spring-boot-2.0.3源码篇 - pageHelper分页,绝对有值得你看的地方
前言
开心一刻
说实话,作为一个宅男,每次被淘宝上的雄性店主追着喊亲,亲,亲,这感觉真是恶心透顶,好像被强吻一样。。。。。。。。。更烦的是我每次为了省钱,还得用个女号,跟那些店主说:“哥哥包邮嘛么叽。”,“哥哥再便宜点呗,我钱不够了嘛,5555555, ”。
”。

知道后的店主
路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索!
github:https://github.com/youzhibing
码云(gitee):https://gitee.com/youzhibing
问题背景
用过pageHelper的都知道(没用过的感觉去google下),实现分页非常简单,service实现层调用dao(mapper)层之前进行page设置,mapper.xml中不处理分页,这样就够了,就能实现分页了,具体如下
UserServiceImpl.java
@Override
public PageInfo listUser(int pageNum, int pageSize) {
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize);
List<User> users = userMapper.listUser();
PageInfo pageInfo = new PageInfo(users);
return pageInfo;
}
UserMapper.xml
<select id="listUser" resultType="User">
SELECT
id,username,password,salt,state,description
FROM
tbl_user
</select>
哎我去,这样就实现分页了? 老牛皮了,这是为什么,这是怎么做到的? 凡事有果必有因,我们一起来看看这个因到底是什么
JDK的动态代理
在进入正题之前了,我们先来做下准备,如果对动态代理很熟悉的直接略过往下看,建议还是看看,权且当做热身
我们来看看JDK下的动态代理的具体实现:proxyDemo,运行ProxyTest的main方法,结果如下

可以看到我们对 张三 进行了增强处理,追加了后缀:_proxy
更多动态代理信息请看:设计模式之代理,手动实现动态代理,揭秘原理实现
Mybatis sql执行流程
当我们对JDK的动态代理有了一个基本认识之后了,我们再完成个一公里的慢跑:熟悉Mybatis的sql执行流程。流程图懒得画了,有人处理的很优秀了,我引用下
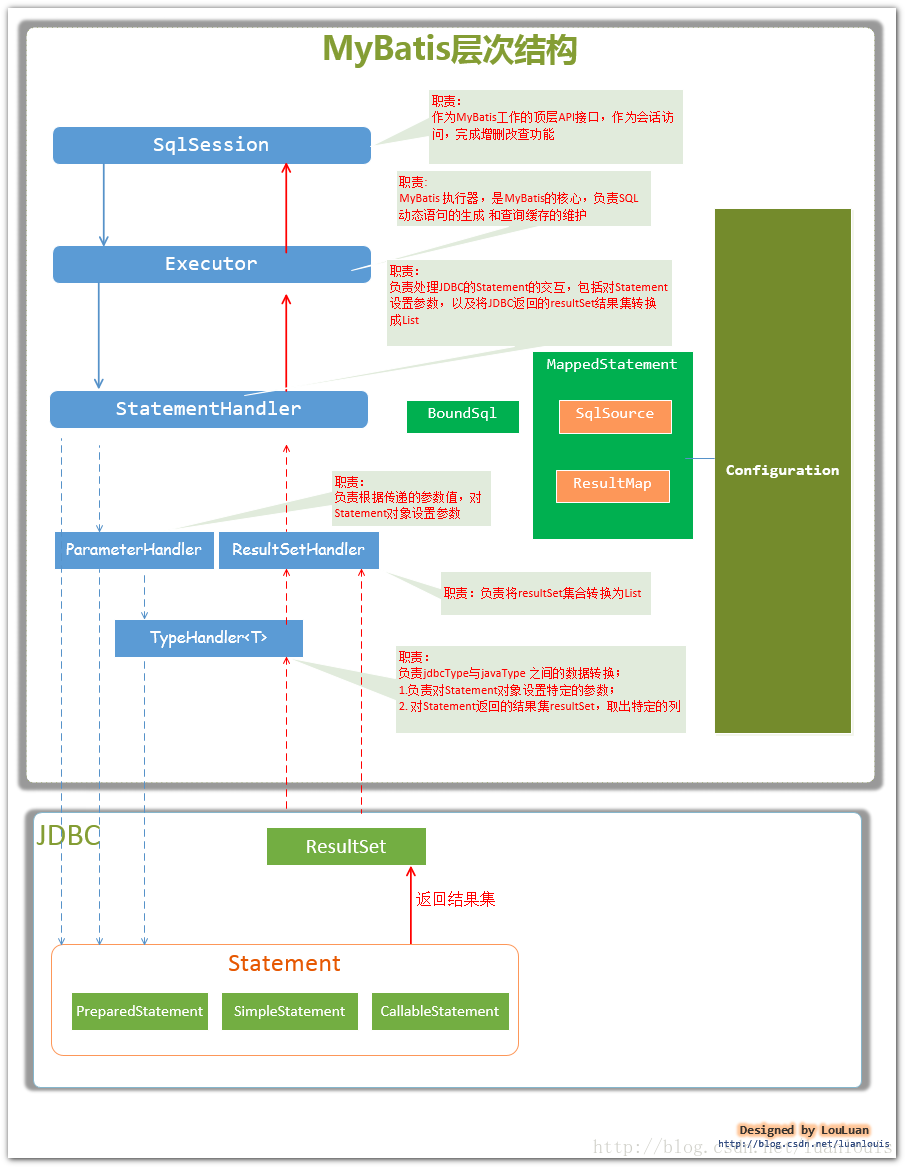
图片摘至《深入理解mybatis原理》 MyBatis的架构设计以及实例分析
