WebGL模型拾取——射线法二
这篇文章是对射线法raycaster的补充,上一篇文章主要讲的是raycaster射线法拾取模型的原理,而这篇文章着重讲使用射线法要注意的地方。首先我们来看下图。
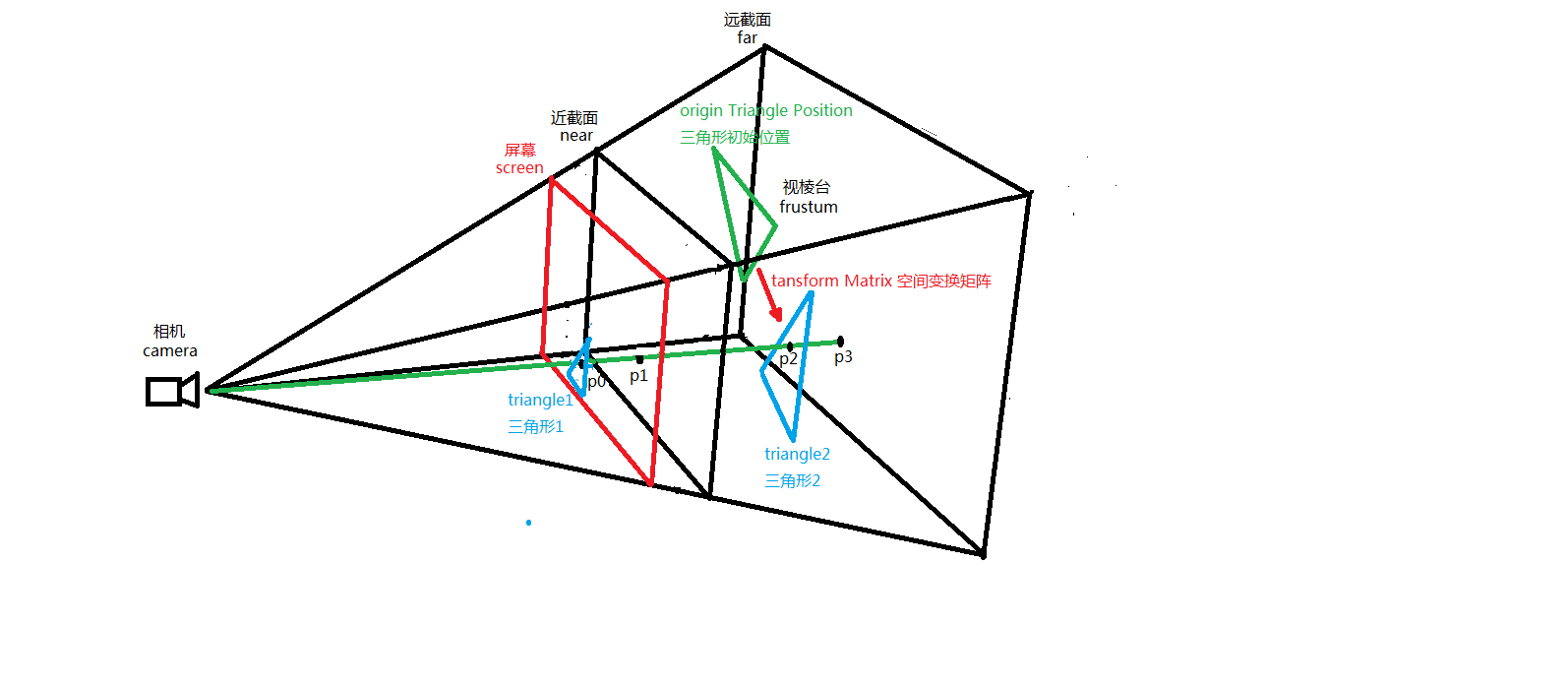
我来解释一下上图中的originTriangle,这就是Triangle2三角形第一次绘制在空间中的位置,而Triangle2当前的位置是经过一系列空间变换而来的(这些位置姿态变换大多是由用户鼠标交互产生),变换矩阵就是transformMatrix。这下就引出了本文第一个重点,那就是做raycaster的时候要保证线段碰撞模型的时候一定是模型当前所处的空间位置,即已经做过transformMatrix空间(姿态,位置)变换,否则线段如果和模型之前的初始化位置求交显然没有交点,就拾取失败了。这就是做raycaster要注意的第一个重点,即射线一定要和空间变换后的模型求交。
接下来我们再看一张图,请看下图。
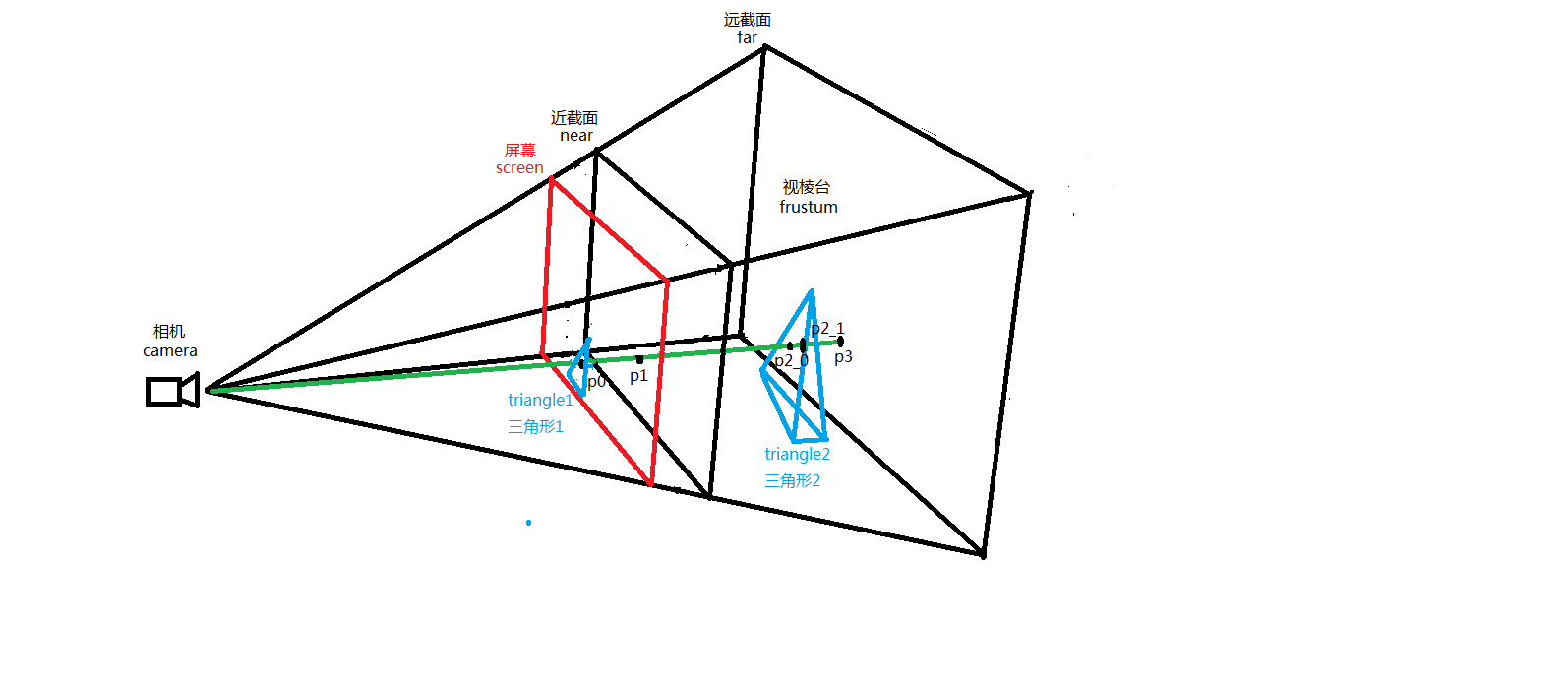
我们看到,射线和模型有2个交点,P2_0和P2_1,分别交四面体的前面于P2_0和交四面体的后面于P2_1。这就是我们要着重关注的本文第二个重点,即raycaster射线拾取模型过程中射线与单个模型有多个交点的问题。处理这个问题其实有很多办法,这里我们采用最简单的方式,就是距离相机(人眼)位置近者胜出的策略。计算交点的算法上一篇文章已经提到,这里不再赘述,但要说明的是,我们计算的每一个面在数据结构中都有自身模型父节点geometry,如果像上图一个四面体的geometry和射线产生了多个面相交,那我们就认为鼠标选中的是该模型geometry离相机(camera)(人眼)最近的交面上的交点。
对于上面2点的叙述,配合部分代码展示,是geometry空间变换的,代码如下。
Object.assign(CubeSection.prototype, {
//重载,每一帧同步数据
sync: function () {
if(this._mode === "face") {//根据剖切模式管理鼠标拖拽逻辑
if (this._selectFace) {
let camera = this._viewer.getMainCamera();
let last = this._mousePoints.getLast();
let lastX = camera.getNormalizedX(last[]);
let lastY = camera.getNormalizedY(last[]);
let current = this._mousePoints.getCurrent();
let currentX = camera.getNormalizedX(current[]);
let currentY = camera.getNormalizedY(current[]);
this._mousePoints.sync();
let deltaX = currentX - lastX;
let deltaY = currentY - lastY;
if (Math.abs(deltaX) < Algorithm.EPSILON && Math.abs(deltaY) < Algorithm.EPSILON)
return;
//如果面被选中,并且有移动量,需要进行剖切面移动处理
let start = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
let end = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
camera.computeScreenToWorldNearFar(lastX, lastY, start, end, true);
//获取起点与平面的交点
let plane = this._cubeClip.getClipPlane(this._selectFace.getName());
let planePt1 = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
if (Plane.intersectLine(planePt1, start, end, plane)) {
//将模型交点再转换到屏幕坐标上,主要为了获取z值给终点
let temppt = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
