Data Management Technology(1) -- Introduction
1.Database concepts
(1)Data & Information
Information
- Is any kind of event that affects the state of a dynamic system
- Is the message (utterance or expression) being conveyed
- Is an ordered sequence of symbols that can be interpreted as a message
As sensory input: Often be viewed as a type of input to an organism or system
Can be recorded and transmitted
Data
Definition
- values of a qualitative or quantitative variables, belonging to a set of items
- Used to record information
- Is the carrier of Information
Data type and Data value
- Data Type: the way values of the data can be stored in computer system
- Data Value: records the meaning of information
Data & Information
Data on its own carries no meaning
Data must be interpreted to take on a meaning, so that the information can be revealed
Data is the lower level of abstraction; is the carrier of information
Information is the interpretation of data
(2)Data Processing VS Data Management
Main categories of Data Manipulation
Data Management: Database
Data Processing: Computer program
Data Transmission: Computer Network
Tasks of Data Management
Data Storage: Organize the data and store them into the storage device such as hard disk;
Data Maintenance: Insert new value, delete invalid data or modify old data;
Data Query & Data statistic: Retrieve information from the data storage
Application Requirements
store the data for a long period of time
- large amounts (100s of GB)
- protect against crashes
- protect against unauthorized use
allow users to query/update:
allow several (100s, 1000s) users to access the data simultaneously
allow administrators to change the schema
Trying Without a DBMS
Storing data: file system is limited
- size less than 4 GB (on 32 bits machines)
- when system crashes we may loose data
- password-based authorization insufficient
Query/update:
- need to write a new C++/Java program for every new query
- need to worry about performance
Concurrency: limited protection
- need to worry about interfering with other users
- need to offer different views to different users (e.g. registrar, students, professors)
Schema change:
- entails changing file formats
- need to rewrite virtually all applications
Schema Versus Data
schema: describes how data is to be structured
defined at set-up time
rarely changes
also called “meta data”
data is actual “instance” of database, changes rapidly
vs. types and variables in programming languages
DBMS
Data Definition Language – DDL
- Easy to define schema
Data Manipulation Language - DML
- query language
Storage management
- Retrieve data from disk automatically for you
Transaction Management
- concurrency control
- recovery
Automate a lot of boring/mundane operations on data
- so that we don’t have to program over and over
- so that we can write complex data manipulations in just a few lines, so that we can concentrate on app logics
Make execution very fast
- so that it scales up to very large data sets
Make concurrent access/modification possible
- so that many users can use the data at the same time
Building an Application with a DBMS
Requirements modeling (conceptual, pictures)
- Decide what entities should be part of the application and how they should be linked.
Schema design and implementation
- Decide on a set of tables, attributes.
- Define the tables in the database system.
- Populate database (insert tuples).
Write application programs using the DBMS
- way easier now that the data management is taken care of.
Querying a Database(查询数据库)
Database Technology
Started from 1960’s
Is an important branch of CS
- Programming language
- OS
- DB
- Network
Is the main component of computer infrastructure
Main Functions of DBMS
Data Definition数据定义
- Provides Data Definition Language to define schema of database
