spring---aop(2)---Spring AOP的JDK动态代理
写在前面
spring 事务是springAOP 的一个实现。我们以分析spring的事务,来分析spring的AOP实现。
基本知识
如果目标方法被spring的事务声明,则执行该目标方法的对象就会是spring动态生成的代理对象。如果目标方法的类有接口实现,那么产生的是jdk的动态代理,反之则是CGLIB。(使用了抽象工厂模式)
代理对象产生过程(以JDK为参考)
1. 产生代理对象的过程是在spring加载的过程中。(一个代理对象和一个InvocationHandler绑定,当代理对象的方法执行时,就会去执行InvocationHandler的invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)方法),在该方法中你可以现在是否处理代理对象的目标方法。
代理对象的产生主要是ProxyFactory的getProxy()方法,内部通过AOPProxyFactory使用了抽象工厂模式,产生JdkDynamicAopProxy、ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
抽象工厂的实现类(参见详细过程)
- public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
- public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
- if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
- Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
- if (targetClass == null) {
- throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
- "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
- }
- if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
- return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
- }
- return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
- }
- else {
- return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
- }
- }
- }
获取代理对象的过程
- final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable {
- @Override
- public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
- if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
- }
- Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised);
- findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
- return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
- }
- }
层级关系如下
AOPProxyFactory 实现了类 DAOPProxyFactory
AOPProxy 实现类JdkDynamicAopProxy、CglibAopProxy
执行代理对象的invoke方法
前面已经讲过,再spring加载的时候,就加载了相关的代理对象。在代理对象执行目标方法之前,会执行与代理对象绑定的InvocationHandler的invoke方法。
JdkDynamicAopProxy本身就实现了InvocationHandler接口
- final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable
JdkDynamicAopProxy有一个重要的属性
- private final AdvisedSupport advised;
最关键的就是这个AdvisedSupport advised属性,它包含了我们在xml中配置的拦截信息,同时还包含了这个JdkDynamicAopProxy要代理的接口及其实现类,对于本文来说就是XXService和XXServiceImpl。JdkDynamicAopProxy可以根据这些配置信息来创建一个代理对象实现拦截,同时又可以执行XXServiceImpl本身的业务方法。
AdvisedSupport有三个重要的内容:
TargetSource是目标类型和目标对象的包裹,在这里是XXServiceImpl类和XXServiceImpl对象。
List<Class<?>> interfaces:包含了目标类型实现的接口,在这里就是目标对象XXService
List<Advisor> advisors:这里包含了我们在xml文件中配置的所有信息。这一部分是每个AdvisedSupport所共享的信息,而前面两个是每个AdvisedSupport所独有的信息。
回到JdkDynamicAopProxy,来看看拦截过程,即调用代理对象的方法,然后被拦截到代理对象的InvocationHandler的invoke方法,JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法如下:
- public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
- MethodInvocation invocation;
- Object oldProxy = null;
- boolean setProxyContext = false;
- TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
- Class<?> targetClass = null;
- Object target = null;
- try {
- if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
- // The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
- return equals(args[0]);
- }
- if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
- // The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
- return hashCode();
- }
- if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
- method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
- // Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
- return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
- }
- Object retVal;
- //关注的重点1:
- if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
- // Make invocation available if necessary.
- oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
- setProxyContext = true;
- }
- // May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
- // in case it comes from a pool.
- target = targetSource.getTarget();
- if (target != null) {
- targetClass = target.getClass();
- }
- // Get the interception chain for this method.
//关注的重点2- List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
- // Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
- // reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
- if (chain.isEmpty()) {
- // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
- // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
- // 关注重点3:
- retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);
- }
- else {
- // 关注的重点4
- invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
- // 关注的重点5
- retVal = invocation.proceed();
- }
- // Massage return value if necessary.
- Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
- if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
- !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
- retVal = proxy;
- }
- else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
- throw new AopInvocationException(
- "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
- }
- return retVal;
- }
- finally {
- if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
- // Must have come from TargetSource.
- targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
- }
- if (setProxyContext) {
- // Restore old proxy.
- AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
- }
- }
- }
关注的重点1:this.advised.exposeProxy即我们在xml文件中所配置的<aop:config expose-proxy="false">。如果配置为true,默认false,则意味着在该线程内将会暴露proxy代理对象,实现共享,即在该线程中的任何地方都可以都可以取到proxy代理对象。具体是由ThreadLocal设计模式来实现的
关注的重点2:根据我们的目标类和方法找到对应的拦截器链 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); 它内部是通过advised的一个this.advisorChainFactory来实现这一过程,advisorChainFactory默认为DefaultAdvisorChainFactory,实现过程如下:
- public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
- MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);
- List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);
- if (cached == null) {
- cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
- this, method, targetClass);
- this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);
- }
- return cached;
- }
- public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
- Advised config, Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
- // This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first,
- // but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
- List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);
- Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
- boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass);
- AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
- for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {
- if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
- // Add it conditionally.
- PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
- if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
- MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
- MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
- if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) {
- if (mm.isRuntime()) {
- // Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
- // isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
- for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
- interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
- }
- }
- else {
- interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
- }
- }
- }
- }
- else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
- IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
- if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
- Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
- interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
- }
- }
- else {
- Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
- interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
- }
- }
- return interceptorList;
- }
上述过程分了三种情况来获取对应的Interceptor拦截器,config.getAdvisors()是我们在xml文件中所配置的所有的拦截情况,对于这些所有的拦截情况:
当Advisor为PointcutAdvisor类型的时:
这是我们本工程的配置的拦截,每个拦截都有pointcut,针对这种情况,首先判断该PointcutAdvisor的ClassFilter是否拦截了targetClass,若拦截则需继续判断PointcutAdvisor的MethodMatcher是否拦截targetClass的method方法。如果也拦截了,就需要将PointcutAdvisor的adice添加进去,则继续判断这个PointcutAdvisor的MethodMatcher是否是动态变化的,若是则需要将interceptor进一步包装成InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher然后添加进去。
当Advisor为IntroductionAdvisor类型的时候:
IntroductionAdvisor应用在类上,不需要判断是否拦截了相应的方法。IntroductionAdvisor只有一个ClassFilter。此时仅仅去判断下是否拦截相应的类即可。
其他情况:
直接获取相应的interceptor。
我们来看下根据Advisor来获取对应的MethodInterceptor方法:
- public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
- List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<MethodInterceptor>(3);
- Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
- if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
- interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
- }
- for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
- if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
- interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
- }
- }
- if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
- throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
- }
- return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);
- }
首先是判断advisor.getAdvice()是否已实现了MethodInterceptor,如AspectJAfterAdvice、AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice等。 然后又是利用适配器模式,将不用的advice封装成对应的MethodInterceptor。如MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter,默认硬编码注册了三个
- public DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry() {
- registerAdvisorAdapter(new MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter());
- registerAdvisorAdapter(new AfterReturningAdviceAdapter());
- registerAdvisorAdapter(new ThrowsAdviceAdapter());
- }
看下MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter:
- class MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable {
- @Override
- public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) {
- return (advice instanceof MethodBeforeAdvice);
- }
- @Override
- public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) {
- MethodBeforeAdvice advice = (MethodBeforeAdvice) advisor.getAdvice();
- return new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(advice);
- }
- }
这就是典型的适配器模式,当Advice为MethodBeforeAdvice时,就会封装成MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor。 至此获取MethodInterceptor链的过程就完成了,回到List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);即List<Object>是一系列的MethodInterceptor构成的。
关注重点3:在获取MethodInterceptor链后,如果为空,则没有拦截器直接执行目标对象的方法。retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, args);中的target对于本工程来说就是XXServiceImpl,所以此方法的本质就是利用反射执行XXServiceImpl的method方法。如下:
- public static Object invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(Object target, Method method, Object[] args)
- throws Throwable {
- // Use reflection to invoke the method.
- try {
- ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
- return method.invoke(target, args);
- }
- catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
- // Invoked method threw a checked exception.
- // We must rethrow it. The client won't see the interceptor.
