笔记43 Spring Web Flow——订购披萨应用详解
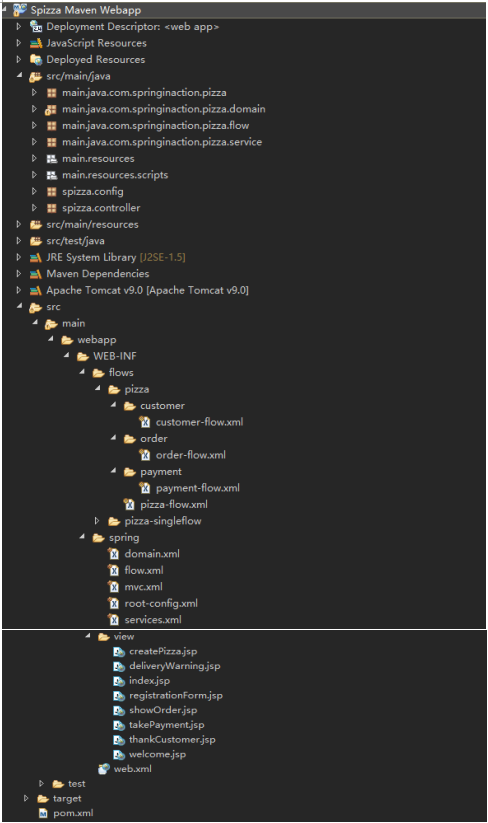
一、项目的目录结构
二、订购流程总体设计
三、订购流程的详细设计
1.定义基本流程pizza-flow.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<flow xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow
http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow/spring-webflow-2.0.xsd"> <var name="order" class="main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Order"/> <!-- Customer -->
<subflow-state id="customer" subflow="customer-flow">
<input name="order" value="order"/>
<transition on="customerReady" to="order" />
</subflow-state> <!-- Order -->
<subflow-state id="order" subflow="order-flow">
<input name="order" value="order"/>
<transition on="orderCreated" to="payment" />
</subflow-state> <!-- Payment -->
<subflow-state id="payment" subflow="payment-flow">
<input name="order" value="order"/>
<transition on="paymentTaken" to="saveOrder"/>
</subflow-state> <action-state id="saveOrder">
<evaluate expression="pizzaFlowActions.saveOrder(order)" />
<transition to="thankCustomer" />
</action-state> <view-state id="thankCustomer">
<transition on="end" to="endState" />
</view-state> <!-- End state -->
<end-state id="endState" /> <global-transitions>
<transition on="cancel" to="endState" />
</global-transitions>
</flow>
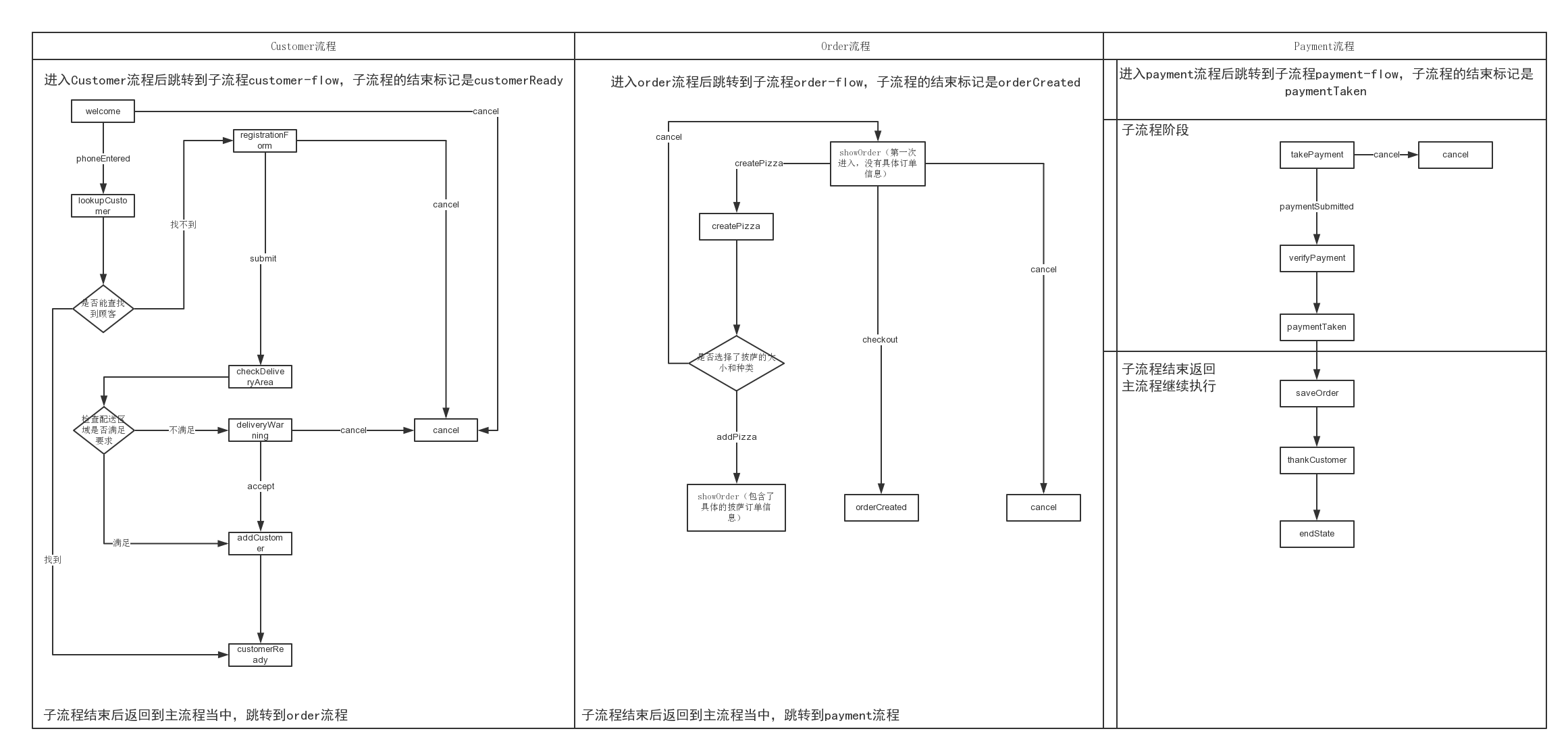
在进入主流程时,必须先新建一个Order的实例,Order类会带有关于订单的所有信息,包含顾客信息、订购的披萨列表以及支付详情。然后进入Customer流程,对应的子流程为customer-flow,而且在进入子流程前,必须将订单对象作为子流程的输入进行传递,如果子流程结束的<end-state>状态ID为customerReady,那么当执行完子流程后就会跳转到名为order的状态。接下来,先介绍customer子流程。
2.子流程customer-flow.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<flow xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow
http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow/spring-webflow-2.0.xsd"> <input name="order" required="true"/> <!-- Customer -->
<view-state id="welcome">
<transition on="phoneEntered" to="lookupCustomer"/>
<transition on="cancel" to="cancel"/>
</view-state> <action-state id="lookupCustomer">
<evaluate result="order.customer" expression=
"pizzaFlowActions.lookupCustomer(requestParameters.phoneNumber)" />
<transition to="registrationForm" on-exception=
"main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service.CustomerNotFoundException" />
<transition to="customerReady" />
</action-state> <view-state id="registrationForm" model="order" popup="true" >
<on-entry>
<evaluate expression=
"order.customer.phoneNumber = requestParameters.phoneNumber" />
</on-entry>
<transition on="submit" to="checkDeliveryArea" />
<transition on="cancel" to="cancel" />
</view-state> <decision-state id="checkDeliveryArea">
<if test="pizzaFlowActions.checkDeliveryArea(order.customer.zipCode)"
then="addCustomer"
else="deliveryWarning"/>
</decision-state> <view-state id="deliveryWarning">
<transition on="accept" to="addCustomer" />
<transition on="cancel" to="cancel" />
</view-state> <action-state id="addCustomer">
<evaluate expression="pizzaFlowActions.addCustomer(order.customer)" />
<transition to="customerReady" />
</action-state> <!-- End state -->
<end-state id="cancel" />
<end-state id="customerReady" />
</flow>
第一个进入的流程是由<view-state>定义的“welcome”视图状态,即用户欢迎界面,需要用户输入电话号码,具体如下图所示,
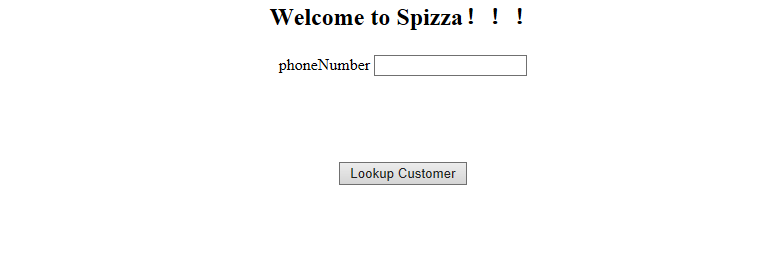
在welcome状态中有两个用<transition>定义的转移,如果触发了phoneEntered事件,即用户输入电话号码,然后点击Lookup Customer按钮后,会跳转到由<action-state>定义的lookupCustomer行为状态,对用户输入的电话号码进行查询。进入到lookupCustomer状态后,首先使用<evaluate>元素计算了一个表达式(SpEL表达式),将计算结果放在order对象的customer变量中。计算过程就是调用pizzaFlowActions(调用的时候首字母小写)类中的lookupCustomer方法,输入参数就是用户输入的电话号码,通过requestParameters.phoneNumber得到。在lookupCustomer中状态的转移是通过抛出异常触发的,因为如果通过电话号码找不到顾客,说明这个顾客是新客户,需要进行信息登记,所以就会抛出自定义异常CustomerNotFoundException,用来触发下一个流程——用户注册。相反,如果通过电话号码找到了用户,则说明是老顾客,那么就直接跳转到customerReady状态,即第一个Customer流程随之结束,跳转到下一个流程——Order。进入由<view-state>定义的registrationForm视图状态后,首先通过设置<view-state>的model属性为表单绑定order对象,具体如下图所示,
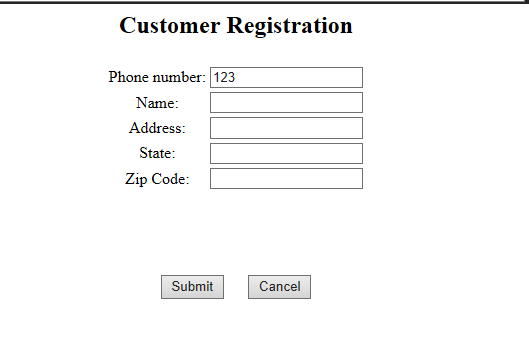
然后使用<on-entry>进行切入,即进入registrationForm状态后,先获取前一个页面用户输入的电话号码,通过requestParameters.phoneNumber得到,然后赋值给order.customer.phoneNumber。当用户输入完全部信息后,点击Submit按钮就会通过<transition>进行状态转移,转移到checkDeliveryArea状态中。如果点击Cancel就会返回首页。checkDeliveryArea是一个由<decision-state>定义的决策状态,通过表达式的值确定下一步的转移方向,表达式是通过调用pizzaFlowActions类中checkDeliveryArea方法对邮编进行判断。如果表达式结果为ture则转移到then属性指定的addCustomer状态中,如果为false,则转移到else属性指定的deliveryWarning状态中。deliveryWarning状态是由于用户所填写的地址超出配送范围,需要用户到店自取,判断用户是否接受这个请求,具体如下图所示。

如果用户点击Accept则会跳转到addCustomer状态中,点击cancel就会返回首页。addCustomer状态是一个行为状态,使用表达式将刚注册的用户信息进行保存,然后跳转到customerReady状态,即子流程的结束状态,最后返回到主流程中,第一个customer流程执行完毕,跳转到order流程。
同样进入到order流程后,会跳转到子流程order-flow,也会需要一个订单对象作为输入。如果子流程结束的<end-state>状态ID为orderCreated,那么子流程执行完毕会跳转到payment状态。具体的流程下面进行详细介绍。
3.子流程order-flow.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<flow xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow
http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow/spring-webflow-2.0.xsd"> <input name="order" required="true" /> <!-- 接收order作为输入 --> <!-- Order -->