分页源码解析
业务代码中的PageHelper
我们先来跟一跟业务代码中的PageHelper的代码
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize);
看它到底做了什么,如下图
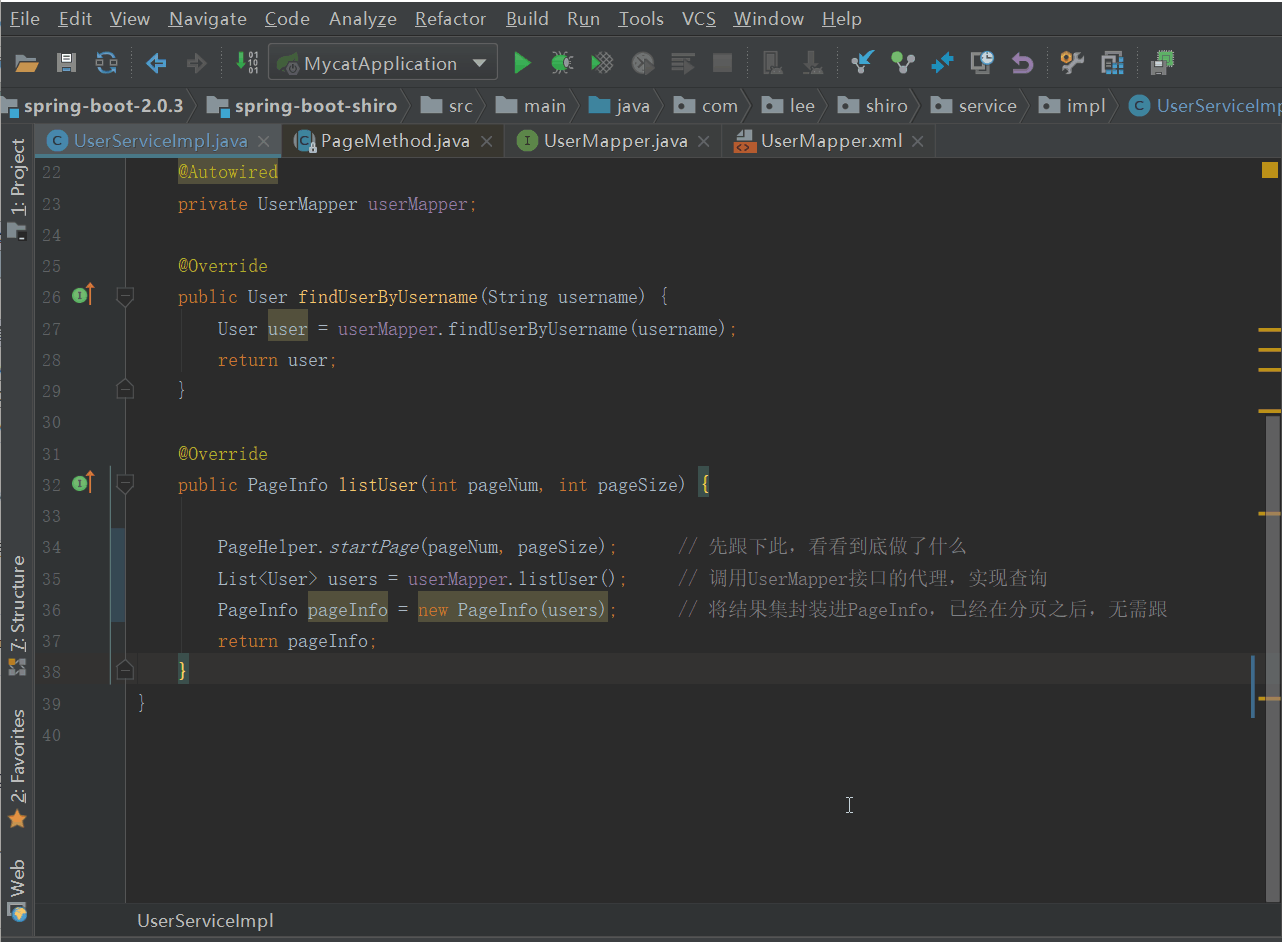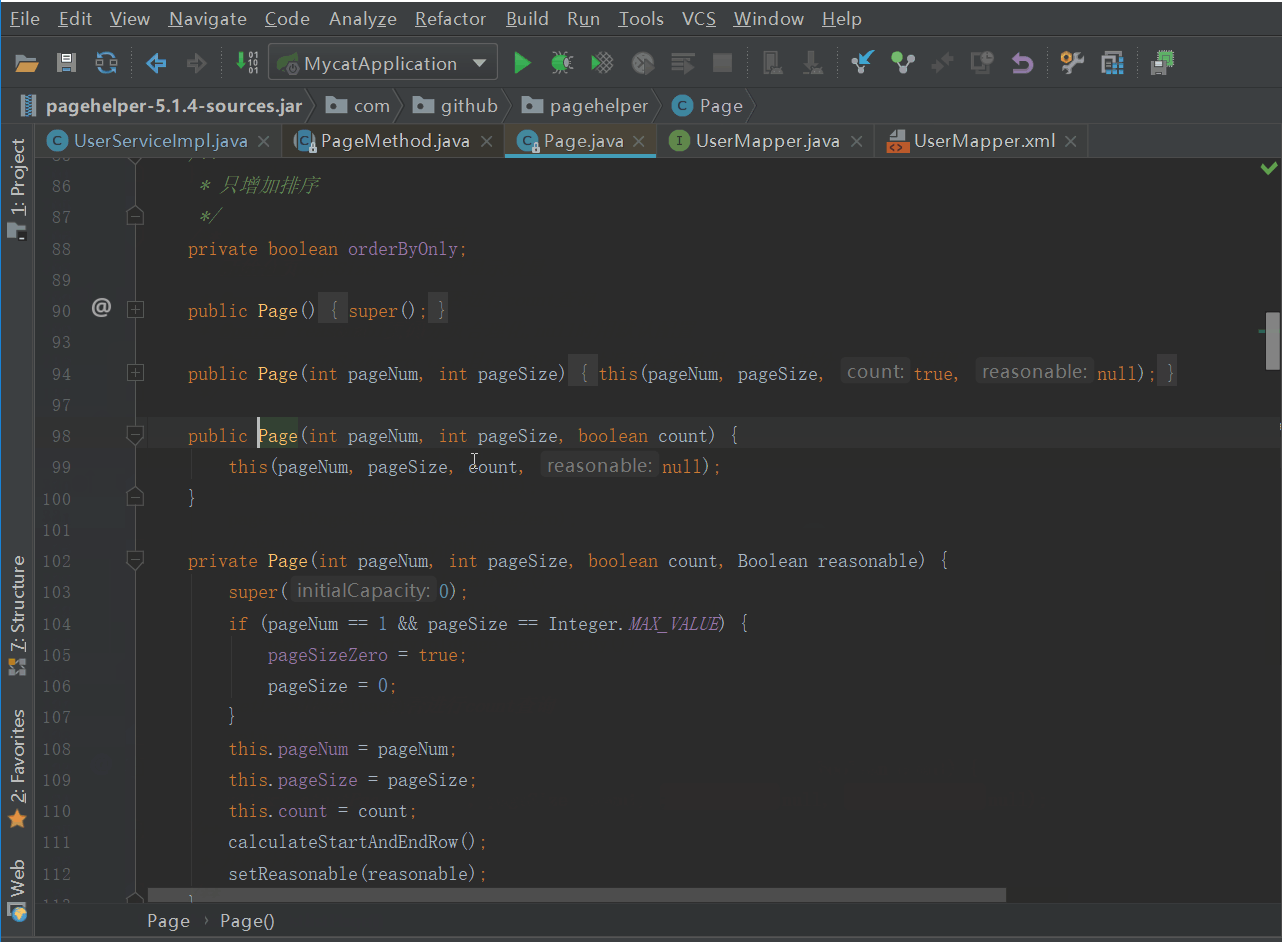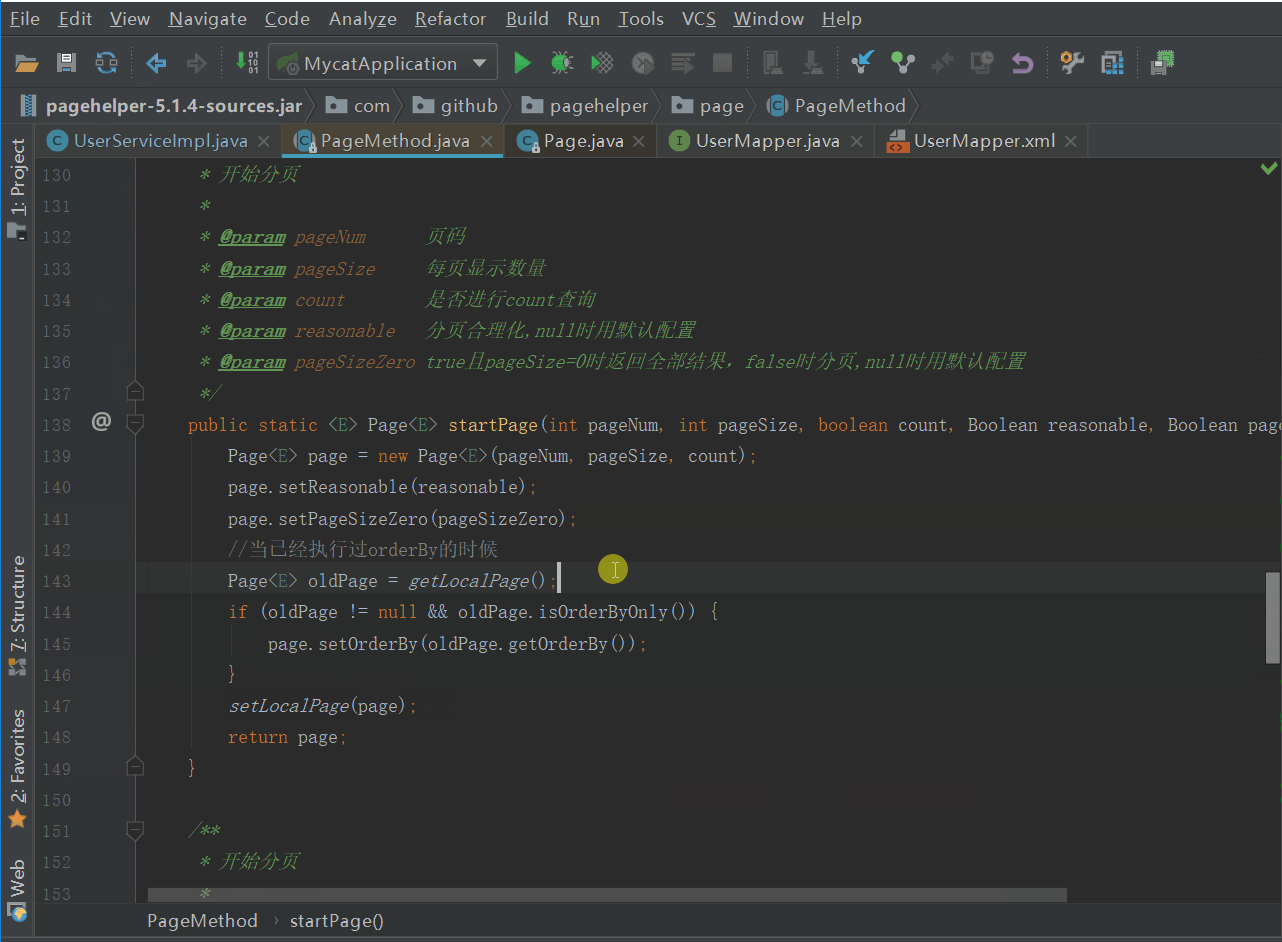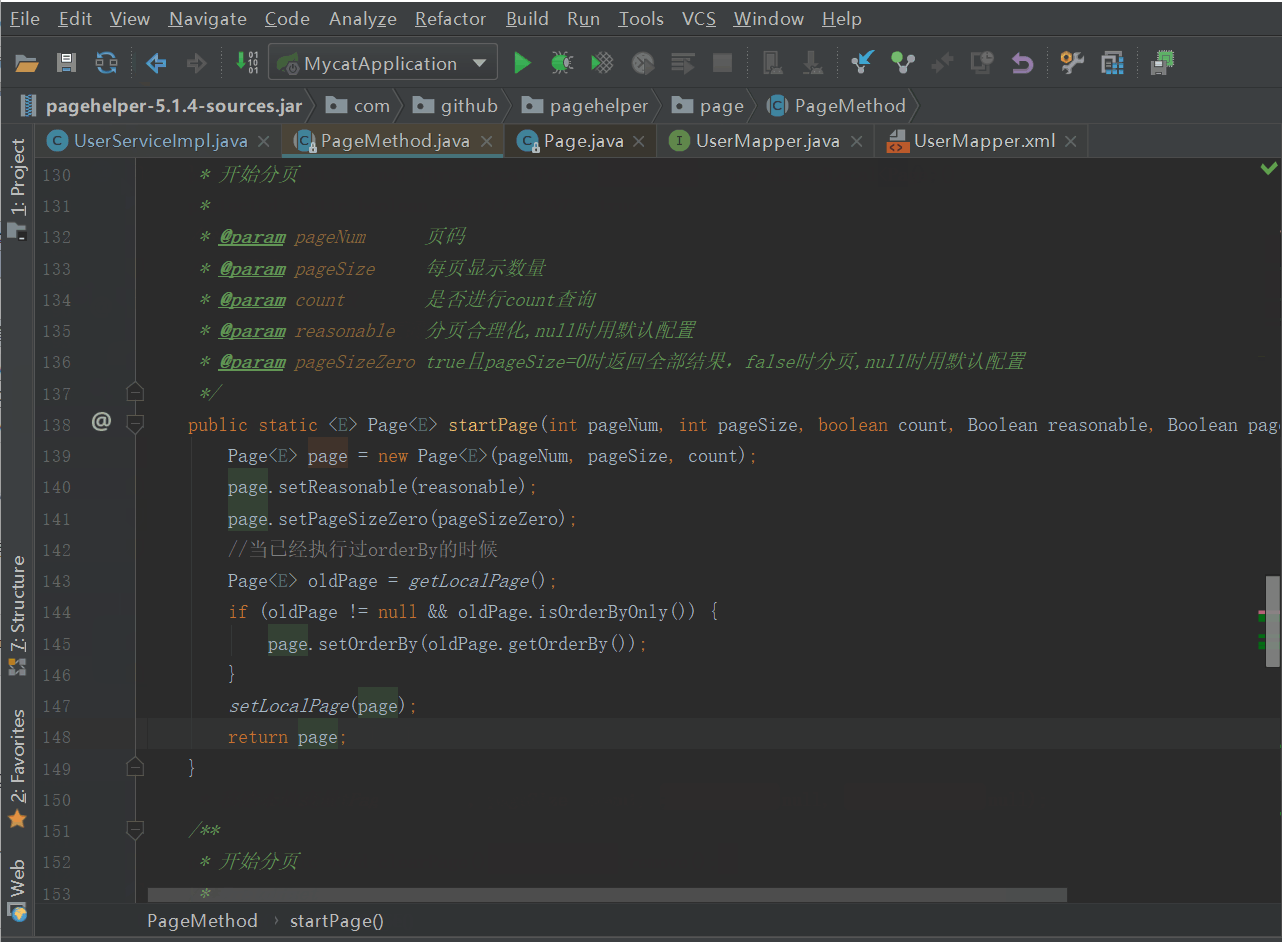
我们发现,进行了Page的相关设置后,将Page放到了当前线程中,没做其他的什么,那么分页肯定不是在这做的。
PageHelper自动配置
关于怎么找自动配置类,可参考:spring-boot-2.0.3启动源码篇一 - SpringApplication构造方法,此时我们找到了PageHelperAutoConfiguration,源代码如下
/**
* 自定注入分页插件
*
* @author liuzh
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnBean(SqlSessionFactory.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PageHelperProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(MybatisAutoConfiguration.class)
public class PageHelperAutoConfiguration { @Autowired
private List<SqlSessionFactory> sqlSessionFactoryList; @Autowired
private PageHelperProperties properties; /**
* 接受分页插件额外的属性
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = PageHelperProperties.PAGEHELPER_PREFIX)
public Properties pageHelperProperties() {
return new Properties();
} @PostConstruct
public void addPageInterceptor() {
PageInterceptor interceptor = new PageInterceptor();
Properties properties = new Properties();
