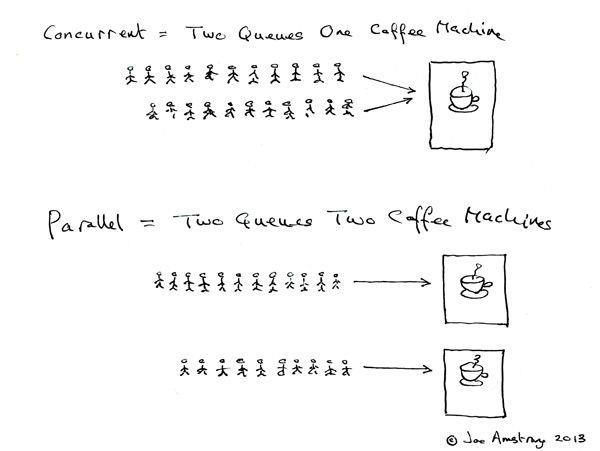
- 并发和并行
- Goroutine初探
- Goroutine实战
- Goroutine原理浅析
- Channel介绍
- Waitgroup介绍
- Workerpool的实现
并发和并行
1、概念
A. 并发:同一时间段内执行多个操作。
B. 并行:同一时刻执行多个操作。
Goroutine初探
1、多线程
A. 线程是由操作系统进行管理,也就是处于内核态。
B. 线程之间进行切换,需要发生用户态到内核态的切换。
C. 当系统中运行大量线程,系统会变的非常慢。
D. 用户态的线程,支持大量线程创建。也叫协程或goroutine。
2、 创建goroutine
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func hello() {
fmt.Println("Hello world goroutine")
}
func main() {
go hello()
fmt.Println("main function")
}
3、修复代码:主进程存在,goroutine才能执行。
package main
import (
"fmt“
“time”
)
func hello() {
fmt.Println("Hello world goroutine")
}
func main() {
go hello()
time.Sleep(1*time.Second)
fmt.Println("main function")
}
Goroutine实战
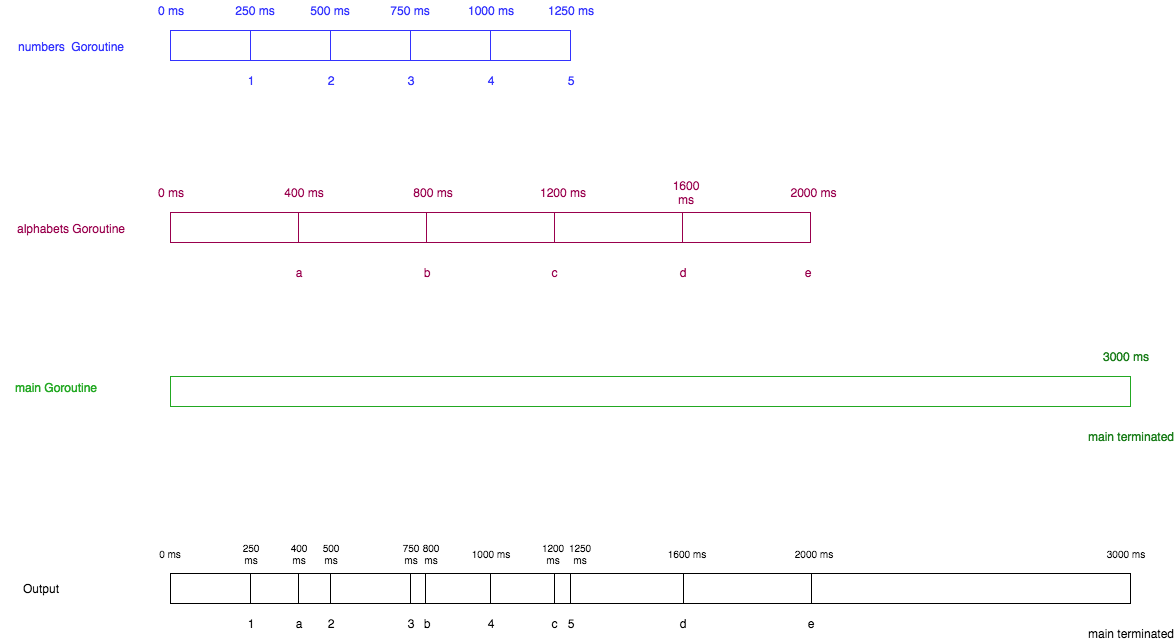
1、 启动多个goroutine
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func numbers() {
for i := 1; i <= 5; i++ {
time.Sleep(250 * time.Millisecond)
fmt.Printf("%d ", i)
}
}
func alphabets() {
for i := 'a'; i <= 'e'; i++ {
time.Sleep(400 * time.Millisecond)
fmt.Printf("%c ", i)
}
}
func main() {
go numbers()
go alphabets()
time.Sleep(3000 * time.Millisecond)
fmt.Println("main terminated")
}
2、程序分析
3、 多核控制
A. 通过runtime包进行多核设置
B. GOMAXPROCS设置当前程序运行时占用的cpu核数
C. NumCPU获取当前系统的cpu核数
package main import (
"fmt"
"time"
) func hello(i int) {
fmt.Println("hello goroutine", i)
} func main() {
//runtime.GOMAXPROCS(1)
//fmt.Println(runtime.NumCPU()) //单线程
//hello()
//fmt.Println("mainthread terminate") // go 多线程
//go hello()
//fmt.Println("mainthread terminate")
//time.Sleep(time.Second) for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go hello(i)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
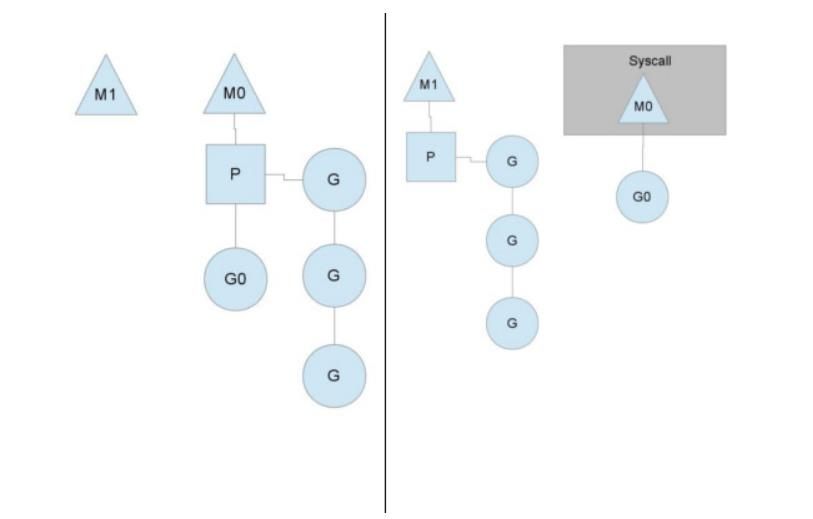