<view-state id="showOrder"><!-- 展现order的状态 -->
<transition on="createPizza" to="createPizza" />
<transition on="checkout" to="orderCreated" />
<transition on="cancel" to="cancel" />
</view-state> <view-state id="createPizza" model="flowScope.pizza"> <!-- 创建披萨的状态 -->
<on-entry>
<set name="flowScope.pizza"
value="new main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Pizza()" />
<evaluate result="viewScope.toppingsList"
expression="T(main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Topping).asList()" />
</on-entry>
<transition on="addPizza" to="showOrder">
<evaluate expression="order.addPizza(flowScope.pizza)" />
</transition>
<transition on="cancel" to="showOrder" />
</view-state> <!-- End state -->
<end-state id="cancel" /> <!-- 取消的结束状态 -->
<end-state id="orderCreated" /> <!-- 创建订单的结束状态 -->
</flow>
首先进入showOrder状态,其中包含三个可以进行转移的状态:createPizza,orderCreated,cancel。showOrder是一个视图状态,对应的页面如下图所示:
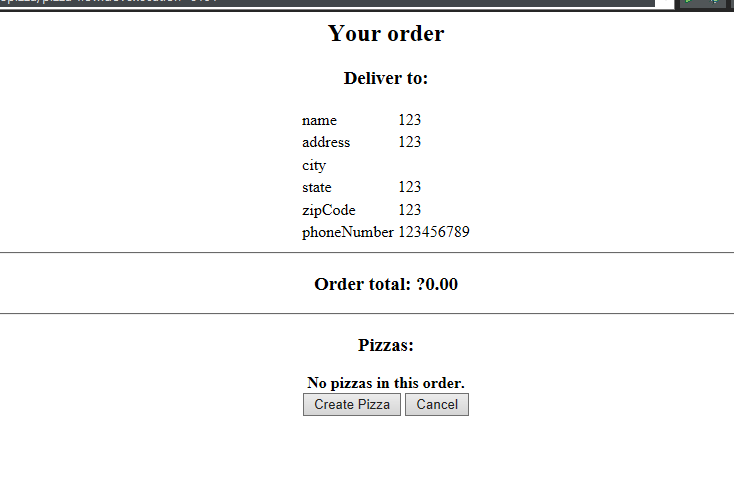
当用户点击Create Pizza按钮后,触发createPizza状态,因为createPizza页面中也有表单,所以先设置model属性进行表单与pizza对象进行绑定。需要注意的是这里的pizza对象的作用域范围是flow,即当流程开始时创建,在流程结束时销毁。只有在创建它的流程中是可见的。在进入createPizza流程后,先设置两个变量。第一个变量是pizza,作用域是flow,通过<set>设置,用于保存pizza信息,当表单提交时,表单的内容会填充到该对象中。需要注意的是,这个视图状态引用的model是流程作用域内的同一个Pizza对象。第二个是toppingsList,作用域是view,即当进入视图状态时创建,当这个状态退出时销毁,只在视图状态内时可见的,所以flow>view。toppingsList是用来保存披萨的种类的。具体的createPizza对应的页面如下所示:
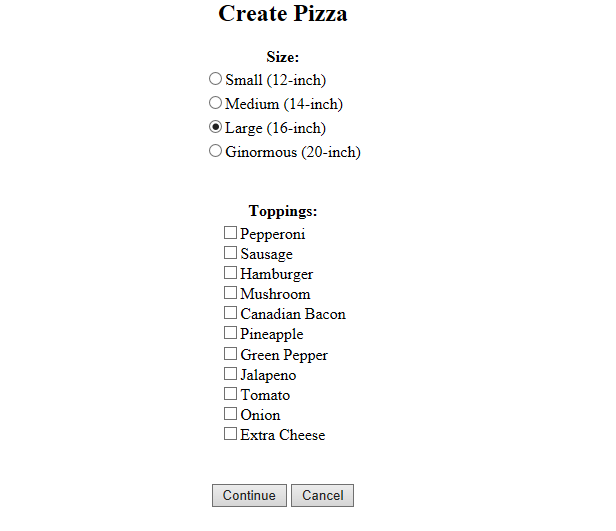
当用户选择完披萨的大小和种类后,点击Continue按钮后,通过触发addPizza进入到视图showOrder,在重新进入showOrder视图的时候,将刚才填充完毕的pizza对象加入到order对象当中,现在的order就不为空了,具体如下图所示:
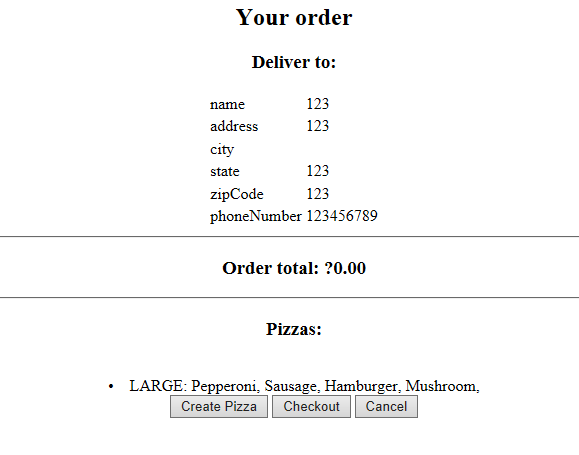
当用户点击Checkout按钮时,转移到orderCreated状态,意味着order子流程的结束,需要跳转到payment流程。下面再对payment流程进行介绍。
4.子流程payment-flow.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<flow xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow
http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow/spring-webflow-2.0.xsd"> <input name="order" required="true"/> <view-state id="takePayment" model="flowScope.paymentDetails">
<on-entry>
<set name="flowScope.paymentDetails"
value="new main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.PaymentDetails()" />
<evaluate result="viewScope.paymentTypeList"
expression="T(main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.PaymentType).asList()" />
</on-entry>
<transition on="paymentSubmitted" to="verifyPayment" />
<transition on="cancel" to="cancel" />
</view-state> <action-state id="verifyPayment">
<evaluate result="order.payment" expression=
"pizzaFlowActions.verifyPayment(flowScope.paymentDetails)" />
<transition to="paymentTaken" />
</action-state> <!-- End state -->
<end-state id="cancel" />
<end-state id="paymentTaken" />
</flow>
首先进入takePayment流程当中,先初始化两个变量。一个是flow级作用域的paymentDetails,另一个是view级的paymentTypeList。takePayment对应的页面如下所示:
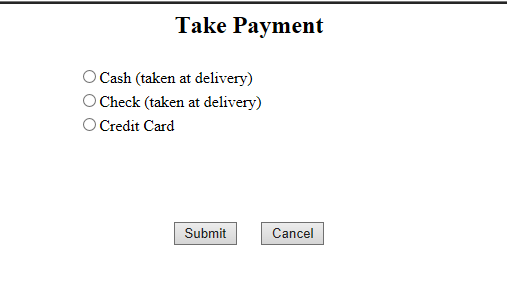
当用户点击Submit触发paymentSubmitted,然后转移到verifyPayment行为状态。verifyPayment主要是通过调用pizzaFlowActions类的verifyPayment方法对用户的支付类型进行判断。最后转移到paymentTaken状态,意味着子流程结束,返回到主流程中。
主流程中和payment相关的流程还有一个行为状态saveOrder,顾名思义将上述流程创建的订单进行保存,然后转移到thankCustomer状态。thankCustomer界面如下所示:

当点击finish就又跳转到首页,重新开始整个流程。
四、具体实现
Spring Web Flow 就是 Spring Web MVC 的一个扩展,如果粗略一些来讲,所谓 flow 就相当于 Spring Web MVC 中一种特殊的 controller ,这种 controller 可通过 XML 文件加以配置。所以必须对Spring Web MVC进行配置,然后再定义相应的flow。
(一)通过Java来配置SpringMVC,但是flow不能通过java配置,必须通过xml来进行配置。使用Java配置的目的是显示欢迎页面。
1.在src/main/java目录下分别创建两个包,一个是spizza.config用来配置SpringMVC,另一个是spizza.controller用来配置控制器。目录结构如下所示:
RootConfig.java
package spizza.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan.Filter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc; @Configuration("RootConfig")
@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "spizza" }, excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, value = EnableWebMvc.class) })
public class RootConfig { }
SpizzaWebApplnitializer.java
package spizza.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class SpizzaWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new Class<?>[] { RootConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new Class<?>[] { WebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
WebConfig.java
package spizza.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver; @Configuration("WebConfig")
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan("spizza.controller")
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/view/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
resolver.setViewClass(org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView.class);
resolver.setExposeContextBeansAsAttributes(true);
return resolver;
} @Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
configurer.enable();
} }
HomeController.java
package spizza.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; @Controller
public class HomeController {
public HomeController() {
} @RequestMapping(value = "welcome", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String home() {
