FutureTask详解
1 基本概念
1.1 Callable与Future
Runnable封装一个异步运行的任务,可以把它想象成为一个没有参数和返回值的异步方法。Callable与Runnable类似,但是有返回值。Callable接口是一个参数化的类型,只有一个方法call。
public interface Callable<V> {
V call() throws Exception;
}
类型参数是返回值的类型。例如,
Callable<Integer>表示一个最终返回Integer对象的异步计算。
Future保存异步计算的结果。可以启动一个计算,将Future对象交给某个线程,然后忘掉它。Future对象的所有者在结果计算好之后就可以获得它。
Future接口具有下面的方法:
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
第一个get方法的调用被阻塞,知道计算完成。如果在计算完成之前,第二个get方法的调用超时,抛出一个TimeoutException异常。如果运行该计算的线程被中断,两个方法都将抛出InterruptedException。如果计算已经完成,那么get方法立即返回。
如果计算还在进行,isDone方法返回false;如果完成了,则返回true。
可以用cancel方法取消该计算。如果计算还没有开始,它被取消且不再开始。如果计算处于运行之中,那么如果mayInterrupt参数为true,它就被中断。
1.2 FutureTask
FutureTask包装器是一种非常便利的机制,同时实现了Future和Runnable接口。
类图如下:
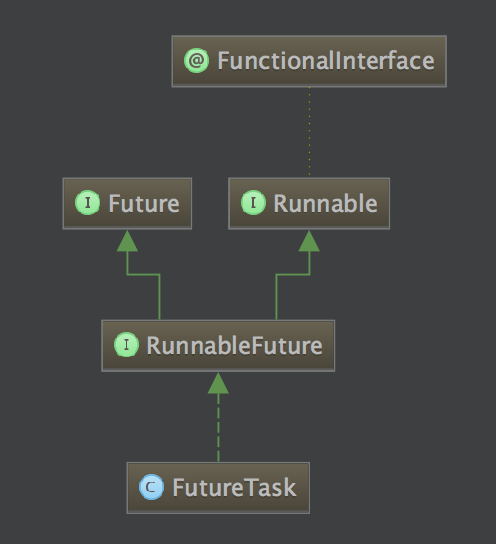
FutureTask的状态转换过程:
* NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL
* NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL
* NEW -> CANCELLED
* NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED
1.3 FutureTask的执行过程
创建一个futureTask对象task
提交task到调度器executor等待调度或者在另外一个线程中执行task
等待调度中...
如果此时currentThread调取执行结果task.get(),会有几种情况
if task 还没有被executor调度或正在执行中
阻塞当前线程,并加入到一个阻塞链表中waitNode
else if task被其它Thread取消,并取消成功 或task处于中断状态
throw exception
else if task执行完毕,返回执行结果,或执行存在异常,返回异常信息
如果此时有另外一个线程调用task.get()
执行过程同上
2 应用场景
1. Future用于异步获取执行结果或者取消任务。
2. 在高并发场景下确保任务只执行一次。
3 基本例子
Callable<Integer> myComputation = ...;
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<Integer>(myComputation);
Thread t = new Thread(task);
t.start();
...
Integer result = task.get(); //获取结果
4 FutureTask源码分析
4.1 核心状态
/**
* The run state of this task, initially NEW. The run state
* transitions to a terminal state only in methods set,
* setException, and cancel. During completion, state may take on
* transient values of COMPLETING (while outcome is being set) or
* INTERRUPTING (only while interrupting the runner to satisfy a
* cancel(true)). Transitions from these intermediate to final
* states use cheaper ordered/lazy writes because values are unique
* and cannot be further modified.
*
* Possible state transitions:
* NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL
* NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL
* NEW -> CANCELLED
* NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED
*/
private volatile int state;
private static final int NEW = 0;
private static final int COMPLETING = 1;
private static final int NORMAL = 2;
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3;
private static final int CANCELLED = 4;
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5;
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6;
4.2 创建FutureTask
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
4.3 获取执行结果
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}
4.4 执行方法
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
4.5 设置状态
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = t;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
5 高级示例
public class Memoizer<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {
private final ConcurrentMap<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentMap<A, Future>>();
private final Computable<A, V> c;
public Memoizer(Computable<A, V> c) {
this.c = c;
}
public C computer(final A arg) throws InterruptedException {
while(true) {
Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);
if(f == null) {
Callable<V> eval = new Callable<V>() {
public V call() throws InterruptedException {
return c.compute(arg);
}
};
FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<V>(eval);
f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);
if(f == null) {
f = ft;
ft.run();
}
}
try {
return f.get();
} catch(CancellationException e) {
cache.remove(arg, f);
} catch(ExecutionException e) {
throw launderThrowable(e.getCause());
}
}
}
}FutureTask详解的更多相关文章
- Callable,Future和FutureTask详解
1.Callable和Runnable 看Callable接口: public interface Callable<V> { /** * Computes a result, or th ...
