WPF命令绑定 自定义命令
WPF的命令系统是wpf中新增加的内容,在以往的winfom中并没有。为什么要增加命令这一块内容。在winform里面的没有命令只使用事件的话也可以实现程序员希望实现的功能。这个问题在很多文章中都提到了。但大家都是引用深入浅出wpf里面的概述。没有用自己的话来阐述。当然你仔细理解一下的话也很容易理解。但在这里我还是用我自己的话来说一下什么情况下使用命令。
命令具有约束力
事件的作用是发布、传播一些消息,消息传达到了接收者,事件的指令也就算完成了,至于如何响应事件送来的消息事件并不做任何限制,每个接收者可已用自己的行为来响应事件。也就是说,事件不具有约束力。命令和事件的区别就在于命令具有约束力。
事件是一种很自由散漫的调用。就像我们平时的自由职业者一样,不受约束,想做什么就做什么。仔细运用的话虽然可以什么功能都实现,但是总是有些凌乱。但是命令不同,命令具有约束力,也就是上班族一样。有一个制度来约束你。必须按照流程来实现功能。所说这样做略显麻烦,但是对于一些复杂特定的情况却能够避免程序员出错。
比如保存事件的处理器,程序员可以写Save()、SaveHandle()、SaveDocument()... 这些都符合代码规范。但迟早有一天整个项目会变的让人无法读懂,新来的程序员或修改bug的程序员会很抓狂。如果使用命令,情况就会好很多----当Save命令到达某个组件的时候,命令会自动去调用组件的Save方法。而这个方法可能定义在基类或者接口里(即保证了这个方法是一定存在的),这就在代码结构和命名上做了约束。
这里所谓的约束力就是指命令系统的几大要素
- 命令(Command):WPF的命令实际上就是实现了ICommand接口的类,平时使用最多的就是RoutedCommand类。我们还会学习使用自定义命令。
- 命令源(Command Source):即命令的发送者,是实现了ICommandSource接口的类。很多界面元素都实现了这个接口,其中包括Button,ListBoxItem,MenuItem等。
- 命令目标(Command Target):即命令发送给谁,或者说命令作用在谁的身上。命令目标必须是实现了IInputElement接口的类。
- 命令关联(Command Binding):负责把一些外围逻辑和命令关联起来,比如执行之前对命令是否可以执行进行判断、命令执行之后还有哪些后续工作等。
要想使用命令,就必须要实现这几大要素。而程序员如果实现了这几大要素,那么程序的逻辑就很明了。也就是让程序员想犯错都难。
命令最常见的使用情况是例如工具栏里面绑定命令,右键命令,菜单绑定命令,保存,撤销,打开文件夹等情境。
命令实现例1
命令的实现可以自定义命令,但对于一些简单的情况我们可以使用wpf内置的已经实现了ICommand接口的RoutedCommand或者RoutedUICommand
注意RoutedUICommand只是比RoutedCommand多了一个说明性的文本参数。
xaml
<Window x:Class="WpfApplication1.Window28"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Window28" Height="" Width="" WindowStyle="ToolWindow">
<StackPanel Background="LightBlue" x:Name="sp1">
<Button Content="Send Command" x:Name="btn1" Margin=""></Button>
<TextBox x:Name="txtA" Margin="5,0" Height=""></TextBox>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
后台cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes; namespace WpfApplication1
{
/// <summary>
/// Window28.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class Window28 : Window
{
public Window28()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeCommand();
}
//声明并定义命令
private RoutedCommand rouutedCommand = new RoutedCommand("Clear",typeof(Window28));
private void InitializeCommand()
{
//把命令赋值给命令源,并定义快捷键
this.btn1.Command = rouutedCommand;
//定义快捷键 gesture 手势
this.rouutedCommand.InputGestures.Add(new KeyGesture(Key.C, ModifierKeys.Alt));
//指定命令目标
this.btn1.CommandTarget = txtA; //创建命令关联
CommandBinding commandBinding = new CommandBinding();
//把命令rouutedCommand和具体的逻辑事件绑定起来。
commandBinding.Command = rouutedCommand;//只关注与rouutedCommand相关的命令
commandBinding.CanExecute += new CanExecuteRoutedEventHandler(cb_CanExecute);
commandBinding.Executed += new ExecutedRoutedEventHandler(cb_Execute);
//把命令关联安置在外围控件上
this.sp1.CommandBindings.Add(commandBinding);
}
//当命令到达目标之后,此方法被调用
private void cb_Execute(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
{
txtA.Clear();
//避免事件继续向上传递而降低程序性能
e.Handled = true;
}
//当探测命令是否可执行的时候该方法会被调用
private void cb_CanExecute(object sender,CanExecuteRoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtA.Text))
{
e.CanExecute = false;
}
else
{
e.CanExecute = true;
}
//避免事件继续向上传递而降低程序性能
e.Handled = true;