- throw ex.getTargetException();
- }
- catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
- throw new AopInvocationException("AOP configuration seems to be invalid: tried calling method [" +
- method + "] on target [" + target + "]", ex);
- }
- catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
- throw new AopInvocationException("Could not access method [" + method + "]", ex);
- }
- }
关注的重点4: 有了拦截器链后,就构造一个ReflectiveMethodInvocation来完成这一个调用过程
首先说下接口情况:ReflectiveMethodInvocation实现了ProxyMethodInvocation,ProxyMethodInvocation继承了MethodInvocation, MethodInvocation继承了Invocation, Invocation继承了Joinpoint,此时的Joinpoint是AOP联盟定义的接口。
关注的重点5:然后看下ReflectiveMethodInvocation作为一个Joinpoint的proceed方法的执行过程:
- public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
- // We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
- if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
- return invokeJoinpoint();
- }
- Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
- this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
- if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
- // Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
- // been evaluated and found to match.
- InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
- (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
- if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
- return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
- }
- else {
- // Dynamic matching failed.
- // Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
- return proceed();
- }
- }
- else {
- // It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
- // been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
- return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
- }
- }
首先就是this.currentInterceptorIndex,它是ReflectiveMethodInvocation的一个属性,从-1开始:当currentInterceptorIndex达到this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1时,拦截器链执行完毕了,就去执行目标对象的方法。invokeJoinpoint()方法就是上文我们所说的通过反射进行目标方法的调用。
继续看,拿出一个interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice,判断它是不是InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher类型,这个类型在获取拦截器链的时候遇见了,我们再次回顾下:
- for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {
- if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
