mysql的一些常用操作(二)
紧跟上一节,我们创建了四个表:
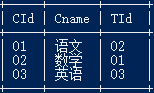
Student、Teacher、Course、Score


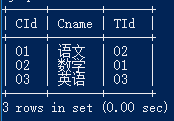

接下来就是实际的一些操作了:
1.求每门课程的学生人数。
select course.cname '课程名称',count(*) '人数' from score,course where score.CId=course.CId group by score.CId

2.查询课程编号为 01 且课程成绩在 80 分及以上的学生的学号和姓名
select a.sid,a.sname from Student a ,Score b where a.sid=b.sid and b.cid='01' and b.scoreore >=80;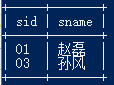
3.统计每门课程的学生选修人数(超过 5 人的课程才统计)
select b.cname '课程',count(*) from course a,score b where a.cid=b.cid group by a.cid having count(*)>5;
4.检索至少选修两门课程的学生学号
select sid from score group by sid having count(cid)>=2;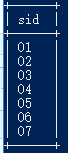
5.选修了全部课程的学生信息
select a.* from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid group by a.sid having count(cid)=(select count(*) from course);

6 .查询存在不及格的课程
select distinct a.* from course a,score b where a.cid=b.cid and b.scoreore<60;
7.查询任何一门课程成绩在 70 分以上的学生姓名、课程名称和分数
select a.sname,b.cname,c.scoreore from student a,course b,score c where a.sid=c.sid and b.cid=c.cid and c.scoreore>70;
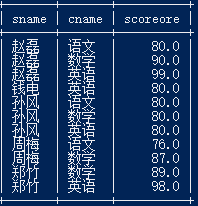
8.查询所有学生的课程及分数情况(存在学生没成绩,没选课的情况
select a.sname,b.cname, c.scoreore from student a left join score c on a.sid=c.sid left join course b on b.cid=c.cid;

9.查询课程名称为「数学」,且分数低于 60 的学生姓名和分数
select a.sname,c.scoreore from student a,course b,score c where a.sid=c.sid and b.cid=c.cid and b.cname="数学" and c.scoreore<60;

10.查询平均成绩大于等于 85 的所有学生的学号、姓名和平均成绩
select a.sid,a.sname,avg(b.scoreore) from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid group by a.sid having avg(b.scoreore)>=85;

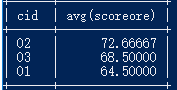
11.查询每门课程的平均成绩,结果按平均成绩降序排列,平均成绩相同时,按课程编号升序排列
select cid,avg(scoreore) from score group by cid order by avg(scoreore) desc,cid asc;
12.查询各科成绩最高分、最低分和平均分
以如下形式显示:课程 ID,课程 name,最高分,最低分,平均分,及格率,中等率,优良率,优秀率
及格为>=60,中等为:70-80,优良为:80-90,优秀为:>=90
要求输出课程号和选修人数,查询结果按人数降序排列,若人数相同,按课程号升序排列
select score.cid,Course.Cname,max(score.scoreore),min(score.scoreore),AVG(score.scoreore),count(score.SId),
sum(case when scoreore <60 then 1 else 0 end)/count(score.cid) '不合格率',
sum(case when scoreore <80 and scoreore >=60 then 1 else 0 end)/count(score.cid) '合格率',
sum(case when scoreore <90 and scoreore >=80 then 1 else 0 end)/count(score.cid) '优良率',
sum(case when scoreore >= 90 then 1 else 0 end)/count(score.cid) '优秀率'
from score,Course
where score.cid = Course.cid
GROUP BY score.cid;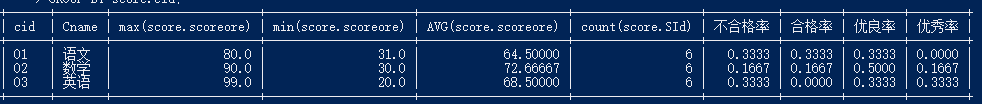
13.查询男生、女生人数
select ssex,count(*) from student group by ssex;

