Codeforces Round #470 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 1)
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Bob is a farmer. He has a large pasture with many sheep. Recently, he has lost some of them due to wolf attacks. He thus decided to place some shepherd dogs in such a way that all his sheep are protected.
The pasture is a rectangle consisting of R × C cells. Each cell is either empty, contains a sheep, a wolf or a dog. Sheep and dogs always stay in place, but wolves can roam freely around the pasture, by repeatedly moving to the left, right, up or down to a neighboring cell. When a wolf enters a cell with a sheep, it consumes it. However, no wolf can enter a cell with a dog.
Initially there are no dogs. Place dogs onto the pasture in such a way that no wolf can reach any sheep, or determine that it is impossible. Note that since you have many dogs, you do not need to minimize their number.
First line contains two integers R (1 ≤ R ≤ 500) and C (1 ≤ C ≤ 500), denoting the number of rows and the numbers of columns respectively.
Each of the following R lines is a string consisting of exactly C characters, representing one row of the pasture. Here, 'S' means a sheep, 'W' a wolf and '.' an empty cell.
If it is impossible to protect all sheep, output a single line with the word "No".
Otherwise, output a line with the word "Yes". Then print R lines, representing the pasture after placing dogs. Again, 'S' means a sheep, 'W' a wolf, 'D' is a dog and '.' an empty space. You are not allowed to move, remove or add a sheep or a wolf.
If there are multiple solutions, you may print any of them. You don't have to minimize the number of dogs.
6 6
..S...
..S.W.
.S....
..W...
...W..
......
Yes
..SD..
..SDW.
.SD...
.DW...
DD.W..
......
1 2
SW
No
5 5
.S...
...S.
S....
...S.
.S...
Yes
.S...
...S.
S.D..
...S.
.S...
In the first example, we can split the pasture into two halves, one containing wolves and one containing sheep. Note that the sheep at (2,1) is safe, as wolves cannot move diagonally.
In the second example, there are no empty spots to put dogs that would guard the lone sheep.
In the third example, there are no wolves, so the task is very easy. We put a dog in the center to observe the peacefulness of the meadow, but the solution would be correct even without him.
保护羊群免受狼群骚扰,防不住的就是周围的狼在羊的四联通块上了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
char s[][];
main()
{
int r,c;
cin>>r>>c;
for(int i=; i<=r; i++)cin>>(s[i]+);
for(int i=; i<=r; i++)
for(int j=; j<=c; j++)
if(s[i][j]=='.')s[i][j]='D';
else if(s[i][j]=='S'&&(s[i-][j]=='W'||s[i+][j]=='W'||s[i][j-]=='W'||s[i][j+]=='W'))
{
cout<<"No";
return ;
}
cout<<"Yes"<<"\n";
for(int i=; i<=r; i++)cout<<s[i]+<<"\n";
}
1.5 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Alice and Bob begin their day with a quick game. They first choose a starting number X0 ≥ 3 and try to reach one million by the process described below.
Alice goes first and then they take alternating turns. In the i-th turn, the player whose turn it is selects a prime number smaller than the current number, and announces the smallest multiple of this prime number that is not smaller than the current number.
Formally, he or she selects a prime p < Xi - 1 and then finds the minimum Xi ≥ Xi - 1 such that p divides Xi. Note that if the selected prime palready divides Xi - 1, then the number does not change.
Eve has witnessed the state of the game after two turns. Given X2, help her determine what is the smallest possible starting number X0. Note that the players don't necessarily play optimally. You should consider all possible game evolutions.
The input contains a single integer X2 (4 ≤ X2 ≤ 106). It is guaranteed that the integer X2 is composite, that is, is not prime.
Output a single integer — the minimum possible X0.
14
6
20
15
8192
8191
In the first test, the smallest possible starting number is X0 = 6. One possible course of the game is as follows:
- Alice picks prime 5 and announces X1 = 10
- Bob picks prime 7 and announces X2 = 14.
