Codefroces432 div2 A,B,C
Arpa is researching the Mexican wave.
There are n spectators in the stadium, labeled from 1 to n. They start the Mexican wave at time 0.
- At time 1, the first spectator stands.
- At time 2, the second spectator stands.
- ...
- At time k, the k-th spectator stands.
- At time k + 1, the (k + 1)-th spectator stands and the first spectator sits.
- At time k + 2, the (k + 2)-th spectator stands and the second spectator sits.
- ...
- At time n, the n-th spectator stands and the (n - k)-th spectator sits.
- At time n + 1, the (n + 1 - k)-th spectator sits.
- ...
- At time n + k, the n-th spectator sits.
Arpa wants to know how many spectators are standing at time t.
The first line contains three integers n, k, t (1 ≤ n ≤ 109, 1 ≤ k ≤ n, 1 ≤ t < n + k).
Print single integer: how many spectators are standing at time t.
10 5 3
3
10 5 7
5
10 5 12
3
In the following a sitting spectator is represented as -, a standing spectator is represented as ^.
- At t = 0 ----------
 number of standing spectators = 0.
number of standing spectators = 0. - At t = 1 ^---------
 number of standing spectators = 1.
number of standing spectators = 1. - At t = 2 ^^--------
 number of standing spectators = 2.
number of standing spectators = 2. - At t = 3 ^^^-------
 number of standing spectators = 3.
number of standing spectators = 3. - At t = 4 ^^^^------
 number of standing spectators = 4.
number of standing spectators = 4. - At t = 5 ^^^^^-----
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 6 -^^^^^----
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 7 --^^^^^---
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 8 ---^^^^^--
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 9 ----^^^^^-
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 10 -----^^^^^
 number of standing spectators = 5.
number of standing spectators = 5. - At t = 11 ------^^^^
 number of standing spectators = 4.
number of standing spectators = 4. - At t = 12 -------^^^
 number of standing spectators = 3.
number of standing spectators = 3. - At t = 13 --------^^
 number of standing spectators = 2.
number of standing spectators = 2. - At t = 14 ---------^
 number of standing spectators = 1.
number of standing spectators = 1. - At t = 15 ----------
 number of standing spectators = 0.
number of standing spectators = 0.
分情况讨论
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <cassert>
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
#define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y)
#define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y)
#define MAX 100000000000000000
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define ei exp(1)
#define PI 3.141592653589793238462
#define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define INF 1044266558
#define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a)))
typedef long long ll;
int n,m,k;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);
if(k>= && k<=m) printf("%d\n",k);
else if(k>m && k<=n) printf("%d\n",m);
else if(k>n && k<=n+m) printf("%d\n",m-k+n);
else printf("0\n");
return ;
}
Arpa is taking a geometry exam. Here is the last problem of the exam.
You are given three points a, b, c.
Find a point and an angle such that if we rotate the page around the point by the angle, the new position of a is the same as the old position of b, and the new position of b is the same as the old position of c.
Arpa is doubting if the problem has a solution or not (i.e. if there exists a point and an angle satisfying the condition). Help Arpa determine if the question has a solution or not.
The only line contains six integers ax, ay, bx, by, cx, cy (|ax|, |ay|, |bx|, |by|, |cx|, |cy| ≤ 109). It's guaranteed that the points are distinct.
Print "Yes" if the problem has a solution, "No" otherwise.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
三点共线一定不存在,除此之外,若a到b的距离等于b到c的距离存在。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <cassert>
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
#define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y)
#define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y)
#define MAX 100000000000000000
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define ei exp(1)
#define PI 3.141592653589793238462
#define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define INF 1044266558
#define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a)))
typedef long long ll;
struct point
{
ll x;
ll y;
}node[];
ll dist(point a,point b)
{
return ((a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y))+((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x));
}
bool check()
{
int ans=;
if(dist(node[],node[])==dist(node[],node[])) ans=;
if(ans) return true;
else return false;
}
bool solve()
{
double a=((node[].y-node[].y)*1.0)/((node[].x-node[].x)*1.0);
double b=((node[].y-node[].y)*1.0)/((node[].x-node[].x)*1.0);
if(a==b) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&node[i].x,&node[i].y);
}
if(solve()) puts("No");
else if(check()) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
return ;
}
You are given set of n points in 5-dimensional space. The points are labeled from 1 to n. No two points coincide.