} }
}
上面这个例子代码写的比较详细,简单些我们也可以这样写
<Window x:Class="WpfApplication1.Window65"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfApplication1"
Title="Window64" Height="" Width="">
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Menu>
<MenuItem Header="文件">
<MenuItem Header="打开文件" Command="{x:Static Member=local:Commands.NewProject}"></MenuItem>
<MenuItem Header="另存为"></MenuItem>
<MenuItem Header="关闭文件"></MenuItem>
</MenuItem>
</Menu>
</Grid>
</Window>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using System.Windows.Media.Animation; namespace WpfApplication1
{
public partial class Window65 : Window
{
public Window65()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.CommandBindings.Add(new CommandBinding(Commands.NewProject, new ExecutedRoutedEventHandler(ExecuteNewProject)));
} private void ExecuteNewProject(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("自定义命令");
}
}
public static class Commands
{
public static ICommand NewProject = new RoutedUICommand("newproject", "NewProject", typeof(Commands));
}
}
自定义命令(深入浅出wpf原版例30)
关于自定义命令,园子里大多文章都是取自深入浅出理解wpf里面的例子。我们也从这个例子开始分析,然后一点一点把这个例子改为我们自己掌握的例子。
xaml窗体
<Window x:Class="WpfApplication1.Window30"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Window30" Height="" Width="" xmlns:my="clr-namespace:WpfApplication1">
<StackPanel>
<my:MyCommandSource x:Name="myCommandSource1">
<TextBlock Text="清除" Width="" FontSize="" TextAlignment="Center" Background="LightGreen"></TextBlock>
</my:MyCommandSource>
<my:MniView x:Name="mniView1" />
</StackPanel>
</Window>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using WpfApplication1.Command; namespace WpfApplication1
{
/// <summary>
/// Window30.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class Window30 : Window
{
public Window30()
{
InitializeComponent();
ClearCommand clearCommand = new ClearCommand();
this.myCommandSource1.Command = clearCommand;
this.myCommandSource1.CommandTarget = mniView1;
}
}
}
命令源:
<UserControl x:Class="WpfApplication1.MyCommandSource"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"> </UserControl>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes; namespace WpfApplication1
{
/// <summary>
/// MyCommandSource.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class MyCommandSource : UserControl,ICommandSource
{ /// <summary>
/// 继承自ICommand的3个属性
/// </summary>
public ICommand Command
{
get;
set;
} public object CommandParameter
{
get;
set;
} public IInputElement CommandTarget
{
get;
set;
}
//在命令目标上执行命令,或者说让命令作用于命令目标
protected override void OnMouseLeftButtonDown(MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
base.OnMouseLeftButtonDown(e);
if(this.CommandTarget!=null)
{
this.Command.Execute(CommandTarget);
}
}
protected override void OnMouseDoubleClick(MouseButtonEventArgs e)
{
base.OnMouseDoubleClick(e);
}
}
}
命令目标:
<UserControl x:Class="WpfApplication1.MniView"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
mc:Ignorable="d"
d:DesignHeight="" d:DesignWidth="">
