CSS 基础 例子 定位及z-index
position 属性指定了元素的定位类型。
position 属性的四个值:
- static 不设置默认为该值,即没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中。不能使用top,bottom,left,right和z-index。
- relative 是相对其正常位置,它原本所占的空间不会改变,经常被用来作为绝对定位元素的容器块。
- absolute 相对于最近的已定位(非static)父元素,如果元素没有已定位的父元素,那么它的位置相对于<html>,使元素的位置与文档流无关,因此不占据空间。
- fixed 相对于浏览器窗口是固定位置。即使窗口是滚动的它也不会移动,改变窗口大小也不会移动。其它特性同absolute定位。
默认是按照标准流显示,指定position属性后,再指定 top, bottom, left, right属性来进行定位。
z-index 元素的定位与文档流无关,所以,会导致元素重叠,这涉及到重叠元素间的显示顺序,z-index,用来控制显示顺序,值越高越显示前边,可以指定负数
注意:两个定位元素重叠,没有指定z - index,后边定位的元素显示在前边。
一、标准顺序排列文档
1、标准流
三个div,从上而下排列,第二个div的margin-left和margin-top为20px。块元素,标准流,每个div大小是100px*100px,border为1px
html代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
background: red;
}
.box2{
margin-left: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
background: green;
}
.box3{
background: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果:
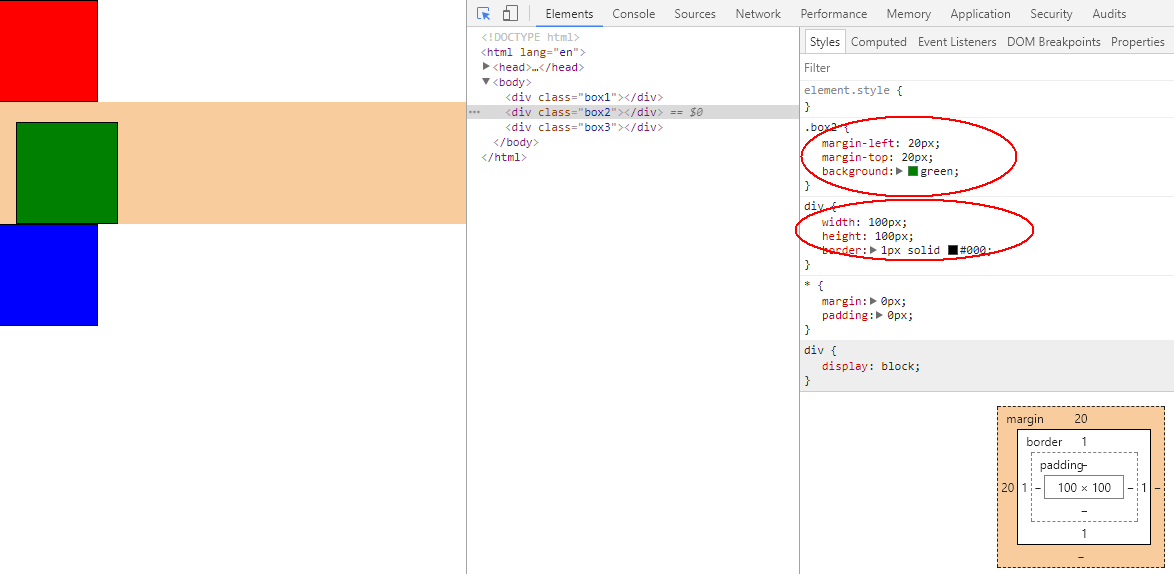
2、相对定位
对第二个元素添加属性,在原来基础上,向下和向左移动了20px,原来的margin-left和margin-top还是有效。
top:20px;
left:20px;
position:relative;
html代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
background: red;
}
.box2{
margin-left: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
background: green;
/*添加以下三个属性*/
top:20px;
left:20px;
position:relative;
}
.box3{
background: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果

相对定位前后对比:

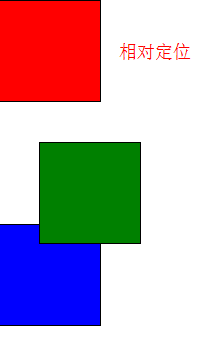
3、绝对定位
把position属性改成absolute
html代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
background: red;
}
.box2{
margin-left: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
background: green;
/*添加以下三个属性*/
top:20px;
left:20px;
/*改成absolute*/
position:absolute;
}
.box3{
background: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果:

运行前后对比:


3、fixed定位
为了演示把最后一个div高度设置大点,再改变窗口大小使其出现滚动条
html代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>fixed定位</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.box1{
background: red;
}
.box2{
margin-left: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
background: green;
/*添加以下三个属性*/
top:20px;
left:20px;
/*改成fixed*/
position:fixed;
}
.box3{
/*添加宽度*/
height: 700px;
background: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果:
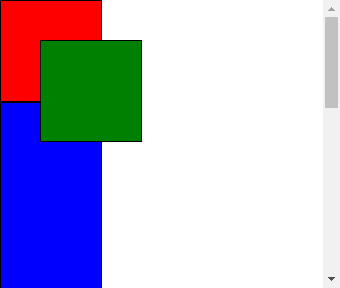 移动滚动条后
移动滚动条后 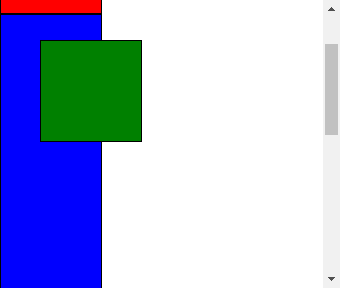
再看下标准文档流
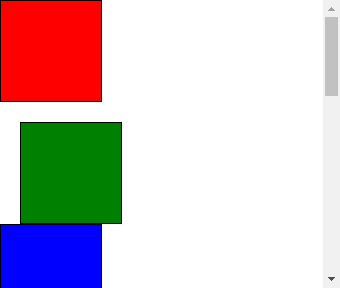
二、父子顺序排列文档
1、标准流
一个div包含两个div。
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*
{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
}
#f
{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
border: solid 5px black;
padding: 0px;
background-color: blue
}
#s1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow
}
#s2
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="f">
<div id="s1">
</div>
<div id="s2">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果:
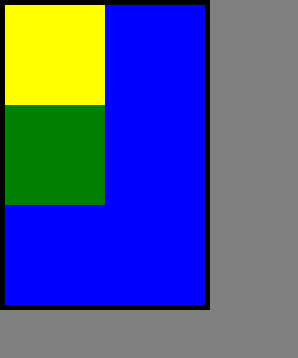
2、相对定位
单独父元素相对定位:
父元素直接相对定位,子元素按正常流显示,所以下边例子,子元素和父元素一起向右和下移动15px
html代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en">
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*
{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
}
#f
{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
border: solid 5px black;
padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: relative;
top: 15px;
left: 15px;
}
#s1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow
}
#s2
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="f">
<div id="s1">
</div>
<div id="s2">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果: 这是标准流:


三个元素都相对定位:
都在其应该所在位置进行了偏移
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*
{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
background-color: gray
}
#f
{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
border: solid 5px black;
padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: relative;
top: 15px;
left: 15px;
}
#s1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
#s2
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: relative;
top: 5px;
left: 15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="f">
<div id="s1">
</div>
<div id="s2">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果: 这是标准流
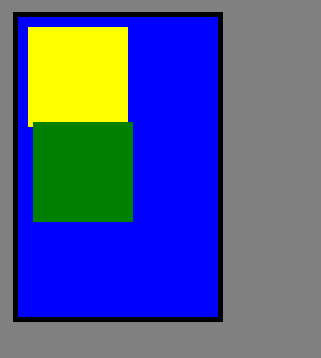

2、绝对定位
单独为两个子元素设定绝对定位
根据原则:找到最近定位的父元素作为基准,如果都没有找到就以html为基准,直接进行偏移,此例为后者,以html为基准。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*
{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
background-color: gray
}
#f
{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
border: solid 5px black;
padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
}
#s1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
#s2
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: absolute;
top: 5px;
left: 15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="f">
<div id="s1">
</div>
<div id="s2">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果: 这是标准流:
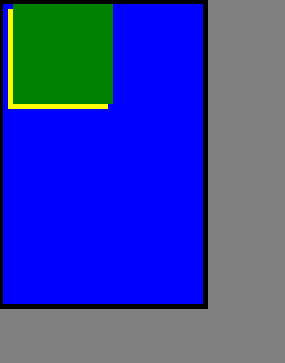

同时为直接父元素进行定位:
注意,如果父元素设置了margin,border,padding等属性,那么这个定位点将忽略padding,将会从padding开始的地方(即只从padding的左上角开始)进行定位。
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*
{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
background-color: gray
}
#f
{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
border: solid 5px black;
padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
#s1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
#s2
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: absolute;
top: 5px;
left: 15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="f">
<div id="s1">
</div>
<div id="s2">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果: 这是标准流:
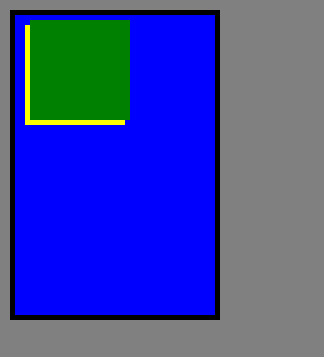

3、fixed定位
fixed是一种特殊的absolute,fixed总是按照浏览器的窗口进行定位,不是body为参照,因为若有滚动条滚动其位置也不会动。f为相对定位,s1增加absolute定位方式,s2 增加fixed定位方式。
s2以body为原点,f相对定位,即以自身原来位置左上角为原点,而s1以直接定位父元素为基准,即f
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*
{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
background-color: gray
}
#f
{
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
border: solid 5px black;
padding: 0px;
background-color: blue;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: relative;
top: 30px;
left: 30px;
}
#s1
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color:yellow;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}
#s2
{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
/*加了下边三句*/
position: fixed;
top: 5px;
left: 15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="f">
<div id="s1">
</div>
<div id="s2">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
运行结果: 这是标准流:

CSS 基础 例子 定位及z-index的更多相关文章
- CSS 基础:定位元素(3)<思维导图>
这段时间利用一下间隙时间学习了CSS的基础知识,主要目的是加深对CSS的理解,虽然个人主要工作基本都是后台开发,但是个人觉得系统学习一下CSS的基础还是很有必要的.下面我学习CSS时做的思维导图(全屏 ...
- CSS基础-4 定位
CSS定位和浮动 css定位:改变页面的位置 定位机制有以下三种 普通流 浮动 绝对布局 定位的属性: position:把元素放在一个静态的.相对的.绝对的.或固定的位置中 top ...
- CSS 基础 例子 display属性:block、inline和inline-block的区别
HTML中块级元素(block)和行级元素(inline):比如div就是常见的块级元素,span就是常见的行级元素. 可以通过css的display属性来设置一个元素到底是块级,还是行级元素:dis ...
- CSS 基础 例子 伪元素和伪类 & 区别
一.概念 CSS 伪类 -------向某些选择器添加特殊的效果,要达到同等效果,通过类来达到效果 CSS 伪元素 -------将特殊的效果添加到某些选择器,要达到同等效果,通过添加元素达到 ...
- CSS 基础 例子 浮动float
一.基本概念 设置了float属性的元素会根据属性值向左或向右浮动,设置了float属性的元素为浮动元素,浮动元素会从普通文档流中脱离,直到它的外边缘碰到包含框或另一个浮动框的边框为止. 浮动元素之后 ...
- CSS 基础 例子 行高line-height
“行高“指一行文字的高度,具体来说是指两行文子间基线间的距离.在CSS,line-height被用来控制行与行之间的垂直距离.line-height 属性会影响行框的布局.在应用到一个块级元素时,它定 ...
- css基础回顾-定位:position
w3school 对position定义和说明是: 定义和用法: position 属性规定元素的定位类型. 说明: 这个属性定义建立元素布局所用的定位机制.任何元素都可以定位,不过绝对或固定元素会生 ...
- CSS 基础 例子 图片拼合技术
利用background-position xpos ypos 就是以图片的左上角顶点为原点,往下和右都为正,反之为负,移动图片 如: background-position: 15px 20px;( ...
- CSS 基础 例子 水平 & 垂直对齐
一.元素居中对齐 margin:auto 水平居中对齐一个元素(如 <div>),即div本身在容器中的对齐,用margin:auto,而且,需要设置 width 属性(或者设置 100% ...
随机推荐
- 如何快速学好Shell脚本?
Shell 语言作为类 Unix 系统的原生脚本,有着非常实用的价值.但对于很多刚刚接触 Shell 脚本的同学来说,搞懂 Shell 语言的语法却是一件非常困难的事情.甚至有人吐槽,或许没有谁能清楚 ...
- iOS.CM5.CM4.CM2
增量数据计算接口: CC_MDx_Init CC_MDx_Update CC_MDx_Final 全量数据计算接口: CC_MDx
- 初学者的分布式Python爬虫教程
下面是一个超级计算机的排行榜,如果我们能拥有其中任意一个,那么我们就不需要搞什么分布式系统.可是我们买不起,即使买得起,也交不起电费,所以我们只好费脑子搞分布式. 分布式的本质就如上期提到的一个概念: ...
- POJ3662或洛谷1948 Telephone Lines
二分答案+单源最短路 POJ原题链接 洛谷原题链接 显然可以二分答案,检验\(mid\)可以使用最短路来解决. 将大于\(mid\)的边看成长度为\(1\)的边,说明要使用免费升级服务,否则长度为\( ...
- nodejs 后台开发 和C++代码开发
https://www.npmjs.com/package/node-gyp node-gyp Node.js native addon build tool Node.js native addon ...
- Mac 下配置Nginx安装环境配置详细说明
环境信息: Mac OS X 10.11.1 Homebrew 0.9.5 正文 一.安装 Nginx 1.终端执行: ? 1 2 brew search nginx brew install ng ...
- pytho常用模块2——random
random模块用来生成随机数,有以下几个常用方法: import random random.random() #产生随机数[0-1) random.randint(a,b) #产生随机整数[a,b ...
- MVVM中viewmodel的理解
网上有人写了这段话,我也有同感,特别是第一种用法,很重要,后一种用法,我觉得是把第一种用法加入controller中了. 第一种 “view model” 是 “model for the view” ...
- 论Java的重要性
最近,最新的世界编程语言排名最近出炉了,Java位居世界第一. 不仅如此,Java以17.856%超过第二名C语言的8.726%两倍以上,其实,这一现象是十分反常的,因为,在前几年, ...
- android开发笔记(2)
我之前完成了SDK的安装,这次需要在eclipse中导入相关的控件. 一.下载ADT 在之前下载的网站上下载相关的ADT的压缩包. 二.在eclipse中进行导入 在eclipse中的Help-> ...
