rovio视觉里程计的笔记
rovio是一个紧耦合,基于图像块的滤波实现的VIO。
他的优点是:计算量小(EKF,稀疏的图像块),但是对应不同的设备需要调参数,参数对精度很重要。没有闭环,没有mapping thread。经常存在误差会残留到下一时刻。
我试了一些设备,要是精度在几十厘米,设备运动不快的,一般摄像头加一般imu,不是硬件同步就是正常的rostopic 发布的时间,也能达到。
代码主要分为EKF实现的部分,和算法相关的部分,EKF是作者自己写的一个框架。先分析EKF代码
lightweight_filtering
FilterBase.hpp
template<typename Meas>
class MeasurementTimeline{
typedef Meas mtMeas;
//imu测量的数据存在map中,相当于一个buffer,key是时间,value 是加速度或者角速度或者图像金字塔
std::map<double,mtMeas> measMap_;
void addMeas(const mtMeas& meas,const double &t);
}
EKF的整个流程框架
template<typename Prediction,typename... Updates>
class FilterBase: public PropertyHandler{
//imu和图像的两个MeasurementTimeline
MeasurementTimeline<typename mtPrediction::mtMeas> predictionTimeline_;
std::tuple<MeasurementTimeline<typename Updates::mtMeas>...> updateTimelineTuple_;
//加入imu测量值
void addPredictionMeas(const typename Prediction::mtMeas& meas, double t){
if(t<= safeWarningTime_) {
std::cout << "[FilterBase::addPredictionMeas] Warning: included measurements at time " << t << " before safeTime " << safeWarningTime_ << std::endl;
}
if(t<= frontWarningTime_) gotFrontWarning_ = true;
predictionTimeline_.addMeas(meas,t);
}
//图像的MeasurementTimeline
template<int i>
void addUpdateMeas(const typename std::tuple_element<i,decltype(mUpdates_)>::type::mtMeas& meas, double t){
if(t<= safeWarningTime_) {
std::cout << "[FilterBase::addUpdateMeas] Warning: included measurements at time " << t << " before safeTime " << safeWarningTime_ << std::endl;
}
if(t<= frontWarningTime_) gotFrontWarning_ = true;
std::get<i>(updateTimelineTuple_).addMeas(meas,t);
}
//根据传入时间进行EKF的更新
void updateSafe(const double *maxTime = nullptr){
//根据最新的imu测量时间,得到最近的图像测量的时间,nextSafeTime返回的是最新的图像测量时间
bool gotSafeTime = getSafeTime(nextSafeTime);
update(safe_,nextSafeTime);
//清楚safetime之前的数据,但是至少留下一个测量量
clean(safe_.t_);
}
void update(mtFilterState& filterState,const double& tEnd){
while(filterState.t_ < tEnd){
tNext = tEnd;
//要是上一次更新之后,没有新的图像来到,就不要更新了
if(!getNextUpdate(filterState.t_,tNext) && updateToUpdateMeasOnly_){
break; // Don't go further if there is no update available
}
int r = 0;
//参数usePredictionMerge_是不是设置,对应的是EKF中的预测方程的f(x)设置的不一样,看代码就知道
if(filterState.usePredictionMerge_){
r = mPrediction_.predictMerged(filterState,tNext,predictionTimeline_.measMap_);
if(r!=0) std::cout << "Error during predictMerged: " << r << std::endl;
logCountMerPre_++;
} else {
while(filterState.t_ < tNext && (predictionTimeline_.itMeas_ = predictionTimeline_.measMap_.upper_bound(filterState.t_)) != predictionTimeline_.measMap_.end()){
r = mPrediction_.performPrediction(filterState,predictionTimeline_.itMeas_->second,std::min(predictionTimeline_.itMeas_->first,tNext)-filterState.t_);