We will call point a bad if there are different points b and c, not equal to a, from the given set such that angle between vectors 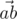 and
and 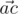 is acute (i.e. strictly less than
is acute (i.e. strictly less than 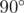 ). Otherwise, the point is called good.
). Otherwise, the point is called good.
The angle between vectors 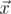 and
and 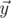 in 5-dimensional space is defined as
in 5-dimensional space is defined as 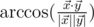 , where
, where 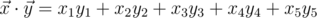 is the scalar product and
is the scalar product and 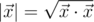 is length of
is length of 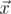 .
.
Given the list of points, print the indices of the good points in ascending order.
The first line of input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 103) — the number of points.
The next n lines of input contain five integers ai, bi, ci, di, ei (|ai|, |bi|, |ci|, |di|, |ei| ≤ 103) — the coordinates of the i-th point. All points are distinct.
First, print a single integer k — the number of good points.
Then, print k integers, each on their own line — the indices of the good points in ascending order.
6
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1
1
1
3
0 0 1 2 0
0 0 9 2 0
0 0 5 9 0
0
In the first sample, the first point forms exactly a 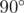 angle with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
angle with all other pairs of points, so it is good.
In the second sample, along the cd plane, we can see the points look as follows:
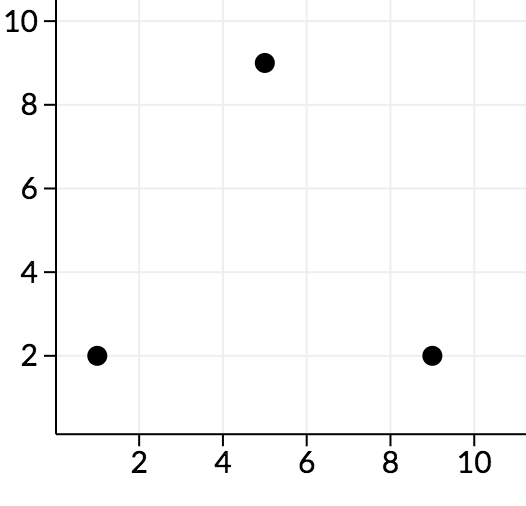
We can see that all angles here are acute, so no points are good.
暴力枚举
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <cassert>
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
#define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y)
#define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y)
#define MAX 100000000000000000
#define MOD 1000000007
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define ei exp(1)
#define PI 3.141592653589793238462
#define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define INF 1044266558
#define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a)))
typedef long long ll;
ll a[][];
int n,vis[];
set<ll>s;
bool check(int x,int y,int z)
{
ll pos=;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
pos+=(a[y][i]-a[x][i])*(a[z][i]-a[x][i]);
if(pos>) return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
s.insert(i+);
for(int j=;j<;j++)
scanf("%lld",&a[i][j]);
}
int l=n;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
{
for(int k=j+;k<n;k++)
{
if(i!=j && i!=k)
{
if(!check(i,j,k))
{
l--;
s.erase(i+);
goto eg;
}
}
}
}
eg:;
}
printf("%d\n",l);
if(s.size())
{
for(set<ll>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++)
{
printf("%lld\n",*it);
}
}
return ;
}
Codefroces432 div2 A,B,C的更多相关文章
- bc#54 div2
用小号做的div2 A:竟然看错了排序顺序...白白WA了两发 注意读入一整行(包括空格):getline(cin,st) [gets也是资瓷的 #include<iostream> us ...
- $('div a') 与$('div>a'),.div+.div2与.div~.div2
$('div a'):div标签下所有层次a元素的jquery对象 $('div>a'):div标签下子元素层次a元素的jquery对象 <body> <div class=' ...
