TensorFlow——卷积神经网络的相关函数
在TensorFlow中,使用tr.nn.conv2d来实现卷积操作,使用tf.nn.max_pool进行最大池化操作。通过闯传入不同的参数,来实现各种不同类型的卷积与池化操作。
卷积函数tf.nn.conv2d
TensorFlow里使用tf.nn.conv2d函数来实现卷积,其格式如下:
tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding, use_cudnn_on_gpu=None, name=None),参数的含义如下:
input:需要进行卷积操作的图像,它要求是一个Tensor,具有[ batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels ]的形状,这是一个四维的数据,其中各个位置参数的具体含义是:训练时一个batch的图片数量,图片高度,图片宽度,图片通道数,数据的类型是float。
filter:相当于CNN中的卷积核,它要求是一个Tensor,具有[ filter_height,filter_width,in_channels,out_channels ]这样的shape,其中具体的含义是“卷积核的高度,卷积核宽度,图片的通道数,滤波器的个数”,要求类型与参数input相同。有一个地方需要关注意,第三维in_channels就是参数input的第四维。
strides:卷积是在图像每一位的步长,这是一个一维的向量,长度为4。
padding:定义元素边框与元素内容之间的空间。string类型的量,只能是SAME和VALID其中之一,这个值决定不同的卷积方式,padding的值VALID时,表示边缘不填充,当其为SAME时,表示填充
到滤波器可以到达图像边缘。
use_cudnn_on_gpu:bool类型,是否使用cudnn加速,默认为true。
返回值:函数的返回值仍然是一个Tensor,就是feature map。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np # [batch, im_height, im_weight, in_channels] input = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1, 5, 5, 1]))
input2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1, 5, 5, 2]))
input3 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1, 4, 4, 1])) # [filter_height, filter_weight, in_channels, in_channels]
filter1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant([-1.0, 0, 0, -1], shape=[2, 2, 1, 1]))
filter2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant([-1.0, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1], shape=[2, 2, 1, 2]))
filter3 = tf.Variable(tf.constant([-1.0, 0, 0, -1,
-1.0, 0, 0, -1,
-1.0, 0, 0, -1], shape=[2, 2, 1, 3])) filter4 = tf.Variable(tf.constant([-1.0, 0, 0, -1,
-1.0, 0, 0, -1,
-1.0, 0, 0, -1,
-1.0, 0, 0, -1], shape=[2, 2, 2, 2])) filter5 = tf.Variable(tf.constant([-1.0, 0, 0, -1, -1.0, 0, 0, -1], shape=[2, 2, 2, 1])) op1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter1, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') op2 = tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter2, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') op3 = tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter3, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') op4 = tf.nn.conv2d(input2, filter4, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') op5 = tf.nn.conv2d(input2, filter5, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') vop1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter1, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID') op6 = tf.nn.conv2d(input3, filter1, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') vop6 = tf.nn.conv2d(input3, filter1, strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID') init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init) print('-op1:\n', sess.run([op1, filter1]))
print('-------------------------------') print('-op2:\n', sess.run([op2, filter2]))
print('-op3:\n', sess.run([op3, filter3]))
print('-------------------------------') print('-op4:\n', sess.run([op4, filter4]))
print('-op5:\n', sess.run([op5, filter5]))
print('-------------------------------') print('-op1:\n', sess.run([op1, filter1]))
print('-vop1:\n', sess.run([vop1, filter1]))
print('-op6:\n', sess.run([op6, filter1]))
print('-vop6:\n', sess.run([vop6, filter1]))
print('-------------------------------')
根据上述程序的运行结果,仔细的分析就能理解卷积是如何的工作的,需要注意的是SAME padding补0的情况,
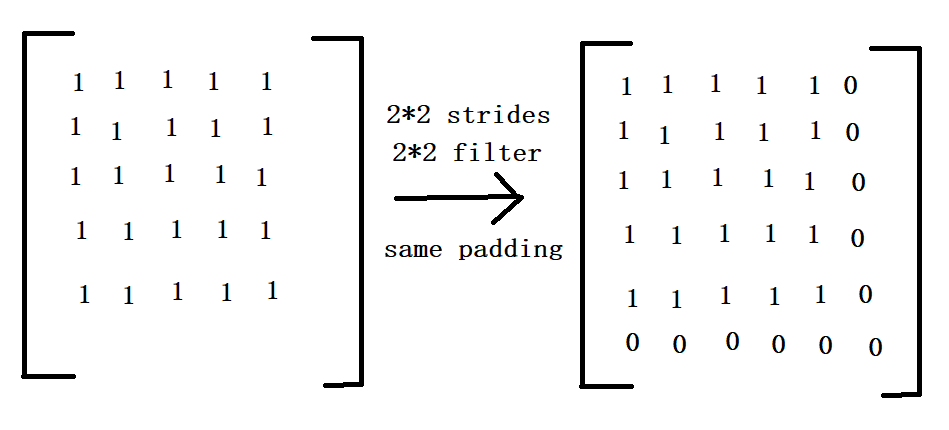
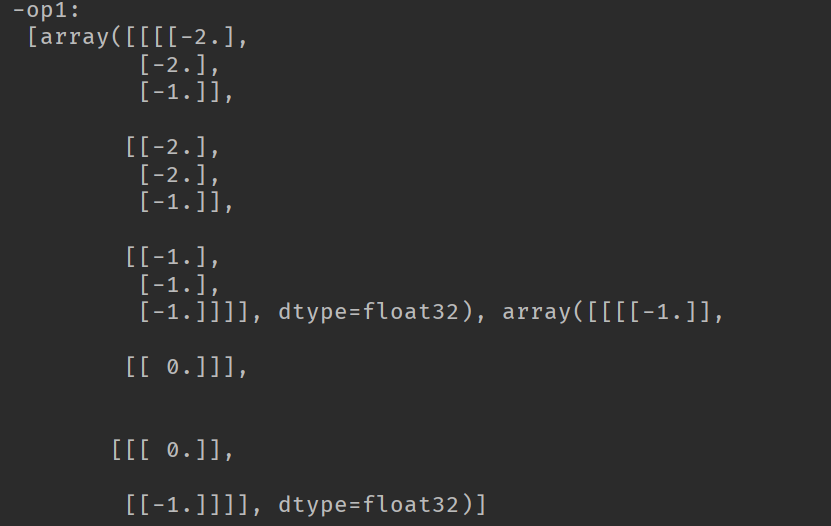
由于可知,op1的卷积操作的结果是3*3的feature map,其他的结果也是类似的情况。当图像是多通道的情况时,卷积操作的结果是将各个通道的feature map的结果相加,作为输出的一张feature map。
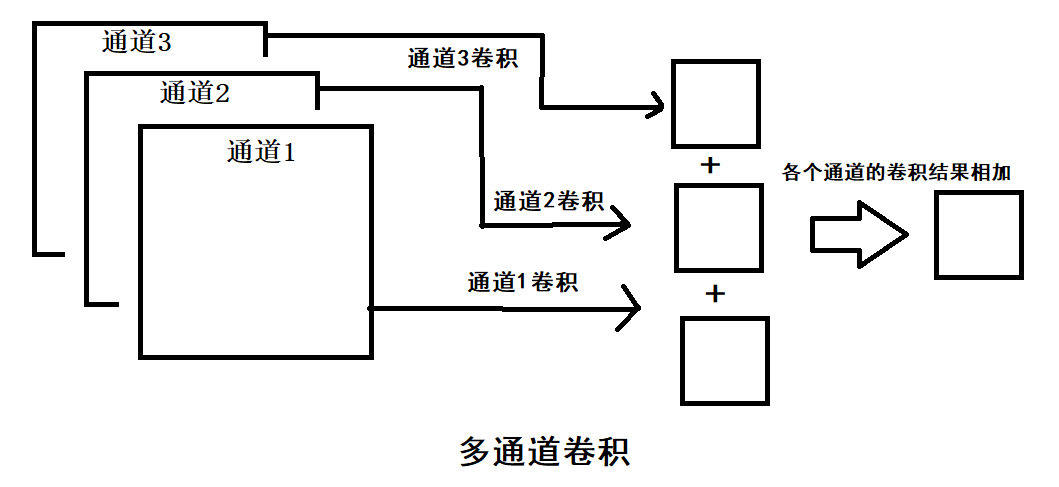
图像卷积示例
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mping path = 'image/1.jpg' img = mping.imread(path) plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
print(img.shape) full = np.reshape(img, [1, 374, 560, 3])
inputfull = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1, 374, 560, 3])) filter = tf.Variable(tf.constant([[-1.0, -1.0, -1.0], [0, 0, 0], [1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
[-2.0, -2.0, -2.0], [0, 0, 0], [2.0, 2.0, 2.0],
[-1.0, -1.0, -1.0], [0, 0, 0], [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]], shape=[3, 3, 3, 1])) op = tf.nn.conv2d(inputfull, filter, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') o = tf.cast(((op - tf.reduce_min(op))/(tf.reduce_max(op)-tf.reduce_min(op)))*255, tf.uint8) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) t, f = sess.run([o, filter], feed_dict={inputfull: full}) t = np.reshape(t, [374, 560]) plt.imshow(t, cmap='Greys_r')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()

池化函数tf.nn.max_pool(avg_pool)
TensorFlow里的池化函数如下:
tf.nn.max_pool(input, ksize, strides, padding, name)
tf.nn.avg_pool(input, ksize, strides, padding, name)
上述的两个池化函数中,4个参数的意义如下:
input:进行池化操作的数据,一般的池化层是在卷积层之后,所以通常的输入是feature map,依然是[ batch, height, width, channels ]的形状。
ksize:池化窗口的大小,4维的向量,一般是[1, height, width, 1],在batch和channles通常是不做池化的。
strides:和卷积参数含义类似,窗口在每一个维度上面滑动,一般也是[1, strides,strides,1]
padding:和卷积参数含义一样,也是取VALID或者SAME。
返回的Tensor:类型不变,shape仍然是[ batch, height, width, channels ]的形状。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mping path = 'image/1.jpg' img = mping.imread(path) plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
print(img.shape) full = np.reshape(img, [1, 374, 560, 3])
inputfull = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1, 374, 560, 3])) pooling = tf.nn.max_pool(inputfull, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
pooling1 = tf.nn.max_pool(inputfull, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
pooling2 = tf.nn.max_pool(inputfull, [1, 4, 4, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
pooling3 = tf.nn.max_pool(inputfull, [1, 4, 4, 1], [1, 4, 4, 1], padding='SAME')
pooling4 = tf.nn.max_pool(inputfull, [1, 2, 2, 1], [1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') o = tf.cast(((pooling - tf.reduce_min(pooling))/(tf.reduce_max(pooling)-tf.reduce_min(pooling)))*255, tf.uint8) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) t = sess.run(o, feed_dict={inputfull: full}) print(t.shape) t = np.reshape(t, [187, 280, 3]) plt.imshow(t)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
池化操作的作用是将特征图中的信息进行放大,使得特性信息更加的明显。
TensorFlow——卷积神经网络的相关函数的更多相关文章
- Tensorflow卷积神经网络[转]
Tensorflow卷积神经网络 卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)是一种前馈神经网络, 在计算机视觉等领域被广泛应用. 本文将简单介绍其原理并分析Te ...
- 深度学习原理与框架-Tensorflow卷积神经网络-cifar10图片分类(代码) 1.tf.nn.lrn(局部响应归一化操作) 2.random.sample(在列表中随机选值) 3.tf.one_hot(对标签进行one_hot编码)
1.tf.nn.lrn(pool_h1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0, beta=0.75) # 局部响应归一化,使用相同位置的前后的filter进行响应归一化操作 参数 ...
- TensorFlow 卷积神经网络实用指南 | iBooker·ApacheCN
原文:Hands-On Convolutional Neural Networks with TensorFlow 协议:CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 自豪地采用谷歌翻译 不要担心自己的形象,只关心 ...
- AI相关 TensorFlow -卷积神经网络 踩坑日记之一
上次写完粗浅的BP算法 介绍 本来应该继续把 卷积神经网络算法写一下的 但是最近一直在踩 TensorFlow的坑.所以就先跳过算法介绍直接来应用场景,原谅我吧. TensorFlow 介绍 TF是g ...