if(r!=0) std::cout << "Error during performPrediction: " << r << std::endl;
logCountRegPre_++;
}
}
// imu和图像的时间戳不是对齐的,存在偏差,这一段时间的imu也要做EKF预测
if(filterState.t_ < tNext){
r = mPrediction_.performPrediction(filterState,tNext-filterState.t_);
if(r!=0) std::cout << "Error during performPrediction: " << r << std::endl;
logCountBadPre_++;
}
// 图像的更新
doAvailableUpdates(filterState,tNext);
}
}
}
Prediction.hpp
int predictMerged(mtFilterState& filterState, double tTarget,const std::map<double, mtMeas>& measMap) {
switch (filterState.mode_) {
case ModeEKF:
return predictMergedEKF(filterState, tTarget, measMap);
case ModeUKF:
return predictMergedUKF(filterState, tTarget, measMap);
case ModeIEKF:
return predictMergedEKF(filterState, tTarget, measMap);
default:
return predictMergedEKF(filterState, tTarget, measMap);
}
}
virtual int predictMergedEKF(mtFilterState& filterState,const double tTarget, const std::map<double, mtMeas>& measMap)
{
const typename std::map<double, mtMeas>::const_iterator itMeasStart = measMap.upper_bound(filterState.t_);
if (itMeasStart == measMap.end())
return 0;
typename std::map<double, mtMeas>::const_iterator itMeasEnd = measMap.lower_bound(tTarget);
if (itMeasEnd != measMap.end())
++itMeasEnd;
double dT = std::min(std::prev(itMeasEnd)->first, tTarget) - filterState.t_;
if (dT <= 0)
return 0;
// Compute mean Measurement
mtMeas meanMeas;
typename mtMeas::mtDifVec vec;
typename mtMeas::mtDifVec difVec;
vec.setZero();
double t = itMeasStart->first;
for (typename std::map<double, mtMeas>::const_iterator itMeas = next(itMeasStart);
itMeas != itMeasEnd; itMeas++) {
itMeasStart->second.boxMinus(itMeas->second, difVec);
//这个是应该是减的
vec = vec - difVec * (std::min(itMeas->first, tTarget) - t);
t = std::min(itMeas->first, tTarget);
}
vec = vec / dT;
//得到这段时间的imu平均测量
itMeasStart->second.boxPlus(vec, meanMeas);
preProcess(filterState, meanMeas, dT);
meas_ = meanMeas;
//雅可比矩阵的求解
this->jacPreviousState(filterState.F_, filterState.state_, dT);
this->jacNoise(filterState.G_, filterState.state_, dT); // Works for time continuous parametrization of noise
for (typename std::map<double, mtMeas>::const_iterator itMeas =
itMeasStart; itMeas != itMeasEnd; itMeas++) {
meas_ = itMeas->second;
this->evalPredictionShort(filterState.state_, filterState.state_,
std::min(itMeas->first, tTarget) - filterState.t_);
filterState.t_ = std::min(itMeas->first, tTarget);
}
filterState.cov_ = filterState.F_ * filterState.cov_
* filterState.F_.transpose()
+ filterState.G_ * prenoiP_ * filterState.G_.transpose();
filterState.state_.fix();
enforceSymmetry(filterState.cov_);
filterState.t_ = std::min(std::prev(itMeasEnd)->first, tTarget);
postProcess(filterState, meanMeas, dT);
return 0;
}
update.hpp