- SRM 657 DIV2
-------一直想打SRM,但是感觉Topcoder用起来太麻烦了.题目还是英文,不过没什么事干还是来打一打好了.但是刚注册的号只能打DIV2,反正我这么弱也只适合DIV2了.. T1: 题目大意: ...
- CodeForces Round 192 Div2
This is the first time I took part in Codeforces Competition.The only felt is that my IQ was contemp ...
- Codeforce Round #211 Div2
真的是b到不行啊! 尼玛C题一个这么简单的题目没出 aabbccddee 正确的是aabccdee 我的是 aabcdee 硬是TM的不够用,想半天还以为自己的是对的... A:题... B:题. ...
- Topcoder srm 632 div2
脑洞太大,简单东西就是想复杂,活该一直DIV2; A:水,基本判断A[I]<=A[I-1],ANS++; B:不知道别人怎么做的,我的是100*N*N;没办法想的太多了,忘记是连续的数列 我们枚 ...
- TopCoder 603 div1 & div2
div2 250pts MiddleCode 题意:s串长度为奇数时,将中间字符取掉并添加到t末尾:长度为偶数时,将中间两个较小的字符取掉并添加到末尾. 分析:直接做,学习了一下substr(s, p ...
- TopCoder 649 div1 & div2
最近一场TC,做得是在是烂,不过最后challenge阶段用一个随机数据cha了一个明显错误的代码,最后免于暴跌rating,还涨了一点.TC题目质量还是很高的,非常锻炼思维,拓展做题的视野,老老实实 ...
- 220 DIV2 B. Inna and Nine
220 DIV2 B. Inna and Nine input 369727 output 2 input 123456789987654321 output 1 题意:比如例子1:369727--& ...
随机推荐
- Linux内存管理与C存储空间
ELF文件 在学习之前我们先看看ELF文件. ELF分为三种类型:.o 可重定位文件(relocalble file),可执行文件以及共享库(shared library),三种格式基本上从结构上是一 ...
- ThinkPhp5-PHPExcel导出数据
PHP-Excel 标签(空格分隔): php 类库下载地址:https://codeload.github.com/PHPOffice/PHPExcel/zip/1.8 php导出excel表格数据 ...
- 使用NiftyModeEffects对话框
最近看到一篇有关个性对话框的文章,里面介绍了非常酷的动画效果,开源的项目下载来试试,用法很简单. NoftyDialogEffects效果参考: http://tympanus.net/D ...
- 滑动切换Activity代码
最近需要对练习项目中的代码进行优化,发现很多代码写起来远比想象的困难很多.刚接触Android时间不长,很多东西都不能融会贯通,所以才会有这样的问题存在,当然学习中遇到的问题很有必要做个总结.想想这个 ...
- 2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛 maze(bfs)
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/105/F来源:牛客网 有q个单向传送阵,每个传送阵各有一个入口和一个出口,入口和出口都在迷宫的格子里,当走到或被传送到 ...
- PL/SQL Developer 关闭Sql窗口快捷键
preferences->keyconfigration->file/close然后设置你喜欢的按键就行了.(ps:这个close是关闭当前活动的那一个页面)
- vue打包后js和css、图片不显示,引用的字体找不到问题
vue打包后js和css.图片不显示,引用的字体找不到问题:图片一般都是背景图片. 一.vue打包出现js和css不显示问题: 1.不使用mode:'history' 2.使用mode:'histor ...
- P3066 [USACO12DEC]逃跑的BarnRunning Away From… 树上差分_树上倍增
code: #include <cstdio> using namespace std; #define ll long long const int N=200005; int n,fa ...
- type与isinstance使用区别
Python中,type与isinstance都可以用来判断变量的类型,但是type具有一定的适用性,用它来判断变量并不总是能够获取到正确的值. Python在定义变量的时候不用指明具体的的类型,解释 ...
- python之禅---对象与元类
众所周知,python是一门面向对象的编程语言,python中一切皆对象,那么我们先探讨一下什么是对象. 一.对象 在生活中一个事物就是一个对象,比如:一只猫就是一个对象,猫的体型.猫毛的颜色等是它的 ...