Data Manipulation数据操作
- Provides Data Manipulation Language to manipulate data in database: RETRIEVE, INSERT, DELETE, MODIFY
Database operation
- Security
- Integrity
- Concurrency
- recovery
Toolsets
- Data loader
- Monitor
- Performance tuning tools
(3)Database
- Efficient, convenient, and safe multi-user storage of massive amounts of well organized persistent data
(4)Database Management System
- A Software System that manages database
- Buy, install, set up for particular application
(5)Database System
DBS, information systems that based on database
Consists of database, DBMS, application, and users
硬件<OS<DBMS<App development tools<Database system
2.Development of DB tech
Stages
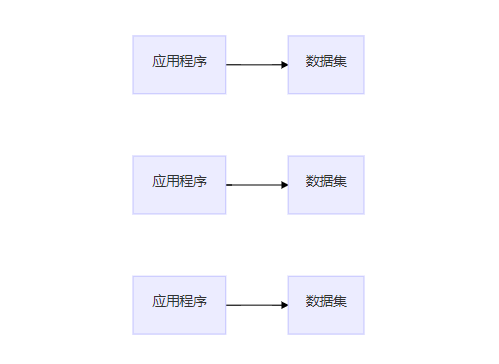
(1)Manual processing
- Data stored in punched-cards
- Data managed by hand
- No data sharing
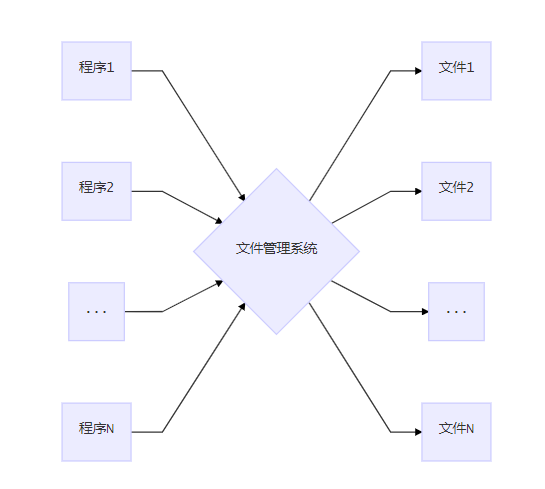
(2)File system
- Data stored in files
- Use OS IO interface to access data
- Measures taken to accelerate the data access
- Primary data-program independence
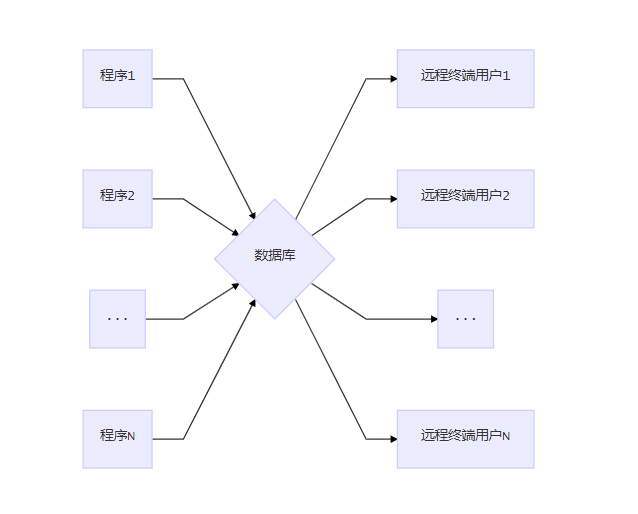
Drawbacks of file systems
Program-Data Dependence
- All programs maintain metadata for each file they use
Data Redundancy (Duplication of data)
- Different systems/programs have separate copies of the same data
- Multiple file formats, duplication of information in different files
- Requires space, effort and result in loss of data & metadata integrity
Limited Data Sharing
- No centralized control of data
- Each application has its own private files & users has little chance to share data outside their own applications
Lengthy Development Times
- For each new application programmers must design their own file formats & descriptions from scratch
Excessive Program Maintenance
- 80% of information systems budget
Difficulty in accessing data
- Need to write a new program to carry out each new task
Integrity problems
- Integrity constraints
- Hard to add new constraints or change existing ones
(3)Database
Main advantages compared to file systems:
data sharing
Less data redundancy
Data- program Independence
Convenient program interface
Efficient data access
Data integrity and data security
Concurrency management
…
Database advantages
Structured data storage
- Organize the data and link them together by their inner relations
- Automatically manage the data relationship
Data sharing
- One copy of data for many applications
- Allow many users to access data simultaneously
Less data redundancy
- 共享数据(对应关系变成表格关系)
Data integrity
- Automatically check the input value of certain data items, according to the data integrity rules
Concurrency并发性
- Isolate the concurrent accesses
- Prevent the dirty use of data
- The modification that may jeopardize the integrity of data
3.Database Architecture
(1)Database Architecture (physical architecture)
The architecture of a database systems is greatly influenced by the underlying computer system on which the database is running:
- Centralized集中的
- Client-server客户端-服务器
- Parallel (multi-processor)并行(多处理器)
- Distributed分布式
(2)Database Users
Users are differentiated by the way they expect to interact with the system
- Application programmers – interact with system through DML calls
- Sophisticated users – form requests in a database query language
- Specialized users – write specialized database applications that do not fit into the traditional data processing framework
- Naive users – invoke one of the permanent application programs that have been written previously. Examples, people accessing database over the web, bank tellers, clerical staff
(3)Database Administrator
Coordinates all the activities of the database system; the database administrator has a good understanding of the enterprise’s information resources and needs.