int performUpdateEKF(mtFilterState& filterState, const mtMeas& meas) {
meas_ = meas;
if (!useSpecialLinearizationPoint_) {
this->jacState(H_, filterState.state_);
Hlin_ = H_;
this->jacNoise(Hn_, filterState.state_);
this->evalInnovationShort(y_, filterState.state_);
} else {
filterState.state_.boxPlus(filterState.difVecLin_, linState_);
this->jacState(H_, linState_);
if (useImprovedJacobian_) {
filterState.state_.boxMinusJac(linState_, boxMinusJac_);
Hlin_ = H_ * boxMinusJac_;
} else {
Hlin_ = H_;
}
this->jacNoise(Hn_, linState_);
this->evalInnovationShort(y_, linState_);
}
if (isCoupled) {
C_ = filterState.G_ * preupdnoiP_ * Hn_.transpose();
Py_ = Hlin_ * filterState.cov_ * Hlin_.transpose()
+ Hn_ * updnoiP_ * Hn_.transpose() + Hlin_ * C_
+ C_.transpose() * Hlin_.transpose();
} else {
Py_ = Hlin_ * filterState.cov_ * Hlin_.transpose() + Hn_ * updnoiP_ * Hn_.transpose();
}
y_.boxMinus(yIdentity_, innVector_);
// Outlier detection // TODO: adapt for special linearization point
//根据方差和residual的乘积是否超多阀值判断outlier
outlierDetection_.doOutlierDetection(innVector_, Py_, Hlin_);
Pyinv_.setIdentity();
Py_.llt().solveInPlace(Pyinv_);
if(outlierDetection_.isOutlier(0)){
LOG(INFO) << "innovation vector: " << innVector_(0) << " , " << innVector_(1);
// LOG(INFO) << "covariance :\n " << Py_.block(0,0,2,2);
}
// Kalman Update
if (isCoupled) {
K_ = (filterState.cov_ * Hlin_.transpose() + C_) * Pyinv_;
} else {
K_ = filterState.cov_ * Hlin_.transpose() * Pyinv_;
}
filterState.cov_ = filterState.cov_ - K_ * Py_ * K_.transpose();
if (!useSpecialLinearizationPoint_) {
updateVec_ = -K_ * innVector_;
} else {
filterState.state_.boxMinus(linState_, difVecLinInv_);
updateVec_ = -K_ * (innVector_ + H_ * difVecLinInv_); // includes correction for offseted linearization point, dif must be recomputed (a-b != (-(b-a)))
}
filterState.state_.boxPlus(updateVec_, filterState.state_);
// LOG(INFO) << "updateVec pos vel:\n " << updateVec_.block(0,0,6,1).transpose();
return 0;
}
State.hpp
旋转量使用四元数表示是4个自由度,但是旋转只要3个自由度表示,要用李代数表示。
这个是bearing vector的参数表示方式。在tangent space 中表示,这部分我只理解部分。具体的可以参考作者的博士论文,最后一章。
class NormalVectorElement: public ElementBase<NormalVectorElement,NormalVectorElement,2>{
public:
QPD q_;
NormalVectorElement(const V3D& vec): e_x(1,0,0), e_y(0,1,0), e_z(0,0,1){
setFromVector(vec); //就是vec和e_z之间的旋转变换
}
void setFromVector(V3D vec){
const double d = vec.norm();
if(d > 1e-6){
vec = vec/d;
q_ = q_.exponentialMap(getRotationFromTwoNormals(e_z,vec,e_x));
} else {
q_.setIdentity();
}
}
// z轴跟bearing vector之间的旋转变换
static V3D getRotationFromTwoNormals(const V3D& a, const V3D& b, const V3D& a_perp) {
const V3D cross = a.cross(b);
const double crossNorm = cross.norm();
const double c = a.dot(b);