In the second case, let X0 = 15.
- Alice picks prime 2 and announces X1 = 16
- Bob picks prime 5 and announces X2 = 20.
这个B还是很有难度的,而且你不一定可以读懂题目的
因为每个合数都可以写成质数的乘积
所以X1,X0的范围也就是有了,X1取值为[X2-P(X2)+1,X2], X0取值在[X1-P(X1)+1,X1]
枚举那个最大素数就可以了,暴力完全可以跑过
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+;
int a[N];
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
if(!a[i])
for(int j=i+i; j<=n; j+=i) a[j]=i;
a[i]=i-a[i]+;
}
int ans=n;
for(int i=a[n]; i<=n; i++) ans=min(ans,a[i]);
cout<<ans;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Alice likes snow a lot! Unfortunately, this year's winter is already over, and she can't expect to have any more of it. Bob has thus bought her a gift — a large snow maker. He plans to make some amount of snow every day. On day i he will make a pile of snow of volume Vi and put it in her garden.
Each day, every pile will shrink a little due to melting. More precisely, when the temperature on a given day is Ti, each pile will reduce its volume by Ti. If this would reduce the volume of a pile to or below zero, it disappears forever. All snow piles are independent of each other.
Note that the pile made on day i already loses part of its volume on the same day. In an extreme case, this may mean that there are no piles left at the end of a particular day.
You are given the initial pile sizes and the temperature on each day. Determine the total volume of snow melted on each day.
The first line contains a single integer N (1 ≤ N ≤ 105) — the number of days.
The second line contains N integers V1, V2, ..., VN (0 ≤ Vi ≤ 109), where Vi is the initial size of a snow pile made on the day i.
The third line contains N integers T1, T2, ..., TN (0 ≤ Ti ≤ 109), where Ti is the temperature on the day i.
Output a single line with N integers, where the i-th integer represents the total volume of snow melted on day i.
3
10 10 5
5 7 2
5 12 4
5
30 25 20 15 10
9 10 12 4 13
9 20 35 11 25
In the first sample, Bob first makes a snow pile of volume 10, which melts to the size of 5 on the same day. On the second day, he makes another pile of size 10. Since it is a bit warmer than the day before, the first pile disappears completely while the second pile shrinks to 3. At the end of the second day, he has only a single pile of size 3. On the third day he makes a smaller pile than usual, but as the temperature dropped too, both piles survive till the end of the day.
C这个造雪还是很有意思的,前缀和
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=1e5+;
ll V[N],T[N],dy[N],L[N];
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)cin>>V[i];
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)cin>>T[i],T[i]+=T[i-];
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
int pos=upper_bound(T+i,T+n+,V[i]+T[i-])-T;
dy[i]++,dy[pos]--,L[pos]+=V[i]+T[i-]-T[pos-];
}
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)dy[i]+=dy[i-],cout<<dy[i]*(T[i]-T[i-])+L[i]<<" ";
return ;
}
3.5 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Alice has a very important message M consisting of some non-negative integers that she wants to keep secret from Eve. Alice knows that the only theoretically secure cipher is one-time pad. Alice generates a random key K of the length equal to the message's length. Alice computes the bitwise xor of each element of the message and the key (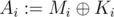 , where
, where  denotes the bitwise XOR operation) and stores this encrypted message A. Alice is smart. Be like Alice.
denotes the bitwise XOR operation) and stores this encrypted message A. Alice is smart. Be like Alice.
For example, Alice may have wanted to store a message M = (0, 15, 9, 18). She generated a key K = (16, 7, 6, 3). The encrypted message is thus A = (16, 8, 15, 17).
Alice realised that she cannot store the key with the encrypted message. Alice sent her key K to Bob and deleted her own copy. Alice is smart. Really, be like Alice.
Bob realised that the encrypted message is only secure as long as the key is secret. Bob thus randomly permuted the key before storing it. Bob thinks that this way, even if Eve gets both the encrypted message and the key, she will not be able to read the message. Bob is not smart. Don't be like Bob.