Goroutine原理浅析
1、模型抽象
A. 操作系统线程: M
B. 用户态线程(goroutine): G
C. 上下文对象:P
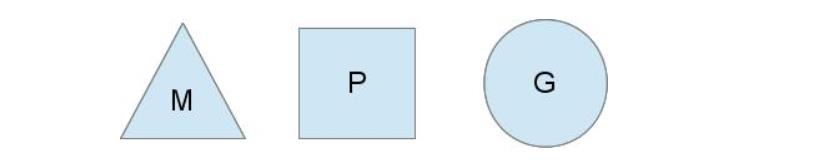
2、goroutine调度
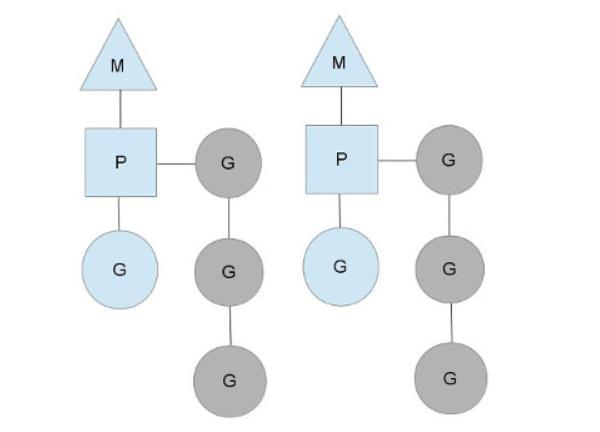
3、系统调用怎么处理
Channel介绍
1、channel介绍
A. 本质上就是一个队列,是一个容器
B. 因此定义的时候,需要只定容器中元素的类型
C. var 变量名 chan 数据类型
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var a chan int
if a == nil {
fmt.Println("channel a is nil, going to define it")
a = make(chan int)
fmt.Printf("Type of a is %T", a)
}
}
2、元素入队和出队
A. 入队操作,a <- 100
B. 出队操作:data := <- a
package channel
import "fmt"
// 管道
func main() {
var c chan int
fmt.Printf("c=%v", c)
// 初始化通道int型,10个元素
c = make(chan int, 10)
fmt.Printf("c=%v", c)
// 插入数据
c <- 100
/*
// 读取数据
data := <- c
fmt.Printf("data:%v\n", data)
*/
// 丢弃元素
<-c
}
3、阻塞chan
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var a chan int
if a == nil {
fmt.Println("channel a is nil, going to define it")
a = make(chan int)
a <- 10
fmt.Printf("Type of a is %T", a)
}
}
4、使用chan来进行goroutine同步
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func hello(done chan bool) {
fmt.Println("Hello world goroutine")
done <- true
}
func main() {
done := make(chan bool)
go hello(done)
<-done
fmt.Println("main function")
}
5、使用chan来进行goroutine同步
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func hello(done chan bool) {
fmt.Println("hello go routine is going to sleep")
time.Sleep(4 * time.Second)
fmt.Println("hello go routine awake and going to write to done")
done <- true
}
func main() {
done := make(chan bool)
fmt.Println("Main going to call hello go goroutine")
go hello(done)
<-done
fmt.Println("Main received data")
}
6、单向chan
package main
import "fmt"
func sendData(sendch chan<- int) {