const double angle = std::acos(c);
if (crossNorm < 1e-6) {
//0度
if (c > 0) {
return cross;
} else {//180 度
return a_perp * M_PI;
}
} else {//\theta a 旋转轴+旋转角的表示
return cross * (angle / crossNorm);
}
}
V3D getVec() const{
return q_.rotate(e_z);
}
V3D getPerp1() const{
return q_.rotate(e_x);
}
V3D getPerp2() const{
return q_.rotate(e_y);
}
Eigen::Matrix<double,3,2> getN() const {
Eigen::Matrix<double,3,2> M;
M.col(0) = getPerp1();
M.col(1) = getPerp2();
return M;
}
}
rovio
博士论文的最后一章对算法的bearing vector的公式详细的推导了。
这部分主要是算法的部分。
RovioNode.hpp
template<typename FILTER>
class RovioNode{
struct FilterInitializationState {
FilterInitializationState()
: WrWM_(V3D::Zero()),
//使用加速度进行初始化的方向确定
state_(State::WaitForInitUsingAccel) {}
};
void imuCallback(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& imu_msg){
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m_filter_);
predictionMeas_.template get<mtPredictionMeas::_acc>() = Eigen::Vector3d(imu_msg->linear_acceleration.x,imu_msg->linear_acceleration.y,imu_msg->linear_acceleration.z);
predictionMeas_.template get<mtPredictionMeas::_gyr>() = Eigen::Vector3d(imu_msg->angular_velocity.x,imu_msg->angular_velocity.y,imu_msg->angular_velocity.z);
if(init_state_.isInitialized()){
//
mpFilter_->addPredictionMeas(predictionMeas_,imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec());
updateAndPublish();
} else {
switch(init_state_.state_) {
case FilterInitializationState::State::WaitForInitExternalPose: {
std::cout << "-- Filter: Initializing using external pose ..." << std::endl;
mpFilter_->resetWithPose(init_state_.WrWM_, init_state_.qMW_, imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec());
break;
}
case FilterInitializationState::State::WaitForInitUsingAccel: {
std::cout << "-- Filter: Initializing using accel. measurement ..." << std::endl;
mpFilter_->resetWithAccelerometer(predictionMeas_.template get<mtPredictionMeas::_acc>(),imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec());
break;
}
default: {
std::cout << "Unhandeld initialization type." << std::endl;
abort();
break;
}
}
std::cout << std::setprecision(12);
std::cout << "-- Filter: Initialized at t = " << imu_msg->header.stamp.toSec() << std::endl;
init_state_.state_ = FilterInitializationState::State::Initialized;
}
}
void imgCallback(const sensor_msgs::ImageConstPtr & img, const int camID = 0){
// Get image from msg
cv_bridge::CvImagePtr cv_ptr;
try {
cv_ptr = cv_bridge::toCvCopy(img, sensor_msgs::image_encodings::TYPE_8UC1);
} catch (cv_bridge::Exception& e) {
ROS_ERROR("cv_bridge exception: %s", e.what());
return;
}
cv::Mat cv_img;
cv_ptr->image.copyTo(cv_img);
if(init_state_.isInitialized() && !cv_img.empty()){
double msgTime = img->header.stamp.toSec();
