CodeForces1006E- Military Problem
E. Military Problem
time limit per test
3 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
In this problem you will have to help Berland army with organizing their command delivery system.
There are nn officers in Berland army. The first officer is the commander of the army, and he does not have any superiors. Every other officer has exactly one direct superior. If officer aa is the direct superior of officer bb, then we also can say that officer bb is a direct subordinate of officer aa.
Officer xx is considered to be a subordinate (direct or indirect) of officer yy if one of the following conditions holds:
- officer yy is the direct superior of officer xx;
- the direct superior of officer xx is a subordinate of officer yy.
For example, on the picture below the subordinates of the officer 33 are: 5,6,7,8,95,6,7,8,9.
The structure of Berland army is organized in such a way that every officer, except for the commander, is a subordinate of the commander of the army.
Formally, let's represent Berland army as a tree consisting of nn vertices, in which vertex uu corresponds to officer uu. The parent of vertex uucorresponds to the direct superior of officer uu. The root (which has index 11) corresponds to the commander of the army.
Berland War Ministry has ordered you to give answers on qq queries, the ii-th query is given as (ui,ki)(ui,ki), where uiui is some officer, and kiki is a positive integer.
To process the ii-th query imagine how a command from uiui spreads to the subordinates of uiui. Typical DFS (depth first search) algorithm is used here.
Suppose the current officer is aa and he spreads a command. Officer aa chooses bb — one of his direct subordinates (i.e. a child in the tree) who has not received this command yet. If there are many such direct subordinates, then aa chooses the one having minimal index. Officer aa gives a command to officer bb. Afterwards, bb uses exactly the same algorithm to spread the command to its subtree. After bb finishes spreading the command, officer aa chooses the next direct subordinate again (using the same strategy). When officer aa cannot choose any direct subordinate who still hasn't received this command, officer aa finishes spreading the command.
Let's look at the following example:
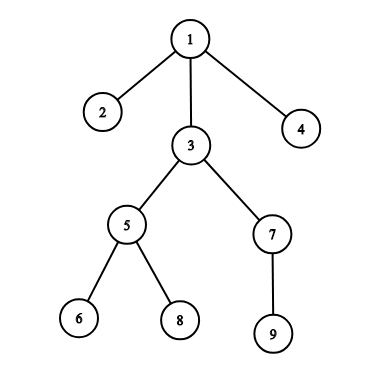
If officer 11 spreads a command, officers receive it in the following order: [1,2,3,5,6,8,7,9,4][1,2,3,5,6,8,7,9,4].
If officer 33 spreads a command, officers receive it in the following order: [3,5,6,8,7,9][3,5,6,8,7,9].
If officer 77 spreads a command, officers receive it in the following order: [7,9][7,9].
If officer 99 spreads a command, officers receive it in the following order: [9][9].
To answer the ii-th query (ui,ki)(ui,ki), construct a sequence which describes the order in which officers will receive the command if the uiui-th officer spreads it. Return the kiki-th element of the constructed list or -1 if there are fewer than kiki elements in it.
You should process queries independently. A query doesn't affect the following queries.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers nn and qq (2≤n≤2⋅105,1≤q≤2⋅1052≤n≤2⋅105,1≤q≤2⋅105) — the number of officers in Berland army and the number of queries.
The second line of the input contains n−1n−1 integers p2,p3,…,pnp2,p3,…,pn (1≤pi<i1≤pi<i), where pipi is the index of the direct superior of the officer having the index ii. The commander has index 11 and doesn't have any superiors.
The next qq lines describe the queries. The ii-th query is given as a pair (ui,kiui,ki) (1≤ui,ki≤n1≤ui,ki≤n), where uiui is the index of the officer which starts spreading a command, and kiki is the index of the required officer in the command spreading sequence.
Output
Print qq numbers, where the ii-th number is the officer at the position kiki in the list which describes the order in which officers will receive the command if it starts spreading from officer uiui. Print "-1" if the number of officers which receive the command is less than kiki.
You should process queries independently. They do not affect each other.
Example
input
Copy
9 6
1 1 1 3 5 3 5 7
3 1
1 5
3 4
7 3
1 8
1 9
output
Copy
3
6
8
-1
9
4
题解:记录每个节点的时间戳和其有几个子节点即可;DFS
AC代码为:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m, a, b, c = 1, d;
bool vis[maxn] = { false };
vector<int> graph[maxn];
int level[maxn],pos[maxn],child[maxn];
int dfs(int src)
{
vis[src] = true;
pos[c] = src;
level[src] = c++;
int temp = 1;
for (int i = 0; i<graph[src].size(); i++)
{
if (!vis[graph[src][i]]) temp += dfs(graph[src][i]);
}
return child[src] = temp;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a;
graph[a].push_back(i);
}
dfs(1);
while (m--)
{
cin >> a >> b;
if (child[a]<b) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << pos[level[a] + b - 1] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
CodeForces1006E- Military Problem的更多相关文章
- Military Problem CodeForces 1006E (dfs序)
J - Military Problem CodeForces - 1006E 就是一道dfs序的问题 给定一个树, 然后有q次询问. 每次给出u,k, 求以u为根的子树经过深搜的第k个儿子,如果一个 ...