- // Add it conditionally.
- PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
- if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
- MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
- MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
- //重点在这里重点在这里重点在这里重点在这里重点在这里
- if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) {
- if (mm.isRuntime()) {
- // Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
- // isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
- for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
- interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
- }
- }
- else {
- interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
- }
- }
- }
- }
- //略
因为InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher的MethodMatcher是可变的,所以在执行前仍要进行判断一次,符合的话就执行InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher中所包含的MethodInterceptor。不符合的话跳过本次拦截器,继续执行下一个拦截器。 当拦截器是MethodInterceptor,则是执行这个拦截器。 然后我们来看下具体有哪些拦截器链,以及具体是怎样的执行过程:
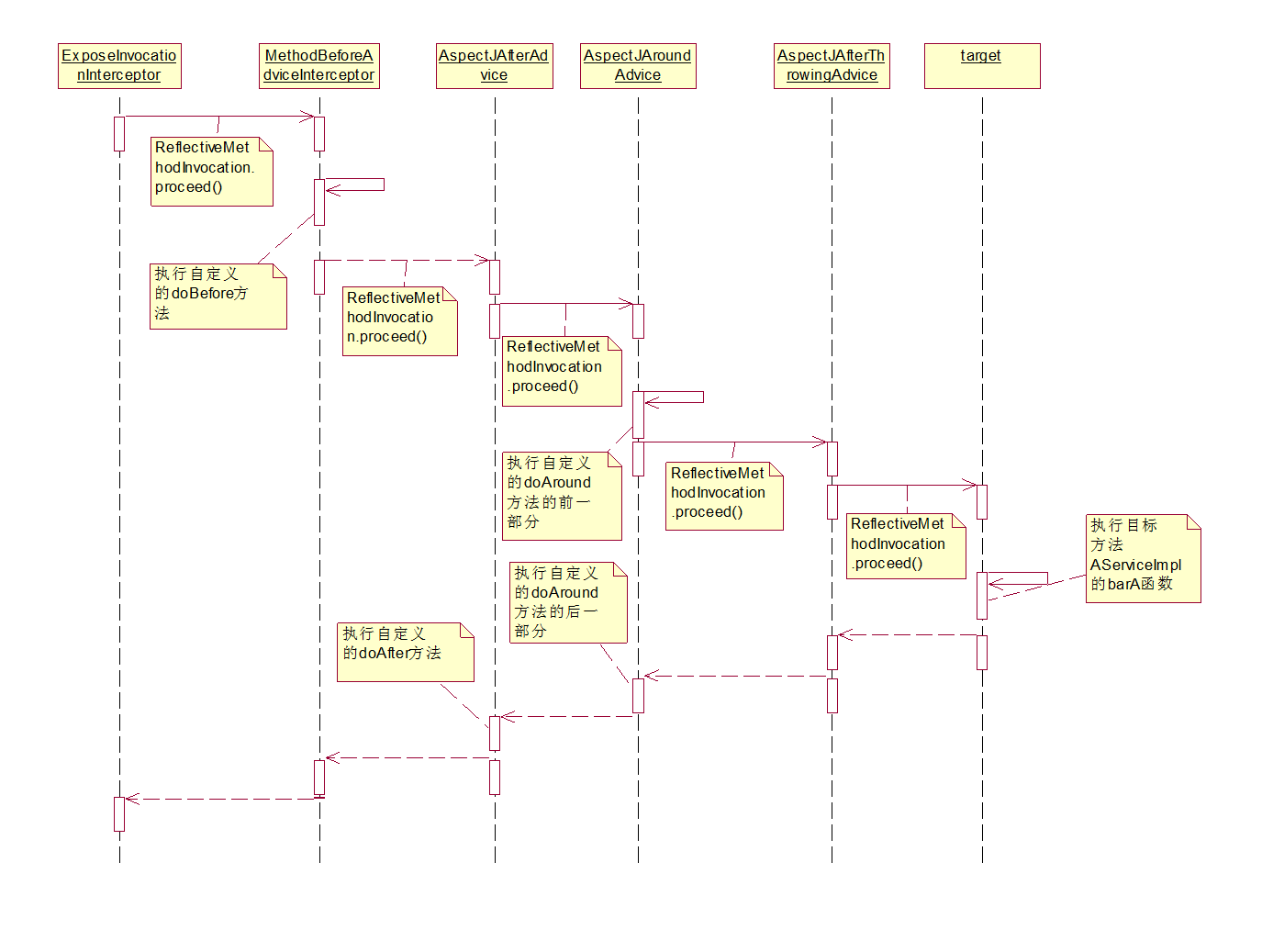
我们会看到会有如下5个拦截器,依次是: ExposeInvocationInterceptor、MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor、AspectJAfterAdvice、AspectJAroundAdvice、AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice。
即先执行后面的拦截器,但后面的拦截器执行过程中出现异常时才会发挥该拦截器的作用。继续执行后面的拦截器,发现已经没了,则终于轮到目标对象的方法了,目标方法执行完毕后,返回上一个proceed的嵌套即AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice的invoke方法,发现没有抛出异常,则继续返回到上一个proceed嵌套,即AspectJAroundAdvice,即我们自定义的doAround中这一行代码Object retVal = pjp.proceed()返回了,继续完成我们自定义的doAround函数,完成后再返回上一个proceed嵌套,来到AspectJAfterAdvice,则开始执行这个advice的处理工作,即我们自定义的doAfter方法。再返回上一个proceed嵌套,来到MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor,发现已经执行完毕继续返回上一个嵌套来到ExposeInvocationInterceptor,继续完成余下的工作,至此整个拦截过程就分析完毕了。在此过程中一个重要的参数就是我们配置的拦截器的顺序,顺序不同时执行过程就不一样,我们可以通过在xml配置中指定,下面附上我画的拦截器链的执行流程图。
spring---aop(2)---Spring AOP的JDK动态代理的更多相关文章
- Spring AOP动态代理实现,解决Spring Boot中无法正常启用JDK动态代理的问题
Spring AOP底层的动态代理实现有两种方式:一种是JDK动态代理,另一种是CGLib动态代理. JDK动态代理 JDK 1.3版本以后提供了动态代理,允许开发者在运行期创建接口的代理实例,而且只 ...
- aop学习总结一------使用jdk动态代理简单实现aop功能
aop学习总结一------使用jdk动态代理实现aop功能 动态代理:不需要为目标对象编写静态代理类,通过第三方或jdk框架动态生成代理对象的字节码 Jdk动态代理(proxy):目标对象必须实现接 ...
- AOP的底层实现:JDK动态代理与Cglib动态代理
转载自 https://www.cnblogs.com/ltfxy/p/9872870.html SpringAOP底层的实现原理: JDK动态代理:只能对实现了接口的类产生代理.(实现接口默认JDK ...