<Border CornerRadius="" BorderBrush="GreenYellow" BorderThickness="">
<StackPanel>
<TextBox Margin="" x:Name="txt1"></TextBox>
<TextBox Margin="" x:Name="txt2"></TextBox>
<TextBox Margin="" x:Name="txt3"></TextBox>
<TextBox Margin="" x:Name="txt4"></TextBox>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</UserControl>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using WpfApplication1.InterFace; namespace WpfApplication1
{
/// <summary>
/// MniView.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class MniView : UserControl,IView
{
//构造器
public MniView()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//继承自IView的成员们
public bool IsChanged
{
get
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
set
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
} public void SetBinding()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
} public void Refresh()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
/// <summary>
/// 用于清除内容的业务逻辑
/// </summary>
public void Clear()
{
this.txt1.Clear();
this.txt2.Clear();
this.txt3.Clear();
this.txt4.Clear();
} public void Save()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
自定义命令:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Input;
using WpfApplication1.InterFace; namespace WpfApplication1.Command
{
/// <summary>
///自定义命令
/// </summary>
public class ClearCommand : ICommand
{
//用来判断命令是否可以执行
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
//当命令可执行状态发送改变时,应当被激发
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged; //命令执行时,带有与业务相关的Clear逻辑
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
IView view = parameter as IView;
if (view != null)
{
view.Clear();
}
}
}
}
定义的接口
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text; namespace WpfApplication1.InterFace
{
public interface IView
{
//属性
bool IsChanged { get; set; }
//方法
void SetBinding();
void Refresh();
void Clear();
void Save();
}
}
原版命令改
原例子中首先对于命令源。:即命令的发送者,是实现了ICommandSource接口的类。很多界面元素都实现了这个接口,其中包括Button,ListBoxItem,MenuItem等。因为wpf中大部分控件都已经实现了这个接口,所以我们可以把例子弄简单些,暂时不用实现自定义的MyCommandSource
我们把我们主窗体中的xaml修改成下面这样
<Window x:Class="WpfApplication1.Window30"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Window30" Height="" Width="" xmlns:my="clr-namespace:WpfApplication1">
<StackPanel>
<!--<my:MyCommandSource x:Name="myCommandSource1">
<TextBlock Text="清除" Width="" FontSize="" TextAlignment="Center" Background="LightGreen"></TextBlock>
</my:MyCommandSource>-->
<Button Name="myCommandSource1">
<TextBlock Text="清除" Width="" FontSize="" TextAlignment="Center" Background="LightGreen"></TextBlock>
</Button>
<my:MniView x:Name="mniView1" />
</StackPanel>
</Window>
用一个button来作为命令源。调试程序,会报错如下

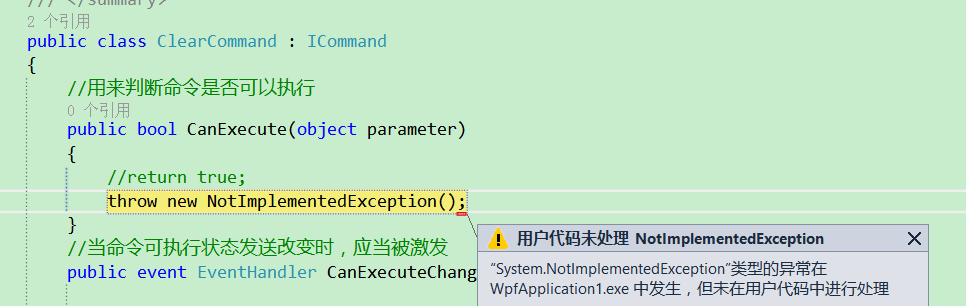
在原版代码里面是没有return true 的,所以在给空间绑定命令的时候会报错。这说明当给wpf自带的控件作为命令源绑定时会初始化执行CanExecute,而在我们自己实现的命令源MyCommandSource并没有实现这一逻辑。也就是当我们初始化命令绑定的时候并没有去执行CanExecute这个方法。当然在这个例子中这无关紧要,但当我们自定义控件的时候最好实现这一逻辑,所以在初始化时候可以首先检查命令是否可以执行。我们现在先把canExecute return true;继续我们的改造。
此时我们点击清除,会发现命令并没有被执行。检查代码我们会发现 public void Execute(object parameter)方法的parameter为null.

