统一流控服务开源:基于.Net Core的流控服务
先前有一篇博文,梳理了流控服务的场景、业界做法和常用算法
最近完成了流控服务的开发,并在生产系统进行了大半年的验证,稳定可靠。今天整理一下核心设计和实现思路,开源到Github上,分享给大家

https://github.com/zhouguoqing/FlowControl
一、令牌桶算法实现
先回顾一下令牌桶算法示意图
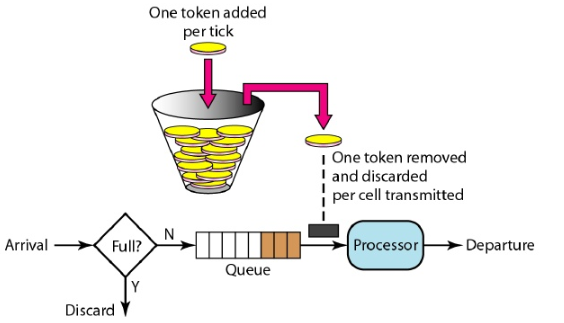
随着时间流逝,系统会按恒定1/QPS时间间隔(如果QPS=100,则间隔是10ms) 往桶里加入Token(想象和漏洞漏水相反,有个水龙头在不断的加水),
如果桶已经满了就不再加了. 新请求来临时, 会各自拿走一个Token,如果没有Token可拿了就阻塞或者拒绝服务.
令牌添加速度支持动态变化,实时控制处理的速率.
令牌桶有两个关键的属性:令牌桶容量(大小)和时间间隔,
有两个关键操作,从令牌桶中取Token;令牌桶定时的Reset重置。
我们看TokenBucket类:
using System; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Service
{
using CZ.FlowControl.Spi;
/// <summary>
/// 令牌桶
/// </summary>
public abstract class TokenBucket : IThrottleStrategy
{
protected long bucketTokenCapacity;
private static readonly object syncRoot = new object();
protected readonly long ticksRefillInterval;
protected long nextRefillTime; //number of tokens in the bucket
protected long tokens; protected TokenBucket(long bucketTokenCapacity, long refillInterval, long refillIntervalInMilliSeconds)
{
if (bucketTokenCapacity <= )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("bucketTokenCapacity", "bucket token capacity can not be negative");
if (refillInterval < )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("refillInterval", "Refill interval cannot be negative");
if (refillIntervalInMilliSeconds <= )
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("refillIntervalInMilliSeconds", "Refill interval in milliseconds cannot be negative"); this.bucketTokenCapacity = bucketTokenCapacity;
ticksRefillInterval = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(refillInterval * refillIntervalInMilliSeconds).Ticks;
} /// <summary>
/// 是否流控
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool ShouldThrottle(long n = )
{
TimeSpan waitTime;
return ShouldThrottle(n, out waitTime);
}
public bool ShouldThrottle(long n, out TimeSpan waitTime)
{
if (n <= ) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("n", "Should be positive integer"); lock (syncRoot)
{
UpdateTokens();
if (tokens < n)
{
var timeToIntervalEnd = nextRefillTime - SystemTime.UtcNow.Ticks;
if (timeToIntervalEnd < ) return ShouldThrottle(n, out waitTime); waitTime = TimeSpan.FromTicks(timeToIntervalEnd);
return true;
}
tokens -= n; waitTime = TimeSpan.Zero;
return false;
}
} /// <summary>
/// 更新令牌
/// </summary>
protected abstract void UpdateTokens(); public bool ShouldThrottle(out TimeSpan waitTime)
{
return ShouldThrottle(, out waitTime);
} public long CurrentTokenCount
{
get
{
lock (syncRoot)
{
UpdateTokens();
return tokens;
}
}
}
}
}
这个抽象类中,将UpdateToken作为抽象方法暴露出来,给实现类更多的灵活去控制令牌桶重置操作。基于此实现了“固定令牌桶”FixedTokenBucket
/// <summary>
/// 固定令牌桶
/// </summary>
class FixedTokenBucket : TokenBucket
{
public FixedTokenBucket(long maxTokens, long refillInterval, long refillIntervalInMilliSeconds)
: base(maxTokens, refillInterval, refillIntervalInMilliSeconds)
{
} protected override void UpdateTokens()
{
var currentTime = SystemTime.UtcNow.Ticks; if (currentTime < nextRefillTime)
return; tokens = bucketTokenCapacity;
nextRefillTime = currentTime + ticksRefillInterval;
}
}
固定令牌桶在每次取Token时,都要执行方法ShouldThrottle。这个方法中:
并发取Token是线程安全的,这个地方用了Lock控制,损失了一部分性能。同时每次获取可用Token的时候,都会实时Check一下是否需要到达Reset令牌桶的时间。
获取到可用令牌后,令牌桶中令牌的数量-1。如果没有足够的可用令牌,则返回等待到下次Reset令牌桶的时间。如下代码:
public bool ShouldThrottle(long n, out TimeSpan waitTime)
{
if (n <= ) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("n", "Should be positive integer"); lock (syncRoot)
{
UpdateTokens();
if (tokens < n)