return "index";
}
}
通过Java来配置SpringMVC也是一种复习回顾,Spring实战中推荐使用Java配置。
2.运行结果:

(二)配置Spring Web Flow
在WEB-IN目录下创建spring文件夹,用来存放有关flow的配置,在WEB-IN目录下创建flows文件夹,用来存放具体的flow流程。具体目录结构如下所示:
1.基础配置,将不同作用的配置文件分开,然后在root-config.xml中进行导入。
flow.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:flow="http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow-config"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow-config
http://www.springframework.org/schema/webflow-config/spring-webflow-config.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.flow" /> <!-- 执行流程:进入Spring Web Flow系统的入口点 -->
<flow:flow-executor id="flowExecutor" /> <!-- 所有 flow 定义文件位置在此配置, flow-builder-services 用于配置 flow 的特性 -->
<flow:flow-registry id="flowRegistry"
flow-builder-services="flowBuilderServices">
<flow:flow-location path="/WEB-INF/flows/pizza/pizza-flow.xml"
id="pizza-flow" />
<flow:flow-location path="/WEB-INF/flows/pizza/customer/customer-flow.xml"
id="customer-flow" />
<flow:flow-location path="/WEB-INF/flows/pizza/order/order-flow.xml"
id="order-flow" />
<flow:flow-location path="/WEB-INF/flows/pizza/payment/payment-flow.xml"
id="payment-flow" />
</flow:flow-registry>
<!--Web Flow 中的视图通过 MVC 框架的视图技术来呈现 -->
<flow:flow-builder-services id="flowBuilderServices"
view-factory-creator="mvcViewFactoryCreator" />
<!-- 指明 MVC 框架的 view resolver ,用于通过 view 名查找资源 -->
<bean id="mvcViewFactoryCreator"
class="org.springframework.webflow.mvc.builder.MvcViewFactoryCreator">
<property name="viewResolvers" ref="viewResolver" />
</bean> </beans>
mvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass"
value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView">
</property>
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/view/">
</property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp">
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="viewMappings"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<!-- /pizza-flow.do 请求由 flowController 来处理 -->
<property name="mappings">
<value> /pizza-flow.do=flowController </value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="flowController" class="org.springframework.webflow.mvc.servlet.FlowController">
<property name="flowExecutor" ref="flowExecutor" />
</bean>
</beans>
domain.xml,加载流程中需要的bean。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd"> <context:spring-configured /> <bean id="order" class="main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Order" abstract="true">
<property name="pricingEngine" ref="pricingEngine" />
</bean> </beans>
services.xml,加载流程中需要的bean。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd"> <bean id="pricingEngine"
class="main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service.PricingEngineImpl" /> <!--
<lang:groovy id="pricingEngineGroovy"
script-source="classpath:scripts/PricingEngineImpl.groovy" />
--> <bean id="customerService"
class="main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service.CustomerServiceImpl" /> <!-- Payment processing bean, as discussed on page 606 -->
<bean id="paymentProcessor"
class="main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service.PaymentProcessor" /> <bean id="orderService"
class="main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service.OrderServiceImpl" /> </beans>
root-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="main.java.com.springinaction.pizza" />
<import resource="domain.xml" />
<import resource="flow.xml" />
<import resource="mvc.xml" />
<import resource="services.xml" /> </beans>
web.xml,虽然以及使用Java配置过Servlet,参考SpizzaWebAppInitializer.java,但是为了执行flow,还需要在web.xml中进行相应的配置。
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>CartServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/spring/root-config.xml
</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>CartServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
2.Flow的定义
整个顾客订购披萨的过程可以分为三个部分,第一部分就是顾客相关信息验证以及查询,第二个部分是订单的创建,第三个部分是支付。所以不应该将全部的流程都放在一个文件中进行定义,应该分别定义为子流程,然后在主流程中进行调用。具体内容参照第三小节。
(三)视图,只给出了主要内容。
1.index.jsp
<h1>Hello!</h1><br/>
<a href="pizza-flow.do">Spizza</a>
2.welcome.jsp
<h2 align="center">Welcome to Spizza!!!</h2>
<form:form>
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td>phoneNumber</td>
<td><input type="hidden" name="_flowExecutionKey"
value="${flowExecutionKey}" /> <input type="text"
name="phoneNumber" /><br /></td>
</tr>
<tr height="80px"></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center"><input type="submit" name="_eventId_phoneEntered"
value="Lookup Customer" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form:form>
<!-- 首先要注意的是隐藏的“_flowExecutionKey”输入域。
当进入视图 状态时,流程暂停并等待用户采取一些行为。
赋予视图的流程执行 key(flow execution key)就是一种返回流程的“回程票”(claim ticket)。
当用户提交表单时,流程执行key会 在“_flowExecutionKey”输入域中返回并在流程暂停的位置进行恢 复。
-->
3.registrationForm.jsp
<h2 align="center">Customer Registration</h2>
