hdfs dfsadmin 命令详解
hdfs dfsadmin
[-report [-live] [-dead] [-decommissioning]]
[-safemode <enter | leave | get | wait>]
[-saveNamespace]
[-rollEdits]
[-restoreFailedStorage true|false|check]
[-refreshNodes]
[-setQuota <quota> <dirname>...<dirname>]
[-clrQuota <dirname>...<dirname>]
[-setSpaceQuota <quota> <dirname>...<dirname>]
[-clrSpaceQuota <dirname>...<dirname>]
[-finalizeUpgrade]
[-rollingUpgrade [<query|prepare|finalize>]]
[-refreshServiceAcl]
[-refreshUserToGroupsMappings]
[-refreshSuperUserGroupsConfiguration]
[-refreshCallQueue]
[-refresh <host:ipc_port> <key> [arg1..argn]
[-reconfig <datanode|...> <host:ipc_port> <start|status>]
[-printTopology]
[-refreshNamenodes datanode_host:ipc_port]
[-deleteBlockPool datanode_host:ipc_port blockpoolId [force]]
[-setBalancerBandwidth <bandwidth in bytes per second>]
[-fetchImage <local directory>]
[-allowSnapshot <snapshotDir>]
[-disallowSnapshot <snapshotDir>]
[-shutdownDatanode <datanode_host:ipc_port> [upgrade]]
[-getDatanodeInfo <datanode_host:ipc_port>]
[-metasave filename]
[-setStoragePolicy path policyName]
[-getStoragePolicy path]
[-help [cmd]]
-report [-live] [-dead] [-decommissioning]:
Reports basic filesystem information and statistics.
Optional flags may be used to filter the list of displayed DNs.
-safemode <enter|leave|get|wait>: Safe mode maintenance command.
Safe mode is a Namenode state in which it
1. does not accept changes to the name space (read-only)
2. does not replicate or delete blocks.
Safe mode is entered automatically at Namenode startup, and
leaves safe mode automatically when the configured minimum
percentage of blocks satisfies the minimum replication
condition. Safe mode can also be entered manually, but then
it can only be turned off manually as well.
-saveNamespace: Save current namespace into storage directories and reset edits log.
Requires safe mode.
-rollEdits: Rolls the edit log.
-restoreFailedStorage: Set/Unset/Check flag to attempt restore of failed storage replicas if they become available.
-refreshNodes: Updates the namenode with the set of datanodes allowed to connect to the namenode.
Namenode re-reads datanode hostnames from the file defined by
dfs.hosts, dfs.hosts.exclude configuration parameters.
Hosts defined in dfs.hosts are the datanodes that are part of
the cluster. If there are entries in dfs.hosts, only the hosts
in it are allowed to register with the namenode.
Entries in dfs.hosts.exclude are datanodes that need to be
decommissioned. Datanodes complete decommissioning when
all the replicas from them are replicated to other datanodes.
Decommissioned nodes are not automatically shutdown and
are not chosen for writing new replicas.
-finalizeUpgrade: Finalize upgrade of HDFS.
Datanodes delete their previous version working directories,
followed by Namenode doing the same.
This completes the upgrade process.
-rollingUpgrade [<query|prepare|finalize>]:
query: query the current rolling upgrade status.
prepare: prepare a new rolling upgrade.
finalize: finalize the current rolling upgrade.
-metasave <filename>: Save Namenode's primary data structures
to <filename> in the directory specified by hadoop.log.dir property.
<filename> is overwritten if it exists.
<filename> will contain one line for each of the following
1. Datanodes heart beating with Namenode
2. Blocks waiting to be replicated
3. Blocks currrently being replicated
4. Blocks waiting to be deleted
-setQuota <quota> <dirname>...<dirname>: Set the quota <quota> for each directory <dirName>.
The directory quota is a long integer that puts a hard limit
on the number of names in the directory tree
For each directory, attempt to set the quota. An error will be reported if
1. N is not a positive integer, or
2. User is not an administrator, or
3. The directory does not exist or is a file.
Note: A quota of 1 would force the directory to remain empty.
-clrQuota <dirname>...<dirname>: Clear the quota for each directory <dirName>.
For each directory, attempt to clear the quota. An error will be reported if
1. the directory does not exist or is a file, or
2. user is not an administrator.
It does not fault if the directory has no quota.
-setSpaceQuota <quota> <dirname>...<dirname>: Set the disk space quota <quota> for each directory <dirName>.
The space quota is a long integer that puts a hard limit
on the total size of all the files under the directory tree.
The extra space required for replication is also counted. E.g.
a 1GB file with replication of 3 consumes 3GB of the quota.