我们看一下原版中当我们左击的时候,源命令源执行了上面这个方法。此时感觉有些奇怪。CommandTarget命令目标是这样使用的么?
我们查看一下msdn,解释如下。
在 Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 命令系统中,仅当 ICommand 为 RoutedCommand 时,ICommandSource 上的 CommandTarget 属性才适用。 如果 CommandTarget 是在 ICommandSource 上设置的,并且对应的命令不是 RoutedCommand,则会忽略该命令目标。
命令目标是只针对RoutedCommand实现的。我们看一下我们最开始的例子,该例使用了wpf内置的 RoutedCommand 命令。
private void ExecuteNewProject(object sender, ExecutedRoutedEventArgs e)
与该命令绑定的方法实现有两个参数,其中sender 就是指的我们的CommandTarget
与 RoutedCommand 一起使用时,命令目标为引发 Executed 和 CanExecute 事件的对象。 如果未设置 CommandTarget 属性,则会将具有键盘焦点的元素用作目标。
所以原版demo中命令目标的使用有些不恰当。此时我们可以将主窗体的代码改为如下。向目标源传递参数
this.myCommandSource1.CommandParameter = mniView1;此时我们发现命令被正确执行。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using WpfApplication1.Command; namespace WpfApplication1
{
/// <summary>
/// Window30.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class Window30 : Window
{
public Window30()
{
InitializeComponent();
ClearCommand clearCommand = new ClearCommand();
this.myCommandSource1.Command = clearCommand;
this.myCommandSource1.CommandParameter = mniView1;
//this.myCommandSource1.CommandTarget = mniView1;
}
}
}
通过这个例子的改造我们发现,很多情况下我们如果不需要实现自定义控件是不需要自定义命令源的,而命令目标很多情况下也不需要。我们只需要向命令绑定传递参数就可以实现很多的应用。
通过构造函数传递参数
另外我们也可以重新命令的构造函数来实现参数的传递。改造后代码如下。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using WpfApplication1.Command; namespace WpfApplication1
{
/// <summary>
/// Window30.xaml 的交互逻辑
/// </summary>
public partial class Window30 : Window
{
public Window30()
{
InitializeComponent();
ClearCommand clearCommand = new ClearCommand(mniView1);
this.myCommandSource1.Command = clearCommand;
//this.myCommandSource1.CommandParameter = mniView1;
//this.myCommandSource1.CommandTarget = mniView1;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Input;
using WpfApplication1.InterFace; namespace WpfApplication1.Command
{
/// <summary>
///自定义命令
/// </summary>
public class ClearCommand : ICommand
{
IView _view;
public ClearCommand(IView view)
{
this._view = view;
}
//用来判断命令是否可以执行
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
return true;
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
//当命令可执行状态发送改变时,应当被激发
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged; //命令执行时,带有与业务相关的Clear逻辑
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
//IView view = parameter as IView;
IView view = _view as IView;
if (view != null)
{
view.Clear();
}
}
}
}
源版代码下载链接:http://download.csdn.net/detail/fwj380891124/4778376(例30)
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/santian/p/4385220.html
博客地址:一天两天三天
WPF命令绑定 自定义命令的更多相关文章
- WPF 原生绑定和命令功能使用指南
WPF 原生绑定和命令功能使用指南 魏刘宏 2020 年 2 月 21 日 如今,当谈到 WPF 时,我们言必称 MVVM.框架(如 Prism)等,似乎已经忘了不用这些的话该怎么使用 WPF 了.当 ...
- WPF使用RoutedCommand自定义命令
主要代码如下所示: /// <summary> /// 声明并定义命令. /// </summary> RoutedCommand ClearCommand = new Rou ...
- wpf DATAgrid模板中button 命令绑定以及命令参数绑定
场景:视频上传功能,上传列表使用DataGrid控件,视频有不同的状态对应不同的操作,DataGrid中最后一列为操作列,里面是Button控件.希望点击Button后执行对应的操作,但是设置Butt ...