<form:form commandName="order">
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td><input type="hidden" name="_flowExecutionKey"
value="${flowExecutionKey}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="center">Phone number:</td>
<td><form:input path="customer.phoneNumber" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="center">Name:</td>
<td><form:input path="customer.name" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="center">Address:</td>
<td><form:input path="customer.address" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="center">State:</td>
<td><form:input path="customer.state" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="center">Zip Code:</td>
<td><form:input path="customer.zipCode" /></td>
</tr>
<tr height="80px"></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center"><input type="submit"
name="_eventId_submit" value="Submit" />
<input type="submit" name="_eventId_cancel" value="Cancel" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form:form>
4.deliveryWarning.jsp
<h2>Delivery Unavailable</h2>
<p>The address is outside of our delivery area. The order may still be taken for carry-out.</p>
<a href="${flowExecutionUrl}&_eventId=accept">Accept</a> |
<a href="${flowExecutionUrl}&_eventId=cancel">Cancel</a>
5.showOrder.jsp
<div align="center">
<h2>Your order</h2> <h3>Deliver to:</h3>
<table>
<tr>
<td>name</td>
<td>${order.customer.name}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>address</td>
<td>${order.customer.address}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>city</td>
<td>${order.customer.city}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>state</td>
<td>${order.customer.state}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>zipCode</td>
<td>${order.customer.zipCode}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>phoneNumber</td>
<td>${order.customer.phoneNumber}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<hr />
<h3>
Order total:
<fmt:formatNumber type="currency" value="${order.total}"></fmt:formatNumber> </h3>
<hr />
<h3>Pizzas:</h3> <c:if test="${fn:length(order.pizzas) eq 0}">
<b>No pizzas in this order.</b>
</c:if> <br />
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Size</th>
<th>Toppings</th>
<th>IsCombo</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${order.pizzas }" var="pizza">
<tr>
<td align="center">${pizza.size}</td>
<td align="center">
<c:forEach items="${pizza.toppings}" var="topping">
<c:out value="${topping}" />
</c:forEach>
</td>
<td align="center">${pizza.isCombo }</td> <td>${pizza.price }</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table> <form:form>
<input type="hidden" name="_flowExecutionKey"
value="${flowExecutionKey}" />
<input type="submit" name="_eventId_createPizza" value="Create Pizza" />
<c:if test="${fn:length(order.pizzas) gt 0}">
<input type="submit" name="_eventId_checkout" value="Checkout" />
</c:if>
<input type="submit" name="_eventId_cancel" value="Cancel" />
</form:form>
</div>
6.createPizza.jsp
<div align="center">
<h2>Create Pizza</h2>
<form:form commandName="pizza" >
<input type="hidden" name="_flowExecutionKey"
value="${flowExecutionKey}" />
<b>Size: </b>
<br />
<table>
<tr>
<td><form:radiobutton path="size" label="Small (12-inch)——————¥6.99"
value="SMALL" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><form:radiobutton path="size" label="Medium (14-inch)——————¥7.99"
value="MEDIUM" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><form:radiobutton path="size" label="Large (16-inch)——————¥8.99"
value="LARGE" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><form:radiobutton path="size" label="Ginormous (20-inch)——————¥9.99"
value="GINORMOUS" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
<br />
<br />
<b>Toppings: PRICE_PER_TOPPING 0.20¥</b>
<br />
<table>
<tr>
<td>
<form:checkboxes name="topping" path="toppings" items="${toppingsList}"
delimiter="<br/>" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br />
<br />
<b>Hyperchannel</b>
<table>
<tr>
<td><form:checkbox path="specialPizza" label="MEAT"
value="MEAT" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><form:checkbox path="specialPizza" label="VEGGIE"
value="VEGGIE" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><form:checkbox path="specialPizza" label="THEWORKS"
value="THEWORKS" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
<input type="submit" class="button" name="_eventId_addPizza"
value="Continue" />
<input type="submit" class="button" name="_eventId_cancel"
value="Cancel" />
</form:form>
</div>
7.takePayment.jsp
<div align="center">
<script>
function showCreditCardField() {
var ccNumberStyle = document.paymentForm.creditCardNumber.style;
ccNumberStyle.visibility = 'visible';
}
function hideCreditCardField() {
var ccNumberStyle = document.paymentForm.creditCardNumber.style;
ccNumberStyle.visibility = 'hidden';
}
</script>
<h2>Take Payment</h2>