//先把一般方式配置的属性放进去
properties.putAll(pageHelperProperties());
//在把特殊配置放进去,由于close-conn 利用上面方式时,属性名就是 close-conn 而不是 closeConn,所以需要额外的一步
properties.putAll(this.properties.getProperties());
interceptor.setProperties(properties);
for (SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory : sqlSessionFactoryList) {
// 将PageInterceptor实例添加到了Configuration实例的interceptor链中
sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
} }
在PageHelperAutoConfiguration的构造方法执行完之后,会执行addPageInterceptor方法,完成配置属性的注入,并将PageInterceptor实例添加到了Configuration实例的interceptorChain中。
从Mybatis的SQL执行流程图中可以Mybatis的四大对象Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler,由他们一起合作完成SQL的执行,那么这四大对象是由谁创建的呢?没错,就是Mybatis的配置中心:Configuration,创建源代码如下:
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
可以看到四大对象创建的最后,都会调用interceptorChain.pluginAll,我们来看看pluginAll方法做了什么
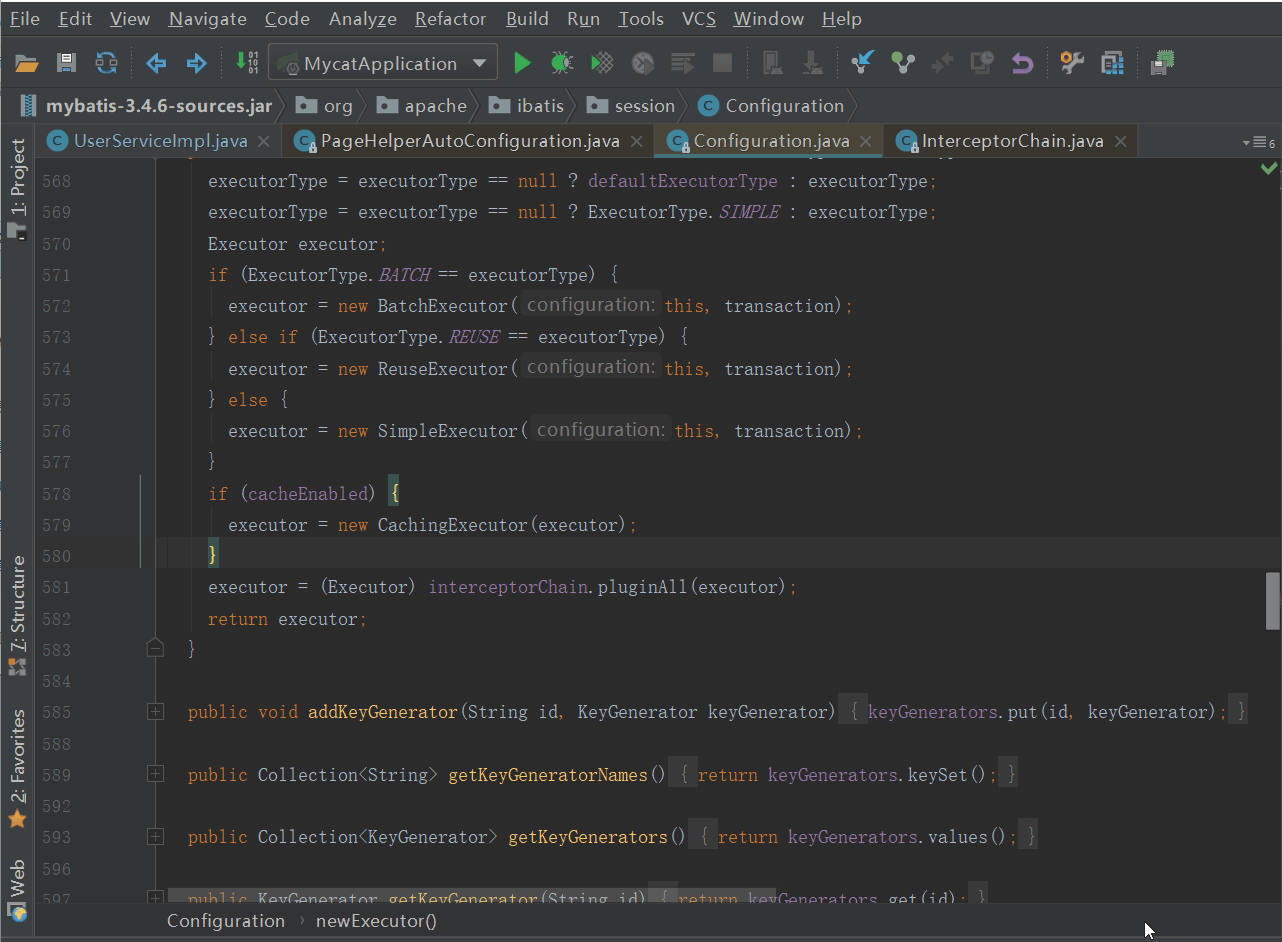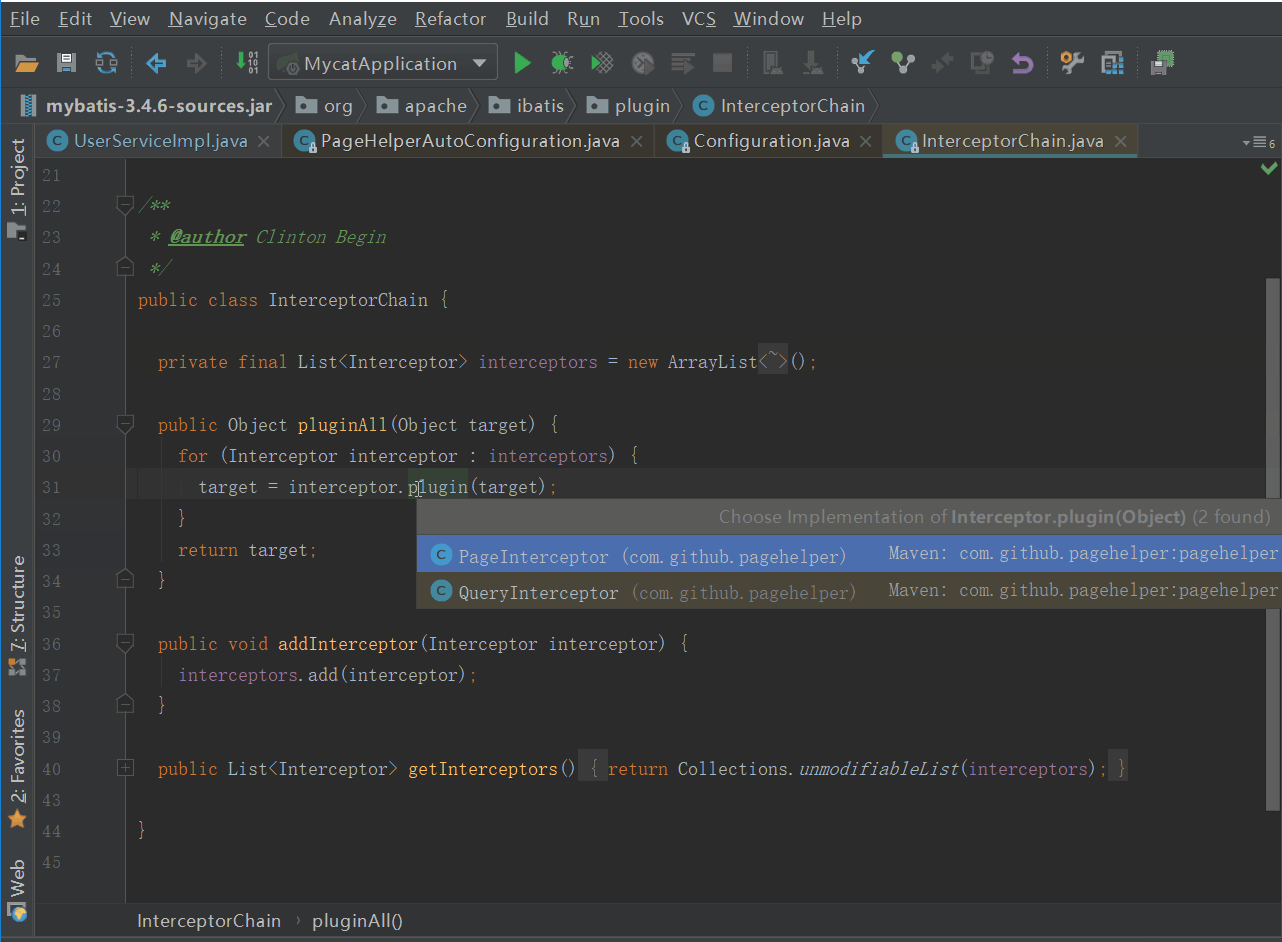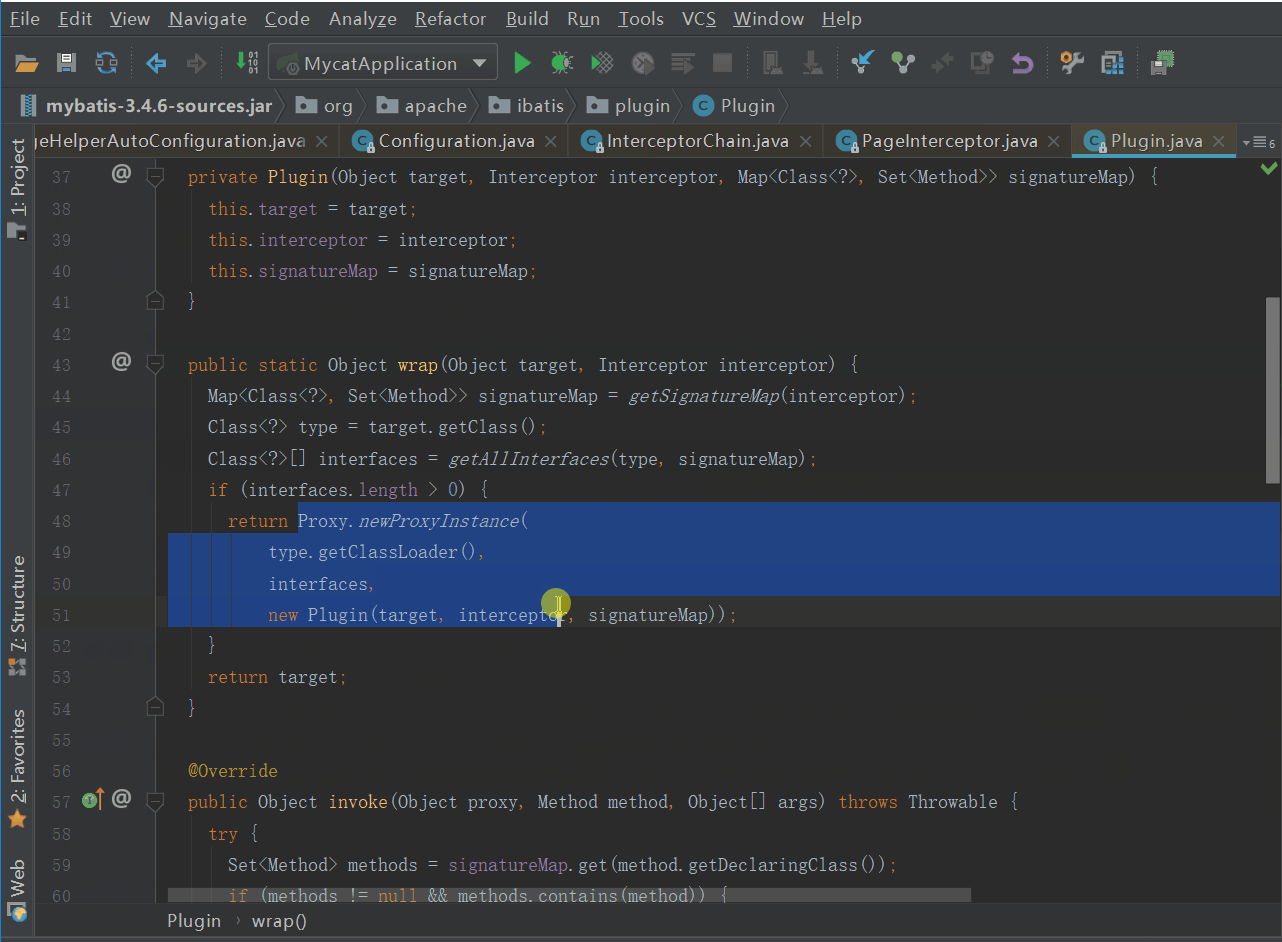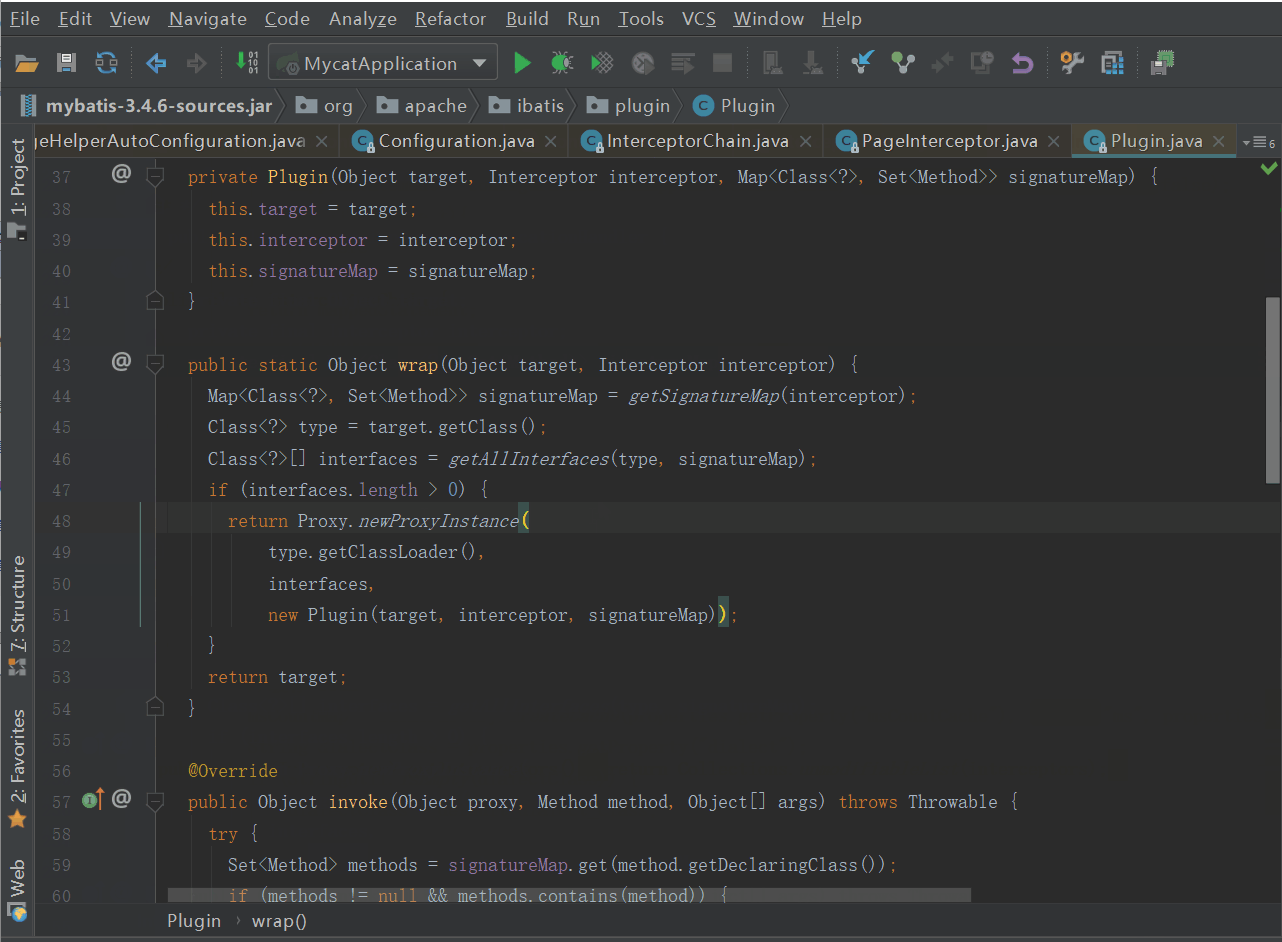
其中Plugin的wrap方法要注意下
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取PageInterceptor的Intercepts注解中@Signature的method,存放到Plugin的signatureMap中
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 获取目标对象实现的全部接口;四大对象是接口,都有默认的子类实现