Quota can also be specified with a binary prefix for terabytes,
petabytes etc (e.g. 50t is 50TB, 5m is 5MB, 3p is 3PB).
For each directory, attempt to set the quota. An error will be reported if
1. N is not a positive integer, or
2. user is not an administrator, or
3. the directory does not exist or is a file, or
-clrSpaceQuota <dirname>...<dirname>: Clear the disk space quota for each directory <dirName>.
For each directory, attempt to clear the quota. An error will be reported if
1. the directory does not exist or is a file, or
2. user is not an administrator.
It does not fault if the directory has no quota.
-refreshServiceAcl: Reload the service-level authorization policy file
Namenode will reload the authorization policy file.
-refreshUserToGroupsMappings: Refresh user-to-groups mappings
-refreshSuperUserGroupsConfiguration: Refresh superuser proxy groups mappings
-refreshCallQueue: Reload the call queue from config
-refresh: Arguments are <hostname:port> <resource_identifier> [arg1..argn]
Triggers a runtime-refresh of the resource specified by <resource_identifier>
on <hostname:port>. All other args after are sent to the host.
-reconfig <datanode|...> <host:ipc_port> <start|status>:
Starts reconfiguration or gets the status of an ongoing reconfiguration.
The second parameter specifies the node type.
Currently, only reloading DataNode's configuration is supported.
-printTopology: Print a tree of the racks and their
nodes as reported by the Namenode
-refreshNamenodes: Takes a datanodehost:port as argument,
For the given datanode, reloads the configuration files,
stops serving the removed block-pools
and starts serving new block-pools
-deleteBlockPool: Arguments are datanodehost:port, blockpool id
and an optional argument "force". If force is passed,
block pool directory for the given blockpool id on the given
datanode is deleted along with its contents, otherwise
the directory is deleted only if it is empty. The command
will fail if datanode is still serving the block pool.
Refer to refreshNamenodes to shutdown a block pool
service on a datanode.
-setBalancerBandwidth <bandwidth>:
Changes the network bandwidth used by each datanode during
HDFS block balancing.
<bandwidth> is the maximum number of bytes per second
that will be used by each datanode. This value overrides
the dfs.balance.bandwidthPerSec parameter.
--- NOTE: The new value is not persistent on the DataNode.---
-fetchImage <local directory>:
Downloads the most recent fsimage from the Name Node and saves it in the specified local directory.
-allowSnapshot <snapshotDir>:
Allow snapshots to be taken on a directory.
-disallowSnapshot <snapshotDir>:
Do not allow snapshots to be taken on a directory any more.
-shutdownDatanode <datanode_host:ipc_port> [upgrade]
Submit a shutdown request for the given datanode. If an optional
"upgrade" argument is specified, clients accessing the datanode
will be advised to wait for it to restart and the fast start-up
mode will be enabled. When the restart does not happen in time,
clients will timeout and ignore the datanode. In such case, the
fast start-up mode will also be disabled.
-getDatanodeInfo <datanode_host:ipc_port>
Get the information about the given datanode. This command can
be used for checking if a datanode is alive.
-setStoragePolicy path policyName
Set the storage policy for a file/directory.
-getStoragePolicy path
Get the storage policy for a file/directory.
-help [cmd]: Displays help for the given command or all commands if none
is specified.
Generic options supported are
-conf <configuration file> specify an application configuration file
-D <property=value> use value for given property
-fs <local|namenode:port> specify a namenode
-jt <local|resourcemanager:port> specify a ResourceManager
-files <comma separated list of files> specify comma separated files to be copied to the map reduce cluster
-libjars <comma separated list of jars> specify comma separated jar files to include in the classpath.
-archives <comma separated list of archives> specify comma separated archives to be unarchived on the compute machines.
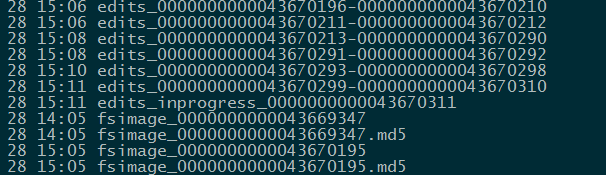
hdfs dfsadmin -rollEdits
说明:roll一个新的editlog 与journal 同步
日志:
Successfully rolled edit logs.
New segment starts at txid 43670311
执行成功后 active-nn 与journal 上的 edits_inprogress txid 都会从43670311开始
hdfs dfsadmin 命令详解的更多相关文章
- Hadoop(四)HDFS集群详解
前言 前面几篇简单介绍了什么是大数据和Hadoop,也说了怎么搭建最简单的伪分布式和全分布式的hadoop集群.接下来这篇我详细的分享一下HDFS. HDFS前言: 设计思想:(分而治之)将大文件.大 ...