<form:form commandName="paymentDetails" name="paymentForm">
<table>
<tr>
<td><input type="hidden" name="_flowExecutionKey"
value="${flowExecutionKey}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><form:radiobutton path="paymentType" value="CASH"
label="Cash (taken at delivery)" onclick="hideCreditCardField()" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><form:radiobutton path="paymentType" value="CHECK"
label="Check (taken at delivery)" onclick="hideCreditCardField()" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><form:radiobutton path="paymentType" value="CREDIT_CARD"
label="Credit Card" onclick="showCreditCardField()" /></td>
<td><form:input path="creditCardNumber"
cssStyle="visibility:hidden;" /></td>
</tr>
<tr height="80px"></tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center"><input type="submit"
class="button" name="_eventId_paymentSubmitted" value="Submit" />
<input type="submit" class="button"
name="_eventId_cancel" value="Cancel" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form:form>
</div>
8.thankCustomer.jsp
<h2>Thank you for your order!</h2>
<h3>付款方式</h3>
${order.payment}
<br>
<a href="${flowExecutionUrl}&_eventId=end">Finish</a>
(四)后台
1.用于保存信息的类Customer,Pizza,PaymentDetails,Order。
Customer保存用户的姓名、地址、城市、详细地址、邮政编码、电话号码等。
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class Customer implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String address;
private String city;
private String state;
private String zipCode;
private String phoneNumber;
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(String phoneNumber) {
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhoneNumber() {
return phoneNumber;
}
public void setPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) {
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getZipCode() {
return zipCode;
}
public void setZipCode(String zipCode) {
this.zipCode = zipCode;
}
}
Pizza保存披萨的大小、添加的配料、价格等信息。
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain; import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List; @SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class Pizza implements Serializable {
private PizzaSize size;
private List<Topping> toppings;
private List<String> specialPizza;
private String isCombo;
private float price; public Pizza() {
size = PizzaSize.LARGE;
} public float getPrice() {
return price;
} public void setPrice(float price) {
this.price = price;
} public String getIsCombo() {
return isCombo;
} public void setIsCombo(String isCombo) {
this.isCombo = isCombo;
} public List<String> getSpecialPizza() {
return specialPizza;
} public void setSpecialPizza(List<String> specialPizza) {
this.specialPizza = specialPizza;
} public PizzaSize getSize() {
return size;
} public void setSize(PizzaSize size) {
this.size = size;
} public void setSize(String sizeString) {
this.size = PizzaSize.valueOf(sizeString);
} public List<Topping> getToppings() {
return toppings;
} public void setToppings(List<Topping> toppings) {
this.toppings = toppings;
} public void setToppings(String[] toppingStrings) {
for (int i = 0; i < toppingStrings.length; i++) {
toppings.add(Topping.valueOf(toppingStrings[i]));
}
}
}
因为在披萨选择页面顾客可以自行选择配料,也可以直接选择已经提供好的套餐,用户可以自由选择。所以在Pizza类中会有specialPizza字段用来存放顾客是否选择了套餐。
其中PizzaSize和Topping都是自定义的枚举类型的类,用来存放披萨大小和配料种类,具体如下所示:
PizzaSize.java
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public enum PizzaSize implements Serializable {
SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, GINORMOUS;
}
Topping.java
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain; import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List; import org.apache.commons.lang3.text.WordUtils; public enum Topping implements Serializable {
PEPPERONI, SAUSAGE, HAMBURGER, MUSHROOM, CANADIAN_BACON, PINEAPPLE, GREEN_PEPPER, JALAPENO, TOMATO, ONION, EXTRA_CHEESE; public static List<Topping> asList() {
Topping[] all = Topping.values();
return Arrays.asList(all);
} @Override
public String toString() {
return WordUtils.capitalizeFully(name().replace('_', ' '));
}
}
PaymentDetails保存顾客的付款信息,其中主要包括付款类型,以及卡号(如果使用信用卡)。
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class PaymentDetails implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private PaymentType paymentType;
private String creditCardNumber;
public PaymentType getPaymentType() {
return paymentType;
}
public void setPaymentType(PaymentType paymentType) {
this.paymentType = paymentType;
}
public String getCreditCardNumber() {
return creditCardNumber;
}
public void setCreditCardNumber(String creditCardNumber) {
this.creditCardNumber = creditCardNumber;
}
}
其中PaymentType是自定义的一个枚举类型的类,用来存放支付的方式,具体如下所示:
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain; import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List; import org.apache.commons.lang3.text.WordUtils; public enum PaymentType {