// JDK的动态代理只支持接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
pluginAll其实就是给四大对象创建代理,一个Interceptor就会创建一层代理,而我们的PageInterceptor只是其中一层代理;我们接着往下看,Plugin继承了InvocationHandler,相当于上述:JDK的动态代理示例中的MyInvocationHandler,那么它的invoke方法肯定会被调用
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 获取PageInterceptor的Intercepts注解中@Signature的method
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
// 当methods包含目标方法时,调用PageInterceptor的intercept方法完成SQL的分页处理
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
拦截器:PageInterceptor
上述我们讲到了,当匹配时会进入到PageInterceptor的intercept方法中,在解读intercept方法之前,我们先来看看PageInterceptor类上的注解
@Intercepts(
{
// 相当于对Executor的query方法做拦截处理
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class}),
}
)
这就标明了PageInterceptor拦截的是Executor的query方法;还记上述wrap方法的
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
吗?读取的就是@Intercepts下@Signature中的内容。我们接着看intercept
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
try {
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0];
Object parameter = args[1];
RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2];
ResultHandler resultHandler = (ResultHandler) args[3];
Executor executor = (Executor) invocation.getTarget();
CacheKey cacheKey;
BoundSql boundSql;
//由于逻辑关系,只会进入一次
if(args.length == 4){
//4 个参数时
boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
cacheKey = executor.createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
} else {
//6 个参数时
cacheKey = (CacheKey) args[4];
boundSql = (BoundSql) args[5];
}
List resultList;
//调用方法判断是否需要进行分页,如果不需要,直接返回结果
// 此处会从当前线程取Page信息,还记得什么时候在哪将Page信息放进当前线程的吗?
if (!dialect.skip(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//反射获取动态参数
String msId = ms.getId();
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
Map<String, Object> additionalParameters = (Map<String, Object>) additionalParametersField.get(boundSql);
//判断是否需要进行 count 查询
if (dialect.beforeCount(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) {
String countMsId = msId + countSuffix;
Long count;
//先判断是否存在手写的 count 查询
MappedStatement countMs = getExistedMappedStatement(configuration, countMsId);
if(countMs != null){
count = executeManualCount(executor, countMs, parameter, boundSql, resultHandler);
} else {
countMs = msCountMap.get(countMsId);
//自动创建
if (countMs == null) {
//根据当前的 ms 创建一个返回值为 Long 类型的 ms
countMs = MSUtils.newCountMappedStatement(ms, countMsId);
msCountMap.put(countMsId, countMs);
}