camera.computeWorldToScreen(planePt1, temppt);
Vec3.set(temppt, currentX, currentY, temppt[]);
let planePt2 = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
camera.computeScreenToWorld(temppt, planePt2);
Vec3.sub(temppt, planePt2, planePt1);
let dist = Vec3.dot(plane, temppt);
this.move(dist);
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(planePt2);
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(temppt);
}
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(planePt1);
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(start);
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(end);
}
} else if(this._mode === "translate"){
if(this._selectAxis) {
let camera = this._viewer.getMainCamera();
let last = this._mousePoints.getLast();//前一帧鼠标的XY坐标
let lastX = camera.getNormalizedX(last[]);
let lastY = camera.getNormalizedY(last[]);
let current = this._mousePoints.getCurrent();//目前帧鼠标的XY坐标
let currentX = camera.getNormalizedX(current[]);
let currentY = camera.getNormalizedY(current[]);
this._mousePoints.sync();//继续下一帧同步鼠标XY坐标
let deltaX = currentX - lastX;//X偏移量
let deltaY = currentY - lastY;//Y偏移量
if (Math.abs(deltaX) < Algorithm.EPSILON && Math.abs(deltaY) < Algorithm.EPSILON) {
//如果XY偏移量都为零,就直接返回,什么操作都不做
return;
}
//坐标系轴被选中,并且有偏移量,就要移动整个包围盒子
let start = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
let end = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
//把屏幕上的XY坐标换算到视棱台near,far截面上的XY坐标
camera.computeScreenToWorldNearFar(lastX, lastY, start, end, true);
//当前pick的坐标轴
let axis = this._selectAxis;
//near-far线段截axis坐标轴的交点
let intersectPoint1 = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
//射线碰撞
let intersections = this._drawActor.linesegmentIntersect(start, end);//对场景中的所有物体进行线段碰撞检测
//遍历intersections列表,按照离相机从远到近排列
for (let i = ; i < intersections.length; i++) {
let geometry = intersections[i].getDrawable().getGeometry();
if (geometry && new String(geometry._name).substring(, ) === "axis") {
intersectPoint1 = intersections[i]._point;//获取到near-far线段和坐标轴的交点