CASH, CHECK, CREDIT_CARD; public static List<PaymentType> asList() {
PaymentType[] all = PaymentType.values();
return Arrays.asList(all);
} @Override
public String toString() {
return WordUtils.capitalizeFully(name().replace('_', ' '));
}
}
Order类中保存整个订单的信息。
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain; import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Configurable;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.flow.SpecialtyPizza;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service.PricingEngineImpl; @Configurable("order")
public class Order implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Customer customer;
private List<Pizza> pizzas;
private Payment payment; public Order() {
pizzas = new ArrayList<Pizza>();
customer = new Customer();
} public Customer getCustomer() {
return customer;
} public void setCustomer(Customer customer) {
this.customer = customer;
} public List<Pizza> getPizzas() {
return pizzas;
} public void setPizzas(List<Pizza> pizzas) {
this.pizzas = pizzas;
} public void addPizza(Pizza pizza) {
// System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(pizza.getToppings()));
// System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(pizza.getSpecialPizza())); Boolean pizza1 = StringUtils.isEmpty(pizza.getToppings());
Boolean pizza2 = StringUtils.isEmpty(pizza.getSpecialPizza()); if (pizza1 == false && pizza2 == true) {
pizza.setIsCombo("—");
pizzas.add(pizza);
} else if (pizza1 == true && pizza2 == false) {
SpecialtyPizza specialtyPizza = new SpecialtyPizza();
List<Pizza> newPizzas = specialtyPizza.getPizza(pizza);
for (Pizza temp : newPizzas) {
pizzas.add(temp);
}
} else if (pizza1 == false && pizza2 == false) {
pizza.setIsCombo("—");
pizzas.add(pizza);
SpecialtyPizza specialtyPizza = new SpecialtyPizza();
List<Pizza> newPizzas = specialtyPizza.getPizza(pizza);
for (Pizza temp : newPizzas) {
pizzas.add(temp);
}
}
} public float getTotal() {
PricingEngineImpl pricingEngineImpl = new PricingEngineImpl();
List<Pizza> pizzas = this.getPizzas(); return pricingEngineImpl.calculateOrderTotal(pizzas);
} public Payment getPayment() {
return payment;
} public void setPayment(Payment payment) {
this.payment = payment;
payment.setAmount(this.getTotal());
} }
<1>需要注意的是在添加披萨到订单当中时,即方法addPizza,其参数是一个Pizza类型的列表。因为在表单中直接绑定了pizza的三个对象,size、topping和specialPizza,而其中topping与specialPizza可以不用同时赋值,所以再添加pizza对象到订单中的时候要对这两个对象判断是否为空,然后根据实际情况添加相应的pizza对象到订单当中。所以还需要一个SpecialtyPizza类返回特殊的pizza对象,具体如下所示:
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.flow; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Pizza;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Topping; public class SpecialtyPizza { public List<Pizza> getPizza(Pizza pizza) {
List<Pizza> newPizza = new ArrayList<Pizza>();
if (pizza.getSpecialPizza().size() != 0) {
for (String type : pizza.getSpecialPizza()) {
if ("MEAT".equals(type)) { List<Topping> meats = new ArrayList<Topping>(); meats.add(Topping.CANADIAN_BACON);
meats.add(Topping.HAMBURGER);
meats.add(Topping.PEPPERONI);
meats.add(Topping.SAUSAGE);
Pizza tempt = new Pizza();
tempt.setSize(pizza.getSize());
tempt.setToppings(meats);
tempt.setIsCombo("MEAT");
newPizza.add(tempt);
} else if ("VEGGIE".equals(type)) { List<Topping> meats = new ArrayList<Topping>(); meats.add(Topping.GREEN_PEPPER);
meats.add(Topping.MUSHROOM);
meats.add(Topping.PINEAPPLE);
meats.add(Topping.TOMATO); Pizza tempt = new Pizza();
tempt.setSize(pizza.getSize());
tempt.setToppings(meats);
tempt.setIsCombo("VEGGIE");
newPizza.add(tempt);
} else if ("THEWORKS".equals(type)) { List<Topping> meats = new ArrayList<Topping>();
System.out.println("THE WORKS!"); meats.add(Topping.CANADIAN_BACON);
meats.add(Topping.HAMBURGER);
meats.add(Topping.PEPPERONI);
meats.add(Topping.SAUSAGE);
meats.add(Topping.GREEN_PEPPER);
meats.add(Topping.MUSHROOM);
meats.add(Topping.PINEAPPLE);
meats.add(Topping.TOMATO);
meats.add(Topping.EXTRA_CHEESE);
meats.add(Topping.ONION);
meats.add(Topping.JALAPENO); Pizza tempt = new Pizza();
tempt.setSize(pizza.getSize());
tempt.setToppings(meats);
tempt.setIsCombo("THEWORKS");
newPizza.add(tempt);
}
}
return newPizza;
} else {
return newPizza;
}
}
}
<2>在初始化payment对象时,同时用订单总金额来初始化payment对象中amount变量,其中的payment是一个抽象类的实例,代码如下所示:
Payment.java
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public abstract class Payment implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private float amount;
private String creditCardNumber;
public String getCreditCardNumber() {
return creditCardNumber;
}
public void setCreditCardNumber(String creditCardNumber) {
this.creditCardNumber = creditCardNumber;
}
public void setAmount(float amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public float getAmount() {
return amount;
}
}
这个抽象类主要包含两个成员变量:amount(需要付款的总金额),creditCardNumber(使用信用卡付款时的卡号)。然后添加了两个类CshOrCheckPayment和CreditCardPayment,它们都继承Payment。
CshOrCheckPayment