{
var timeToIntervalEnd = nextRefillTime - SystemTime.UtcNow.Ticks;
if (timeToIntervalEnd < ) return ShouldThrottle(n, out waitTime); waitTime = TimeSpan.FromTicks(timeToIntervalEnd);
return true;
}
tokens -= n; waitTime = TimeSpan.Zero;
return false;
}
}
以上就是令牌桶算法的实现。我们继续看漏桶算法。
二、漏桶算法实现
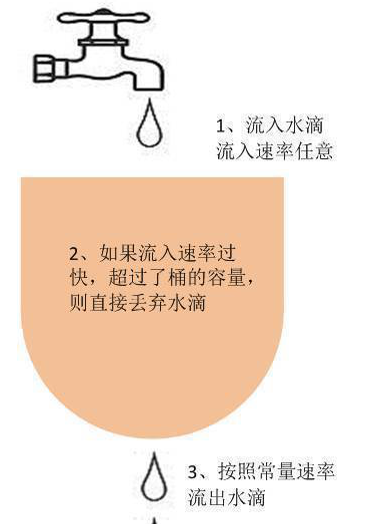
首先回顾一下漏桶算法的原理:
 ‘
‘
水(请求)先进入到漏桶里,漏桶以一定的速度出水(接口有响应速率),
当水流入速度过大会直接溢出(访问频率超过接口响应速率), 然后就拒绝请求,
可以看出漏桶算法能强行限制数据的传输速率.
有两个变量:
- 一个是桶的大小,支持流量突发增多时可以存多少的水(burst),
- 另一个是水桶漏洞的大小(rate)。
漏桶抽象类:LeakTokenBucket,继承与令牌桶抽象父类 TokenBucket,说明了获取令牌(漏出令牌)在底层的方式是一致的,不一样的是重置令牌的方式(务必理解这一点)
using System; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Service
{
/// <summary>
/// 漏桶
/// </summary>
abstract class LeakyTokenBucket : TokenBucket
{
protected readonly long stepTokens;
protected long ticksStepInterval; protected LeakyTokenBucket(long maxTokens, long refillInterval, int refillIntervalInMilliSeconds,
long stepTokens, long stepInterval, int stepIntervalInMilliseconds)
: base(maxTokens, refillInterval, refillIntervalInMilliSeconds)
{
this.stepTokens = stepTokens;
if (stepInterval < ) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("stepInterval", "Step interval cannot be negative");
if (stepTokens < ) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("stepTokens", "Step tokens cannot be negative");
if (stepIntervalInMilliseconds <= ) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("stepIntervalInMilliseconds", "Step interval in milliseconds cannot be negative"); ticksStepInterval = TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(stepInterval * stepIntervalInMilliseconds).Ticks;
}
}
}
可以看出,漏桶是在令牌桶的基础上增加了二个重要的属性:这两个属性决定了重置令牌桶的方式
stepTokens:每间隔时间内漏的数量
ticksStepInterval:漏的间隔时间
举个例子:TPS 100,即每秒漏出100个Token,stepTokens =100, ticksStepInterval=1000ms
漏桶的具体实现有两种:空桶和满桶
StepDownTokenBucket 满桶:即一把将令牌桶填充满
using System; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Service
{
/// <summary>
/// 漏桶(满桶)
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// StepDownLeakyTokenBucketStrategy resembles a bucket which has been filled with tokens at the beginning but subsequently leaks tokens at a fixed interval
/// </remarks>
class StepDownTokenBucket : LeakyTokenBucket
{
public StepDownTokenBucket(long maxTokens, long refillInterval, int refillIntervalInMilliSeconds, long stepTokens, long stepInterval, int stepIntervalInMilliseconds) : base(maxTokens, refillInterval, refillIntervalInMilliSeconds, stepTokens, stepInterval, stepIntervalInMilliseconds)
{
} protected override void UpdateTokens()
{
var currentTime = SystemTime.UtcNow.Ticks; if (currentTime >= nextRefillTime)
{
//set tokens to max
tokens = bucketTokenCapacity; //compute next refill time
nextRefillTime = currentTime + ticksRefillInterval;
return;
} //calculate max tokens possible till the end
var timeToNextRefill = nextRefillTime - currentTime;
var stepsToNextRefill = timeToNextRefill/ticksStepInterval; var maxPossibleTokens = stepsToNextRefill*stepTokens; if ((timeToNextRefill%ticksStepInterval) > ) maxPossibleTokens += stepTokens;
if (maxPossibleTokens < tokens) tokens = maxPossibleTokens;
}
}
}
StepUpLeakyTokenBucket 空桶:即每次只将stepTokens个数的令牌放到桶中
using System; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Service
{
/// <summary>
/// 漏桶(空桶)
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// StepUpLeakyTokenBucketStrategy resemembles an empty bucket at the beginning but get filled will tokens over a fixed interval.