14.检索" 01 "课程分数小于 60,按分数降序排列的学生信息
select a.*,b.scoreore from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid and b.cid="01" and b.scoreore<60 order by scoreore desc;
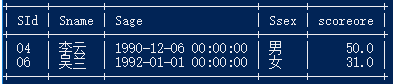
15.按平均成绩从高到低显示所有学生的所有课程的成绩以及平均成绩
select a.sid,a.scoreore, b.`平均成绩` from score a right join (select sid,avg(scoreore) '平均成绩'from score group by sid) b
on a.sid = b .sid
ORDER BY b.`平均成绩` desc;

16.查询没学过"张三"老师讲授的任一门课程的学生姓名
select distinct student.sname from student where student.sid not in
(select c.sid from teacher a,course b,score c where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and a.tname="张三") ;

17.成绩不重复,查询选修「张三」老师所授课程的学生中,成绩最高的学生信息及其成绩
select d.*,c.scoreore from teacher a,course b,score c,student d
where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and d.sid=c.sid and tname="张三"
order by c.scoreore desc limit 1;
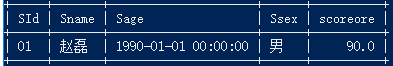
18.成绩有重复的情况下,查询选修「张三」老师所授课程的学生中,成绩最高的学生信息及其成绩
目前我们表中没有重复的成绩,先修改一下:update score set score=90 where skey=17;
若是取出张三老师下的所有学生信息和成绩,即:
select d.*,c.scoreore from teacher a,course b,score c,student d
where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and d.sid=c.sid and tname="张三"
order by c.scoreore desc;则有:
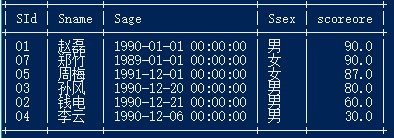
select d.*,c.scoreore from teacher a,course b,score c,student d
where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and d.sid=c.sid and tname="张三" and scoreore =
(select max(scoreore) from teacher a,course b,score c where a.tid=b.tid and b.cid=c.cid and a.tname="张三");

19.查询不同课程成绩相同的学生的学生编号、课程编号、学生成绩
select any_value(a.sid),any_value(a.cid),any_value(a.scoreore) from score a
inner join score b on a.sid=b.sid and a.cid!=b.cid and a.scoreore=b.scoreore group by a.cid,b.cid;

20.查询每门功成绩最好的前两名
select any_value(a.sid),any_value(a.cid),any_value(a.scoreore) from score a left join score as b
on a.cid = b.cid
and a.scoreore < b.scoreore
group by a.cid,a.sid
having count(b.scoreore)<2
order by a.cid;

21.查询每门课程被选修的学生数
select cid,count(*) from score group by cid;
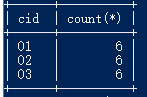
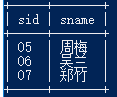
22.查询出只选修两门课程的学生学号和姓名
select a.sid,a.sname from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid group by a.sid having count(*)=2;
23.查询同名学生名单,并统计同名人数
select sname,count(*) from student group by sname having count(*)>1;
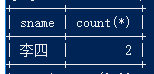
24.查询 1990 年出生的学生名单
select sname from student where year(sage)=1990;

25.查询各学生的年龄.
select sid,sname,timestampdiff(year,sage,curdate()) from student;

26.查询本周过生日的学生
select sname from student where week(curdate())=week(sage);
没有学生;
27.查询本月过生日的学生
select sname from student where month(curdate())=month(sage);
没有学生;
28.查询「李」姓老师的数量
select count(*) from teacher where tname like "李%";