count = executeAutoCount(executor, countMs, parameter, boundSql, rowBounds, resultHandler);
}
//处理查询总数
//返回 true 时继续分页查询,false 时直接返回
if (!dialect.afterCount(count, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//当查询总数为 0 时,直接返回空的结果
return dialect.afterPage(new ArrayList(), parameter, rowBounds);
}
}
//判断是否需要进行分页查询
if (dialect.beforePage(ms, parameter, rowBounds)) {
//生成分页的缓存 key
CacheKey pageKey = cacheKey;
//处理参数对象
parameter = dialect.processParameterObject(ms, parameter, boundSql, pageKey);
//调用方言获取分页 sql
String pageSql = dialect.getPageSql(ms, boundSql, parameter, rowBounds, pageKey);
BoundSql pageBoundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, pageSql, boundSql.getParameterMappings(), parameter);
//设置动态参数
for (String key : additionalParameters.keySet()) {
pageBoundSql.setAdditionalParameter(key, additionalParameters.get(key));
}
//执行分页查询
resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, pageKey, pageBoundSql);
} else {
//不执行分页的情况下,也不执行内存分页
resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, resultHandler, cacheKey, boundSql);
}
} else {
//rowBounds用参数值,不使用分页插件处理时,仍然支持默认的内存分页
resultList = executor.query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, cacheKey, boundSql);