In the above example, Bob may have, for instance, selected a permutation (3, 4, 1, 2) and stored the permuted key P = (6, 3, 16, 7).
One year has passed and Alice wants to decrypt her message. Only now Bob has realised that this is impossible. As he has permuted the key randomly, the message is lost forever. Did we mention that Bob isn't smart?
Bob wants to salvage at least some information from the message. Since he is not so smart, he asks for your help. You know the encrypted message A and the permuted key P. What is the lexicographically smallest message that could have resulted in the given encrypted text?
More precisely, for given A and P, find the lexicographically smallest message O, for which there exists a permutation π such that 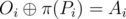 for every i.
for every i.
Note that the sequence S is lexicographically smaller than the sequence T, if there is an index i such that Si < Ti and for all j < i the condition Sj = Tj holds.
The first line contains a single integer N (1 ≤ N ≤ 300000), the length of the message.
The second line contains N integers A1, A2, ..., AN (0 ≤ Ai < 230) representing the encrypted message.
The third line contains N integers P1, P2, ..., PN (0 ≤ Pi < 230) representing the permuted encryption key.
Output a single line with N integers, the lexicographically smallest possible message O. Note that all its elements should be non-negative.
3
8 4 13
17 2 7
10 3 28
5
12 7 87 22 11
18 39 9 12 16
0 14 69 6 44
10
331415699 278745619 998190004 423175621 42983144 166555524 843586353 802130100 337889448 685310951
226011312 266003835 342809544 504667531 529814910 684873393 817026985 844010788 993949858 1031395667
128965467 243912600 4281110 112029883 223689619 76924724 429589 119397893 613490433 362863284
In the first case, the solution is (10, 3, 28), since 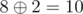 ,
, 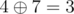 and
and 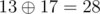 . Other possible permutations of key yield messages (25, 6, 10), (25, 3, 15), (10, 21, 10), (15, 21, 15) and (15, 6, 28), which are all lexicographically larger than the solution.
. Other possible permutations of key yield messages (25, 6, 10), (25, 3, 15), (10, 21, 10), (15, 21, 15) and (15, 6, 28), which are all lexicographically larger than the solution.
D是裸的01字典树?我不会啊
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+;
int cnt[N*],nt[N*][];
int tot=,k;
long long ans=;
int a[N],b[N];
void Insert(int a,int st,int rt)
{
cnt[rt]++;
if (st==-)return ;
int pos=(a>>st)&;
if (!nt[rt][pos])nt[rt][pos]=tot++;
Insert(a,st-,nt[rt][pos]);
}
void Find(int rt,int st)
{
cnt[rt]--;
if(st==-)
{
return;
}
int lim=(k>>st)&;
if (nt[rt][lim]&&cnt[nt[rt][lim]])Find(nt[rt][lim],st-);
else Find(nt[rt][lim^],st-),ans^=(<<st);
return ;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=; i<n; i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]),Insert(b[i],,);
for (int i=; i<n; i++)
{
ans=,k=a[i];
Find(,);
printf("%d ",ans);
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #470 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 1)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #470 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 1)A. Protect Sheep
http://codeforces.com/contest/948/problem/A A. Protect Sheep Bob is a farmer. He has a large pastu ...
- Codeforces Round #470 (rated, Div. 1, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 1) 923D 947D 948E D. Picking Strings
题: OvO http://codeforces.com/contest/947/problem/D 923D 947D 948E 解: 记要改变的串为 P1 ,记目标串为 P2 由变化规则可得: ...
- Codeforces Round #470 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 1) C.Producing Snow
题目链接 题意 每天有体积为Vi的一堆雪,所有存在的雪每天都会融化Ti体积,求出每天具体融化的雪的体积数. 分析 对于第i天的雪堆,不妨假设其从一开始就存在,那么它的初始体积就为V[i]+T[1. ...