29.查有成绩的学生信息
select * from student where sid in (select sid from score);
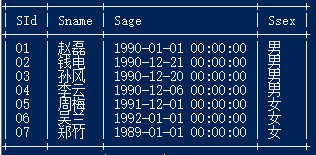
30.查询所有同学的学生编号、学生姓名、选课总数、所有课程的成绩总和
select a.SId,a.Sname,count(b.cid),sum(b.scoreore) from student a left join score b on a.sid = b.sid GROUP BY a.sid;
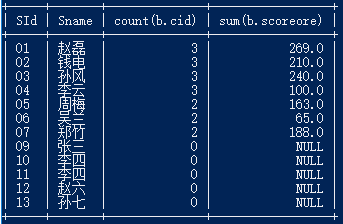
31.查询平均成绩大于等于 60 分的同学的学生编号和学生姓名和平均成绩
select a.sid,a.sname,avg(b.scoreore) from student a,score b where a.sid=b.sid having avg(b.scoreore)>60;

32.查询不存在" 01 "课程但存在" 02 "课程的情况
select * from score where cid = '02' and sid not in (select sid from score where cid='01');

33.查询存在" 01 "课程但可能不存在" 02 "课程的情况
select * from score where cid="01";
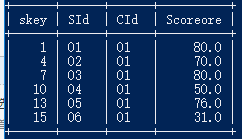
34.按各科成绩进行排序,并显示排名, Score 重复时保留名次空缺
select a.cid ,a.sid ,any_value(a.scoreore),count(b.sid)+1 from score a left join score b
on a.cid=b.cid
and a.scoreore<b.scoreore
GROUP BY a.cid,a.sid
order by a.cid ,count(b.sid)+1;
35.查询" 01 "课程比" 02 "课程成绩高的学生的信息及课程分数
select c.* ,a.scoreore,b.scoreore from student c ,
(select scoreore,sid from score where cid = '01')a,
(select scoreore,sid from score where cid = '02')b
where a.sid = b.sid
and c.sid=b.sid
and a.scoreore >b.scoreore;
36.查询没有学全所有课程的同学的信息
select a.* from Student a left join score b
on a.sid = b.sid
group by a.SId
having count(b.cid)<(select count(cname) from Course);
37.查询至少有一门课与学号为" 01 "的同学所学相同的同学的信息
select a.* from student a ,score b where a.sid = b.sid and b.cid in
(select cid from score where sid ='01')
group by a.sid;
38.查询和" 01 "号的同学学习的课程完全相同的其他同学的信息
select * from Student where sid in
(select sid from score where sid not in
(select sid from score where cid not in
(select cid from score where sid ='01'))
GROUP BY sid
having count(*)=(select count(cid) from score where sid ='01')and sid<>'01');