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain;
public class CashOrCheckPayment extends Payment {
public CashOrCheckPayment() {
}
public String toString() {
return "CASH or CHECK: ¥" + getAmount();
}
}
CreditCardPayment
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain;
public class CreditCardPayment extends Payment {
public CreditCardPayment() {
}
public String toString() {
return "CREDIT: ¥" + getAmount() + " ; AUTH: " + this.getCreditCardNumber(); //调用父类的成员变量
}
}
2.流程执行过程中需要用到的方法。
<1>CustomerServiceImpl,实现CustomerService接口,接口中只有一个方法,lookupCustomer。
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Customer;
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
public CustomerServiceImpl() {
}
public Customer lookupCustomer(String phoneNumber) throws CustomerNotFoundException {
if ("9725551234".equals(phoneNumber)) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setId(123);
customer.setName("Craig Walls");
customer.setAddress("3700 Dunlavy Rd");
customer.setCity("Denton");
customer.setState("TX");
customer.setZipCode("76210");
customer.setPhoneNumber(phoneNumber);
return customer;
} else {
throw new CustomerNotFoundException();
}
}
}
<2>OrderServiceImpl将用户订单保存到日志当中,因为没有连接数据库。
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Order;
public class OrderServiceImpl {
private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(OrderServiceImpl.class);
public OrderServiceImpl() {
}
public void saveOrder(Order order) {
LOGGER.debug("SAVING ORDER: ");
LOGGER.debug(" Customer: " + order.getCustomer().getName());
LOGGER.debug(" # of Pizzas: " + order.getPizzas().size());
LOGGER.debug(" Payment: " + order.getPayment());
}
}
<3>PricingEngineImpl实现PricingEngine接口,接口中只有一个方法calculateOrderTotal,计算每个披萨的价格,以及订单中披萨的总价。
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service; import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Pizza;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.PizzaSize; @SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class PricingEngineImpl implements PricingEngine, Serializable {
private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(PricingEngineImpl.class); private static Map<PizzaSize, Float> SIZE_PRICES;
static {
SIZE_PRICES = new HashMap<PizzaSize, Float>();
SIZE_PRICES.put(PizzaSize.SMALL, 7.00f);
SIZE_PRICES.put(PizzaSize.MEDIUM, 8.00f);
SIZE_PRICES.put(PizzaSize.LARGE, 9.00f);
SIZE_PRICES.put(PizzaSize.GINORMOUS, 10.00f);
}
private static float PRICE_PER_TOPPING = 2.00f; public PricingEngineImpl() {
} public float calculateOrderTotal(List<Pizza> pizzas) { float total = 0.0f;
if (pizzas.size() == 0) {
return total;
} else {
for (Pizza pizza : pizzas) {
float pizzaPrice = SIZE_PRICES.get(pizza.getSize());
if (pizza.getToppings().size() > 0) {
pizzaPrice += (pizza.getToppings().size() * PRICE_PER_TOPPING);
}
pizza.setPrice(pizzaPrice);
total += pizzaPrice;
} return total;
}
} }
3.在执行总流程中调用所需的方法时通过PizzaFlowActions类。
package main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.flow; import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.CashOrCheckPayment;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.CreditCardPayment;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Customer;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Order;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.Payment;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.PaymentDetails;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.domain.PaymentType;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service.CustomerNotFoundException;
import main.java.com.springinaction.pizza.service.CustomerService; @Service
public class PizzaFlowActions { private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(PizzaFlowActions.class); public Customer lookupCustomer(String phoneNumber) throws CustomerNotFoundException {
Customer customer = customerService.lookupCustomer(phoneNumber);
if (customer != null) {
return customer;
} else {
throw new CustomerNotFoundException();
}
} public void addCustomer(Customer customer) {
LOGGER.warn("TODO: Flesh out the addCustomer() method.");
} public Payment verifyPayment(PaymentDetails paymentDetails) {
Payment payment = null;
if (paymentDetails.getPaymentType() == PaymentType.CREDIT_CARD) {
payment = new CreditCardPayment();
} else {
payment = new CashOrCheckPayment();
} return payment;
} public void saveOrder(Order order) {
LOGGER.warn("TODO: Flesh out the saveOrder() method.");
} public boolean checkDeliveryArea(String zipCode) {
LOGGER.warn("TODO: Flesh out the checkDeliveryArea() method.");
return "75075".equals(zipCode);
} @Autowired
CustomerService customerService;
}
五、程序源码
https://github.com/lyj8330328/Spizza.git
笔记43 Spring Web Flow——订购披萨应用详解的更多相关文章
- Spring实战第八章学习笔记————使用Spring Web Flow
Spring实战第八章学习笔记----使用Spring Web Flow Spring Web Flow是一个Web框架,它适用于元素按规定流程运行的程序. 其实我们可以使用任何WEB框架写流程化的应 ...