- Tensorflow卷积神经网络
卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)是一种前馈神经网络, 在计算机视觉等领域被广泛应用. 本文将简单介绍其原理并分析Tensorflow官方提供的示例. ...
- tensorflow卷积神经网络-【老鱼学tensorflow】
前面我们曾有篇文章中提到过关于用tensorflow训练手写2828像素点的数字的识别,在那篇文章中我们把手写数字图像直接碾压成了一个784列的数据进行识别,但实际上,这个图像是2828长宽结构的,我 ...
- 深度学习原理与框架-Tensorflow卷积神经网络-卷积神经网络mnist分类 1.tf.nn.conv2d(卷积操作) 2.tf.nn.max_pool(最大池化操作) 3.tf.nn.dropout(执行dropout操作) 4.tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(交叉熵损失) 5.tf.truncated_normal(两个标准差内的正态分布)
1. tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') # 对数据进行卷积操作 参数说明:x表示输入数据,w表示卷积核, stride ...
- tensorflow卷积神经网络与手写字识别
1.知识点 """ 基础知识: 1.神经网络(neural networks)的基本组成包括输入层.隐藏层.输出层.而卷积神经网络的特点在于隐藏层分为卷积层和池化层(po ...
- TensorFlow卷积神经网络实现手写数字识别以及可视化
边学习边笔记 https://www.cnblogs.com/felixwang2/p/9190602.html # https://www.cnblogs.com/felixwang2/p/9190 ...
随机推荐
- ios9.3.3 h5的js代码全部失效
做微信公众号页面时,ios9.3.3 h5的js代码全部失效描述: 机型iphone6 plus,ios9.3.3js代码全部失效,刚开始还以为是ios和jq兼容问题, 后来发现是es6语法不能读,导 ...
- mpvue的坑,持续更新-.-
mpvue... 坑 怎么说呢,去github看一下,发现还是有很多问题没有解决... 不支持filter 亲,到现在还没有支持filter哦.只能用替代方法了,用computed或者渲染前先处理数据 ...
- win10 uwp 好看的时间选择控件
本文告诉大家我找到的好看的时间选择控件 先给大家看一下图,然后就知道我说的是什么 首先需要安装 Nuget ,搜索 DeanChalk.UWP.TimePicker 或输入Install-Packag ...
- CSS---文本相关属性
text-transform 检索或设置对象中的文本的大小写. 属性值 none:无转换 capitalize:将每个单词的第一个字母转换成大写 uppercase:将每个单词转换成大写 lowerc ...
- Jquery Validate表单验证,自定义校验正整数
// 添加自定义校验规则,校验正整数 jQuery.validator.addMethod("positiveinteger", function(value, element) ...
- Arcgis api for javascript学习笔记(3.2版本) - 匀速行驶轨迹动画效果
一.前言 有这样一个需求:已知某条线上的n个点的经纬度数组 ,实现物体运行轨迹. 如果这些点中两个距离很近,那么我们可以用一个定时器在地图上每次重新画一个点,这样肉眼看到这个点上的运动效果,如下图代码 ...
- 这群程序员疯了!他们想成为IT界最会带货的男人
随着网红主播越来越火,通过直播带货种草的形式也成了今年双12的热点. 不过,网红主播带货早已见怪不怪,但你们见过程序员直播带货吗!? 近日,趁着阿里云双12年末采购节,阿里云邀请了一波程序员GG来为大 ...
- ArcGIS-PictureMarkerSymbol-向地图添加图片标记
1.基于4.13 版本 <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://js.arcgis.com/4.13/esri/themes/li ...
- Hibernate映射文件详解(News***.hbm.xml)二
转自 http://blog.csdn.net/a9529lty/article/details/6454924 一.hibernate映射文件的作用: Hibernate映射文件是Hibernate ...
- 33.python之操作系统,进程,线程
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/6248025.html 操作系统 一 为什么要有操作系统? 现代计算机系统是由一个或者多个处理器,主存, ...
