c++11之std::bind简单使用
note
- 更多用法,请参考: cppreference
- 用的少,容易忘。
我的理解
- 类似延迟计算。 比如,回调函数,将回调函数传入后,回调函数不一定马上被调用。
- 它是一个模板类,调用后将生成一个新的调用对象A。调用该对象A与调用原函数是等价的。
声明
截至目前,它的声明如下

需要包含头文件
#include <functional>
一个例子
代码
下面的print函数负责输出参数的值, 通过使用std::bind, 生成一个新的对象 func, 此时, func(a, b, c);与print(a, b, c);**的调用结果是等价的。
#include <functional>
void print(int a, int b, int c)
{
std::cout << "a = " << a << ", b=" << b << ", c=" << c << "\n\n";
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[], char* env[])
{
auto func = std::bind(print, std::placeholders::_2, 2, std::placeholders::_1);
func(3, 4);
return 0;
}
std::placeholders 说明
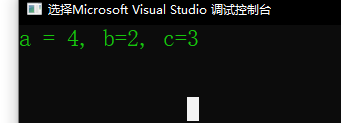
std::placeholders::_2和std::placeholders::_1表示参数的顺序,比如, 上面的代码示例中, 3是func的第一个参数,但是,func在声明时,指定了第一个参数的位置,放在了最后。 所以,上面的代码输出结果: a=4, b=2, c=3。
注意
- std::bind的函数参数默认使用的是拷贝, 如果需要使用引用,则需要配合std::ref。
- 下面一个例子,帮助理解。
print2函数负责输出参数的值,且参数都是引用, print2函数内完成对参数的自增
#include <functional>
void print2(int &a, int &b)
{
std::cout << "函数调用:a=" << a << ", b=" << b << "\n";
++a;
++b;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[], char* env[])
{
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
auto func2 = std::bind(print2, a, std::ref(b));
std::cout << "调用前,a=" << a << ", b=" << b << "\n";
func2();
std::cout << "调用后,a=" << a << ", b=" << b << "\n";
return 0;
}
调用时,尽管都采用了传入引用的方式,但略有不同。参数a使用的是传统的方式,参数b采用的是 std::ref的方式。 观察输出结果
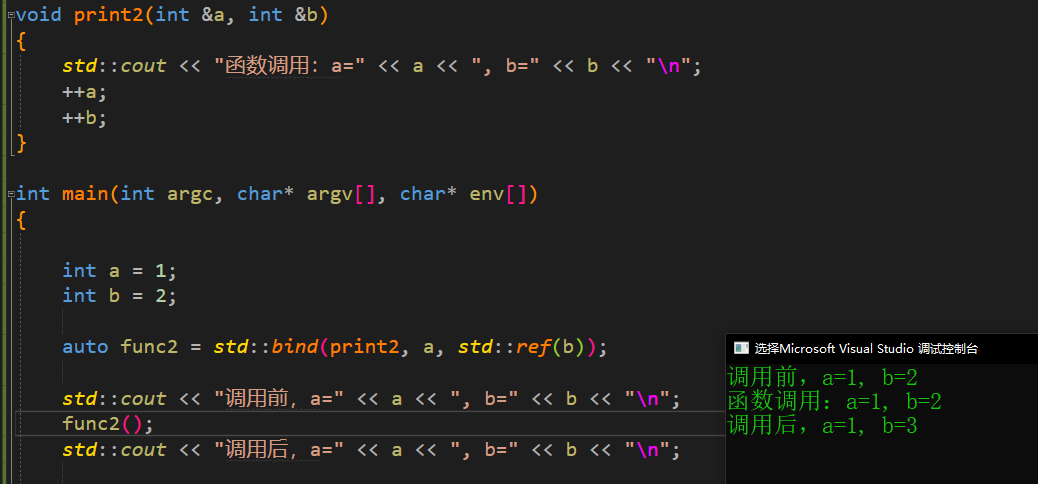
可以看到,std::bind的参数是以 拷贝的方式,使用 std::ref 的方式可以实现参数在std::bind的引用。
官方的例子
#include <random>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
void f(int n1, int n2, int n3, const int& n4, int n5)
{
std::cout << n1 << ' ' << n2 << ' ' << n3 << ' ' << n4 << ' ' << n5 << '\n';
}
int g(int n1)
{
return n1;
}
struct Foo {
void print_sum(int n1, int n2)
{
std::cout << n1+n2 << '\n';
}
int data = 10;
};
int main()
{
using namespace std::placeholders; // for _1, _2, _3...
