四、poll()、select()和epoll()
在用户程序中,poll()和select()系统调用用于对设备进行无阻塞访问。poll()和select()最终会调用设备驱动中的poll()函数,在我所使用的Linux内核中,还有扩展的poll()函数epoll()
一、poll()函数
应用程序中的poll()函数原型为:
#include <poll.h> int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
函数参数以及返回值:
fds:用于描述监听的文件描述符集
nfds:fds的数量
timeout:监听超时时间
返回值:成功返回0;出错返回-1。
示例代码如下:
struct pollfd fdsa[]; fdsa[].fd = fd; /* 监听fd */
fdsa[].events = POLLIN; /* 监听输入事件,除 */ while() {
/* 5000ms内若有输入,返回大于0的数;否则返回0 */
ret = poll(&fdsa[], , );
if (!ret)
printf("time out\n");
else {
read(fd, buf, );
printf("buf = %d\n", buf[]);
}
}
现在,我们来看看poll()函数的调用过程:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(poll, ...)
-> do_sys_poll(ufds, nfds, to);
-> poll_initwait(&table); // 初始化等待队列
-> do_poll(nfds, head, &table, end_time);
-> do_pollfd(pfd, pt, &can_busy_loop, busy_flag); // 处理进程的每一个fd的poll操作
-> f.file->f_op->poll(f.file, pwait); // 执行驱动程序的poll()函数
二、select()函数
应用程序中的select()函数原型为:
#include <sys/select.h> int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,
fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout); void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *set);
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *set);
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *set);
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *set);
select()函数中参数nfs表示监听所有的fd的最大值 + 1;readfds、writefds和exceptfds分别是被监听的读、写和异常的文件描述符集;timeout表示监听超时时间,结构体如下:
struct timeval {
__kernel_time_t tv_sec; /* 秒 */
__kernel_suseconds_t tv_usec; /* 微秒 */
};
FD_SET()、FD_ZERO()、FD_CLR()、FD_ISSET()分别用于加入fd、清除fd集合、清除fd、判断fd是否被加入集合中
示例代码如下:
fd_set rfds; FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_SET(fd, &rfds); tv.tv_sec = ;
tv.tv_usec = ; // 设置等待时间5s ret = select(fd + , &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv); if (ret > ) {
if(FD_ISSET(fd, &rfds)) /* 测试是否有数据 */ {
read(fd, buf, );
printf("buf = %d\n", buf[]);
}
}
select()函数的调用过程:
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(select, ...)
-> core_sys_select(n, inp, outp, exp, to);
-> do_select(n, &fds, end_time); //
-> poll_initwait(&table); // 初始化等待队列
-> mask = (*f_op->poll)(f.file, wait); // 执行驱动程序的poll()函数
当poll()和select()的文件数量庞大、I/O流量频繁时,poll()和select()的性能表现较差,我们宜使用epoll(),epoll()不会随着fd的数目增长而降低效率
三、epoll()函数
epoll()函数原型为:
#include <sys/epoll.h> /* 创建epoll文件描述符 */
int epoll_create(int size); /* 添加、修改或删除需要监听的文件描述符及其事件 */
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event); /* 等待被监听的描述符的I/O事件 */
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
代码中maxevents表示每次能处理的事件数
代码中的struct epoll_event声明为:
struct epoll_event {
uint32_t events; /* epoll事件 */
epoll_data_t data; /* epoll数据 */
};
typedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd;
uint32_t u32;
uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;
示例代码如下:
int efd, nfds, i;
struct epoll_event event; efd = epoll_create();
if (efd == -) {
return -;
} event.data.fd = fd;
/*
* EPOLLIN: 表示对应的文件描述符可以读
* EPOLLOUT: 表示对应的文件描述符可以写
* EPOLLET: 表示对应的文件描述符有事件发生
*/
event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET; /* 除EPOLL_CTL_ADD之外还有EPOLL_CTL_DEL(删除)和EPOLL_CTL_MOD(修改) */
s = epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &event); while () {
nfds = epoll_wait(epfd, event, , ); for (i = ; i < nfds; ++i) {
if (event[i].events & EPOLLIN) /* 有数据可读 */ {
read(event[i].data.fd, buf, );