if(msgTime != imgUpdateMeas_.template get<mtImgMeas::_aux>().imgTime_){
for(int i=0;i<mtState::nCam_;i++){
if(imgUpdateMeas_.template get<mtImgMeas::_aux>().isValidPyr_[i]){
std::cout << " \033[31mFailed Synchronization of Camera Frames, t = " << msgTime << "\033[0m" << std::endl;
}
}
imgUpdateMeas_.template get<mtImgMeas::_aux>().reset(msgTime);
}
imgUpdateMeas_.template get<mtImgMeas::_aux>().pyr_[camID].computeFromImage(cv_img,true);
imgUpdateMeas_.template get<mtImgMeas::_aux>().isValidPyr_[camID] = true;
if(imgUpdateMeas_.template get<mtImgMeas::_aux>().areAllValid()){
mpFilter_->template addUpdateMeas<0>(imgUpdateMeas_,msgTime);
imgUpdateMeas_.template get<mtImgMeas::_aux>().reset(msgTime);
updateAndPublish();
}
}
}
}
ImuPrediction.hpp
公式的推导可以参考的论文,
A Primer on the Differential Calculus of 3D Orientations
\sideset{_I\,}{_{IB}}{\overline r} = \sideset{_I\,}{_{IB}}r + \Delta t \Phi _{IB}(\sideset {_B\,}{_B}{v} + \sideset{_B\,}{_v}{n})
\label{eq:position}
\end{equation}
\]
\sideset {_B\,}{_B}{ \overline v} = \sideset {_B\,}{_B}{v} + \Delta t (\Phi {_{IB}^{-1}} (g) + f - {w^{\times}}_{B}v_{B})
\label{eq:velocity}
\end{equation}
\]
{\overline \Phi} _{IB} = \Phi _{IB} \circ exp(\Delta t \omega)
\label{eq:orientation}
\end{equation}
\]
\sideset {_B\,}{_f}{\overline b} = \sideset {_B\,}{_f}b + \Delta t \sideset{_B \,}{_{bf}} n
\label{eq:noise1}
\end{equation}
\]
\sideset {_B\,}{_ \omega}{\overline b} = \sideset {_B\,}{_ \omega}b + \Delta t \sideset{_B \,}{_{b\omega}} n
\label{eq:noise2}
\end{equation}
\]
{\mu _{i}}' = N^T(\mu _{i}) \hat {\omega} _{v} -
\begin{bmatrix}
0 & 1 \\
-1 & 0
\end{bmatrix}
N^T(\mu _i) \frac{\hat v_{v}}{d (\rho _i)} + \omega _{\mu , i} \text{ , bearing vector}
\label{eq:bearingVector}
\end{equation}
\]
{\rho _i}' = \frac{d \rho}{dt} = \frac{d \rho}{d d} \frac{d d}{dt} = \frac{ -\mu_i^T \hat{v_v}}{d'(\rho _i)} + \omega_{\rho,i} \text{, inverse distance}
\label{eq:inversedistance}
\end{equation}
\]
template<typename FILTERSTATE>
class ImuPrediction: public LWF::Prediction<FILTERSTATE>{
{
void evalPrediction(mtState& output, const mtState& state, const mtNoise& noise, double dt) const
{
output.aux().MwWMmeas_ = meas_.template get<mtMeas::_gyr>();
output.aux().MwWMest_ = meas_.template get<mtMeas::_gyr>()-state.gyb();
const V3D imuRor = output.aux().MwWMest_+noise.template get<mtNoise::_att>()/sqrt(dt);
const V3D dOmega = dt*imuRor;
QPD dQ = dQ.exponentialMap(dOmega);
for(unsigned int i=0;i<mtState::nMax_;i++){
const int camID = state.CfP(i).camID_;
if(&output != &state){
output.CfP(i) = state.CfP(i);
output.dep(i) = state.dep(i);
}
if(camID >= 0 && camID < mtState::nCam_){
//cam的角速度,在camera 坐标系