break;
}
}
//将near-far和坐标轴的交点再转换到屏幕坐标上,主要为了获取z值给终点
let screenPoint = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
camera.computeWorldToScreen(intersectPoint1, screenPoint);
//screePoint(currentX, currentY, screenPoint.z)
Vec3.set(screenPoint, currentX, currentY, screenPoint[]);
//鼠标移动的第二个场景坐标系里的点坐标
let intersectPoint2 = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
//把屏幕归一化坐标转化为场景世界坐标
camera.computeScreenToWorld(screenPoint, intersectPoint2);
Vec3.sub(screenPoint, intersectPoint2, intersectPoint1);
let dist = ;
if(this._selectAxis._name === "axisX"){
dist = screenPoint[];
}else if(this._selectAxis._name === "axisY"){
dist = screenPoint[];
}else if(this._selectAxis._name === "axisZ"){
dist = screenPoint[];
}
this.move(dist);
//析构向量
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(intersectPoint1);
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(intersectPoint2);
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(screenPoint);
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(start);
Vec3.MemoryPool.free(end);
}
} else if(this._mode === "rotate"){
} else if(this._mode === "scale"){
}
},
updateTransform: function () {
let mat = this._cubeRoot.getMatrix();
//重新计算坐标系模型的_matrix
this._coordinateSection.update(this._clipBox, this._scale, this._translate, this._rotate, this._scaleMatrix, this._translateMatrix, this._rotateMatrix, mat);
Mat4.fromScaling(this._scaleMatrix, this._scale);
Mat4.fromTranslation(this._translateMatrix, this._translate);
Mat4.fromQuat(this._rotateMatrix, this._rotate);
Mat4.mul(mat, this._translateMatrix, this._rotateMatrix);
Mat4.mul(mat, mat, this._scaleMatrix);
//剖切面数据的变换
this._cubeClip.resetClipPlane();
this._cubeClip.transformClipPlane(mat);
//包围盒子更新
this._clipBox.setMaxValue(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
this._clipBox.setMinValue(-0.5, -0.5, -0.5);
this._clipBox.transformMat4(mat);
},
接下来是选取离相机近的交点,代码如下
//拾取物体,根据当前剖切模式选择intersections列表中的碰撞对象