printf("buf = %d\n", buf[]);
}
}
}
epoll()系列函数的调用过程:
/* epoll_create() */
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create, int, size)
-> sys_epoll_create1();
-> evetpoll_init(); /* epoll_ctl() */
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,
struct epoll_event __user *, event)
-> case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:
-> ep_insert(ep, &epds, tfile, fd);
-> tfile->f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt); /* 调用驱动的poll()函数 */ /* epoll_wait() */
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_wait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *, events,
int, maxevents, int, timeout)
-> ep_poll(ep, events, maxevents, timeout);
-> 判断timeout
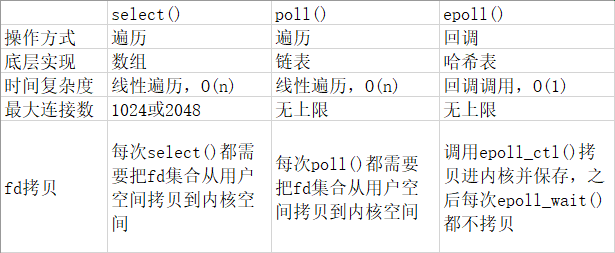
四、poll()、select()和epoll()的区别
五、驱动程序的poll()函数
poll()函数需要#include <linux/poll.h>
为了更方便演示poll()函数,我在代码中加入了一个全局变量ev_press,如果有按键按下置1;然后重新置0
static struct file_operations key_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = key_read,
.poll = key_poll, /* 加入poll()函数 */
.open = key_open,
.release = key_release,
};
poll()函数示例如下:
static unsigned int key_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *table)
{
struct key_device *dev = filp->private_data; unsigned int mask = ; poll_wait(filp, &dev->r_head, table); if (ev_press)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; return mask;
}
代码中的poll_wait()并不会像wait_event()系列函数一样阻塞地等待事件发生,poll_wait()并不会引起阻塞。它只是把当前进程加入到poll_table_struct等待列表
key源代码:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/poll.h> #include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/io.h> #include <mach/gpio.h> #define KEY_MAJOR 255 struct pin_desc {
int gpio;
int val;
char *name;
}; struct key_device {
struct cdev cdev;
wait_queue_head_t r_head;
wait_queue_head_t w_head;
}; static struct pin_desc desc[] = {
{ EXYNOS4_GPX3(), 0x01, "KEY0" },
{ EXYNOS4_GPX3(), 0x02, "KEY1" },
{ EXYNOS4_GPX3(), 0x03, "KEY2" },
{ EXYNOS4_GPX3(), 0x04, "KEY3" },
}; static int g_major = KEY_MAJOR;
module_param(g_major, int, S_IRUGO); static struct key_device* dev;
static struct class* scls;
static struct device* sdev;
static unsigned char key_val;
static volatile int ev_press = ; static irqreturn_t key_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct pin_desc *pindesc = (struct pin_desc *)dev_id;
unsigned int tmp; tmp = gpio_get_value(pindesc->gpio); /* active low */
printk(KERN_DEBUG "KEY %d: %08x\n", pindesc->val, tmp); if (tmp)
key_val = pindesc->val;
else
key_val = pindesc->val | 0x80; set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); ev_press = ; return IRQ_HANDLED;
} static ssize_t key_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t len, loff_t * loff)
{
struct key_device *dev = filp->private_data; // 声明等待队列
DECLARE_WAITQUEUE(rwait, current);
add_wait_queue(&dev->r_head, &rwait); // 休眠
__set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
schedule(); // 有数据
copy_to_user(buf, &key_val, ); remove_wait_queue(&dev->r_head, &rwait);
set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); ev_press = ; return ;
} static unsigned int key_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *table)
{
struct key_device *dev = filp->private_data; unsigned int mask = ; poll_wait(filp, &dev->r_head, table); if (ev_press)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; return mask;