}
return dialect.afterPage(resultList, parameter, rowBounds);
} finally {
dialect.afterAll();
}
}
其中会读取当前线程中的Page信息,根据Page信息来断定是否需要分页;而Page信息就是从我们的业务代码中存放到当前线程的。PageHelper的作者已经将intercept方法中的注释写的非常清楚了,相信大家都能看懂。
到了此刻,相信大家都清楚了,还不清楚的静下心来好好捋一捋。
总结
1、PageHelper属于Mybatis插件拓展,也可称拦截器拓展,是基于Mybatis的Interceptor实现;
2、Page信息是在我们的业务代码中放到当前线程的,作为后续是否需要分页的条件;
3、Mybatis创建mapper代理的过程(详情请看:Mybatis源码解析 - mapper代理对象的生成)中,也会创建四大对象的代理(有必要的话),而PageInterceptor对应的四大对象的代理会拦截Executor的query方法,将分页参数添加到目标SQL中;
4、不管我们是否需要分页,只要我们集成了PageHelper,那么四大对象的代理实现中肯定包含了一层PageHelper的代理(可能是多层代理,包括其他第三方的Mybatis插件,或者我们自定义的Mybatis插件),如果当前线程中设置了Page,那么就表示需要分页,PageHelper就会读取当前线程中的Page信息,将分页条件添加到目标SQL中(Mysql是后面添加LIMIT,而Oracle则不一样),那么此时发送到数据库的SQL是有分页条件的,也就完成了分页处理;
5、@Interceptors、@Signature以及Plugin类,三者配合起来,完成了分页逻辑的植入,Mybatis这么做便于拓展,使用起来更灵活,包容性更强;我们自定义插件的话,可以基于此,也可以抛弃这3个类,直接在plugin方法内部根据target实例的类型做相应的操作;个人推荐基于这3个来实现;
6、Mybatis的Interceptor是基于JDK的动态代理,只能针对接口进行处理;另外,当我们进行Mybatis插件开发的时候,需要注意顺序问题,可能会与其他的Mybatis插件有冲突。
参考
《深入理解mybatis原理》 MyBatis的架构设计以及实例分析
spring-boot-2.0.3源码篇 - pageHelper分页,绝对有值得你看的地方的更多相关文章
- spring-boot-2.0.3源码篇 - filter的注册,值得一看
前言 开心一刻 过年女婿来岳父家走亲戚,当时小舅子主就问:姐夫,你什么时候能给我姐幸福,让我姐好好享受生活的美好.你们这辈子不准备买一套大点的房子吗?姐夫说:现在没钱啊!不过我有一个美丽可爱的女儿,等 ...