const V3D camRor = state.qCM(camID).rotate(imuRor);
//这里的速度取了负号,camera 速度,在camera 坐标系
const V3D camVel = state.qCM(camID).rotate(V3D(imuRor.cross(state.MrMC(camID))-state.MvM()));
oldC_ = state.CfP(i);
oldD_ = state.dep(i);
//公式7的离散公式,一阶积分
output.dep(i).p_ = oldD_.p_-dt*oldD_.getParameterDerivative()*oldC_.get_nor().getVec().transpose()*camVel + noise.template get<mtNoise::_fea>(i)(2)*sqrt(dt);
V3D dm = -dt*(gSM(oldC_.get_nor().getVec())*camVel/oldD_.getDistance()
+ (M3D::Identity()-oldC_.get_nor().getVec()*oldC_.get_nor().getVec().transpose())*camRor)
+ oldC_.get_nor().getN()*noise.template get<mtNoise::_fea>(i).template block<2,1>(0,0)*sqrt(dt);
QPD qm = qm.exponentialMap(dm);
output.CfP(i).set_nor(oldC_.get_nor().rotated(qm));
// WARP corners
if(state.CfP(i).trackWarping_){
bearingVectorJac_ = output.CfP(i).get_nor().getM().transpose()*(dt*gSM(qm.rotate(oldC_.get_nor().getVec()))*Lmat(dm)*(
-1.0/oldD_.getDistance()*gSM(camVel)
- (M3D::Identity()*(oldC_.get_nor().getVec().dot(camRor))+oldC_.get_nor().getVec()*camRor.transpose()))
+MPD(qm).matrix())*oldC_.get_nor().getM();
output.CfP(i).set_warp_nor(bearingVectorJac_*oldC_.get_warp_nor());
}
}
}
// 上面的1-5公式
output.WrWM() = state.WrWM()-dt*(state.qWM().rotate(state.MvM())-noise.template get<mtNoise::_pos>()/sqrt(dt));
output.MvM() = (M3D::Identity()-gSM(dOmega))*state.MvM()-dt*(meas_.template get<mtMeas::_acc>()-state.acb()+state.qWM().inverseRotate(g_)-noise.template get<mtNoise::_vel>()/sqrt(dt));
output.acb() = state.acb()+noise.template get<mtNoise::_acb>()*sqrt(dt);
output.gyb() = state.gyb()+noise.template get<mtNoise::_gyb>()*sqrt(dt);
output.qWM() = state.qWM()*dQ;
//camera 和imu 的外参数
for(unsigned int i=0;i<mtState::nCam_;i++){
output.MrMC(i) = state.MrMC(i)+noise.template get<mtNoise::_vep>(i)*sqrt(dt);
dQ = dQ.exponentialMap(noise.template get<mtNoise::_vea>(i)*sqrt(dt));
output.qCM(i) = state.qCM(i)*dQ;
}
output.aux().wMeasCov_ = prenoiP_.template block<3,3>(mtNoise::template getId<mtNoise::_att>(),mtNoise::template getId<mtNoise::_att>())/dt;
output.fix();
}
}
ImgUpdate.hpp
- Stack all photometric error terms into a vector b, you get b(p)
- Linearize the error around \(\hat{p}\), you get \(b(dp) = b(\hat{p}) + A(\hat{p}) dp\)
- Set it to zero and solve for dp, you get the equation $-b(\hat{p}) = A(\hat{p}) dp $
template<typename FILTERSTATE>
class ImgUpdate: public LWF::Update<ImgInnovation<typename FILTERSTATE::mtState>,FILTERSTATE,ImgUpdateMeas<typename FILTERSTATE::mtState>,ImgUpdateNoise<typename FILTERSTATE::mtState>,
ImgOutlierDetection<typename FILTERSTATE::mtState>,false>{
void preProcess(mtFilterState& filterState, const mtMeas& meas, bool& isFinished){
}
void evalInnovation(mtInnovation& y, const mtState& state, const mtNoise& noise) const{