- Codeforces Round #470 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 1)B. Primal Sport
Alice and Bob begin their day with a quick game. They first choose a starting number X0 ≥ 3 and try ...
- Codeforces Round #477 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 3) F 构造
http://codeforces.com/contest/967/problem/F 题目大意: 有n个点,n*(n-1)/2条边的无向图,其中有m条路目前开启(即能走),剩下的都是关闭状态 定义: ...
- Codeforces Round #477 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 3) E 贪心
http://codeforces.com/contest/967/problem/E 题目大意: 给你一个数组a,a的长度为n 定义:b(i) = a(1)^a(2)^......^a(i), 问, ...
- Codeforces Round #477 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 3) D 贪心
http://codeforces.com/contest/967/problem/D 题目大意: 有n个服务器,标号为1~n,每个服务器有C[i]个资源.现在,有两个任务需要同时进行,令他为x1,x ...
- 【枚举】【二分】Codeforces Round #477 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 3) D. Resource Distribution
题意:有两个服务要求被满足,服务S1要求x1数量的资源,S2要求x2数量的资源.有n个服务器来提供资源,第i台能提供a[i]的资源.当你选择一定数量的服务器来为某个服务提供资源后,资源需求会等量地分担 ...
- 【推导】【贪心】Codeforces Round #472 (rated, Div. 2, based on VK Cup 2018 Round 2) D. Riverside Curio
题意:海平面每天高度会变化,一个人会在每天海平面的位置刻下一道痕迹(如果当前位置没有已经刻划过的痕迹),并且记录下当天比海平面高的痕迹有多少条,记为a[i].让你最小化每天比海平面低的痕迹条数之和. ...
随机推荐
- 获取cell中的button在整个屏幕上的位置
编写cell中得button点击事件 - (IBAction)showButtonClick:(id)sender { UIButton *button = (UIButton *)sender; U ...
- uvm_reg_fifo——寄存器模型(十五)
当我们对寄存器register, 存储器memory, 都进行了建模,是时候对FIFO进行建模了 uvm_reg_fifo毫无旁贷底承担起了这个责任,包括:set, get, update, read ...
- python中的getcwd
Help on built-in function getcwd in module posix: getcwd(...) getcwd() -> path Return a ...
- ERROR 2013 (HY000): Lost connection to MySQL server at 'reading authorization packet', system error: 0
最近遇到一个MySQL连接的问题,远程连接MySQL时遇到"ERROR 2013 (HY000): Lost connection to MySQL server at 'reading a ...
- CAS 配置NLB 负载均衡网络无法连接
在虚拟机与虚拟机.虚拟机与实机之间利用Windows操作系统自带的网络负载均衡功能如选择单播集群模式,网络就无法通讯,NLB不成功. Scenario #1 在虚拟机与虚拟机之间选择多播模式NLB可正 ...
- Python+selenium之fixtures
fixtures即可以表示测试用例的开始和结束,也可以表示测试类和测试模块的开始和结束. import unittest def setUpModule(): print("test mod ...
- Java 集合框架_中
Set接口 特点: [1]Set接口表示一个唯一.无序的容器(和添加顺序无关) Set接口常用实现类有 HashSet [1]HashSet是Set接口的实现类,底层数据结构是哈希表. [2]Hash ...
- python_79_模块定义导入优化
''' 1.定义 模块:用来从逻辑上组织python代码(变量,函数,类,逻辑:实现一个功能),本质就是.py结尾的python文件 (文件名:test.py,对应的模块名:test. import ...
- DB2中创建表
CONNECT TO TEST; CREATE TABLE DB2ADMIN.PERSON ( ID BIGINT NOT NULL , NAME BIGINT , FLAG BIGINT , ADD ...
- Bootstrap历练实例:向列表组添加内容
向列表组添加自定义内容 我们可以向上面已添加链接的列表组添加任意的 HTML 内容.下面的实例演示了这点: <!DOCTYPE html><html><head>& ...