sendch <- 10
}
func readData(sendch <-chan int) {
sendch <- 10
}
func main() {
chnl := make(chan int)
go sendData(chnl)
readData(chn1)
}
7、chan关闭
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func producer(chnl chan int) {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
chnl <- i
}
close(chnl)
}
func main() {
ch := make(chan int)
go producer(ch)
for {
v, ok := <-ch
if ok == false {
break
}
fmt.Println("Received ", v, ok)
}
}
8、 for range操作
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func producer(chnl chan int) {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
chnl <- i
}
close(chnl)
}
func main() {
ch := make(chan int)
go producer(ch)
for v := range ch {
fmt.Println("Received ",v)
}
}
9、 带缓冲区的chanel
A. Ch := make(chan type, capacity)
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
ch := make(chan string, 2)
ch <- “hello"
ch <- “world"
fmt.Println(<- ch)
fmt.Println(<- ch)
}
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func write(ch chan int) {
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
ch <- i
fmt.Println("successfully wrote", i, "to ch")
}
close(ch)
}
func main() {
ch := make(chan int, 2)
go write(ch)
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
for v := range ch {
fmt.Println("read value", v,"from ch")
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
}
}
10、channel的长度和容量
A. Ch := make(chan type, capacity)
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
ch := make(chan string, 3)
ch <- "naveen"
ch <- "paul"
fmt.Println("capacity is", cap(ch))
fmt.Println("length is", len(ch))
fmt.Println("read value", <-ch)
fmt.Println("new length is", len(ch))
}
Waitgroup介绍
1、 如何等待一组goroutine结束?