} static int key_open(struct inode *nodep, struct file *filp)
{
struct key_device *dev = container_of(nodep->i_cdev, struct key_device, cdev);
// 放入私有数据中
filp->private_data = dev; int irq;
int i, err = ; for (i = ; i < ARRAY_SIZE(desc); i++) {
if (!desc[i].gpio)
continue; irq = gpio_to_irq(desc[i].gpio);
err = request_irq(irq, key_interrupt, IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_BOTH,
desc[i].name, (void *)&desc[i]);
if (err)
break;
} if (err) {
i--;
for (; i >= ; i--) {
if (!desc[i].gpio)
continue; irq = gpio_to_irq(desc[i].gpio);
free_irq(irq, (void *)&desc[i]);
}
return -EBUSY;
} init_waitqueue_head(&dev->r_head); return ;
} static int key_release(struct inode *nodep, struct file *filp)
{
// 释放中断
int irq, i; for (i = ; i < ARRAY_SIZE(desc); i++) {
if (!desc[i].gpio)
continue; irq = gpio_to_irq(desc[i].gpio);
free_irq(irq, (void *)&desc[i]);
} return ;
} static struct file_operations key_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = key_read,
.poll = key_poll,
.open = key_open,
.release = key_release,
}; static int keys_init(void)
{
int ret;
int devt;
if (g_major) {
devt = MKDEV(g_major, );
ret = register_chrdev_region(devt, , "key");
}
else {
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devt, , , "key");
g_major = MAJOR(devt);
} if (ret)
return ret; dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct key_device), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto fail_alloc;
} cdev_init(&dev->cdev, &key_fops);
ret = cdev_add(&dev->cdev, devt, );
if (ret)
return ret; scls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "key");
sdev = device_create(scls, NULL, devt, NULL, "key"); return ; fail_alloc:
unregister_chrdev_region(devt, ); return ret;
} static void keys_exit(void)
{
dev_t devt = MKDEV(g_major, ); device_destroy(scls, devt);
class_destroy(scls); cdev_del(&(dev->cdev));
kfree(dev); unregister_chrdev_region(devt, );
} module_init(keys_init);
module_exit(keys_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile:
KERN_DIR = /work/tiny4412/tools/linux-3.5 all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order obj-m += key.o
测试文件:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h> int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int fd, ret;
fd = open("/dev/key", O_RDWR);
if (fd < ) {
printf("can't open /dev/key\n");
return -;
} unsigned char key_val; fd_set rfds;
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_SET(fd, &rfds); struct timeval tv;
tv.tv_sec = ;
tv.tv_usec = ; while () {
ret = select(fd + , &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv); if(ret == ) /* 超时 */ {
printf("select time out!\n");
break;
}
else if (ret > ) {
if (FD_ISSET(fd, &rfds)) {
read(fd, &key_val, );
printf("key_val = 0x%x\n", key_val);
}
}
} close(fd); return ;
}
下一章 五、并发控制
四、poll()、select()和epoll()的更多相关文章
- IO多路复用(select、poll、epoll)介绍及select、epoll的实现
IO多路复用(select.poll.epoll)介绍及select.epoll的实现 IO多路复用中包括 select.pool.epoll,这些都属于同步,还不属于异步 一.IO多路复用介绍 1. ...
- Epoll,Poll,Select模型比较
http://blog.csdn.net/liangyuannao/article/details/7776057 先说Select: 1.Socket数量限制:该模式可操作的Socket数由FD_S ...
- /dev/poll, kqueue(2), event ports, POSIX select(2), Windows select(), poll(2), and epoll(4)
/dev/poll, kqueue(2), event ports, POSIX select(2), Windows select(), poll(2), and epoll(4) libevent ...