/// </remarks>
class StepUpLeakyTokenBucket : LeakyTokenBucket
{
private long lastActivityTime; public StepUpLeakyTokenBucket(long maxTokens, long refillInterval, int refillIntervalInMilliSeconds, long stepTokens, long stepInterval, int stepIntervalInMilliseconds)
: base(maxTokens, refillInterval, refillIntervalInMilliSeconds, stepTokens, stepInterval, stepIntervalInMilliseconds)
{
} protected override void UpdateTokens()
{
var currentTime = SystemTime.UtcNow.Ticks; if (currentTime >= nextRefillTime)
{
tokens = stepTokens; lastActivityTime = currentTime;
nextRefillTime = currentTime + ticksRefillInterval; return;
} //calculate tokens at current step long elapsedTimeSinceLastActivity = currentTime - lastActivityTime;
long elapsedStepsSinceLastActivity = elapsedTimeSinceLastActivity / ticksStepInterval; tokens += (elapsedStepsSinceLastActivity*stepTokens); if (tokens > bucketTokenCapacity) tokens = bucketTokenCapacity;
lastActivityTime = currentTime;
}
}
}
三、流控服务封装
第二章节,详细介绍了令牌桶和漏桶的具体实现。基于以上,要重点介绍接口:IThrottleStrategy:流控的具体方式
using System; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Spi
{
/// <summary>
/// 流量控制算法策略
/// </summary>
public interface IThrottleStrategy
{
/// <summary>
/// 是否流控
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
bool ShouldThrottle(long n = ); /// <summary>
/// 是否流控
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
/// <param name="waitTime"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
bool ShouldThrottle(long n, out TimeSpan waitTime); /// <summary>
/// 是否流控
/// </summary>
/// <param name="waitTime"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
bool ShouldThrottle(out TimeSpan waitTime); /// <summary>
/// 当前令牌个数
/// </summary>
long CurrentTokenCount { get; }
}
}
有了这个流控方式接口后,我们还需要一个流控策略定义类:FlowControlStrategy
即定义具体的流控策略:以下是这个类的详细属性和成员: 不仅定义了流控策略类型,还定义了流控的维度信息和流控阈值,这样流控就做成依赖注入的方式了!