Eigen::Vector2d pixError;
pixError(0) = static_cast<double>(state.aux().feaCoorMeas_[ID].get_c().x - featureOutput_.c().get_c().x);
pixError(1) = static_cast<double>(state.aux().feaCoorMeas_[ID].get_c().y - featureOutput_.c().get_c().y);
y.template get<mtInnovation::_pix>() = pixError + noise.template get<mtNoise::_pix>();
}
}
world坐标和imu坐标的关系
template<unsigned int nMax, int nLevels, int patchSize,int nCam,int nPose>
class FilterState: public LWF::FilterState<State<nMax,nLevels,patchSize,nCam,nPose>,
PredictionMeas,PredictionNoise<State<nMax,nLevels,patchSize,nCam,nPose>>,0>{
void initWithAccelerometer(const V3D& fMeasInit) {
V3D unitZ(0, 0, 1);
if (fMeasInit.norm() > 1e-6) {
state_.qWM().setFromVectors(fMeasInit, unitZ);
} else {
state_.qWM().setIdentity();
}
}
图像部分主要的代码是
MultilevelPatchAlignement.hpp
这里就是一个高斯牛顿法优化,目标点的位置。
bool align2D(FeatureCoordinates& cOut, const ImagePyramid<nLevels>& pyr, const MultilevelPatch<nLevels,patch_size>& mp,
const FeatureCoordinates& cInit ,const int l1, const int l2, const int maxIter = 10, const double minPixUpd = 0.03){
for(int iter = 0; iter<maxIter; ++iter){
if(std::isnan(cOut.get_c().x) || std::isnan(cOut.get_c().y)){
assert(false);
return false;
}
if(!getLinearAlignEquations(pyr,mp,cOut,l1,l2,A_,b_)){
return false;
}
svd_.compute(A_, Eigen::ComputeThinU | Eigen::ComputeThinV);
if(svd_.nonzeroSingularValues()<2){
return false;
}
update = svd_.solve(b_);
cOut.set_c(cv::Point2f(cOut.get_c().x + update[0],cOut.get_c().y + update[1]),false);
s = update[0]*update[0]+update[1]*update[1];
if(s < min_update_squared){
converged=true;
break;
}
}
}
//这个函数就是上面那个怎么构造图像块像素差作为EKF的更新
bool getLinearAlignEquations(const ImagePyramid<nLevels>& pyr, const MultilevelPatch<nLevels,patch_size>& mp,
const FeatureCoordinates& c, const int l1, const int l2,
Eigen::MatrixXf& A, Eigen::MatrixXf& b){
}
总结
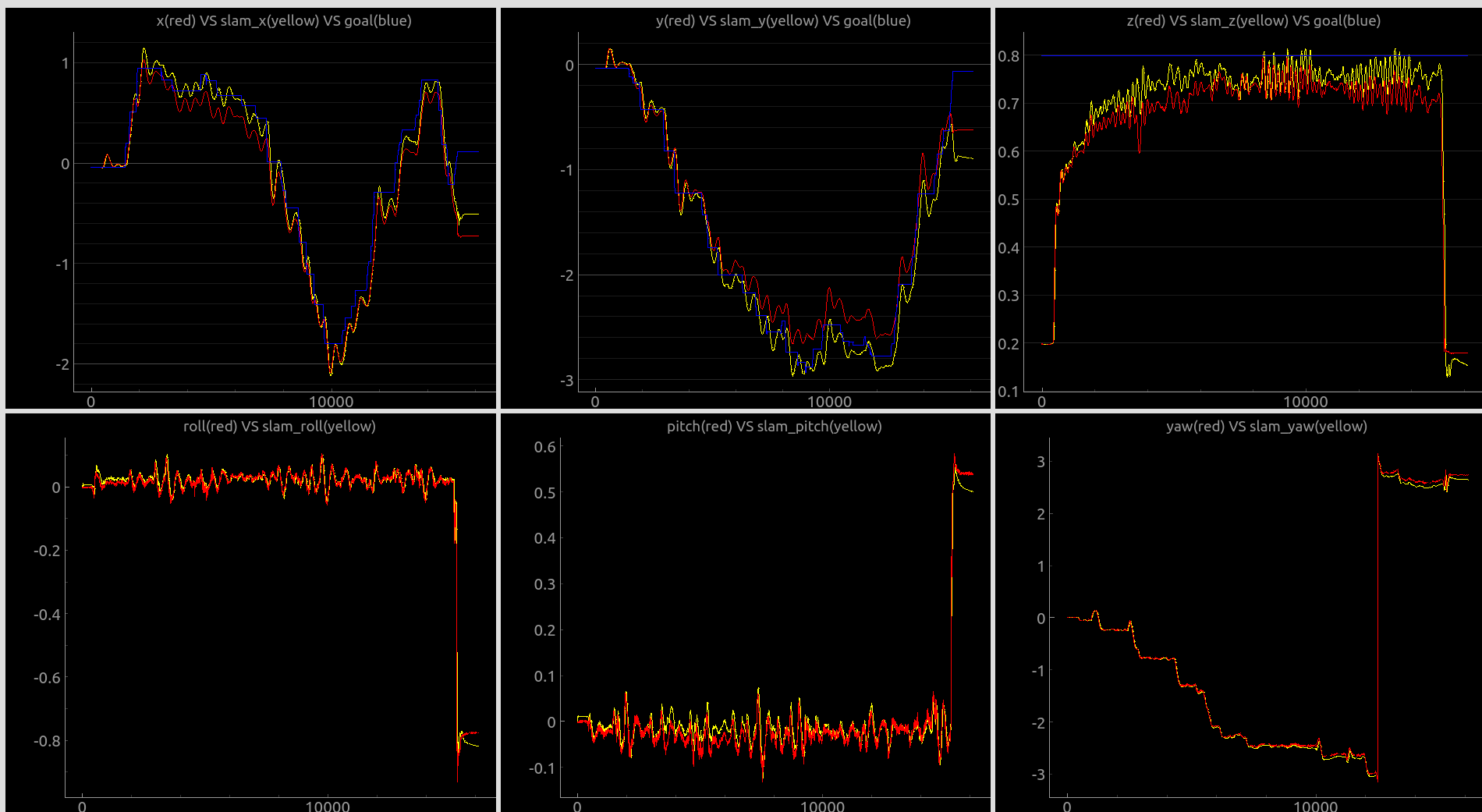
上面是我自己的无人机跑的和真实的运动捕捉系统的对比,是比较好的数据。说明在调的比较好的数据下是可以得到不错的效果。(红色是vrpn,黄色是rovio,蓝色是我给飞机的设定点,红色和黄色的差距还行,有时候比较大)
我使用的是EKF的优化是特征点位置,要是换成IEKF,优化图像块的像素差,可能效果会更好。毕竟这东西是个高度非线性函数。
那个bearing vector的公式我还不会推导,对新增的feature 的initial depth的比较精确的估计对算法精度有帮助,可以维护个地图,
当然在地图中做个local mapping thread, 也是可以的,但是感觉不能很好的和原来的算法耦合起来就没做。
这里最需要改进的应该是特征点的选取,原来算法的效率太低了。而且会发现选取的很多特征点不是那么明显的角点,有更好的选择,不过为了保持距离的限制,妥协了。还有就是速度太慢了。
出现发散的情况,一般就是outlier太多了,没有追踪足够的特征点。因为速度发散,会导致图像更新为了矫正在特征点深度位置上存在巨大的错误速度,把深度设到
无穷远去,这样图像更新就没有作用,进一步导致速度发散。一发散就不可能回来了。
rovio视觉里程计的笔记的更多相关文章
- rovio 视觉里程计的笔记
rovio是一个紧耦合,基于图像块的滤波实现的VIO. 他的优点是:计算量小(EKF,稀疏的图像块),但是对应不同的设备需要调参数,参数对精度很重要.没有闭环,没有mapping thread.经常存 ...
- 关于视觉里程计以及VI融合的相关研究(长期更新)
1. svo 源码:https://github.com/uzh-rpg/rpg_svo 国内对齐文章源码的研究: (1)冯斌: 对其代码重写 https://github.com/yueying/O ...