- Future、Callable 、FutureTask详解
1.Future和Callable Future是一个接口表示异步计算的结果,它提供了检查计算是否完成的方法,以等待计算的完成,并获取计算的结果.Future提供了get().cancel().isC ...
- [转]FutureTask详解
FutureTask类是Future 的一个实现,并实现了Runnable,所以可通过Excutor(线程池) 来执行,也可传递给Thread对象执行.如果在主线程中需要执行比较耗时的操作时,但又不 ...
- Java并发编程的艺术笔记(九)——FutureTask详解
FutureTask是一种可以取消的异步的计算任务.它的计算是通过Callable实现的,多用于耗时的计算. 一.FutureTask的三种状态 二.get()和cancel()执行示意 三.使用 一 ...
- 最强Java并发编程详解:知识点梳理,BAT面试题等
本文原创更多内容可以参考: Java 全栈知识体系.如需转载请说明原处. 知识体系系统性梳理 Java 并发之基础 A. Java进阶 - Java 并发之基础:首先全局的了解并发的知识体系,同时了解 ...
- (转)深入详解Java线程池——Executor框架
转:https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/633782?utm_content=m_1000015330 在Java中,使用线程来异步执行任务.Java线程的创建与销毁需要一定 ...
- JAVA线程池原理详解二
Executor框架的两级调度模型 在HotSpot VM的模型中,JAVA线程被一对一映射为本地操作系统线程.JAVA线程启动时会创建一个本地操作系统线程,当JAVA线程终止时,对应的操作系统线程也 ...
- Java多线程编程中Future模式的详解
Java多线程编程中,常用的多线程设计模式包括:Future模式.Master-Worker模式.Guarded Suspeionsion模式.不变模式和生产者-消费者模式等.这篇文章主要讲述Futu ...
- 详解Executor框架
在Java中,使用线程来异步执行任务.Java线程的创建与销毁需要一定的开销,如果我们为每一个任务创建一个新线程来执行,这些线程的创建与销毁将消耗大量的计算资源.同时,为每一个任务创建一个新线程来执行 ...
随机推荐
- 一种新型远距临场机器人 Fusion / Full Body Surrogacy for Collaborative Communication
近日,来自日本庆应大学的机器人专家开发出一种新型远距临场机器人 Fusion,允许操作者远程控制别人的身体来帮助他们完成操作任务.Fusion「栖居」在代理者的背上,具备立体视觉和双声道听觉,可以通过 ...
- 软件测试——Peer Review(简介)
1. 同行评审的种类和对象 同行评审活动的关注点应该是工作产品中的缺陷,而不应该是工作产品的作者或者生产者,管理者也不应使用同行评审的结果去评价个人的行为. 同行评审的分类有很多种,自从IBM的Fag ...
- oracle10偶然性卡住登陆
连接数据库异常:登陆数据库后以"conn /as sysdba"方式登陆正常,数据库轻载,无压力:于是检查数据库的监听器,输入"lsntctl services" ...
- OpenACC Hello World
▶ 在 windows 10 上搭建 OpenACC 环境,挺麻烦 ● 安装顺序:Visual Studio 2015(PGI 编译器不支持 Visual Studio 2017):CUDA Tool ...
- style css
Title 语文 用户名 用户名 数学 英语 <!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta ch ...
- JAVA WEB开发中的会话跟踪
常用的会话跟踪技术是Cookie与Session.Cookie通过在客户端记录信息确定用户身份,Session通过在服务器端记录信息确定用户身份. Http协议是一种无状态的协议,一旦数据交换完毕,客 ...
- ResponseUtil数据传递至前端
package com.java1234.util; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.ser ...
- 如何将Wav文件做到EXE文件里
1)编写.RC文件 ..RC文件是资源的源文件,编译器也就编译这个文件,生成.RES的资源文件 首先在我们的项目子目录中建立一个纯文本文件,起名叫Sound.rc,文件中 有一行,内容为: SOUND ...
- Javaweb连接数据库
在JSP中使用JDBC驱动连接mysql数据库. 1: 下载mysql的Java连接程序 2: 解压目录下的mysql-connector-java-5.0.24-bin.jar文件就是连接MySql ...
- ArcMap导入图层出现General function failure问题
问题描述: 使用ArcMap的FeatureClassToFeatureClass命令导入图层,出现如下图的错误提示: 解决方法: 参考http://forums.esri.com/thread.as ...