Database administrator’s duties include:
- Schema definition
- Storage structure and access method definition
- Schema and physical organization modification
- Granting user authority to access the database
- Specifying integrity constraints
- Acting as liaison with users
- Monitoring performance and responding to changes in requirements
Data Management Technology(1) -- Introduction的更多相关文章
- Data Management Technology(5) -- Recovery
Recovery Types of Failures Wrong data entry Prevent by having constraints in the database Fix with d ...
- Data Management Technology(3) -- SQL
SQL is a very-high-level language, in which the programmer is able to avoid specifying a lot of data ...
- Data Management Technology(2) -- Data Model
1.Data Model Model Is the abstraction of real world Reveal the essence of objects, help people to lo ...
- Data Management Technology(4) -- 关系数据库理论
规范化问题的提出 在规范化理论出现以前,层次和网状数据库的设计只是遵循其模型本身固有的原则,而无具体的理论依据可言,因而带有盲目性,可能在以后的运行和使用中发生许多预想不到的问题. 在关系数据库系统中 ...
- Building Applications with Force.com and VisualForce(Dev401)(十六):Data Management: Introduction to Upsert
Dev401-017:Data Management: Introduction to Upsert Module Objectives1.Define upsert.2.Define externa ...
- MySQL vs. MongoDB: Choosing a Data Management Solution
原文地址:http://www.javacodegeeks.com/2015/07/mysql-vs-mongodb.html 1. Introduction It would be fair to ...
- [Windows Azure] Data Management and Business Analytics
http://www.windowsazure.com/en-us/develop/net/fundamentals/cloud-storage/ Managing and analyzing dat ...
- Intel Active Management Technology
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_Active_Management_Technology Intel Active Management Technology F ...
- Data Management and Data Management Tools
Data Management ObjectivesBy the end o this module, you should understand the fundamentals of data m ...
随机推荐
- mariadb 学习笔记
安装:yum install mariadb-server mariadb vim /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnfinnodb_file_per_table = on#设置后当创建数 ...
- Python 下JSON的两种编解码方式实例解析
概念 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于人阅读和编写.在日常的工作中,应用范围极其广泛.这里就介绍python下它的两种编解码方法: ...
- 我用 Python 破解了同事的加密压缩包!
作者 | 朱小五 又是一杯奶茶. 事情的经过是这样的: 又是奶茶,行吧快点开工,争取李大伟回来之前搞定 李大伟说是6位数字密码 那么我们可以利用python生成全部的六位数字密码 #生成从 ...
- 基于H7的串口WIFI模块ESP8266的TCP客户端例子和操作说明(AP兼STA模式)
说明: 1.如果不熟悉网络的话,等我这几天更新V7用户手册的ESP8266章节,如果熟悉的话,直接操作即可,这里将操作说明发出来. 2.串口WIFI是采用的AT指令操作,简单易用,指令手册在这个帖子里 ...
- HTML DOM的创建,删除及替换
创建HTML元素 document.appendChild() 将新元素作为父元素的最后一个子元素进行添加 如需向HTML DOM添加新元素,首先必须创建该元素,然后把它追加到已有的元素上 var n ...
- js实现常见排序算法
电脑配置 CPU:AMD X4 640 内存: 宏想 DDR3 1600MHz 8g 主板:华擎 980DE3/U3S3 R2.0 浏览器:chrome 79.0.3945.88(正式版本) (64 ...
- 如何安装 IntelliJ IDEA 最新版本——详细教程
IntelliJ IDEA 简称 IDEA,被业界公认为最好的 Java 集成开发工具,尤其在智能代码助手.代码自动提示.代码重构.代码版本管理(Git.SVN.Maven).单元测试.代码分析等方面 ...
- Spring Boot2解决idea console 控制台输出乱码
Idea默认配置是采用GBK, 而项目工程文件采用的是UTF-8. 编码不一致,导致idea Console控制台输出乱码. 网上的解决方案,大都是直接修改Settings=>Editor=&g ...
- MFC程序出现uafxcwd.lib(afxmem.obj) : error LNK2005: "void * __cdecl operator new(unsigned int)解决办法
在同一个地方摔倒两次之后,决定记录下来这个东西. 问题 1>uafxcwd.lib(afxmem.obj) : error LNK2005: "void * __cdecl opera ...
- MySQL 是如何处理死锁的
MySQL(InnoDB)是如何处理死锁的 一.什么是死锁 官方定义如下:两个事务都持有对方需要的锁,并且在等待对方释放,并且双方都不会释放自己的锁. 这个就好比你有一个人质,对方有一个人质,你们俩去 ...