pick: function (x, y) {
let camera = this._viewer.getMainCamera();
let start = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
let end = Vec3.MemoryPool.alloc();
camera.computeScreenToWorldNearFar(x, y, start, end);
let intersections = this._drawActor.linesegmentIntersect(start, end);
let l = intersections.length;
if (l !== ) {
switch(this._mode){
case "face" : {//面剖切
let intersection = intersections[];//LineSegmentIntersection
let geometry = intersection.getDrawable().getGeometry();
if (geometry) {
this._selectFace = geometry;
this._selectFace.setStateSet(this._selectState);
return true;
}
}
case "translate" : {//平移剖切
//遍历intersections列表,按照离相机从远到近排列
for(var i=; i<l; i++){
let geometry = intersections[i].getDrawable().getGeometry();
if(geometry && new String(geometry._name).substring(, ) === "axis"){
this._selectAxis = geometry;
this._selectAxis.setStateSet(this._selectStateAxis);
break;
}
}
return true;
}
case "rotate" : {//旋转剖切
//遍历intersections列表,按照离相机从远到近排列
for(var i=; i<l; i++){
let geometry = intersections[i].getDrawable().getGeometry();
if(geometry && new String(geometry._name).substring(, ) === "face"){
this._selectAxisFace = geometry;
this._selectAxisFace.setStateSet(this._selectStateAxisFace);
break;
}
}
return true;
}
case "scale" : {//缩放剖切
//遍历intersections列表,按照离相机从远到近排列
for(var i=; i<l; i++){
let geometry = intersections[i].getDrawable().getGeometry();
if(geometry && new String(geometry._name).substring(, ) === "axis"){
this._selectAxis = geometry;
this._selectAxis.setStateSet(this._selectStateAxis);
break;
}
}
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
},
其中intersections[]交点列表是按照离相机由远到近距离排序的,intersection[i]交点离相机距离比intersection[i+1]交点离相机距离要近。这就是我们采取的离相机近交点胜出原则。
好了,以上就是raycaster射线拾取模型要注意的地方,如有错误,希望读者斧正,欢迎诸位同学留言。如需转载本文,请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/ccentry/p/9977490.html
WebGL模型拾取——射线法二的更多相关文章
- WebGL模型拾取——射线法
今天要把WebGL中一个非常重要的算法记录下来——raycaster射线法拾取模型.首先我们来了解一下为什么要做模型拾取,我们在做webgl场景交互的时候经常要选中场景中的某个模型,比如鼠标拖拽旋转, ...