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Spi
{
/// <summary>
/// 流控策略
/// </summary>
public class FlowControlStrategy
{
/// <summary>
/// 标识
/// </summary>
public string ID { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 名称
/// </summary>
public string Name { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 流控策略类型
/// </summary>
public FlowControlStrategyType StrategyType { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 流控阈值-Int
/// </summary>
public long IntThreshold { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 流控阈值-Double
/// </summary>
public decimal DoubleThreshold { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 时间区间跨度
/// </summary>
public FlowControlTimespan TimeSpan { get; set; } private Dictionary<string, string> flowControlConfigs; /// <summary>
/// 流控维度信息
/// </summary>
public Dictionary<string, string> FlowControlConfigs
{
get
{
if (flowControlConfigs == null)
flowControlConfigs = new Dictionary<string, string>(); return flowControlConfigs;
}
set
{
flowControlConfigs = value;
}
} /// <summary>
/// 描述
/// </summary>
public string Descriptions { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 触发流控后是否直接拒绝请求
/// </summary>
public bool IsRefusedRequest { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 创建时间
/// </summary>
public DateTime CreateTime { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 创建人
/// </summary>
public string Creator { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 最后修改时间
/// </summary>
public DateTime LastModifyTime { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 最后修改人
/// </summary>
public string LastModifier { get; set; }
}
}
同时,流控策略类型,我们抽象了一个枚举:FlowControlStrategyType
支持3种流控策略:TPS、Sum(指定时间段内请求的次数),Delay延迟
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Spi
{
/// <summary>
/// 流控策略类型枚举
/// </summary>
public enum FlowControlStrategyType
{
/// <summary>
/// TPS控制策略
/// </summary>
TPS,
/// <summary>
/// 总数控制策略
/// </summary>
Sum, /// <summary>
/// 延迟控制策略
/// </summary>
Delay
}
}
面向每种流控策略类型,提供了一个对应的流控器,比如说TPS的流控器
TPSFlowController,内部使用了固定令牌桶算法
using System; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Service
{
using CZ.FlowControl.Spi; /// <summary>
/// TPS流量控制器
/// </summary>
class TPSFlowController : IFlowController
{
public IThrottleStrategy InnerThrottleStrategy
{
get; private set;
} public FlowControlStrategy FlowControlStrategy { get; private set; } public bool ShouldThrottle(long n, out TimeSpan waitTime)
{
return InnerThrottleStrategy.ShouldThrottle(n, out waitTime);
} public TPSFlowController(FlowControlStrategy strategy)
{
FlowControlStrategy = strategy; InnerThrottleStrategy = new FixedTokenBucket(strategy.IntThreshold, , );
}
}
}
Sum(指定时间段内请求的次数)流控器:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Service
{
using CZ.FlowControl.Spi; /// <summary>
/// 一段时间内合计值流量控制器
/// </summary>
class SumFlowController : IFlowController
{
public IThrottleStrategy InnerThrottleStrategy
{
get; private set;
} public FlowControlStrategy FlowControlStrategy { get; private set; } public bool ShouldThrottle(long n, out TimeSpan waitTime)
{
return InnerThrottleStrategy.ShouldThrottle(n, out waitTime);
} public SumFlowController(FlowControlStrategy strategy)
{
FlowControlStrategy = strategy; var refillInterval = GetTokenBucketRefillInterval(strategy); InnerThrottleStrategy = new FixedTokenBucket(strategy.IntThreshold, refillInterval, );
} private long GetTokenBucketRefillInterval(FlowControlStrategy strategy)
{
long refillInterval = ; switch (strategy.TimeSpan)
{
case FlowControlTimespan.Second:
refillInterval = ;
break;
case FlowControlTimespan.Minute:
refillInterval = ;
break;
case FlowControlTimespan.Hour:
refillInterval = * ;
break;
case FlowControlTimespan.Day:
refillInterval = * * ;
break;
} return refillInterval;
}
}
}