- Spring AOP详解 、 JDK动态代理、CGLib动态代理
AOP是Aspect Oriented Programing的简称,面向切面编程.AOP适合于那些具有横切逻辑的应用:如性能监测,访问控制,事务管理以及日志记录.AOP将这些分散在各个业务逻辑中的代码 ...
- jdk动态代理与cglib代理、spring aop代理实现原理
原创声明:本博客来源与本人另一博客[http://blog.csdn.net/liaohaojian/article/details/63683317]原创作品,绝非他处摘取 代理(proxy)的定义 ...
- jdk动态代理与cglib代理、spring aop代理实现原理解析
原创声明:本博客来源为本人原创作品,绝非他处摘取,转摘请联系博主 代理(proxy)的定义:为某对象提供代理服务,拥有操作代理对象的功能,在某些情况下,当客户不想或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象 ...
- 何为代理?jdk动态代理与cglib代理、spring Aop代理原理浅析
原创声明:本博客来源为本人原创作品,绝非他处摘取,转摘请联系博主 代理(proxy)的定义:为某对象提供代理服务,拥有操作代理对象的功能,在某些情况下,当客户不想或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象 ...
- Spring AOP高级——源码实现(3)AopProxy代理对象之JDK动态代理的创建过程
spring-aop-4.3.7.RELEASE 在<Spring AOP高级——源码实现(1)动态代理技术>中介绍了两种动态代理技术,当然在Spring AOP中代理对象的生成也是运用 ...
- 【转载】Spring AOP详解 、 JDK动态代理、CGLib动态代理
Spring AOP详解 . JDK动态代理.CGLib动态代理 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/kukudelaomao/p/5897893.html AOP是Aspec ...
- spring AOP底层原理实现——jdk动态代理
spring AOP底层原理实现——jdk动态代理
随机推荐
- Python 使用 Redis 操作
1.redis简介 redis是一款开源免费的高性能key-value数据库,redis特点: 支持更多的数据类型:字符串(String).列表(List).哈希(Map).数字(Int).集合(Se ...
- mac idea内存溢出
VM options: -mx2048m -XX:MaxPermSize=2048m -Drebel.spring_plugin=true -Drebel.hibernate_plugin=true
- 配置vuejs加载模拟数据
[个人笔记,非技术博客] 1.使用前确保安装axios插件,vuejs官方推荐,当然使用其他插件也可以 2.配置dev-server.js var router = express.Router(); ...
- 一步步教你编写不可维护的 PHP 代码
译者注:这是一篇很棒文章,使用有趣的叙述方式,从反面讲解了作为一个优秀的 PHP 工程师,有哪些事情是你不能做的.请注意哦,此篇文章罗列的行为,都是你要尽量避免的. 随着失业率越来越高,很多人意识到保 ...
- Owin 自定义中间件
/// <summary> /// 自定义的中间件 /// </summary> public class CustomMiddleware : OwinMiddleware ...
- canvas 笔记整理
canvas Retina 屏幕优化 /** * HiDPI Canvas Polyfill (1.0.9) * * Author: Jonathan D. Johnson (http://jonda ...
- LR检查点
LR检查点 之前使用LoadRunner工具,一直认为,在开发脚本中检查点的设置是最容易的,直到现在,有一段时间没碰LR,今天录制了一段脚本,设置了文本检查点,回放脚本后,总是报错,描述一下我设置 ...
- 7-10 守卫棋盘 uva11214
输入要给n*m的棋盘 均小于10 某些格子有标记 用最少的皇后 辐射到所有的标记 限时 6666ms 用IDA* 时间6000 尴尬. #include<bits/stdc++ ...
- docker动态绑定端口
一.背景 在创建容器的时候,我们可以使用命令 docker container run -p host:container container-name 的方式来绑定端口,还可以使用docker-co ...
- Ionic Js九:列表操作
列表是一个应用广泛在几乎所有移动app中的界面元素.ionList 和 ionItem 这两个指令还支持多种多样的交互模式,比如移除其中的某一项,拖动重新排序,滑动编辑等等. <ion-list ...