A. 方法一,使用不带缓冲区的channel实现
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func process(i int, ch chan bool) {
fmt.Println("started Goroutine ", i)
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
fmt.Printf("Goroutine %d ended\n", i)
ch <- true
}
func main() {
no := 3
exitChan := make(chan bool, no)
for i := 0; i < no; i++ {
go process(i, exitChan)
}
for i := 0; I < no;i++{
<-exitChan
}
fmt.Println("All go routines finished executing")
}
B. 方法二,使用sync. WaitGroup实现
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
"time"
)
func process(i int, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
fmt.Println("started Goroutine ", i)
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
fmt.Printf("Goroutine %d ended\n", i)
wg.Done()
}
func main() {
no := 3
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < no; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go process(i, &wg)
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println("All go routines finished executing")
}
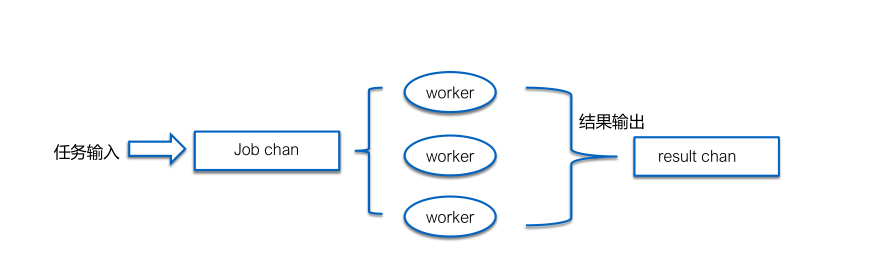
Workerpool的实现
1、worker池的实现
A. 生产者、消费者模型,简单有效
B. 控制goroutine的数量,防止goroutine泄露和暴涨
C. 基于goroutine和chan,构建workerpool非常简单
package mail import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
) // worker生产者消费者模型
type Job struct {
Number int
Id int
} type Result struct {
job *Job
sum int
} func calc(job *Job, result chan *Result){
var sum int
number := job.Number
for number != 0 {
tmp := number % 10
sum += tmp
number /= 10
} r := &Result{
job: job,
sum: sum, } result <- r
} func Worker(){
for job:= range jobChan {
calc(job, resultChan)
}
} func startWorkerPool(num int, JobChan chan *Job, resultChan *Result){
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
go Worker(JobChan, resultChan)
}
} func printResult(resultChan chan*Result) {
for result := range resultChan {
fmt.Printf("job id:%v number:%v result:%d\n",result.job.Id, result.job.Number, result.sum)
}
} func main(){
jobChan := make(chan *Job, 1000)
resultChan := make(chan *Result, 1000) startWorkerPool(128, jobChan, resultChan) for i := 0; i < 128; i ++ {
go calc()
} go printResult(resultChan)
var id int
for {
id++
number := rand.Int()
job := &Job {
Id: id,
Number: number,
} jobChan <- job
}
}
2、项目需求分析
A. 计算一个数字的各个位数之和,比如123,和等于1+2+3=6
B. 需要计算的数字使用随机算法生成
3、方案介绍
A. 任务抽象成一个个job
B. 使用job队列和result队列
C. 开一组goroutine进行实际任务计算,并把结果放回result队列
【原创】go语言学习(二十)并发编程的更多相关文章
- 《java学习二》并发编程
多线程创建方式 1.继承thread类,重写run方法 CreateThread createThread = new CreateThread(); ------createThread ...
- [CSAPP笔记][第十二章并发编程]
第十二章 并发编程 如果逻辑控制流在时间上是重叠,那么它们就是并发的(concurrent).这种常见的现象称为并发(concurrency). 硬件异常处理程序,进程和Unix信号处理程序都是大家熟 ...
- CSAPP:第十二章 并发编程
CSAPP:第十二章 并发编程 12.1 线程执行模型12.2 多线程之间并发通信12.3 其他并发问题 使用应用级并发的应用程序称为并发程序.现代操作系统提供三种基本的构造并发程序的方法: 进程 ...