同时,通过一个创建者工厂,根据不同的流控策略,创建对应的流控器(做了一层缓存,性能更好):
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Service
{
using CZ.FlowControl.Spi; /// <summary>
/// 流控策略工厂
/// </summary>
class FlowControllerFactory
{
private static Dictionary<string, IFlowController> fcControllers;
private static object syncObj = new object(); private static FlowControllerFactory instance; private FlowControllerFactory()
{
fcControllers = new Dictionary<string, IFlowController>();
} public static FlowControllerFactory GetInstance()
{
if (instance == null)
{
lock (syncObj)
{
if (instance == null)
{
instance = new FlowControllerFactory();
}
}
} return instance;
} public IFlowController GetOrCreateFlowController(FlowControlStrategy strategy)
{
if (strategy == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("FlowControllerFactory.GetOrCreateFlowController.strategy"); if (!fcControllers.ContainsKey(strategy.ID))
{
lock (syncObj)
{
if (!fcControllers.ContainsKey(strategy.ID))
{
var fcController = CreateFlowController(strategy);
if (fcController != null)
fcControllers.Add(strategy.ID, fcController);
}
}
} if (fcControllers.ContainsKey(strategy.ID))
{
var controller = fcControllers[strategy.ID];
return controller;
} return null;
} private IFlowController CreateFlowController(FlowControlStrategy strategy)
{
if (strategy == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("FlowControllerFactory.CreateFlowController.strategy"); IFlowController controller = null; switch (strategy.StrategyType)
{
case FlowControlStrategyType.TPS:
controller = new TPSFlowController(strategy);
break;
case FlowControlStrategyType.Delay:
controller = new DelayFlowController(strategy);
break;
case FlowControlStrategyType.Sum:
controller = new SumFlowController(strategy);
break;
default:
break;
} return controller;
}
}
}
有了流控策略定义、我们更进一步,继续封装了流控Facade服务,这样把流控的变化封装到内部。对外只提供流控服务接口,流控时动态传入流控策略和流控个数:FlowControlService
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text; namespace CZ.FlowControl.Service
{
using CZ.FlowControl.Spi;
using System.Threading; /// <summary>
/// 统一流控服务
/// </summary>
public class FlowControlService
{
/// <summary>
/// 流控
/// </summary>
/// <param name="strategy">流控策略</param>
/// <param name="count">请求次数</param>
public static void FlowControl(FlowControlStrategy strategy, int count = )
{
var controller = FlowControllerFactory.GetInstance().GetOrCreateFlowController(strategy); TimeSpan waitTimespan = TimeSpan.Zero; var result = controller.ShouldThrottle(count, out waitTimespan);
if (result)
{
if (strategy.IsRefusedRequest == false && waitTimespan != TimeSpan.Zero)
{
WaitForAvailable(strategy, controller, waitTimespan, count);
}
else if (strategy.IsRefusedRequest)
{
throw new Exception("触发流控!");
}
}
} /// <summary>
/// 等待可用
/// </summary>
/// <param name="strategy">流控策略</param>
/// <param name="controller">流控器</param>
/// <param name="waitTimespan">等待时间</param>
/// <param name="count">请求次数</param>
private static void WaitForAvailable(FlowControlStrategy strategy, IFlowController controller, TimeSpan waitTimespan, int count)
{
var timespan = waitTimespan;
if (strategy.StrategyType == FlowControlStrategyType.Delay)
{
Thread.Sleep(timespan);
return;
} while (controller.ShouldThrottle(count, out timespan))
{
Thread.Sleep(timespan);
}
}
}
}
以上,统一流控服务完成了第一个版本的封装。接下来我们看示例代码
四、示例代码
先安装Nuget:
Install-Package CZ.FlowControl.Service -Version 1.0.
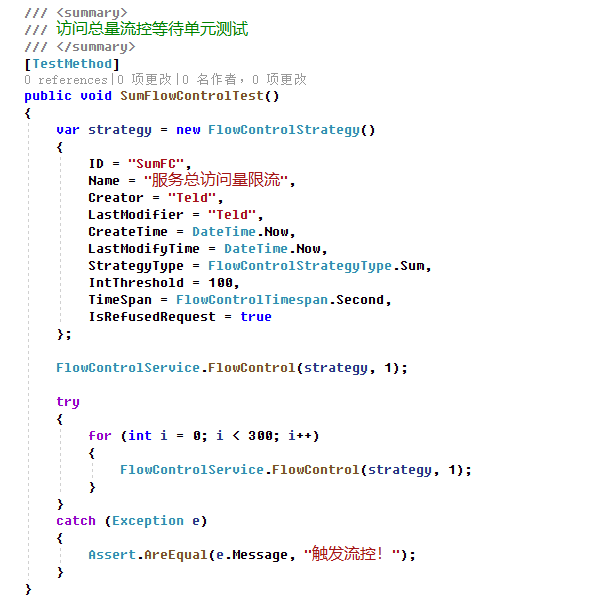
是不是很简单。
大家如果希望了解详细的代码,请参考这个项目的GitHub地址:
https://github.com/zhouguoqing/FlowControl
同时也欢迎大家一起改进完善。
周国庆
2019/8/9
统一流控服务开源:基于.Net Core的流控服务的更多相关文章
- .NET Core微服务之基于IdentityServer建立授权与验证服务
Tip: 此篇已加入.NET Core微服务基础系列文章索引 一.IdentityServer的预备知识 要学习IdentityServer,事先得了解一下基于Token的验证体系,这是一个庞大的主题 ...
- WPF窗体中嵌入/使用WinForm类/控件(基于.NET Core)
如题,WPF中嵌入WinForm的做法,网络上已经很多示例,都是基于.NET XXX版的. 今天King様在尝试WPF(基于.NET Core 3.1)中加入Windows.Forms.ColorDi ...