首先,筛选出01同学的课程——选出有谁没有选择01同学课程的学生sid——再对上一层逻辑做否定,选择了01号同学的子集或者含有01号同学所选课程之外的含有其他课程的 同学。因此最后再加上判断条件,课程数量相等。就可以判断是和01号同学学习相同的课程。
mysql的一些常用操作(二)的更多相关文章
- [转]Mysql命令行常用操作
Mysql命令行常用操作 一.从命令行登录MySQL数据库服务器 1.登录使用默认3306端口的MySQL /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -u root -p 2.通过TCP连 ...
- 百万年薪python之路 -- MySQL数据库之 MySQL行(记录)的操作(二) -- 多表查询
MySQL行(记录)的操作(二) -- 多表查询 数据的准备 #建表 create table department( id int, name varchar(20) ); create table ...
- linux下对应mysql数据库的常用操作
ssh管理工具连接mysql数据库. 一.连接mysql数据库: 通过shh管理工具,登录linux的用户名,密码,进入ssh的命令行界面后,执行如下命令: mysql -u 数据库用户名 -p 然后 ...
- 【技术博客】MySQL和Django常用操作
MySQL和Django是搭建网站常用的配置之一,在此记录一下在Windows系统搭建网站时MySQL以及Django常用的操作. MySQL MySQL的SQL语句不区分大小写,推荐将保留字大写,数 ...
- Python脚本控制的WebDriver 常用操作 <二> 关闭浏览器
下面将模拟一个WebDriver关闭浏览器的操作 测试用例场景 在一个自动化测试脚本运行完毕后,我们很可能会采取关闭浏览器的操作,而关闭浏览器的常用操作有如下两种: close quit close ...
- mysql数据库中常用操作汇总
一.查询数据库的基本信息: 1. /* 查询数据库 ‘boss’ 所有表及注释 */SELECT TABLE_NAME,TABLE_COMMENT FROM information_schema ...
- mysql下的常用操作
本文继 linux下安装mysql,记录下在工作中最常用的mysql语句 MySQL添加字段和删除字段 添加字段: alter table `user_movement_log`Add column ...
- mysql 批量更新常用操作
mysql更新语句很简单,更新一条数据的某个字段,一般这样写:复制代码 代码如下: UPDATE mytable SET myfield = 'value' WHERE other_field = ' ...
- Python脚本控制的WebDriver 常用操作 <二十> 处理表单元素
测试用例场景 表单对象的操作比较简单,只需要记住下面几点 使用send_keys方法往多行文本框和单行文本框赋值: 使用click方法选择checkbox 使用click方法选择radio 使用cli ...
随机推荐
- Scrapy入门操作
一.安装Scrapy: 如果您还未安装,请参考https://www.cnblogs.com/dalyday/p/9277212.html 二.Scrapy基本配置 1.创建Scrapy程序 cd D ...
- .net core 使用Rotativa创建PDF文档
一.下载Rotaiva 工具 = > NuGet包管理器 = > 管理解决方案的NuGet程序包 在打开的页面中搜索 Rotativa.AspNetCore 如下图: 选中红框的记 ...
- Spring Cloud Config 配置中心实践过程中,你需要了解这些细节!
本文导读: Spring Cloud Config 基本概念 Spring Cloud Config 客户端加载流程 Spring Cloud Config 基于消息总线配置 Spring Cloud ...
- js三级联动效果city-picker
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1NE_EO5_xGvR-y-lboYap7g 提取码:h00e 效果展示: 解决: 动态赋值: 注意:在执行赋值之前,必须执行reset和des ...
- 使用Thymeleaf给前端绑定值
1.pom依赖 <!-- thymeleaf --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</grou ...
- SOFAJRaft—初次使用
SOFAJRaft-初次使用 SOFAJRaft 是基于 Raft 算法的生产级高性能 Java 实现,支持 MULTI-RAFT-GROUP.应用场景有 Leader 选举.分布式锁服务.高可靠的元 ...
- K8s 从懵圈到熟练 – 集群网络详解
作者 | 声东 阿里云售后技术专家 导读:阿里云 K8S 集群网络目前有两种方案:一种是 flannel 方案:另外一种是基于 calico 和弹性网卡 eni 的 terway 方案.Terway ...
- python爬虫——京东评论、jieba分词、wordcloud词云统计
接上一章,动态页面抓取——抓取京东评论区内容. url=‘https://club.jd.com/comment/productPageComments.action?callback=fetchJS ...
- Docker5-docker私库的搭建及常用方法-harbor-registry方式
一.简介 1.官方已经提供registry镜像为什么还需要用harbor 1)registry缺少镜像清理机制,可以push但是不能删除,耗费空间 2)registry缺乏相应的扩展机制 3)harb ...
- 给老师安排课表JAVA项目及登录窗口的实现
实现一个安排课表的Java实验. 有以下几点要求: ①用所给的教师姓名进行课表安排 ②用所给的地点进行课表安排 ③不得有重复的课程名称出现 ④将信息写入到文件里 ⑤用窗口来进行实现 package c ...