- Away3D引擎学习笔记(三)模型拾取(翻译)
原文详见http://away3d.com/tutorials/Introduction_to_Mouse_Picking.本文若有翻译不对的地方,敬请指出. 本教程详细介绍了Away3D 4.x中鼠 ...
- 射线法(1190 - Sleepwalking )
题目:http://lightoj.com/volume_showproblem.php?problem=1190 参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/gkingzheng/arti ...
- matlab练习程序(射线法判断点与多边形关系)
依然是计算几何. 射线法判断点与多边形关系原理如下: 从待判断点引出一条射线,射线与多边形相交,如果交点为偶数,则点不在多边形内,如果交点为奇数,则点在多边形内. 原理虽是这样,有些细节还是要注意一下 ...
- LightOj1190 - Sleepwalking(判断点与多边形的位置关系--射线法模板)
题目链接:http://lightoj.com/volume_showproblem.php?problem=1190 题意:给你一个多边形含有n个点:然后又m个查询,每次判断点(x, y)是否在多边 ...
- Codeforces 375C Circling Round Treasures - 最短路 - 射线法 - 位运算
You have a map as a rectangle table. Each cell of the table is either an obstacle, or a treasure wit ...
- Revit API射线法读取空间中相交的元素
Revit API提供根据射线来寻找经过的元素.方法是固定模式,没什么好说.关键代码:doc.FindReferencesWithContextByDirection(ptStart, (ptEnd ...
- 【BZOJ1294】[SCOI2009]围豆豆Bean 射线法+状压DP+SPFA
[BZOJ1294][SCOI2009]围豆豆Bean Description Input 第一行两个整数N和M,为矩阵的边长. 第二行一个整数D,为豆子的总个数. 第三行包含D个整数V1到VD,分别 ...
- SGU 124. Broken line 射线法 eps的精准运用,计算几何 难度:3
124. Broken line time limit per test: 0.25 sec. memory limit per test: 4096 KB There is a closed bro ...
随机推荐
- javascript中注册和移除事件的4种方式
对于html中的一些元素注册事件的方式有多种 第一种: 复制代码代码如下: <script> function test() { alert("OK"); } < ...
- tali -f 和 tail -F 之间的区别
tail -f 等同于--follow=descriptor,根据文件描述符进行追踪,当文件改名或被删除,追踪停止 tail -F 等同于--follow=name --retry ...
- Linux 快速查看系统配置-熟悉新环境的配置
问题背景: 当我们使用新的环境的时候,需要很快得熟悉自己环境的配置,这时候我们如果知道一些命令就极为方便了.这样你就能对自己的环境较为熟悉,进行工作的时候也能随心所欲了. 如果你使用workstati ...
- 【SQL SERVER】语法复习
一.数据类型 截图来源:http://www.w3school.com.cn/sql/sql_datatypes.asp 二.数据表操作 1.创建数据表 USE [Test] GO /****** ...
- iptables实战演练
iptables禁止 ip 10.10.10.1 访问本地80端口: iptables -t filter -I INPUT -s 10.10.10.1 -p tcp –dport 80 -j DRO ...
- Docker容器学习与分享03
Docker容器的基本操作 所有的docker命令都是以docker开头,也就是指调用docker程序.我学习的第一个命令就是docker run,运行一个容器.以Docker分享02中的容器为例: ...
- vc MFC 通过IDispatch调用默认成员函数
CComPtr<IDispatch> spDisp(IDispatch *); if(!spDisp) return; DISPPARAMS dispParam={0}; //没有参数 V ...
- leetcode 1. Two Sum [java]
注意点: HashMap<Integer, Integer> return new int[]{}; 3 2 4 target:6 return null; public int[] tw ...
- 2.python数据结构的性能分析
一.引言 - 现在大家对 大O 算法和不同函数之间的差异有了了解.本节的目标是告诉你 Python 列表和字典操作的 大O 性能.然后我们将做一些基于时间的实验来说明每个数据结构的花销和使用这些数据结 ...
- jQ判断一个元素是否为空
// 方法一 if (!$('#jb51').html()) { //http://www.jb51.net 什么都没有找到; } // 方法二 if ($('#jb51').is(":em ...