- 笔记42 Spring Web Flow——Demo(2)
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/lyj-gyq/p/9117339.html 为了更好的理解披萨订购应用,再做一个小的Demo. 一.Spring Web Flow 2.0新特性 ...
- 笔记41 Spring Web Flow——Demo
订购披萨的应用整体比较比较复杂,现拿出其中一个简化版的流程:即用户访问首页,然后输入电话号(假定未注册)后跳转到注册页面,注册完成后跳转到配送区域检查页面,最后再跳转回首页.通过这个简单的Demo用来 ...
- 笔记39 Spring Web Flow——订单流程(收集顾客信息)
如果你曾经订购过披萨,你可能会知道流程.他们首先会询问你的电 话号码.电话号码除了能够让送货司机在找不到你家的时候打电话给 你,还可以作为你在这个披萨店的标识.如果你是回头客,他们可以 使用这个电话号 ...
- 笔记38 Spring Web Flow——订单流程(定义基本流程)
做一个在线的披萨订购应用 实际上,订购披萨的过程可以很好地定义在一个流程中.我们首先从 构建一个高层次的流程开始,它定义了订购披萨的整体过程.接下 来,我们会将这个流程拆分成子流程,这些子流程在较低的 ...
- 笔记36 Spring Web Flow——配置
Spring Web Flow是一个Web框架,它适用于元素按规定流程运行的程序.Spring Web Flow是Spring MVC的扩展,它支持开发基于流程的应用程 序.它将流程的定义与实现流程行 ...
- 笔记37 Spring Web Flow——流程的组件
在Spring Web Flow中,流程是由三个主要元素定义的:状态.转移和 流程数据. 一.状态 Spring Web Flow定义了五种不同类型的状态.通过选择Spring Web Flow的状态 ...
- 笔记40 Spring Web Flow——订单流程(构建订单)
二.订单子流程 在识别完顾客之后,主流程的下一件事情就是确定他们想要什么类型 的披萨.订单子流程就是用于提示用户创建披萨并将其放入订单中 的,如下图所示. showOrder状态位于订单子流程的中心位 ...
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记43:jstl 介绍,core库详解:表达式操作,流程控制,迭代操作,url操作
本博客为原创:综合 尚硅谷(http://www.atguigu.com)的系统教程(深表感谢)和 网络上的现有资源(博客,文档,图书等),资源的出处我会标明 本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当 ...
随机推荐
- Source object main.o has EABI version 0, but target ../../../bin/ad has EABI version 5
编译的时候,遇到了一些问题:Source object main.o has EABI version 0, but target ../../../bin/ad has EABI version 5 ...
- 《代码大全2》读书笔记 week 7
博主终于继续更<代码大全2>了 (*´・ω・`)⊃,课上老师一再强调读书笔记要写出自己的心得不能简单摘抄,所以我现在基本上只会写一下自己在阅读过程中印象深刻或者有发散思考的地方,字数可能 ...
- 使用PL/SQL连接oracle数据库,并将数据进行导出备份和导入恢复
使用PL/SQL连接oracle数据库,并将数据进行导出备份和导入恢复 这种操作百度一搜一大片,今天整理以前做的项目时自己备份了一下数据库,试着将数据进行导出备份和导入恢复了一下:下面是操作过程: 1 ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest1开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
注意,以前的比赛我是自己开了 virtual contest.这个阶段的目标是加快手速,思考问题的能力和 bug-free 的能力. 前面已经有了100个contest.计划是每周做三个到五个cont ...
- PHP-在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target.找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置. 你的算法时间复杂度必须是 O(log n) 级别. 如果数组中不存在目标值,返回 [ ...
- concurrent=false/true的定时任务job策略介绍
前言: 四种测试情况,cronExpression = 0/30 * * * * ? : 1,一个trigger,job设置的是每30s执行一次,实际需要75s:concurrent=false: 2 ...
- hive UDAF开发和运行全过程
介绍 hive的用户自定义聚合函数(UDAF)是一个很好的功能,集成了先进的数据处理.hive有两种UDAF:简单和通用.顾名思义,简单的UDAF,写的相当简单的,但因为使用Java反射导致性能损失, ...
- BZOJ 3998: [TJOI2015]弦论(后缀自动机)
传送门 解题思路 \(T=0\)时就和SP7258一样,\(T=1\)时其实也差不多,只不过要把每个点原来是\(1\)的权值改为\(Right\)集合的大小. 代码 #include<iostr ...
- CF B. Planning The Expedition
题意:有n个人和m个食物,给出每一个食物的种类,每个人只会吃一种食物,每个人一天吃一个食物,问这n个人可以撑多少天. 分析:因为题目给出的天数范围比较小所以我们可以从1到100天开始枚举,我们判断如果 ...
- shell重定向的顺序问题
三个默认的文件描述符 0: stdin(标准输入) 1: stdout(标准输出) 2: stderr(标准错误输出) 系统中这3个文件描述符所对应的文件: 重定向顺序 示例脚本 echo " ...
