2016弱校联盟十一专场10.2---Around the World(深搜+组合数、逆元)
题目链接
https://acm.bnu.edu.cn/v3/problem_show.php?pid=52305
problem description
In ICPCCamp, there are n cities and (n−1) (bidirectional) roads between cities. The i-th road is between the ai-th and bi-th cities. It is guaranteed that cities are connected. Recently, there are 2×ci −1 new roads built between the ai-th and bi-th cities. Bobo soon comes up with an idea to travel around the world! He plans to start in city 1 and returns to city 1 after traveling along every road exactly once. It is clear that Bobo has many plans to choose from. He would like to find out the number of different plans, modulo (109 + 7). Note that two plans A and B are considered different only if there exists an i where the i-th traveled road in plan A is different from the i-th road in plan B.
Input
The first line contains an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 105 ). The i-th of the following (n − 1) lines contains 3 integers ai , bi , ci (1 ≤ ai , bi ≤ n, ci ≥ 1, c1 + c2 + · · · + cn−1 ≤ 106 ).
Output
An integer denotes the number of plans modulo (109 + 7).
Examples
standard input
3
1 2 1
2 3 1
3
1 2 1
1 3 2
standard output
4
144
题意:输入n 表示由n个节点构成的树,然后输入n-1条边,n-1行每行输入ai bi c 表示ai点和bi点之间有2*c条边相连,现在求从1号点开始走完所有边且每条边只走一次的方案数?
思路:深搜,然后排列组合,举两个例子:
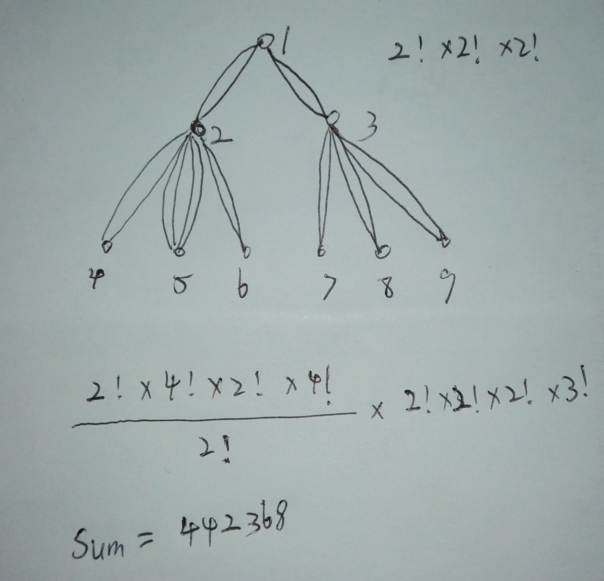
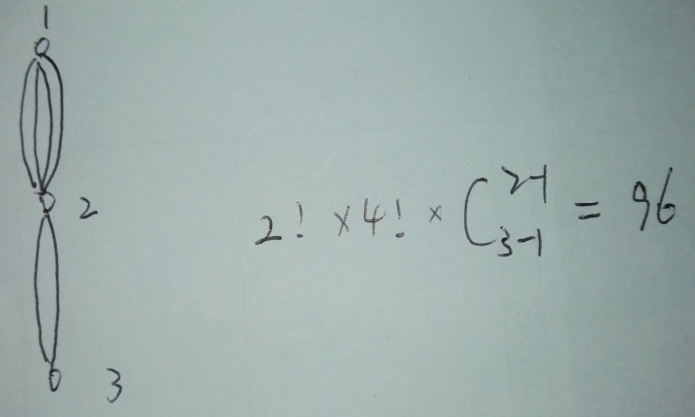
第一个图片中:定义sum=1,从1号点开始向下深搜,到达孩子2号点的时候sum*=2! 表示从1到2号点走遍边的方法数,然后继续向下深搜到4号点,sum*=2! 然后返回再到5号点,sum*=4! 再返回走到6号点,sum*=2! ,然后返回2号点,这时sum*=4!/2! 为什么呢? 因为从2号点开始走完它的直系(儿子)孩子节点时,它的儿子路径之间存在先后顺序,所以乘上路径数的阶乘,但要除去重复的部分比如从2号点到5号点时这两条路径的先后顺序在之前的4!中已经考虑了,接下来就是相同的过程了......注意的是下面的孩子节点算完了,再计算上层节点时就不需要考虑了,但是相邻两层的节点之间还是有影响的,这个图看不出来,我用下面一个图作解释。
第二个图片中:按照之前的算法为sum=4!*2!=48 其实正确的解是96 ,少乘了一个2,为什么呢? 因为上面一层的路径对下面一层的路径产生了影响,上一层有两条路径,下面一层只有一条路径,那么可以分析存在两种情况:1、 1->2->3->2->1->2->1 2、 1->2->1->2->3->2->1 怎么产生的? 其实是在走上一层的路径时,在哪一次走的这一层的路径,用挡板法,设上一层有t条路径,这一层有s条路径,那么得在t次把下面的s条路径走完,也就是C(t+s-1,t-1) 。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
typedef long long LL;
const LL maxn=1e5+;
const LL mod=1e9+;
using namespace std;
struct Tree
{
LL to,next,c;
} edge[maxn*];
LL Inv[*maxn];
LL tot,head[maxn];
LL jc[maxn*];
LL sum;
void Init()
{
Inv[]=;
Inv[] = ;
for(LL i=; i<*maxn; i++)
Inv[i] = (mod-mod/i)*Inv[mod%i]%mod;
for(LL i=; i<*maxn; i++)
Inv[i] = (Inv[i-]*Inv[i])%mod;
}
void init()
{
tot=;
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
}
void add_edge(LL u,LL v,LL c)
{
edge[tot].to=v;
edge[tot].c=c;
edge[tot].next=head[u];
head[u]=tot++;
} void init2()
{
jc[]=;
for(LL i=; i<maxn*; i++)
jc[i]=((jc[i-]*i)%mod);
}
LL road[maxn];
void dfs(LL u,LL pre)
{
road[u]=;
for(LL i=head[u]; i!=-; i=edge[i].next)
{
LL v=edge[i].to;
if(v==pre) continue;
dfs(v,u);
road[u]+=edge[i].c;
sum=(((sum*jc[edge[i].c*])%mod)*Inv[edge[i].c])%mod;
sum=((sum* jc[(road[v]+edge[i].c-)]%mod)*Inv[edge[i].c-] )%mod;
sum=(sum*Inv[road[v]])%mod;
}
sum=(sum*jc[road[u]])%mod;
} int main()
{
Init();
init2();
LL n,u,v,c;
while(scanf("%lld",&n)!=-)
{
sum=;
init();
for(LL i=; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&u,&v,&c);
add_edge(u,v,c);
add_edge(v,u,c);
}
dfs(,);
printf("%lld\n",sum);
}
return ;
}
2016弱校联盟十一专场10.2---Around the World(深搜+组合数、逆元)的更多相关文章
- 2016弱校联盟十一专场10.3---Similarity of Subtrees(深搜+hash、映射)
题目链接 https://acm.bnu.edu.cn/v3/problem_show.php?pid=52310 problem description Define the depth of a ...