- WPF中的命令与命令绑定(一)
原文:WPF中的命令与命令绑定(一) WPF中的命令与命令绑定(一) 周银辉说到用户输入,可能我们更多地会联想到 ...
- Linux使用alias自定义命令自定义快捷键
比如我经常需要进入一个很深的目录如 /home/walking/weblogic/devlop/script/application/.../... 这样每次进入这个目录操作是不是很麻烦,可能有时候记 ...
- MVVM模式解析和在WPF中的实现(三)命令绑定
MVVM模式解析和在WPF中的实现(三) 命令绑定 系列目录: MVVM模式解析和在WPF中的实现(一)MVVM模式简介 MVVM模式解析和在WPF中的实现(二)数据绑定 MVVM模式解析和在WPF中 ...
- WPF 自定义命令 以及 命令的启用与禁用
自定义命令: 在WPF中有5个命令类(ApplicationCommands.NavigationCommands.EditingCommands.ComponentCommands 以及 M ...
- WPF中的命令与命令绑定(二)
原文:WPF中的命令与命令绑定(二) WPF中的命令与命令绑定(二) 周银辉在WPF中,命令(Commandi ...
- 整理:WPF用于绑定命令和触发路由事件的自定义控件写法
原文:整理:WPF用于绑定命令和触发路由事件的自定义控件写法 目的:自定义一个控件,当点击按钮是触发到ViewModel(业务逻辑部分)和Xaml路由事件(页面逻辑部分) 自定义控件增加IComman ...
随机推荐
- Simple JavaScript Inheritance(John Resig)
I’ve been doing a lot of work, lately, with JavaScript inheritance – namely for my work-in-progress ...
- Docker解析及轻量级PaaS平台演练(三)--Dockerfile编写
在本篇中将介绍Dockerfile的编写 除了通过修改Image,创建Container,在打包成Image来创建我们需要的Image之外 我们还可以编写Dockerfile文件,通过build来创建 ...
- Windows下pip安装scipy报错no lapack/blas resources found
Windows下升级了pandas,但是发现scipy包随后引用出错,后来确认需重新安装scipy, 在用pip安装scipy出现no lapack/blas resources found的错误. ...
- Netty4 initAndRegister 解析
我们从框架的应用层面来分析,NioEventLoopGroup在netty中的使用. 这是我们需要配置的地方. 紧接着我们进入netty的运行中.ServerBootstrap.bind(PORT); ...
- 对帝国cms、dedecms、phpcms等负载测试总结
来自:http://www.chinaz.com/web/2013/0729/311360.shtml 担心被骂,本不想写这篇文章.犹豫良久,最终还是决定写.希望能够帮助到一些朋友,认识到数据库索引正 ...
- [Unity3D]查看与设置游戏帧数FPS
原地址:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5b6cb9500101bta4.html 关于FPS,在PC端来说,游戏帧数跑得越高越好,FPS跑得越高游戏就越流畅,当然太高也 ...
- HTML5中音频视频标签使用
HTML5中音频视频标签使用的最好方式 Html5中提供了<audio> <vedio>元素实现音频视频的引入播放 然而更好的方式
- PHP函数之HTMLSPECIALCHARS_DECODE
PHP函数之htmlspecialchars_decode htmlspecialchars_decode :将特殊的 HTML 实体转换回普通字符 htmlspecialchars: 将普通 ...
- .Net之路(十五)图解LoadRunner压力測试
在项目编码阶段结束后,就须要进行软件測试. 成为软件开发过程中一个不可缺少的环节.而自己主动化測试也是将逐步取代人工繁杂的測试.压力測试就是软件測试对软件性能评估的一个方面,以下就简介我在使用load ...
- JavaScript 事件循环及异步原理(完全指北)
引言 最近面试被问到,JS 既然是单线程的,为什么可以执行异步操作? 当时脑子蒙了,思维一直被困在 单线程 这个问题上,一直在思考单线程为什么可以额外运行任务,其实在我很早以前写的博客里面有写相关的内 ...