- Spring Boot 2.0系列文章(五):Spring Boot 2.0 项目源码结构预览
关注我 转载请务必注明原创地址为:http://www.54tianzhisheng.cn/2018/04/15/springboot2_code/ 项目结构 结构分析: Spring-boot-pr ...
- springboot2.0.3源码篇 - 自动配置的实现,发现也不是那么复杂
前言 开心一刻 女儿: “妈妈,你这么漂亮,当年怎么嫁给了爸爸呢?” 妈妈: “当年你爸不是穷嘛!‘ 女儿: “穷你还嫁给他!” 妈妈: “那时候刚刚毕业参加工作,领导对我说,他是我的扶贫对象,我年轻 ...
- Spring Boot 揭秘与实战 源码分析 - 工作原理剖析
文章目录 1. EnableAutoConfiguration 帮助我们做了什么 2. 配置参数类 – FreeMarkerProperties 3. 自动配置类 – FreeMarkerAutoCo ...
- Spring Boot 揭秘与实战 源码分析 - 开箱即用,内藏玄机
文章目录 1. 开箱即用,内藏玄机 2. 总结 3. 源代码 Spring Boot提供了很多”开箱即用“的依赖模块,那么,Spring Boot 如何巧妙的做到开箱即用,自动配置的呢? 开箱即用,内 ...
- Spring Boot 注解之ObjectProvider源码追踪
最近依旧在学习阅读Spring Boot的源代码,在此过程中涉及到很多在日常项目中比较少见的功能特性,对此深入研究一下,也挺有意思,这也是阅读源码的魅力之一.这里写成文章,分享给大家. 自动配置中的O ...
- spring-boot-2.0.3源码篇 - 国际化
前言 针对spring boot,网上已有很多优质的系列教程,我就不再班门弄斧了(实际上是担心没别人写的好,哈哈哈!).但是还是想蹭蹭spring boot的热度,即使不考虑微服务,spring bo ...
- SpringBoot 源码解析 (八)----- Spring Boot 精髓:事务源码解析
本篇来讲一下SpringBoot是怎么自动开启事务的,我们先来回顾一下以前SSM中是如何使用事务的 SSM使用事务 导入JDBC依赖包 众所周知,凡是需要跟数据库打交道的,基本上都要添加jdbc的依赖 ...
- spring-boot-2.0.3源码篇 - @Configuration、Condition与@Conditional
前言 开心一刻 一名劫匪慌忙中窜上了一辆车的后座,上车后发现主驾和副驾的一男一女疑惑地回头看着他,他立即拔出枪威胁到:“赶快开车,甩掉后面的警车,否则老子一枪崩了你!”,于是副驾上的男人转过脸对那女的 ...
随机推荐
- 数据分析——pandas
简介 import pandas as pd # 在数据挖掘前一个数据分析.筛选.清理的多功能工具 ''' pandas 可以读入excel.csv等文件:可以创建Series序列,DataFrame ...
- vue Error: No PostCSS Config found in
最近在做一个vue的移动端的项目,遇到一个问题,我本地的项目运行正常,可是上传到github上的一启动就报错,就是标题上的错误,找了很久,刚开始以为是某个css没有配置,就把本地的复制过去还是报错,无 ...
- 删除PeopleSoft Process Scheduler服务器定义
DELETE FROM PS_SERVERDEFN WHERE SERVERNAME= 'PSNT2' ; DELETE FROM PSSERVERSTAT where SERVERNAME = 'P ...
- Spring源码学习-容器BeanFactory(四) BeanDefinition的创建-自定义标签的解析.md
写在前面 上文Spring源码学习-容器BeanFactory(三) BeanDefinition的创建-解析Spring的默认标签对Spring默认标签的解析做了详解,在xml元素的解析中,Spri ...
- 2019_BUAAOO_第二单元总结
第一次作业:单部多线程傻瓜调度电梯 设计策略 本次作业我才用的是生产者消费者模式,创建一个RequestList类,将输入线程InputThread作为生产者,负责将请求放入RequestList:将 ...
- String类,StringBuffer类转字符数组
String不可变类型和StringBuffer可变类型 String类和StringBuffer类都是字符串表示类,区别在于String对象引用变量是不可变的,而StringBuffer类对象引用变 ...
- CSS引用方式及样式层叠机制
CSS引用方式有3种,三种分别为:外部引入.内部引入.行内样式,下面一 一进行介绍. 1.外部引入:CSS代码在一个独立的文件中,HTML通过Link标签引入到页面. 代码格式:<link re ...
- Cloud Native 云化架构阅读笔记
一• Cloud Native CloudNative是什么? Cloud Native翻译为云原生,是Matt Stine提出的一个概念,它是一个思想的集合,包括DevOps.持续交付(Contin ...
- ubuntu amd64 的锐捷连接解决办法---武汉大学
昨日博主闲来弄了个ubuntu玩玩,于是上网成了个问题,博主武大信息学部,锐捷上校园网.装的是13.04的amd64. 凑巧在珞珈山水bbs上看到我在解决上网出现问题出现的相同情况,但是没有人回答,于 ...
- 使用 TRESTClient 与 TRESTRequest 作为 HTTP Client
在 Delphi XE 推出以前的年代,Delphi的发展方向是笔直朝向资料库连结Windows 应用程式这个目标不断前进的,从Delphi 1开始,到Delphi 7,Delphi奠定了VB Kil ...