// demonstrates argument reordering and pass-by-reference
int n = 7;
// (_1 and _2 are from std::placeholders, and represent future
// arguments that will be passed to f1)
auto f1 = std::bind(f, _2, 42, _1, std::cref(n), n);
n = 10;
f1(1, 2, 1001); // 1 is bound by _1, 2 is bound by _2, 1001 is unused
// makes a call to f(2, 42, 1, n, 7)
// nested bind subexpressions share the placeholders
auto f2 = std::bind(f, _3, std::bind(g, _3), _3, 4, 5);
f2(10, 11, 12); // makes a call to f(12, g(12), 12, 4, 5);
// common use case: binding a RNG with a distribution
std::default_random_engine e;
std::uniform_int_distribution<> d(0, 10);
auto rnd = std::bind(d, e); // a copy of e is stored in rnd
for(int n=0; n<10; ++n)
std::cout << rnd() << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
// bind to a pointer to member function
Foo foo;
auto f3 = std::bind(&Foo::print_sum, &foo, 95, _1);
f3(5);
// bind to a pointer to data member
auto f4 = std::bind(&Foo::data, _1);
std::cout << f4(foo) << '\n';
// smart pointers can be used to call members of the referenced objects, too
std::cout << f4(std::make_shared<Foo>(foo)) << '\n'
<< f4(std::make_unique<Foo>(foo)) << '\n';
}
官方例子输出
2 42 1 10 7
12 12 12 4 5
1 5 0 2 0 8 2 2 10 8
100
10
10
10
c++11之std::bind简单使用的更多相关文章
- C++11中std::bind的使用
std::bind: Each argument may either be bound to a value or be a placeholder: (1).If bound to a value ...
- 第11课 std::bind和std::function(2)_std::bind绑定器
1. 温故知新:std::bind1st和std::bind2nd (1)bind1st.bind2nd首先它们都是函数模板,用于将参数绑定到可调用对象(如函数.仿函数等)的第1个或第2个参数上. ( ...
- std::bind技术内幕
引子 最近群里比较热闹,大家都在山寨c++11的std::bind,三位童孩分别实现了自己的bind,代码分别在这里: 木头云的实现 mr.li的实现 null的实现,null的另一个版本的实现 这些 ...
- std::bind与std::ref, why and how
首先解释下为什么有时候需要bind. 我们可以用bind从函数T add(T a, T b)造出个inc()来,即把b写死为1.这个例子本身比较傻,但有不傻的应用. template<typen ...
- C++11多线程std::thread的简单使用
在cocos2dx 2.0时代,我们使用的是pthread库,是一套用户级线程库,被广泛地使用在跨平台应用上.但在cocos2dx 3.0中并未发现有pthread的支持文件,原来c++11中已经拥有 ...
- C++11中提供了std::bind
再来看看std::bind C++11中提供了std::bind.bind()函数的意义就像它的函数名一样,是用来绑定函数调用的某些参数的. bind的思想实际上是一种延迟计算的思想,将可调用对象保存 ...
- c++11 符号修饰与函数签名、函数指针、匿名函数、仿函数、std::function与std::bind
一.符号修饰与函数签名 1.符号修饰 编译器将c++源代码编译成目标文件时,用函数签名的信息对函数名进行改编,形成修饰名.GCC的C++符号修饰方法如下: 1)所有符号都以_z开头 2)名字空间的名字 ...
- C++11之std::function和std::bind
std::function是可调用对象的包装器,它最重要的功能是实现延时调用: #include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream>// std ...
- [C/C++11]_[初级]_[std::bind介绍和使用]
场景 1.C++11 引入了std::function 对象, 这个对象可以通过std::bind封装所有的函数, 并通过代理调用这个std::function的方式调用这个函数. 比如通过统一的方式 ...
随机推荐
- 小方法——匹配ip地址
[root@MiWiFi-R1CM-srv ~]# ifconfig |sed -n '2p' inet addr:192.168.139.128 Bcast:192.168.139.255 Mask ...
- php操作mongodb手册地址
php操作mongodb手册地址: http://php.net/manual/zh/class.mongocollection.php
- Java 读取TXT文件的多种方式
1).按行读取TXT文件package zc;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.File;import java.io.FileNotFound ...
- 年底巩固下 CS 知识「GitHub 热点速览 v.21.49」
作者:HelloGitHub-小鱼干 期末到了!是时候来一波 CS 复习资料了,从本科基础知识开始到实用编程技术.本周 GitHub 热点趋势榜给你提供了最全的复习资料:清华的 CS 四年学习资料.W ...
- 日常Java 2021/10/21
Java Iterator(迭代器) 如果需要使用iterator类需要从java.util包中引入它 Java Iterator不是一个集合,它是一种访问集合的方法,用于迭代ArrayList和Ha ...
- day13 cookie与session和中间件
day13 cookie与session和中间件 今日内容概要 cookie与session简介 django操作cookie与session django中间件简介 如何自定义中间件 csrf跨站请 ...
- Linux网络(网络模型和收发流程)
网络模型 为了解决网络互联中异构设备的兼容性问题,并解耦复杂的网络包处理流程,国际标准化组织制定的开放式系统互联通信参考模型(Open System Interconnection Reference ...
- 100个Shell脚本——【脚本3】tomcat启动脚本
[脚本3]tomcat启动脚本 一.脚本tomcatd.sh #!/bin/bash # chkconfig:2345 64 36 # description: Tomcat start/stop/r ...
- Mybatis 批量插入
一.首先对于批量数据的插入有两种解决方案(下面内容只讨论和Mysql交互的情况) 1)for循环调用Dao中的单条插入方法 2)传一个List<Object>参数,使用Mybatis的批量 ...
- ganglia -api
setup 命令: virtualenv ve source ve/bin/activate pip install -r requirements.txt python ganglia/gangli ...