- SLAM入门之视觉里程计(2):相机模型(内参数,外参数)
相机成像的过程实际是将真实的三维空间中的三维点映射到成像平面(二维空间)过程,可以简单的使用小孔成像模型来描述该过程,以了解成像过程中三维空间到二位图像空间的变换过程. 本文包含两部分内容,首先介绍小 ...
- SLAM入门之视觉里程计(5):单应矩阵
在之前的博文OpenCV,计算两幅图像的单应矩阵,介绍调用OpenCV中的函数,通过4对对应的点的坐标计算两个图像之间单应矩阵\(H\),然后调用射影变换函数,将一幅图像变换到另一幅图像的视角中.当时 ...
- SLAM入门之视觉里程计(1):特征点的匹配
SLAM 主要分为两个部分:前端和后端,前端也就是视觉里程计(VO),它根据相邻图像的信息粗略的估计出相机的运动,给后端提供较好的初始值.VO的实现方法可以根据是否需要提取特征分为两类:基于特征点的方 ...
- (3)视觉里程计 Visual Odometry
首先分析include头文件下的slamBase.h文件 # pragma once // 各种头文件 // C++标准库 #include <fstream> #include < ...
- 第三篇 视觉里程计(VO)的初始化过程以及openvslam中的相关实现详解
视觉里程计(Visual Odometry, VO),通过使用相机提供的连续帧图像信息(以及局部地图,先不考虑)来估计相邻帧的相机运动,将这些相对运行转换为以第一帧为参考的位姿信息,就得到了相机载体( ...
- 视觉slam十四讲个人理解(ch7视觉里程计1)
参考博文::https://blog.csdn.net/david_han008/article/details/53560736 https://blog.csdn.net/n66040927/ar ...
- SLAM——视觉里程计(一)feature
从现在开始下面两篇文章来介绍SLAM中的视觉里程计(Visual Odometry).这个是我们正式进入SLAM工程的第一步,而之前介绍的更多的是一些基础理论.视觉里程计完成的事情是视觉里程计VO的目 ...
随机推荐
- [译文]c#扩展方法(Extension Method In C#)
原文链接: https://www.codeproject.com/Tips/709310/Extension-Method-In-Csharp 介绍 扩展方法是C# 3.0引入的新特性.扩展方法使你 ...
- 微信公众号开发笔记1(nodejs开发)
本篇记录了微信公众号开发的一些笔记 一.微信服务器与我们服务器的交流 微信开发者拥有自己的服务器,在我们服务器上可以与微信服务器进行交流.既然可以交流,那就必定需要前提条件(微信认证),也就是说,只有 ...
- iOS开发学习-资源打包
图片是被放到Images.xcassets中 1.部署版本在>=iOS8的时候,打包的资源包中的图片会被放到Assets.car 图片被压缩: 2.部署版本在<iOS8的时候,打包的资源包 ...
- Task 4.4二维环形数组求最大子矩阵之和
任务: (1)输入一个二维整形数组,数组里有正数也有负数. (2)二维数组首尾相接,象个一条首尾相接带子一样. (3)数组中连续的一个或多个整数组成一个子数组,每个子数组都有一个和. (4)求所有子数 ...
- 【CS231N】4、神经网络
一.疑问 二.常用激活函数 1. Sigmoid sigmoid将输入实数值"挤压"到0到1范围内.更具体地说,很大的负数变成0,很大的正数变成1.它对于神经元的激活频率有良好 ...
- 结对作业-四则运算GUI
目录: 一.项目地址二.PSP三.接口设计四.计算模块接口的设计与实现过程五.计算模块接口部分的性能改进六.计算模块部分单元测试展示七.计算模块部分异常处理说明八.界面模块的详细设计过程九.界面模块与 ...
- String 类 常用函数
构造方法摘要: String(byte[] bytes) 通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String. String(char[] value) ...
- angularJS1笔记-(2)-$watch方法监听变量的变化
html: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF ...
- [转]string和stringstream用法总结
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/xw20084898/article/details/21939811 作者:xw20084898 一.string string 是 C++ 提供的字 ...
- node 加密音频文件 和 解密音频文件
fs.readFile('./downsuccess/'+name+'', {flag: 'r+', encoding: ''}, function (err, data) { c ...