- 轮询、select、 epoll
网卡设备对应一个中断号, 当网卡收到网络端的消息的时候会向CPU发起中断请求, 然后CPU处理该请求. 通过驱动程序 进而操作系统得到通知, 系统然后通知epoll, epoll通知用户代码. 一. ...
- [转]谈谈select, iocp, epoll,kqueue及各种网络I/O复用机制
参考原文:再谈select, iocp, epoll,kqueue及各种I/O复用机制 一.I/O模型概述 介绍几种常见的I/O模型及其区别,如下: blocking I/O nonblocking ...
- Select与Epoll比较
一.问题引出 联系区别 问题的引出,当需要读两个以上的I/O的时候,如果使用阻塞式的I/O,那么可能长时间的阻塞在一个描述符上面,另外的描述符虽然有数据但是不能读出来,这样实时性不能满足要求,大概的解 ...
- 【网络】再谈select, iocp, epoll,kqueue及各种I/O复用机制 && Reactor与Proactor的概念
首先,介绍几种常见的I/O模型及其区别,如下: blocking I/O nonblocking I/O I/O multiplexing (select and poll) signal drive ...
- 网络编程基础——学习阻塞,非阻塞(select和epoll)
<h3 class="xyn" helvetica="" neue',="" helvetica,="" aria ...
- 多路复用select和epoll的区别(转)
先说下本文框架,先是问题引出,然后概括两个机制的区别和联系,最后介绍每个接口的用法 一.问题引出 联系区别 问题的引出,当需要读两个以上的I/O的时候,如果使用阻塞式的I/O,那么可能长时间的阻塞在一 ...
随机推荐
- chtMultiRegionSimpleFoam求解器的热源不在边界上【翻译】
翻译自:CFD-online 帖子地址:http://www.cfd-online.com/Forums/openfoam-solving/126777-chtmultiregionsimplefoa ...
- 2018-2019-2 《网络对抗技术》Exp8 Web基础 Week11-12 20165233
Exp8 Web基础 目录 一.基础问题 二.实验步骤 实验点一:Web前端HTML 能正常安装.启停Apache.理解HTML,理解表单,理解GET与POST方法,编写一个含有表单的HTML. 实验 ...
- linux删除目录下指定后缀的文件
这几天在Colab上使用ImageAI训练模型时每次都会保存精确度有所提升的模型,这些模型可以算是中间产物,不太重要.为了避免混淆,运行完通过以下命令删除. find . -name "*. ...
- httpPostedFile实现WEBAPI文件上传
public void PostUpload() { var httpPostedFile = HttpContext.Current.Request.Files; foreach(string p ...
- 唯品会HDFS性能挑战和优化实践
唯品会HDFS性能挑战和优化实践 原创: 大数据平台 唯技术 4月1日 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/LMa99ubgACI4eaDV3G-6gw
- grub下如何指定哪个分区为根文件系统?
答: 使用root命令,如: grub> set root=(hd0,msdos1)
- hystrix流程图收藏
最近在看张开涛的亿级流量的书,学习了一个新的防雪崩的功能hystrix,在学习这个功能的过程中,看了一些网站也温习了一些知识,例如double_check locking功能,还有cache的击穿作为 ...
- 0.9.0.RELEASE版本的spring cloud alibaba nacos+feign实例
这里的feign依然是原来的feign,只不过将注册中心由eureka换成了nacos.服务提供方参见0.9.0.RELEASE版本的spring cloud alibaba nacos实例,消费方跟 ...
- Qt编写自定义控件51-可输入仪表盘
一.前言 这个控件是近期定制的控件,还是比较实用的控件之一,用户主要是提了三点需求,一点是切换焦点的时候控件放大突出显示,一点是可直接输入或者编辑值,还有一点是支持上下键及翻页键和鼠标滚轮来动态修改值 ...
- C#将HTML代码转换为图片
前端通过富文本控件接收到了一段html代码,后端想通过图片的形式展示到另外的地方,这种情况怎么处理呢.直接上代码: using System; using System.Collections.Gen ...