- .NET Core微服务之基于IdentityServer建立授权与验证服务(续)
Tip: 此篇已加入.NET Core微服务基础系列文章索引 上一篇我们基于IdentityServer4建立了一个AuthorizationServer,并且继承了QuickStartUI,能够成功 ...
- Net Core的流控服务
统一流控服务开源:基于.Net Core的流控服务 先前有一篇博文,梳理了流控服务的场景.业界做法和常用算法 统一流控服务开源-1:场景&业界做法&算法篇 最近完成了流控服务的开发 ...
- .Net Core Grpc Consul 实现服务注册 服务发现 负载均衡
本文是基于..net core grpc consul 实现服务注册 服务发现 负载均衡(二)的,很多内容是直接复制过来的,..net core grpc consul 实现服务注册 服务发现 负载均 ...
- 统一流控服务开源-1:场景&业界做法&算法篇
最近团队在搞流量安全控制,为了应对不断增大的流量安全风险.Waf防护能做一下接入端的拦截,但是实际流量会打到整个分布式系统的每一环:Nginx.API网关.RPC服务.MQ消息应用中心.数据库.瞬间的 ...
- .NET Core微服务之基于Apollo实现统一配置中心
Tip: 此篇已加入.NET Core微服务基础系列文章索引 一.关于统一配置中心与Apollo 在微服务架构环境中,项目中配置文件比较繁杂,而且不同环境的不同配置修改相对频繁,每次发布都需要对应修改 ...
- 基于.NET CORE微服务框架 -surging的介绍和简单示例 (开源)
一.前言 至今为止编程开发已经11个年头,从 VB6.0,ASP时代到ASP.NET再到MVC, 从中见证了.NET技术发展,从无畏无知的懵懂少年,到现在的中年大叔,从中的酸甜苦辣也只有本人自知.随着 ...
- 基于.NET CORE微服务框架 -谈谈surging API网关
1.前言 对于最近surging更新的API 网关大家也有所关注,也收到了不少反馈提出是否能介绍下Api网关,那么我们将在此篇文章中剥析下surging的Api 网关 开源地址:https://git ...
随机推荐
- 阿里系手淘weex学习第一天
官网原文:https://weex.apache.org/zh/tools/extension.html#功能 功能 创建Weex项目. 支持在VSCode对Weex的语法支持. 检查iOS和Andr ...
- Java编程思想:泛型接口
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Random; public class Test { public static void main(Stri ...
- 【DFS练习】-翻棋子-C++
Description 有一个4*4的棋盘,放有16枚棋子. 每个棋子都是一面黑一面白,一开始有的黑面朝上,有的白面朝上. 下面是一个例子,这个例子用文字描述为: bwbw wwww bbwb bww ...
- liunx某台服务器无法访问其他服务器!!!!!!!!
针对于可以ping通ip地址,但是无法访问端口!!! 访问端口卡死,未响应, 例如mysql出现当前主机无法远程连接数据库,而其他主机都可以 前提条件:防火墙,mysql账号ip限制问题已经解决 问题 ...
- Android 开发感想
18年从.net转行做安卓开发,现在已经过去一年多了.说一下感想和心得体会! 一.开始 说一下我的经厉,从毕业开始出来工作一直是从事.net方向的开发工作.一开始也是没什么经验,加上也没有其他手艺就找 ...
- Baozi Leetcode Solution 205: Isomorphic Strings
Problem Statement Given two strings s and t, determine if they are isomorphic. Two strings are isomo ...
- html+css-->background-img(背景图的设置)
背景图:(相关验证代码请查看代码,在验证时需将当前不需要验证的代码注释掉) 1.inherit:从父元素继承属性设置 2.background-repeat:平铺(在图片大小小于元素尺寸时 ...
- Java中常见的异常类型
一. Java中常见的异常类 异常类 说明 ClassCastException 类型准换异常 ClassNotFoundException 未找到相应类异常 ArithmeticException ...
- Java 读写 excel 实战完全解析
本文微信公众号「AndroidTraveler」首发. 背景 时值毕业季,很多毕业生初入职场. 因此,这边也写了一些新手相关的 Android 技术点. 比如上一篇的 Android 开发你需要了解的 ...
- 2019牛客多校第二场F-Partition problem(搜索+剪枝)
Partition problem 题目传送门 解题思路 假设当前两队的对抗值为s,如果把红队中的一个人a分配到白队,s+= a对红队中所有人的对抗值,s-= a对白队中所有人的对抗值.所以我们可以先 ...