- CodeForces 1006E Military Problem(DFS,树的选择性遍历)
http://codeforces.com/contest/1006/problem/E 题意: 就是给出n,m,共n个点[1,n],m次询问.第二行给出n-1个数a[i],2<=i<=n ...
- Codeforces Round #498 (Div. 3)--E. Military Problem
题意问,这个点的然后求子树的第i个节点. 这道题是个非常明显的DFS序: 我们只需要记录DFS的入DFS的时间,以及出DFS的时间,也就是DFS序, 然后判断第i个子树是否在这个节点的时间段之间. 最 ...
- Military Problem CodeForces - 1006E(dfs搜一下 标记一下)
题意: 就是有一颗树 然后每次询问 父结点 的 第k个结点是不是他的子嗣...是的话就输出这个子嗣..不是 就输出-1 解析: 突然想到后缀数组的sa 和 x的用法..就是我们可以用一个id标记当前 ...
- Codeforces Round #498 (Div. 3) E. Military Problem (DFS)
题意:建一颗以\(1\)为根结点的树,询问\(q\)次,每次询问一个结点,问该结点的第\(k\)个子结点,如果不存在则输出\(-1\). 题解:该题数据范围较大,需要采用dfs预处理的方法,我们从结点 ...
- 树&图 记录
A - Lake Counting POJ - 2386 最最最最最基础的dfs 挂这道题为了提高AC率(糖水不等式 B - Paint it really, really dark gray Cod ...
- Codeforces Div3 #498 A-F
. A. Adjacent Replacement ...
- Codeforces Round #498 (Div. 3) 简要题解
[比赛链接] https://codeforces.com/contest/1006 [题解] Problem A. Adjacent Replacements [算法] 将序列中的所有 ...
- DFS序专题
牛客专题之DFS序 简介 dfs序: 每个节点在dfs深度优先遍历中的进出栈的时间序列,也就是tarjan算法中的dfn数组. 画个图理解一下: 这棵树的dfs序:1 3 2 4 2 5 6 7 6 ...
随机推荐
- Linux中SSH服务基于key认证实践
众所周知ssh是目前较可靠,专为远程登录会话和其他网络服务提供安全性的协议,它默认工作在tcp的22号端口,具体实现的软件有:openssh(centos默认安装的),dropbear.ssh协议目前 ...
- Linux中文件的SUID、SGID、Sticky权限说明
1.SUID 首先我们要了解,在Linux中启动一个程序或者启动一个进程是需要有用户的,一个文件的存在是要有用户和组的,一个进程启动后,它的属主取决于进程的发起者,比如 我用root用户启动了一个 c ...
- 图片转换成base64预览
来源:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/FileReader/readAsDataURL 真心不错写得,思路比较清晰.已经测试过 注意: ...
- 领扣(LeetCode)独特的电子邮箱地址 个人题解
每封电子邮件都由一个本地名称和一个域名组成,以 @ 符号分隔. 例如,在 alice@leetcode.com中, alice 是本地名称,而 leetcode.com 是域名. 除了小写字母,这些电 ...
- 领扣(LeetCode)删除链表的倒数第N个节点 个人题解
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点. 示例: 给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2. 当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 ...
- shell脚本2——控制语句
1.顺序结构体 命令从上往下顺序执行 2.分支结构体 1)判断真假 test 表达式 或者 [ 表达式 ](必须有空格) 真返回0,假返回1 test的别名是[, 参数是] 判断表达式 记忆 解释 ! ...
- ZeroC ICE源代码中的那些事 - 嵌套类和局部类
使用嵌套类(类中定义的类,c++没有静态类)或局部类(在函数或成员方法中定义的类),进行行为模式的委托(委托请求)或异步 . java中嵌套类和局部类隐式完成了你对外部对象(实例)访问的私有堆栈的初始 ...
- 初探three.js
相信大多数选择前端的小伙伴都有一个设计师的梦,今天我来说一说three.js.three.js是一款运行在浏览器中的 3D 引擎,你可以用它创建各种三维场景,包括了摄影机.光影.材质等各种对象.学习了 ...
- Spring基于构造函数和设值函数的依赖注入
基于构造函数的依赖注入 我们知道,bean标签中指定的类会进行初始化,这个初始化过程中自然会调用构造函数,那我们也可以利用这个构造函数完成依赖注入. 先创建一个类: public class Text ...
- JavaWeb04-JSP及会话跟踪技术
JSP入门 1 JSP概述 1.1 什么是JSP JSP(Java Server Pages)是JavaWeb服务器端的动态资源.它与html页面的作用是相同的,显示数据和获取数据. 1.2 JSP的 ...