- Go语言学习笔记十二: 范围(Range)
Go语言学习笔记十二: 范围(Range) rang这个关键字主要用来遍历数组,切片,通道或Map.在数组和切片中返回索引值,在Map中返回key. 这个特别像python的方式.不过写法上比较怪异使 ...
- Go语言学习笔记十: 结构体
Go语言学习笔记十: 结构体 Go语言的结构体语法和C语言类似.而结构体这个概念就类似高级语言Java中的类. 结构体定义 结构体有两个关键字type和struct,中间夹着一个结构体名称.大括号里面 ...
- 十二. Go并发编程--sync/errGroup
一.序 这一篇算是并发编程的一个补充,起因是当前有个项目,大概の 需求是,根据kafka的分区(partition)数,创建同等数量的 消费者( goroutine)从不同的分区中消费者消费数据,但是 ...
- (转)《深入理解java虚拟机》学习笔记10——并发编程(二)
Java的并发编程是依赖虚拟机内存模型的三个特性实现的: (1).原子性(Atomicity): 原子性是指不可再分的最小操作指令,即单条机器指令,原子性操作任意时刻只能有一个线程,因此是线程安全的. ...
- 深入理解计算机系统 第十二章 并发编程 part1 第二遍
三种构造并发程序的方法及其优缺点 1.进程 用这种方法,每个逻辑控制流都是一个进程,由内核来调度和维护.因为进程有独立的虚拟地址空间,想要和其他流通信,控制流必须使用某种显式的进程间通信机制. 优点: ...
- Java 面试知识点解析(二)——高并发编程篇
前言: 在遨游了一番 Java Web 的世界之后,发现了自己的一些缺失,所以就着一篇深度好文:知名互联网公司校招 Java 开发岗面试知识点解析 ,来好好的对 Java 知识点进行复习和学习一番,大 ...
- 二 python并发编程之多进程-重点
一 multiprocessing模块介绍 python中的多线程无法利用多核优势,如果想要充分地使用多核CPU的资源(os.cpu_count()查看),在python中大部分情况需要使用多进程.P ...
随机推荐
- vscode之万里挑一
前置 我们经常在工作区中打开很多项目文件夹,找起来比较麻烦. 步骤
- hdu 1501 贪心问题
这道题目的关键就是逐个搜索的过程 找个时间得复习一下dfs了 这里使用temp作为参照变量 每次比较以后(由于已经排序好) 已temp为参照进行下一次的比较
- linux的scp命令可以在linux服务器之间复制文件和目录
scp是secure copy的简写,用于在Linux下进行远程拷贝文件的命令,和它类似的命令有cp,不过cp只是在本机进行拷贝不能跨服务器,而且scp传输是加密的.可能会稍微影响一下速度.当你服务器 ...
- weui中的picker滑动报错
html { touch-action: none; } 在页面插入上述代码即可解决
- for循环的耗时问题
结论——用变量来缓存数组长度,效率会更高
- zabbix server搭建遇到的问题
环境 CentOS 6.3 server nginx-1.6.3 MySQL-5.6.25 安装nginx遇到的问题 启动nginx时候提示错误“/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx ...
- 解决服务器openssh漏洞
解决服务器openssh漏洞 发表于 2019 年 11 月 27 日 1. 检查升级 下载7.4p1 ,链接如下 http://www.openssh.com/portable.html 2.安 ...
- Nmap一些参数的具体作用
目标说明 1234 -iL <inputfilename> 读取文档-iR <hostnum> 随机选择目标--exclude <host1[,host2][,...]& ...
- 个性化召回算法实践(五)——item2vec
item2vec将用户的行为序列转化成item组成的句子,模仿word2vec训练word embedding将item embedding.基本思想是把原来高维稀疏的表示方式(one_hot)映射到 ...
- archlinux 使用 postgresql
一.安装与初始化 1.初始化数据目录 默认安装后已创建 postgres 系统用户 切换到 postgres 用户 $ sudo -iu postgres # Or su - postgres for ...