- adoop(四)HDFS集群详解
阅读目录(Content) 一.HDFS概述 1.1.HDFS概述 1.2.HDFS的概念和特性 1.3.HDFS的局限性 1.4.HDFS保证可靠性的措施 二.HDFS基本概念 2.1.HDFS主从 ...
- hdfs文件系统架构详解
hdfs文件系统架构详解 官方hdfs分布式介绍 NameNode *Namenode负责文件系统的namespace以及客户端文件访问 *NameNode负责文件元数据操作,DataNode负责文件 ...
- hbase shell基础和常用命令详解(转)
HBase shell的基本用法 hbase提供了一个shell的终端给用户交互.使用命令hbase shell进入命令界面.通过执行 help可以看到命令的帮助信息. 以网上的一个学生成绩表的例子来 ...
- Linux进程实时IO监控iotop命令详解
介绍 Linux下的IO统计工具如iostat, nmon等大多数是只能统计到per设备的读写情况, 如果你想知道每个进程是如何使用IO的就比较麻烦. iotop 是一个用来监视磁盘 I/O 使用状况 ...
- Sqoop 导入及导出表数据子集命令详解
Sqoop命令详解 1.import命令 案例1:将mysql表test中的数据导入hive的hivetest表,hive的hivetest表不存在. sqoop import --connect j ...
- hbase shell基础和常用命令详解
HBase是Google Bigtable的开源实现,它利用Hadoop HDFS作为其文件存储系统,利用Hadoop MapReduce来处理HBase中的海量数据,利用Zookeeper作为协同服 ...
- Git初探--笔记整理和Git命令详解
几个重要的概念 首先先明确几个概念: WorkPlace : 工作区 Index: 暂存区 Repository: 本地仓库/版本库 Remote: 远程仓库 当在Remote(如Github)上面c ...
- linux yum命令详解
yum(全称为 Yellow dog Updater, Modified)是一个在Fedora和RedHat以及SUSE中的Shell前端软件包管理器.基於RPM包管理,能够从指定的服务器自动下载RP ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu 17.10.1 安装 virtual box 增强工具
ubuntu 17.10.1 安装 virtual box 增强工具遇到 “ Please install the gcc make perl packages from your distribu ...
- docker-compose网络设置之networks
networks使用方式之官网教程 官网的docker-compose.yml参考文档:Compose file version 3 reference 较为准确的中文翻译版:Compose file ...
- vagrant 虚拟机中安装 lnamp 环境
转载自 :http://git.oschina.net/apanly/mooc/tree/master/vagrant 替换源 sudo cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/a ...
- VC禁止或允许拖拽改变窗口尺寸
创建窗口时用WS_THICKFRAME控制 BOOL CMainFrame::PreCreateWindow(CREATESTRUCT& cs) { if( !CMDIFrameWndEx:: ...
- MFC系统自动生成的停靠窗格关掉后,如何重新显示?
就是这几个x,关闭之后,再也显示不出来了: 原来,系统会默认记忆上次的状态,可以用函数来清除这个设置: 在MainFrame那个类中,CreateDocablePane之前,调用EnableLoadD ...
- 关闭AutoCAD 2019快速访问工具栏的web和moblie保存文件功能
解决方法如下:1.先关闭CAD,再打开注册表编辑器:开始--运行--输入 regedit2.定位到 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Autodesk\AutoCAD\R23. ...
- CAD 中绘制点
首先开启点样式,否则点是看不到的 系统变量 PDMODE 和 PDSIZE 控制点对象的显示外观. PDMODE 取值为 0.2.3 .4 时指定表示点的图形,取值为 1 表示不显示任何图形,如下图所 ...
- Java第02次实验提纲(Java基本语法与类库)
1. 熟悉Git 1.1 学会使用网页版的操作代码仓库(gitee) 申请账号,然后根据老师提供的链接或者二维码加入团队,然后修改昵称. fork老师提供的代码库项目,新建自己学号命名的文件并上传一些 ...
- Python使用plotly绘制数据图表的方法
转载:http://www.jb51.net/article/118936.htm 本篇文章主要介绍了Python使用plotly绘制数据图表的方法,实例分析了plotly绘制的技巧. 导语:使用 p ...
- Mongod服务器安装
第一步下载mongodb 目前最新版本:3.4.4 第二步安装vc_redist.x64 服务器安装可能会需要到,如果没有出现以下错误不需要安装 --------------------------- ...