- 2016弱校联盟十一专场10.5---As Easy As Possible(倍增)
题目链接 https://acm.bnu.edu.cn/v3/contest_show.php?cid=8506#problem/A problem description As we know, t ...
- (2016弱校联盟十一专场10.3) D Parentheses
题目链接 把左括号看成A右括号看成B,推一下就行了.好久之前写的,推到最后发现是一个有规律的序列. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ...
- (2016弱校联盟十一专场10.3) B.Help the Princess!
题目链接 宽搜一下就行. #include <iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<qu ...
- (2016弱校联盟十一专场10.3) A.Best Matched Pair
题目链接 #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<stack> ...
- 2016弱校联盟十一专场10.3---We don't wanna work!(STL--set的使用)
题目链接 https://acm.bnu.edu.cn/v3/contest_show.php?cid=8504#problem/C 代码如下: #include <iostream> # ...
- (2016弱校联盟十一专场10.2) A.Nearest Neighbor Search
题目链接 水题,算一下就行. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; ll x[],y[], ...
- (2016弱校联盟十一专场10.2) E.Coins
题目链接 很久之前写的了,好像是对拍打表过的,推一下就行了. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ...
- (2016弱校联盟十一专场10.5) F. Fibonacci of Fibonacci
题目链接 题目大意就是这个,先找出下标的循环节,再快速幂对20160519取余就行了. 找出下标循环节: #include <cstdio> #include <iostream&g ...
随机推荐
- Atitti usrQBf1801 翻页控件规范 v2
Atitti usrQBf1801 翻页控件规范 v2 1. 参考api 参考easyui ,.net系列的1 1.1. 翻页流程 初始化翻页控件,以及绑定新页面event onSelectPa ...
- Atitit html5 Canvas 如何自适应屏幕大小
Atitit html5 Canvas 如何自适应屏幕大小 可以用JS监控屏幕大小,然后调整Canvas的大小.在代码中加入JS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 $(window).resize ...
- asp.net 站点重启
有时一些特殊情况需要重启站点,在System.Web.dll程序集下HttpRuntime类下有一个静态方法UnloadAppDomain,使用这个方法可以重启站点: protected void b ...
- Oracle日期函数和循环总结
一,日期相关的函数 Select to_char(sysdate,'Q') from dual;--指定日期的季度 Select to_char(sysdate,'MM') from dual;--月 ...
- 【WP开发】认清“不透明度”与“可见性”的区别
这两种情况,许多朋友平时都没有注意到: 1.设置Opacity属性的值为0: 2.将Visibility属性设置为Collapsed. 不少人会简单地认为这两种情况是一样的,都是让UI元素看不见. 我 ...
- HTML的音频和视频
目录 [1]媒体格式 音频格式 视频格式 [2]元素 插件元素 HTML5元素 [3]HTML音频 [4]HTML视频 前面的话 多媒体元素(比如视频和音频)存储于媒体文件中,确定媒体类型的最常用的方 ...
- sqlserver -- 解决sqlserver2008“Prevent saving changes that require table re_creation(阻止保存要求重新创建表的更改)”的问题
电脑重装了sqlserver2008 R2(英文版)后,新建数据表,新建字段,发现有个字段类型设置错了,想修改字段类型,而该表已经保存好了,即保存后修改字段属性.但无法保存修改后的设置,提示“Savi ...
- 开发笔记:基于EntityFramework.Extended用EF实现指定字段的更新
今天在将一个项目中使用存储过程的遗留代码迁移至新的架构时,遇到了一个问题——如何用EF实现数据库中指定字段的更新(根据UserId更新Users表中的FaceUrl与AvatarUrl字段)? 原先调 ...
- Spark入门实战系列--2.Spark编译与部署(上)--基础环境搭建
[注] 1.该系列文章以及使用到安装包/测试数据 可以在<倾情大奉送--Spark入门实战系列>获取: 2.Spark编译与部署将以CentOS 64位操作系统为基础,主要是考虑到实际应用 ...
- resin4的初次配置与使用
之前用的resin3,结果发布新项目老师文件冲突,我也找不到是哪里有问题,于是尝试使用resin4. 首先从官网下载最新resin4. 然后放到opt下,tar -zvxf 解压. 然后修改conf/ ...
